|
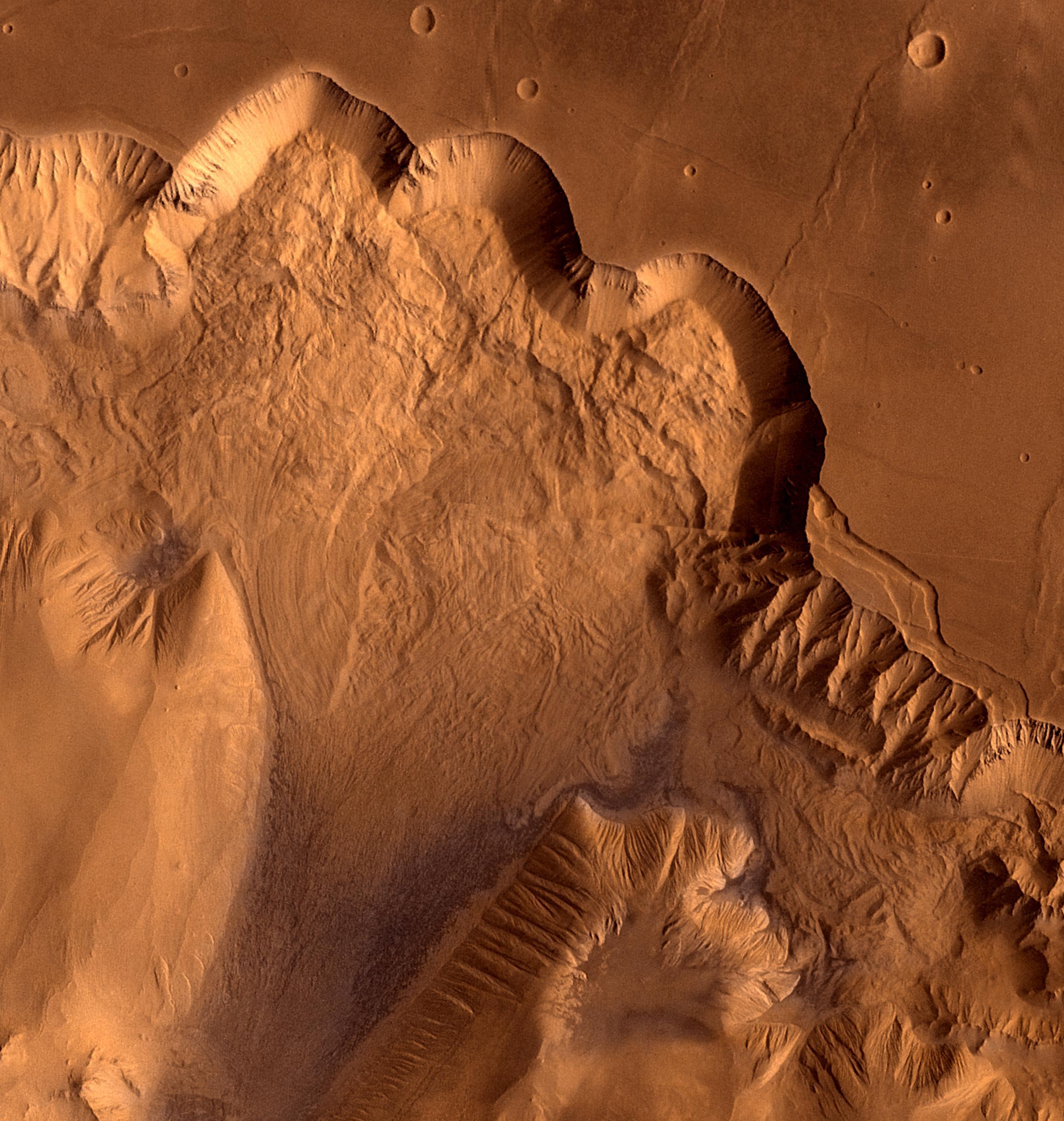
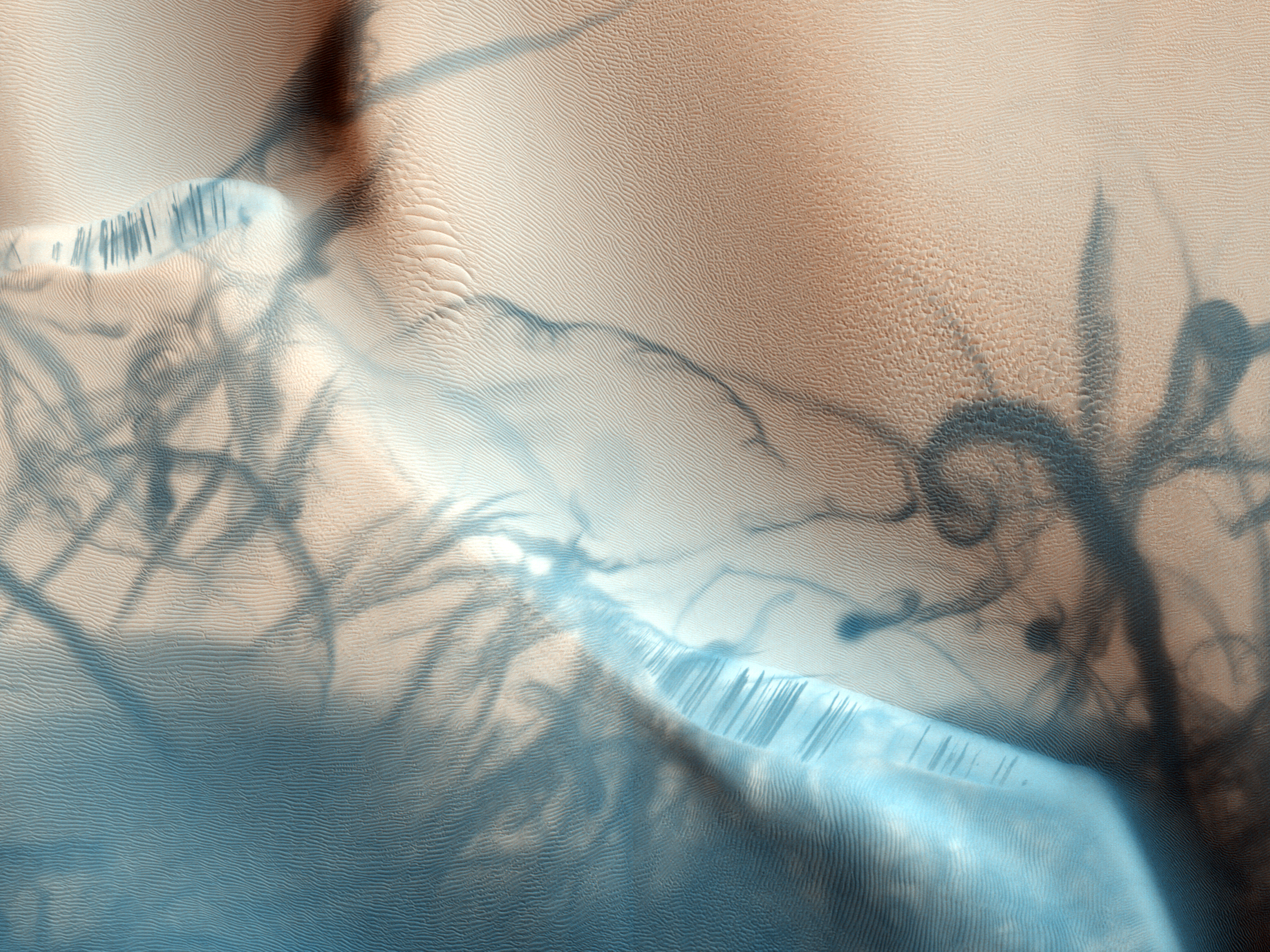
Ius Chasma
Ius Chasma is a large canyon in the Coprates quadrangle of Mars at 7° south latitude and 85.8° west longitude. It is about 938 km long and was named after a classical albedo feature name. Valles Marineris Canyon System Ius Chasma is a major part of Valles Marineris, the largest canyon system in the solar system; this great canyon would go almost all the way across the United States. Starting at the west with Noctis Labyrinthus in the Phoenicis Lacus quadrangle, the canyon system ends in the Margaritifer Sinus quadrangle with Capri Chasma and Eos Chasma (in the south). The word ''chasma'' has been designated by the International Astronomical Union to refer to an elongate, steep-sided depression. Valles Marineris was discovered by and named for the Mariner 9 mission. Moving east from Noctis Labyrinthus, the canyon splits into two troughs, Tithonium and Ius Chasma in the south. In the middle of the system are very wide valleys of Ophir Chasma (north), Candor Chasma, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ius Chasma THEMIS Mosaic
__NOTOC__ ''Ius'' or ''Jus'' (Latin, plural ''iura'') in ancient Rome was a right to which a citizen (''civis'') was entitled by virtue of his citizenship (''civitas''). The ''iura'' were specified by laws, so ''ius'' sometimes meant law. As one went to the law courts to sue for one's rights, ''ius'' also meant justice and the place where justice was sought. On the whole, the Romans valued their rights as the greatest good of Roman citizenship (''civitas romana''), as opposed to citizenship in other city-states under the jurisdiction of Rome but without Roman rights. Outsiders (''peregrini'') and freedmen (''libertini'') perforce used Roman lawyers to represent them in actions undertaken under the jurisdiction of Roman law. Representation was one of the civic obligations (''munera'') owed to the state by citizens. These ''munera'' (on which account the citizens were ''municipes'') included military service as well as paying taxes, but specialized obligations might also be associa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophir Chasma
Ophir Chasma is a canyon in the Coprates quadrangle of Mars at 4° south latitude and 72.5° west longitude. It is about 317 km long and was named after Ophir, a land mentioned in the Bible. In the Bible it was the land which King Solomon sent an expedition that returned with gold. It is a classical albedo feature name. Valles Marineris canyon system Ophir Chasma is part of the largest canyon system in the solar system; this great canyon would go almost all the way across the United States. The name for the whole system of canyons is Valles Marineris. Starting at the west with Noctis Labyrinthus in the Phoenicis Lacus quadrangle, the canyon system ends in the Margaritifer Sinus quadrangle with Capri Chasma and Eos Chasma (in the south). The word ''chasma'' has been designated by the International Astronomical Union to refer to an elongate, steep-sided depression. Valles Marineris was discovered by and named for the Mariner 9 mission. Moving east from Noctis Labyri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tectonics Of Mars
Like the Earth, the crustal properties and structure of the surface of Mars are thought to have evolved through time; in other words, as on Earth, tectonic processes have shaped the planet. However, both the ways this change has happened and the properties of the planet's lithosphere are very different when compared to the Earth. Today, Mars is believed to be largely tectonically inactive. However, observational evidence and its interpretation suggests that this was not the case further back in Mars' geological history. At the scale of the whole planet, two large scale physiographic features are apparent on the surface. The first is that the northern hemisphere of the planet is much lower than the southern, and has been more recently resurfaced – also implying that the crustal thickness beneath the surface is distinctly bimodal. This feature is referred to as the " hemispheric dichotomy". The second is the Tharsis rise, a massive volcanic province that has had major tectonic in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graben
In geology, a graben () is a depressed block of the crust of a planet or moon, bordered by parallel normal faults. Etymology ''Graben'' is a loan word from German, meaning 'ditch' or 'trench'. The word was first used in the geologic context by Eduard Suess in 1883. The plural form is either ''graben'' or ''grabens''. Formation A graben is a valley with a distinct escarpment on each side caused by the displacement of a block of land downward. Graben often occur side by side with horsts. Horst and graben structures indicate tensional forces and crustal stretching. Graben are produced from parallel normal faults, where the displacement of the hanging wall is downward, while that of the footwall is upward. The faults typically dip toward the center of the graben from both sides. Horsts are parallel blocks that remain between graben; the bounding faults of a horst typically dip away from the center line of the horst. Single or multiple graben can produce a rift valley. Half-g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
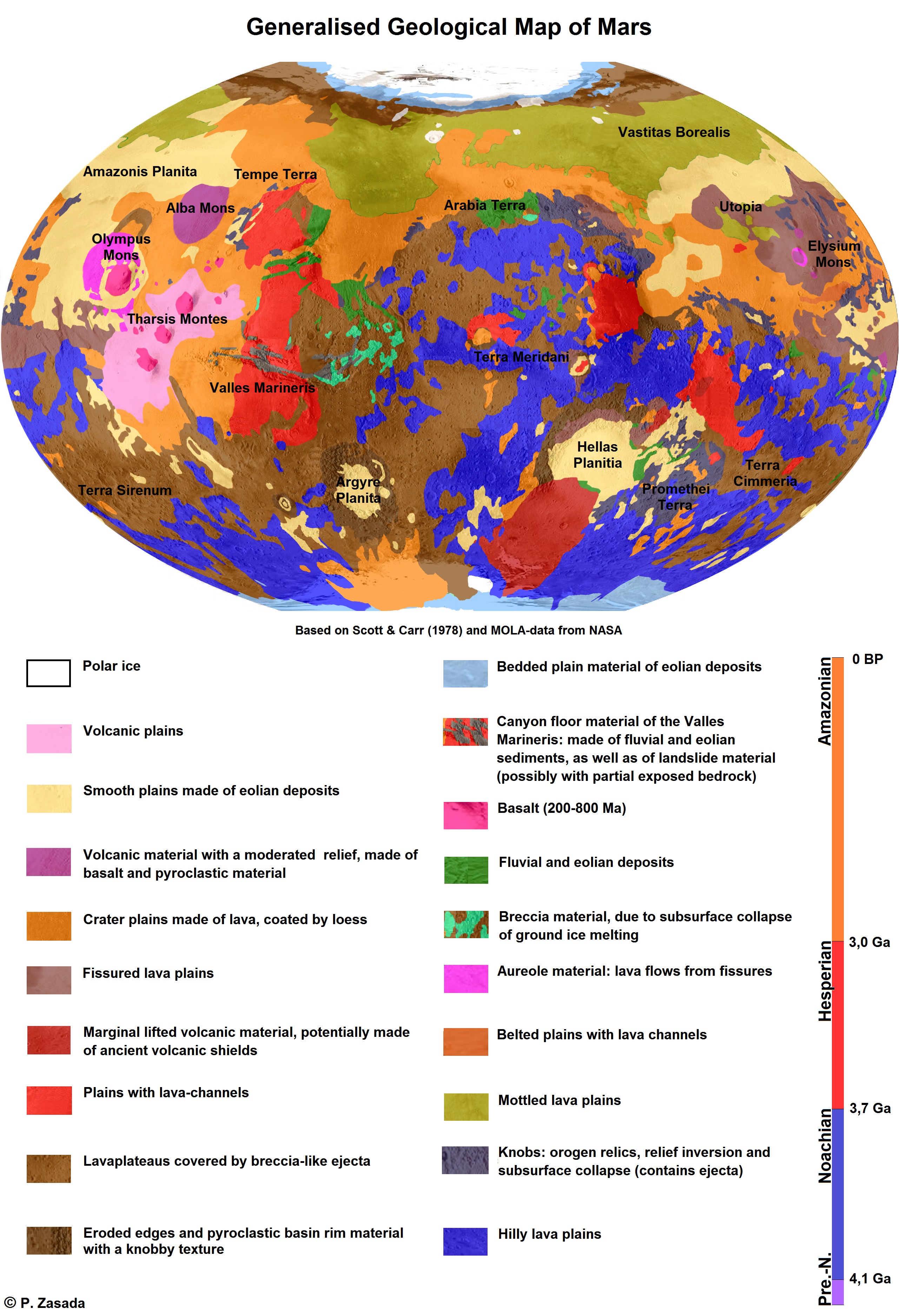
Geology Of Mars
The geology of Mars is the scientific study of the surface, crust, and interior of the planet Mars. It emphasizes the composition, structure, history, and physical processes that shape the planet. It is analogous to the field of terrestrial geology. In planetary science, the term ''geology'' is used in its broadest sense to mean the study of the solid parts of planets and moons. The term incorporates aspects of geophysics, geochemistry, mineralogy, geodesy, and cartography. A neologism, areology, from the Greek word ''Arēs'' (Mars), sometimes appears as a synonym for Mars's geology in the popular media and works of science fiction (e.g. Kim Stanley Robinson, Kim Stanley Robinson's Mars trilogy). The term areology is also used by the Areological Society. Geological map of Mars (2014) File:Geologic Map of Mars figure2.pdf, Figure 2 for the geologic map of Mars Global Martian topography and large-scale features Composition of Mars Mars is a terrestrial planet, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate On Mars
The climate of Mars has been a topic of scientific curiosity for centuries, in part because it is the only terrestrial planet whose surface can be directly observed in detail from the Earth with help from a telescope. Although Mars is smaller than the Earth, 11% of Earth's mass, and 50% farther from the Sun than the Earth, its climate has important similarities, such as the presence of polar ice caps, seasonal changes and observable weather patterns. It has attracted sustained study from planetologists and climatologists. While Mars' climate has similarities to Earth's, including periodic ice ages, there are also important differences, such as much lower thermal inertia. Mars' atmosphere has a scale height of approximately , 60% greater than that on Earth. The climate is of considerable relevance to the question of whether life is or ever has been present on the planet. The climate briefly received more interest in the news due to NASA measurements indicating increased sublima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chasma
In planetary nomenclature, a chasma (''plural'': chasmata ) is a deep, elongated, steep-sided depression. As of 2020, the IAU has named 122 such features in the Solar System, on Venus (63), Mars (25), Saturn's satellites Mimas (6), Tethys (2), Dione (8) and Rhea (5), Uranus's satellites Ariel (7), Titania (2) and Oberon (1) and Pluto's satellite Charon (3). An example is Eos Chasma on Mars. Mars Below are images of some of the major chasmata of Mars. The map shows their relative locations. Interior layered deposits and sulfate Parts of the floor of Candor Chasma contains layered deposits that have been termed interior layered deposits (ILD's). These layers may have formed when the whole area was a giant lake. Some places on Mars contain hydrated sulfate deposits. Sulfate formation involves the presence of water. The European Space Agency's Mars Express found evidence of perhaps epsomite and kieserite. Scientists want to visit these areas with robotic rovers. Layers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ius Channels
__NOTOC__ ''Ius'' or ''Jus'' (Latin, plural ''iura'') in ancient Rome was a right to which a citizen (''civis'') was entitled by virtue of his citizenship (''civitas''). The ''iura'' were specified by laws, so ''ius'' sometimes meant law. As one went to the law courts to sue for one's rights, ''ius'' also meant justice and the place where justice was sought. On the whole, the Romans valued their rights as the greatest good of Roman citizenship (''civitas romana''), as opposed to citizenship in other city-states under the jurisdiction of Rome but without Roman rights. Outsiders (''peregrini'') and freedmen (''libertini'') perforce used Roman lawyers to represent them in actions undertaken under the jurisdiction of Roman law. Representation was one of the civic obligations (''munera'') owed to the state by citizens. These ''munera'' (on which account the citizens were ''municipes'') included military service as well as paying taxes, but specialized obligations might also be associa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter
''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' (MRO) is a spacecraft designed to study the geology and climate of Mars, provide reconnaissance of future landing sites, and relay data from surface missions back to Earth. It was launched on August 12, 2005, and reached Mars on March 10, 2006. In November 2006, after five months of aerobraking, it entered its final science orbit and began its primary science phase. The cost to develop and operate MRO through the end of its prime mission in 2010 was . The spacecraft continues to operate at Mars, far beyond its intended design life. Due to its critical role as a high-speed data-relay for ground missions, NASA intends to continue the mission as long as possible, at least through the late 2020s. Pre-launch After the twin failures of the ''Mars Climate Orbiter'' and the Mars Polar Lander missions in 1999, NASA reorganized and replanned its Mars Exploration Program. In October 2000, NASA announced its reformulated Mars plans, which reduced the numb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HiRISE
High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment is a camera on board the ''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' which has been orbiting and studying Mars since 2006. The 65 kg (143 lb), US$40 million instrument was built under the direction of the University of Arizona's Lunar and Planetary Laboratory by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp. It consists of a 0.5m (19.7 in) aperture reflecting telescope, the largest so far of any deep space mission, which allows it to take pictures of Mars with resolutions of 0.3m/pixel (1ft/pixel), resolving objects below a meter across. HiRISE has imaged Mars exploration rovers on the surface, including the ''Opportunity'' rover and the ongoing ''Curiosity'' mission. History In the late 1980s, of Ball Aerospace & Technologies began planning the kind of high-resolution imaging needed to support sample return and surface exploration of Mars. In early 2001 he teamed up with Alfred McEwen of the University of Arizona to propose such a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the planetary surface, surface of a terrestrial planet, rocky planet or natural satellite, moon. More than 90% of all volcanic rock on Earth is basalt. Rapid-cooling, fine-grained basalt is chemically equivalent to slow-cooling, coarse-grained gabbro. The eruption of basalt lava is observed by geologists at about 20 volcanoes per year. Basalt is also an important rock type on other planetary bodies in the Solar System. For example, the bulk of the plains of volcanism on Venus, Venus, which cover ~80% of the surface, are basaltic; the lunar mare, lunar maria are plains of flood-basaltic lava flows; and basalt is a common rock on the surface of Mars. Molten basalt lava has a low viscosity due to its relatively low silica content (between 45% and 52%), resulting in rapidly moving lava flo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
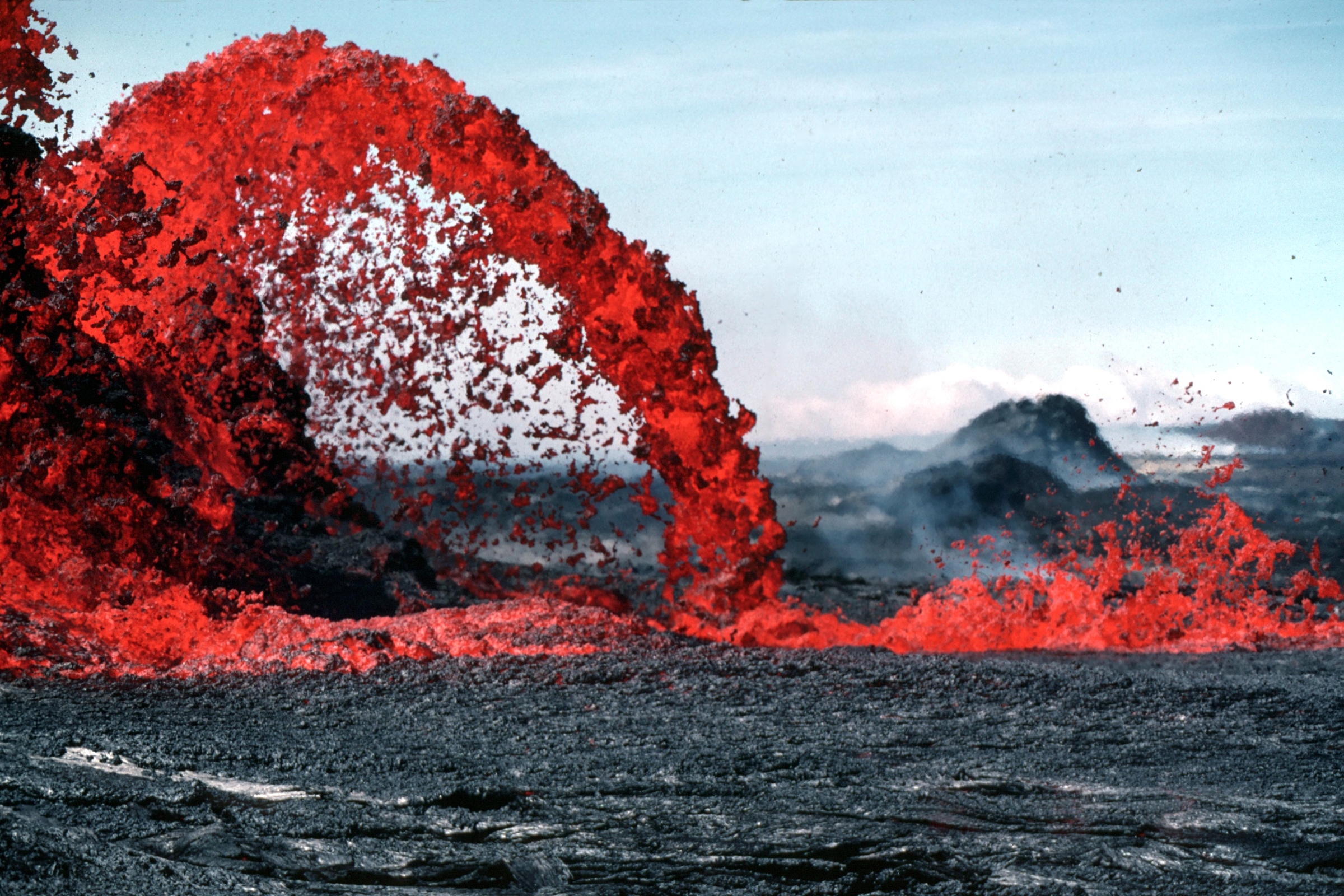
Lava
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust, on land or underwater, usually at temperatures from . The volcanic rock resulting from subsequent cooling is also often called ''lava''. A lava flow is an outpouring of lava during an effusive eruption. (An explosive eruption, by contrast, produces a mixture of volcanic ash and other fragments called tephra, not lava flows.) The viscosity of most lava is about that of ketchup, roughly 10,000 to 100,000 times that of water. Even so, lava can flow great distances before cooling causes it to solidify, because lava exposed to air quickly develops a solid crust that insulates the remaining liquid lava, helping to keep it hot and inviscid enough to continue flowing. The word ''lava'' comes from Italian and is probably derived from the Latin word ''labes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |