|
Israelian Hebrew
Israelian Hebrew (or IH) is a northern dialect of biblical Hebrew (BH) proposed as an explanation for various irregular linguistic features of the Masoretic Text (MT) of the Hebrew Bible. It competes with the alternative explanation that such features are Aramaic language, Aramaisms, indicative either of late dates of composition, or of Textual criticism#Process, editorial emendations. Although IH is not a new proposal, it only started gaining ground as a challenge to older arguments to late dates for some biblical texts since about a decade before the turn of the 21st century: linguistic variation in the Hebrew Bible might be ''better'' explained by Synchronic analysis, synchronic rather than Historical linguistics, diachronic linguistics, meaning various biblical texts could be significantly older than many 20th century scholars supposed. What constitutes linguistic irregularity in the MT is not in dispute, nor is the affinity of many these features to aspects of Aramaic. What ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levant 01
The Levant () is an approximation, approximate historical geography, historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is equivalent to a stretch of land bordering the Mediterranean in South-western Asia,Gasiorowski, Mark (2016). ''The Government and Politics of the Middle East and North Africa''. }, ), meaning "the eastern place, where the Sun rises". In the 13th and 14th centuries, the term ''levante'' was used for Italian maritime commerce in the Eastern Mediterranean, including Greece, Anatolia, Syria (region), Syria-Palestine, and Egypt, that is, the lands east of Republic of Venice, Venice. Eventually the term was restricted to the Muslim countries of Syria-Palestine and Egypt. In 1581, England set up the Levant Company to monopolize commerce with the Ottoman Empire. The name ''Levant States'' was used to refer to the Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isogloss
An isogloss, also called a heterogloss (see Etymology below), is the geographic boundary of a certain linguistic feature, such as the pronunciation of a vowel, the meaning of a word, or the use of some morphological or syntactic feature. Major dialects are typically demarcated by ''bundles'' of isoglosses, such as the Benrath line that distinguishes High German from the other West Germanic languages and the La Spezia–Rimini Line that divides the Northern Italian languages and Romance languages west of Italy from Central Italian dialects and Romance languages east of Italy. However, an ''individual'' isogloss may or may not have any coterminus with a language border. For example, the front-rounding of /y/ cuts across France and Germany, while the /y/ is absent from Italian and Spanish words that are cognates with the /y/-containing French words. One of the best-known isoglosses is the centum-satem isogloss. Similar to an isogloss, an isograph is a distinguishing feature of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
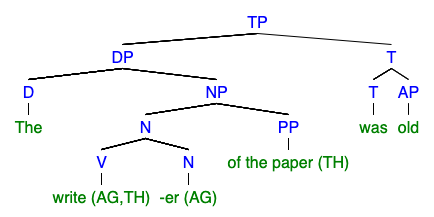
Nominalization
In linguistics, nominalization or nominalisation is the use of a word that is not a noun (e.g., a verb, an adjective or an adverb) as a noun, or as the head of a noun phrase. This change in functional category can occur through morphological transformation, but it does not always. Nominalization can refer, for instance, to the process of producing a noun from another part of speech by adding a derivational affix (e.g., the noun ''legalization'' from the verb ''legalize''), but it can also refer to the complex noun that is formed as a result. Nominalization is also known as "nouning". Some languages simply allow verbs to be used as nouns without inflectional difference (conversion or zero derivation), while others require some form of morphological transformation. English has cases of both. Nominalization is a natural part of language, but some instances are more noticeable than others. Writing advice sometimes focuses on avoiding overuse of nominalization. In various langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ketiv
Qere and Ketiv, from the Aramaic ''qere'' or ''q're'', ("hat isread") and ''ketiv'', or ''ketib'', ''kethib'', ''kethibh'', ''kethiv'', ("hat iswritten"), also known as "q're uchsiv" or "q're uchtiv," refers to a system for marking differences between what is written in the consonantal text of the Hebrew Bible, as preserved by scribal tradition, and what is read. In such situations, the Qere is the technical orthographic device used to indicate the pronunciation of the words in the Masoretic text of the Hebrew language scriptures (Tanakh), while the Ketiv indicates their written form, as inherited from tradition. The word is often pointed and pronounced "kri" or "keri", reflecting the opinion that it is a passive participle rather than an imperative. This is reflected in the Ashkenazi pronunciation "keri uchesiv" mentioned above. The Masoretic tradition Torah scrolls for use in public reading in synagogues contain only the Hebrew language consonantal text, handed down by tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonite Language
Ammonite is the extinct Canaanite language of the Ammonite people mentioned in the Bible, who used to live in modern-day Jordan, and after whom its capital Amman is named. Only fragments of their language survive - chiefly the 9th century BC Amman Citadel Inscription, the 7th-6th century BC Tel Siran bronze bottle, and a few ostraca. As far as can be determined from the small corpus, it was extremely similar to Biblical Hebrew, with some possible Aramaic influence including the use of the verb ''‘bd'' (עבד) instead of the more common Biblical Hebrew ''‘śh'' (עשה) for 'make'. The only other notable difference with Biblical Hebrew is the sporadic retention of feminine singular ''-t'' (''’šħt'' 'cistern', but ''‘lyh'' 'high (fem.)'.) Ammonite also appears to have possessed largely typical correspondences of diphthongs, with words such as ''ywmt'' (יומת ''*yawmōt'', 'days') both preserving /aw/ and showing a shift to /o/, and other words such as ''yn'' (ין 'wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoenician Language
Phoenician ( ) is an extinct language, extinct Canaanite languages, Canaanite Semitic languages, Semitic language originally spoken in the region surrounding the cities of Tyre, Lebanon, Tyre and Sidon. Extensive Tyro-Sidonian trade and commercial dominance led to Phoenician becoming a lingua franca of the maritime Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean during the Iron Age. The Phoenician alphabet History of the Greek alphabet, spread to Greece during this period, where it became the source of all modern Alphabet#European_alphabets, European scripts. The area in which Phoenician was spoken includes the northern Levant and, at least as a prestige language, Anatolia, specifically the areas now including Syria, Lebanon, parts of Cyprus and some adjacent areas of Turkey. It was also spoken in the area of Phoenician colonies, Phoenician colonization along the coasts of the southwestern Mediterranean Sea, including those of modern Tunisia, Morocco, Libya and Algeria as well as Malta, the we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mishnaic Hebrew
Mishnaic Hebrew is the Hebrew of Talmudic texts. Mishnaic Hebrew can be sub-divided into Mishnaic Hebrew proper (also called Tannaitic Hebrew, Early Rabbinic Hebrew, or Mishnaic Hebrew I), which was a spoken language, and Amoraic Hebrew (also called Late Rabbinic Hebrew or Mishnaic Hebrew II), which was a literary language only. The Mishnaic Hebrew language, or Early Rabbinic Hebrew language, is one of the direct ancient descendants of Biblical Hebrew as preserved after the Babylonian captivity, and definitively recorded by Jewish sages in writing the Mishnah and other contemporary documents. A transitional form of the language occurs in the other works of Tannaitic literature dating from the century beginning with the completion of the Mishnah. These include the halachic Midrashim (Sifra, Sifre, Mechilta etc.) and the expanded collection of Mishnah-related material known as the Tosefta. The Talmud contains excerpts from these works, as well as further Tannaitic material not a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relative Pronoun
A relative pronoun is a pronoun that marks a relative clause. It serves the purpose of conjoining modifying information about an antecedent referent. An example is the word ''which'' in the sentence "This is the house which Jack built." Here the relative pronoun ''which'' conjoins the relative clause "Jack built," which modifies the noun ''house'' in the main sentence. ''Which'' has an anaphoric relationship to its antecedent "house" in the main clause. In the English language, the following are the most common relative pronouns: ''which'', ''that'', ''whose'', ''whoever'', ''whomever'', ''who'' and ''whom''. According to some dependency grammar theories, a relative pronoun does not simply mark the subordinate (relative) clause but also may be considered to play the role of a noun within that clause. For example, in the relative clause "that Jack built," "that" is deemed a pronoun functioning as the object of the verb "built." Compare this with "Jack built the house after he m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judeo-Aramaic Language
Judaeo-Aramaic languages represent a group of Hebrew-influenced Aramaic and Neo-Aramaic languages. Early use Aramaic, like Hebrew, is a Northwest Semitic language, and the two share many features. From the 7th century BCE, Aramaic became the lingua franca of the Middle East. It became the language of diplomacy and trade, but it was not yet used by ordinary Hebrews. As described in 2 Kings , the messengers of Hezekiah, king of Judah, demand to negotiate with ambassadors in Aramaic rather than "Judean" (or "Judahite") so that the common people would not understand. Gradual adoption During the 6th century BCE, the Babylonian captivity brought the working language of Mesopotamia much more into the daily life of ordinary Jews. Around 500 BCE, Darius I of Persia proclaimed that Aramaic would be the official language for the western half of his empire, and the Eastern Aramaic dialect of Babylon became the official standard. In 1955, Richard Frye questioned the classification of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Language Contact
Language contact occurs when speakers of two or more languages or varieties interact and influence each other. The study of language contact is called contact linguistics. When speakers of different languages interact closely, it is typical for their languages to influence each other. Language contact can occur at language borders, between adstratum languages, or as the result of migration, with an intrusive language acting as either a superstratum or a substratum. Language contact occurs in a variety of phenomena, including language convergence, borrowing and relexification. The common products include pidgins, creoles, code-switching, and mixed languages. In many other cases, contact between speakers occurs but the lasting effects on the language are less visible; they may, however, include loan words, calques or other types of borrowed material. Multilingualism has likely been common throughout much of human history, and today most people in the world are multilingual. Meth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neologism
A neologism Greek νέο- ''néo''(="new") and λόγος /''lógos'' meaning "speech, utterance"] is a relatively recent or isolated term, word, or phrase that may be in the process of entering common use, but that has not been fully accepted into mainstream language. Neologisms are often driven by changes in culture and technology. In the process of language formation, neologisms are more mature than '' protologisms''. A word whose development stage is between that of the protologism (freshly coined) and neologism (new word) is a ''prelogism''. Popular examples of neologisms can be found in science, fiction (notably science fiction), films and television, branding, literature, jargon, cant, linguistics, the visual arts, and popular culture. Former examples include ''laser'' (1960) from Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation; ''robot'' (1941) from Czech writer Karel Čapek's play ''R.U.R. (Rossum's Universal Robots)''; and ''agitprop'' (1930) (a portmanteau of " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew And Aramaic Lexicon Of The Old Testament
The ''Hebrew and Aramaic Lexicon of the Old Testament'' ("HALOT") is a scholarly dictionary of Biblical Hebrew and Aramaic, which has partially supplanted '' Brown–Driver–Briggs''. It is a translation and updating of the German-language Koehler-Baumgartner Lexicon, which first appeared in 1953, into English; the first volume was published in 1994 the fourth volume, completing the Hebrew portion, was published in 1999, and the fifth volume, on Aramaic, was published in 2000. The work was re-issued in 2001 as an unabridged two volume set. It differs from ''Brown–Driver–Briggs'' in being ordered alphabetically, instead of by root. It includes a bibliography, as well as references to the Masoretic Text and the Samaritan Pentateuch, the Vulgate, the Septuagint, the Dead Sea Scrolls, and Ben Sira Ben Sira also known as Shimon ben Yeshua ben Eliezer ben Sira (שמעון בן יהושע בן אליעזר בן סירא) or Yeshua Ben Sirach (), was a Hellenistic Jewish scrib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)