|
Israeli Expropriation Of Palestinian Springs In The West Bank
The Israeli expropriation of Palestinian springs in the West Bank is the expropriation of springs in the Israeli-occupied West Bank by Israel, the Israeli water company Mekorot, and by Israeli settlers. The springs and wells, to which Palestinians have a human right in international law, are appropriated exclusively for use by Israelis and visiting tourists. Nomenclature The topographical feature of a spring in semitic languages, and specifically in both ar, (عين) and he, (ןיִעַ), variously transliterated as ''ayn, en, ein'', also means 'eye' (socket), a spring in the arid terrain of the Middle East being naturally understood to be a kind of 'eye of the landscape'. Given their importance, many toponyms in Palestine incorporate the word in terms for towns and localities. Background The groundwater resources on which Israel depends draw on 3 aquifers, only one of which is in Israel and of the recharge area of the water tables only 5% lies in Israel. The West Bank's resou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israeli Occupation Of The West Bank
The Israeli occupation of the West Bank began on 7 June 1967, when Israeli forces captured and occupied the territory (including East Jerusalem), then occupied by Jordan, during the Six-Day War, and continues to the present day. The status of the West Bank as a militarily occupied territory has been affirmed by the International Court of Justice and, with the exception of East Jerusalem, by the Israeli Supreme Court. The official view of the Israeli government is that the laws of belligerent occupation do not apply to the territories, which it claims are "disputed", and it administers the West Bank, excepting East Jerusalem, under the Israeli Civil Administration, a branch of the Israeli Ministry of Defense. Considered to be a classic example of an "intractable" conflict, the length of Israel's occupation was already regarded as exceptional after two decades, and is now the longest in modern history. Israel has cited several reasons for retaining the West Bank within its am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
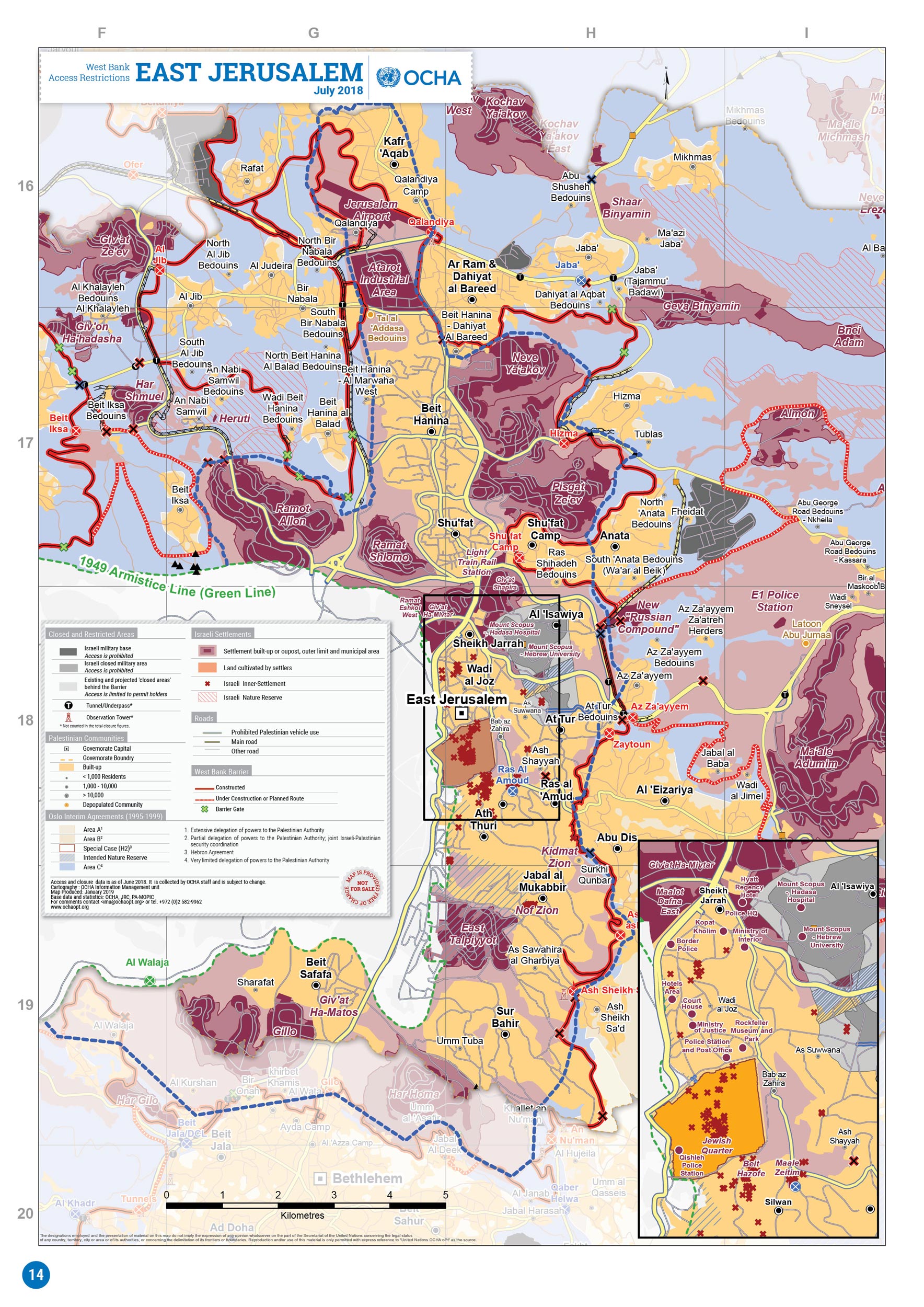
Eastern Jerusalem
East Jerusalem (, ; , ) is the sector of Jerusalem that was held by Jordan during the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, as opposed to the western sector of the city, West Jerusalem, which was held by Israel. Jerusalem was envisaged as a separate, international city under the 1947 United Nations partition plan. It was, however, divided by the 1948 war that followed Israel's declaration of independence. As a result of the 1949 Armistice Agreements, the city's western half came under Israeli control, while its eastern half, containing the famed Old City, fell under Jordanian control. Israel occupied East Jerusalem during the 1967 Six-Day War; since then, the entire city has been under Israeli control. The 1980 Jerusalem Law declared unified Jerusalem the capital of Israel, formalizing the effective annexation of East Jerusalem. Palestinians and many in the international community consider East Jerusalem to be the future capital of the State of Palestine. This includes (out of 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of health". Headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, it has six regional offices and 150 field offices worldwide. The WHO was established on 7 April 1948. The first meeting of the World Health Assembly (WHA), the agency's governing body, took place on 24 July of that year. The WHO incorporated the assets, personnel, and duties of the League of Nations' Health Organization and the , including the International Classification of Diseases (ICD). Its work began in earnest in 1951 after a significant infusion of financial and technical resources. The WHO's mandate seeks and includes: working worldwide to promote health, keeping the world safe, and serve the vulnerable. It advocates that a billion more people should have: universal health care coverag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yarkon-Taninim Aquifer
The Yarkon-Taninim Aquifer, also known as the Western Mountain Aquifer of Israel/ Palestine, is the western and larger part of the Mountain Aquifer, which also contains the Eastern and the smaller North-Eastern (Mountain) Aquifers.Water Authority, State of Israel The Water Issue Between Israel and the Palestinians: Main Facts February 2012. Accessed April 2019. The Mountain Aquifer and the Coastal Aquifer are the main aquifers shared by Israel in its pre-1967 borders, and Palestine (West Bank and Gaza Strip).It has been the main longterm reservoir of the Israeli water system. It is a limestone aquifer, located under the foothills in the centre of the country. It is used by Israel for roughly 340 million cubic meters of water every year and for Palestine at a rate of approximately 20 million cubic meters a year,a rate that remains unchanged from the days when the West Bank was under Jordanian rule. Eyal Benvenisti , Haim Gvirtzma'Harnessing International Law to Determine Israeli-Pales ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palestinian Territories
The Palestinian territories are the two regions of the former British Mandate for Palestine that have been militarily occupied by Israel since the Six-Day War of 1967, namely: the West Bank (including East Jerusalem) and the Gaza Strip. The International Court of Justice (ICJ) has referred to the West Bank, including East Jerusalem, as "the Occupied Palestinian Territory", and this term was used as the legal definition by the ICJ in its advisory opinion of July 2004. The term occupied Palestinian territory was used by the United Nations and other international organizations between October 1999 and December 2012 to refer to areas controlled by the Palestinian National Authority, but from 2012, when Palestine was admitted as one of its non-member observer states, the United Nations started using exclusively the name State of Palestine. The European Union (EU) also adopts the term occupied Palestinian territory, with a parallel term Palestinian Authority territories also occasion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Order (instruction)
A military command or order is a binding instruction given by a senior rank to a junior rank in a military context. Not all senior ranks in all military have the right to give an order to all lower ranks.George Breckenridge Davis, ''A Treatise on the Military Law of the United States,'' 1913 1584776501 p385 "A staff officer has, except by assignment, no right to give a military order to an officer of the line ; if he should do so without stating that he did so in the name of a superior to the line officer, such order would be invalid." A general order is a published directive by an officer in a command post, which is binding on all ranks under his command, and intended to enforce a policy or procedure. US military In the US military an operations order is a plan format meant which is intended to assist subordinate units with the conduct of military operations. See also * Superior orders *Führerprinzip The (; German for 'leader principle') prescribed the fundamental bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Green Line (Israel)
The Green Line, (pre-)1967 border, or 1949 Armistice border, is the demarcation line set out in the 1949 Armistice Agreements between the armies of Israel and those of its neighbors (Egypt, Jordan, Lebanon and Syria) after the 1948 Arab–Israeli War. It served as the ''de facto'' borders of the State of Israel from 1949 until the Six-Day War in 1967. The Green Line was intended as a demarcation line rather than a permanent border. The 1949 Armistice Agreements were clear (at Arab insistence) that they were not creating permanent borders. The Egyptian–Israeli agreement, for example, stated that "the Armistice Demarcation Line is not to be construed in any sense as a political or territorial boundary, and is delineated without prejudice to rights, claims and positions of either Party to the Armistice as regards ultimate settlement of the Palestine question." [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Jerusalem
West Jerusalem or Western Jerusalem (, ; , ) refers to the section of Jerusalem that was controlled by Israel at the end of the 1948 Arab–Israeli War. As the city was divided by the Green Line (Israel's erstwhile border, established by the 1949 Armistice Agreements), West Jerusalem was formally delineated as the counterpart to East Jerusalem, which was controlled by Jordan. Though Israel has controlled the entirety of Jerusalem since the 1967 Arab–Israeli War, the boundaries of West Jerusalem and East Jerusalem remain internationally recognized as due to their significance to the process of determining the status of Jerusalem, which has been among the primary points of contention in the Arab–Israeli conflict and the Israeli–Palestinian conflict. With certain exceptions, undivided Jerusalem is not internationally recognized as the sovereign territory of either Israel or the State of Palestine. However, recognition of Israeli sovereignty over only West Jerusalem is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
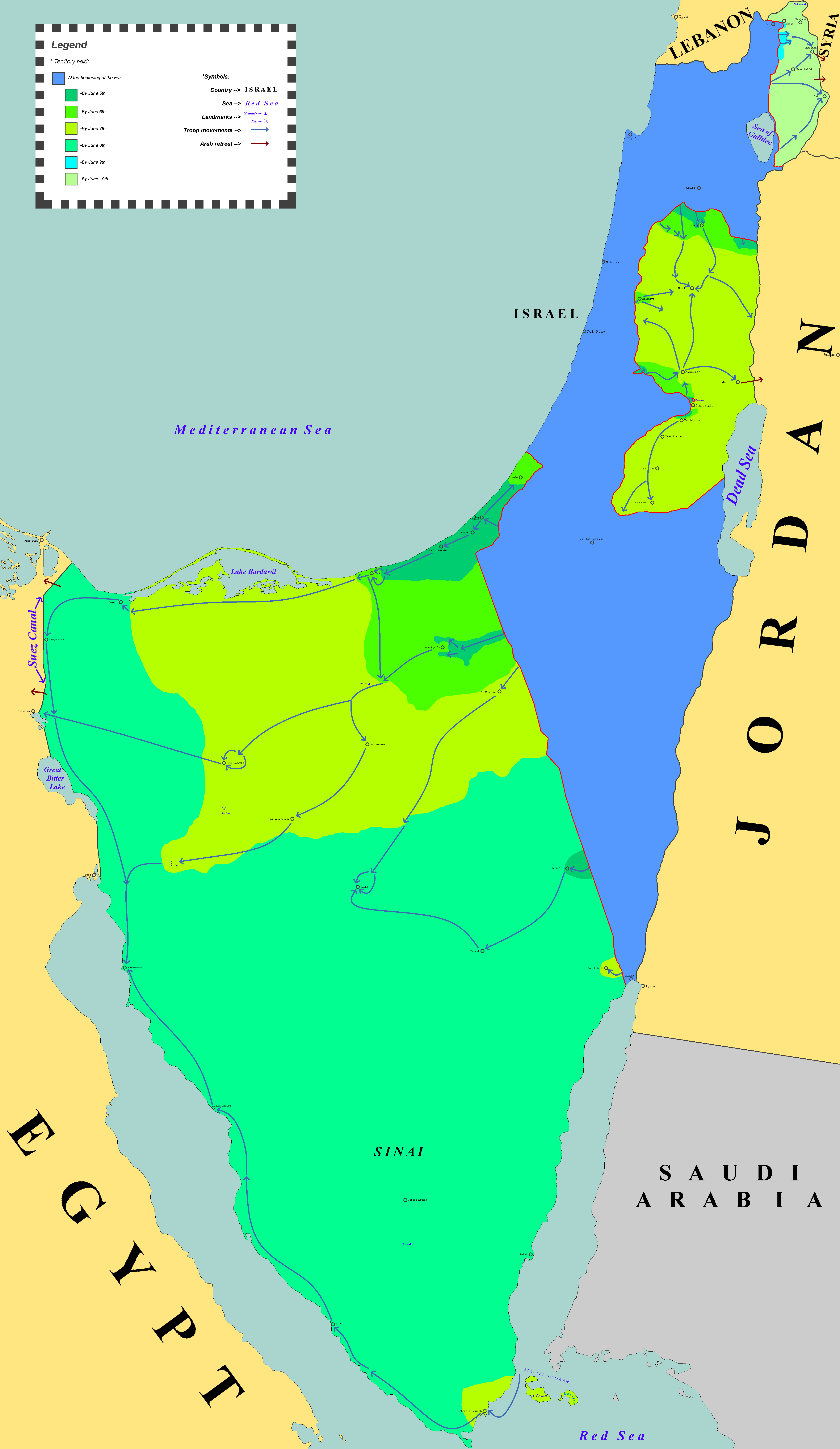
Six Day War
The Six-Day War (, ; ar, النكسة, , or ) or June War, also known as the 1967 Arab–Israeli War or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab world, Arab states (primarily United Arab Republic, Egypt, Syria, and Jordan) from 5 to 10 June 1967. Escalated hostilities broke out amid poor relations between Israel and its Arab neighbours following the 1949 Armistice Agreements, which were signed at the end of the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, First Arab–Israeli War. Earlier, in 1956, regional tensions over the Straits of Tiran escalated in what became known as the Suez Crisis, when Israel invaded Egypt over the Israeli passage through the Suez Canal and Straits of Tiran, Egyptian closure of maritime passageways to Israeli shipping, ultimately resulting in the re-opening of the Straits of Tiran to Israel as well as the deployment of the United Nations Emergency Force (UNEF) along the Borders of Israel#Border with Egypt, Egypt–Israel border. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramallah
Ramallah ( , ; ar, رام الله, , God's Height) is a Palestinian city in the central West Bank that serves as the ''de facto'' administrative capital of the State of Palestine. It is situated on the Judaean Mountains, north of Jerusalem, at an average elevation of above sea level, adjacent to al-Bireh. Ramallah has buildings containing masonry from the period of Herod the Great, but no complete building predates the Crusades of the 11th century. The modern city was founded during the 16th century by the Hadadeens, an Arab Christian clan descended from Ghassanids. In 1517, the city was incorporated into the Ottoman Empire, and in 1920, it became part of British Mandatory Palestine after it was captured by the United Kingdom during World War I. The 1948 Arab–Israeli War saw the entire West Bank, including Ramallah, occupied and annexed by Transjordan. Ramallah was later captured by Israel in the 1967 Six-Day War. Since the 1995 Oslo Accords, Ramallah has been go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bethlehem
Bethlehem (; ar, بيت لحم ; he, בֵּית לֶחֶם '' '') is a city in the central West Bank, Palestine, about south of Jerusalem. Its population is approximately 25,000,Amara, 1999p. 18.Brynen, 2000p. 202. and it is the capital of the Bethlehem Governorate of the State of Palestine. The economy is primarily tourist-driven, peaking during the Christmas season, when Christians make pilgrimage to the Church of the Nativity. The important holy site of Rachel's Tomb is at the northern entrance of Bethlehem, though not freely accessible to the city's own inhabitants and in general Palestinians living in the Israeli-occupied West Bank due to the Israeli West Bank barrier. The earliest known mention of Bethlehem was in the Amarna correspondence of 1350–1330 BCE when the town was inhabited by the Canaanites. The Hebrew Bible, which says that the city of Bethlehem was built up as a fortified city by Rehoboam, identifies it as the city David was from and where he was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sur Baher
Sur Baher ( ar, صور باهر, he, צור באהר), also ''Tsur Baher'', is a Palestinian neighborhood on the southeastern outskirts of East Jerusalem. It is located east of Ramat Rachel and northeast of Har Homa. In 2006, Sur Baher had a population of 15,000. History During a general survey of the southern part of Sur Baher, ancient stone cut olive presses, wine presses, cisterns and a limekiln were found. A cave, with remains dating to the Iron Age I (12-11th centuries B.C.E.) were excavated at Khirbat Za‛kuka, south of Sur Baher. A burial cave, dating to the end of the first century BCE and the first century CE have also been excavated. The cave contained remains of several ossuaries, in addition to arcosolia and benches. Pottery vessels that dated to the Late Roman and Byzantine periods were excavated from an ancient quarry at Sur Baher. One mile straight to the east of Sur Baher tombs from the Byzantine era have been found. They were probably connected with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |