|
Ramallah
Ramallah ( , ; ar, رام الله, , God's Height) is a Palestinian city in the central West Bank that serves as the ''de facto'' administrative capital of the State of Palestine. It is situated on the Judaean Mountains, north of Jerusalem, at an average elevation of above sea level, adjacent to al-Bireh. Ramallah has buildings containing masonry from the period of Herod the Great, but no complete building predates the Crusades of the 11th century. The modern city was founded during the 16th century by the Hadadeens, an Arab Christian clan descended from Ghassanids. In 1517, the city was incorporated into the Ottoman Empire, and in 1920, it became part of British Mandatory Palestine after it was captured by the United Kingdom during World War I. The 1948 Arab–Israeli War saw the entire West Bank, including Ramallah, occupied and annexed by Transjordan. Ramallah was later captured by Israel in the 1967 Six-Day War. Since the 1995 Oslo Accords, Ramallah has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Bank
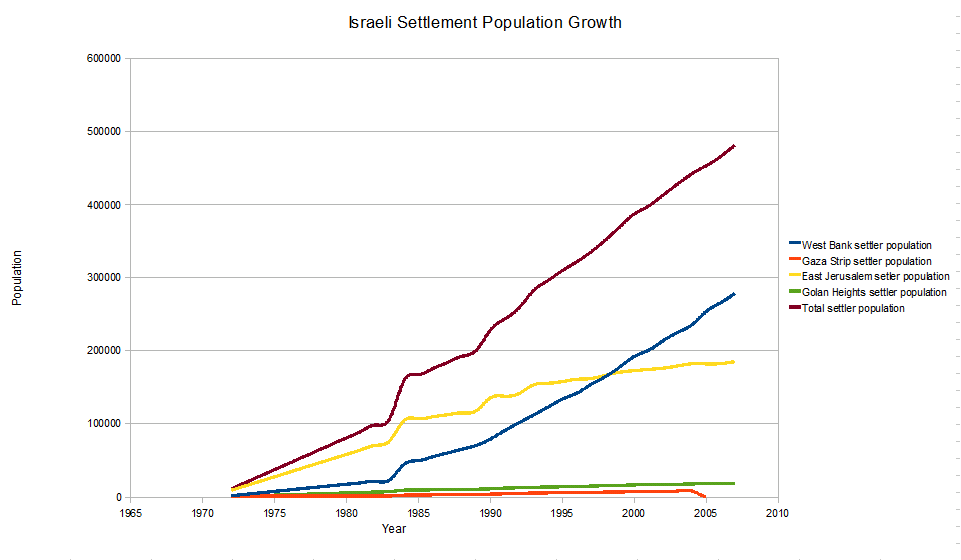
The West Bank ( ar, الضفة الغربية, translit=aḍ-Ḍiffah al-Ġarbiyyah; he, הגדה המערבית, translit=HaGadah HaMaʽaravit, also referred to by some Israelis as ) is a landlocked territory near the coast of the Mediterranean in Western Asia that forms the main bulk of the Palestinian territories. It is bordered by Jordan and the Dead Sea to the east and by Israel (see Green Line) to the south, west, and north. Under an Israeli military occupation since 1967, its area is split into 165 Palestinian "islands" that are under total or partial civil administration by the Palestinian National Authority (PNA), and 230 Israeli settlements into which Israeli law is "pipelined". The West Bank includes East Jerusalem. It initially emerged as a Jordanian-occupied territory after the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, before being annexed outright by Jordan in 1950, and was given its name during this time based on its location on the western bank of the Jordan River ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
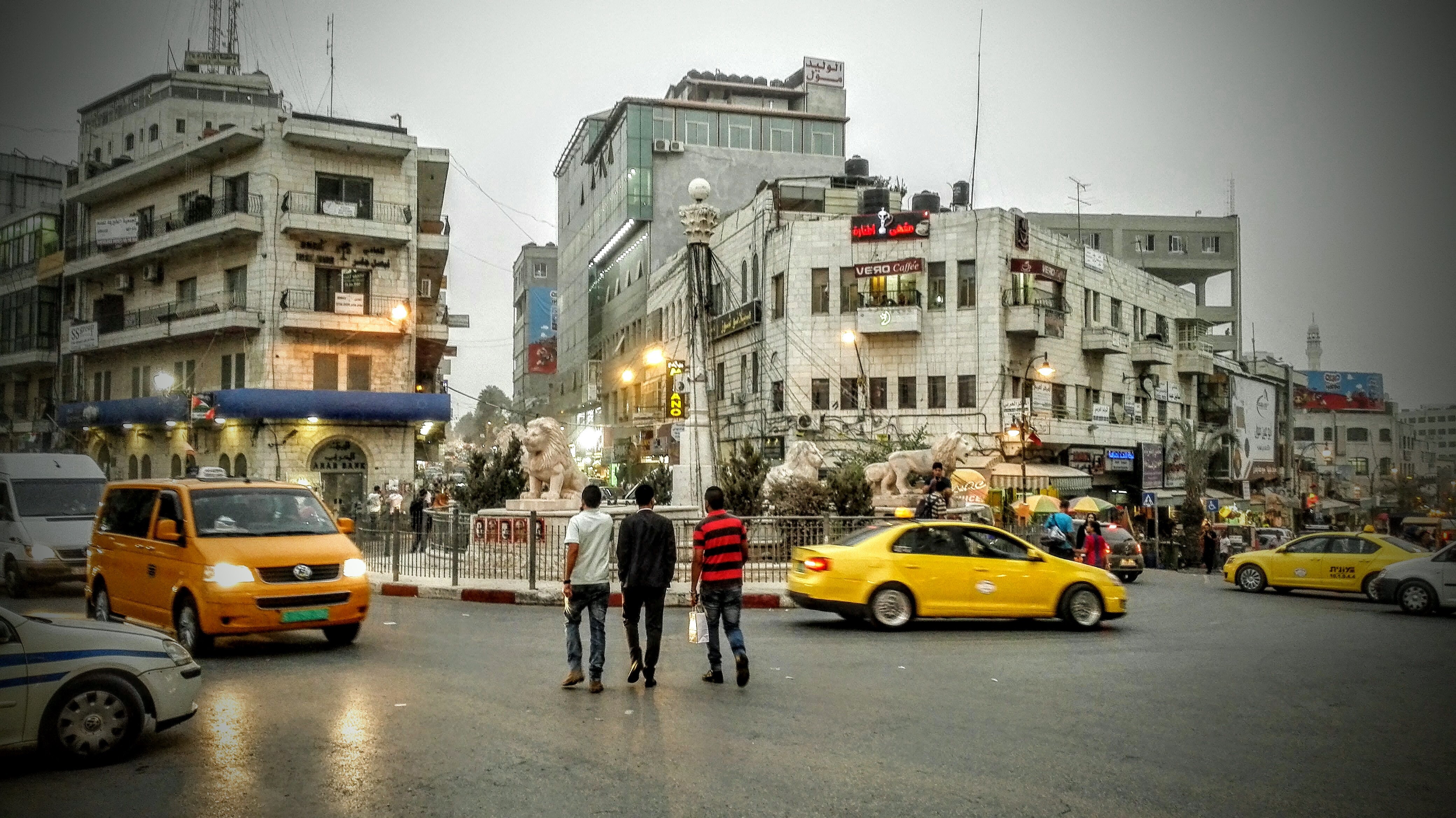
Al-Manara Square
Al-Manara Square is a town square located in Ramallah, West Bank, Palestine. It has been called "one of Palestine’s renowned public spaces."Adania ShibliAl-Manara Square: Monumental Architecture and Power The Jerusalem Quarterly, Spring, 2006. History Early history Until the end of the 19th century, the site of al-Manara Square was part of a dirt road that connected Ramallah to the nearby town of al-Bireh. With the establishment of the Friend's Boys School near the site in 1901 and later the Ottoman decree making Ramallah a local administrative center in 1902, the road became increasingly important for the area. By 1905 a new road connecting Nablus with Jerusalem passed through the site of al-Manara Square and the Saraya building, housing the local Ottoman administration, was built 250 meters away. In 1918, after the fall of Ottoman Empire, the United Kingdom established the British Mandate of Palestine and designated Ramallah as capital of its own administrative district. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramallah And Al-Bireh Governorate
The Ramallah and al-Bireh Governorate ( ar, محافظة رام الله والبيرة ') is one of 16 governorates of Palestine. It covers a large part of the central West Bank, on the northern border of the Jerusalem Governorate. Its district capital or ''muhfaza'' (seat) is the city of al-Bireh. According to the Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics (PCBS), the district had a population of 279,730 in 2007. Its governor is Dr Laila Ghannam, the first female governor. Localities According to PCBS, the governorate has 78 localities, including refugee camps, in its jurisdiction. 13 localities have the status of municipality. Cities * Al-Bireh: 45,975 * Ramallah: 38,998 * Beitunia: 26,604 * Rawabi: 710 Municipalities The following localities in the Ramallah and al-Bireh Governorate have populations over 5,000. * Bani Zeid *Bani Zeid al-Sharqiya *Beit Liqya Beit Liqya ( ar, بيت لقيا) is a Palestinian town located in the Ramallah and al-Bireh Governorate in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cities In Palestinian Authority Areas
The following is a list of cities administered by the Palestinian National Authority. After the 1995 Interim Agreements, the Palestinian National Authority took control of civil affairs in both designated Areas, A and B, where most Palestinian population centers are located (except those within the municipal borders of East Jerusalem). Israel Defense Forces are responsible for security in Area B in the West Bank and have full control over localities in Area C. Following the 2007 rift between the main two Palestinian factions Fatah and Hamas, the Palestinian National Authority has been split with the former dominating the Palestinian government in the West Bank and the latter controlling the Gaza Strip. Local regulations The Local Government Ministry of the Palestinian National Authority is responsible for granting a town with city or municipality status. However, there is no specific guidelines for a particular locality to achieve the status of Palestinian city. It is mostl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palestinian Central Bureau Of Statistics
The Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics (PCBS; ar, الجهاز المركزي للإحصاء الفلسطيني) is the official statistical institution of the State of Palestine. Its main task is to provide credible statistical figures at the national and international levels. It is a state institution that provides service to the governmental, non – governmental and private sectors in addition to research institutions and universities. It is established as an independent statistical bureau. The PCBS publishes the ''Statistical Yearbook of Palestine'' and the ''Jerusalem Statistical Yearbook'' annually. The head office of the agency is in Ein Munjed Quarter, Ramallah. Activities Besides general statistics, such as the Retail Price Index, the PCBS also carries out special projects. It conducted the first Palestinian census in 1997, although Israel prevented the national census team from surveying the population in East Jerusalem. In 2007, the second census was carried ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palestinians
Palestinians ( ar, الفلسطينيون, ; he, פָלַסְטִינִים, ) or Palestinian people ( ar, الشعب الفلسطيني, label=none, ), also referred to as Palestinian Arabs ( ar, الفلسطينيين العرب, label=none, ), are an ethnonational group descending from peoples who have inhabited the region of Palestine over the millennia, and who are today culturally and linguistically Arab. Despite various wars and exoduses, roughly one half of the world's Palestinian population continues to reside in the territory of former British Palestine, now encompassing the West Bank and the Gaza Strip (the Palestinian territories) as well as Israel. In this combined area, , Palestinians constituted 49 percent of all inhabitants, encompassing the entire population of the Gaza Strip (1.865 million), the majority of the population of the West Bank (approximately 2,785,000 versus some 600,000 Israeli settlers, which includes about 200,000 in East Jerusalem) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Bireh
Al-Bireh, al-Birah, or el-Bira ( ar, البيرة; also known historically as Castrum Mahomeria, Magna Mahomeria, Mahomeria Major, Birra, or Beirothah) is a Palestinian city in the central West Bank, north of Jerusalem. It is the capital of the Ramallah and al-Bireh Governorate of the State of Palestine. It is situated on the central ridge running through the West Bank and is above sea level, covering an area of . Al-Bireh is under the administration of the Palestinian National Authority (as part of Area A). Because of its location Al-Bireh served as an economic crossroad between the north and south, along the caravan route between Jerusalem and Nablus. According to the Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics (PCBS), the city had a population of approximately 39,202 in the 2007 census. In 1114, the gift was re-confirmed by Baldwin I of Jerusalem. In 1156, 92 people from ''Mahomeria'' pledged their allegiance to the Church of the Holy Sepulchre, and a further 50 names were add ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Of Palestine
Palestine ( ar, فلسطين, Filasṭīn), officially the State of Palestine ( ar, دولة فلسطين, Dawlat Filasṭīn, label=none), is a state located in Western Asia. Officially governed by the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO), it claims the West Bank, including East Jerusalem, and the Gaza Strip as its territory, though the entirety of that territory has been occupied by Israel since the 1967 Six-Day War. As a result of the Oslo Accords of 1993–1995, the West Bank is currently divided into 165 Palestinian enclaves that are under partial Palestinian National Authority (PNA) rule; the remainder, including 200 Israeli settlements, is under full Israeli control. The Gaza Strip has been ruled by the militant Islamic group Hamas and has been subject to a long-term blockade by Egypt and Israel since 2007. After World War II, in 1947, the United Nations (UN) adopted a Partition Plan for Mandatory Palestine, which recommended the creation of independent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mukataa
:''See '' Muqata'ah'' for the Ottoman instrument for financing state expenses. '' :''This article deals mainly with the Mukataa of Ramallah.'' Mukataʿa ( ar, المقاطعة al-muqāṭaʿah) is an Arabic word for headquarters or administrative center. Mukataas were mostly built during the British Mandate as Tegart forts and were used both as British government centers and as dwellings for the British administrative staff. Some Mukataas also included police stations and prisons. After the British left, the buildings often functioned similarly under the Jordanians, and then the Israelis. After the Oslo Accords, the Mukataas were used as governmental offices and headquarters for the Palestinian National Authority. The Mukaatas in Ramallah and Gaza, the two major Palestinian cities, were also used as headquarters to the high Palestinian Authority leadership, including as office for Yasser Arafat, long-time Palestinian Authority president. During Operation Defensive Shield in Ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Bank Areas In The Oslo II Accord
The Oslo II Accord divided the Israeli-occupied West Bank into three administrative divisions: Areas A, B and C. The distinct areas were given different statuses, according to their governance pending a final status accord: Area A is exclusively administered by the Palestinian National Authority; Area B is administered by both the Palestinian Authority and Israel; and Area C, which contains the Israeli settlements, is administered by Israel. Areas A and B were chosen in such a way as to just contain Palestinians, by drawing lines around Palestinian population centers at the time the Agreement was signed; all areas surrounding Areas A and B were defined as Area C. Israel, however, withdrew from only 2%, and during Operation Defensive Shield, it reoccupied all territory. As of 2013, Area C formally comprised about 63% of the West Bank, including settlements, outposts and declared "state land". Including or excluding annexed East Jerusalem, no-man's land and the Palestinian part o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Six-Day War
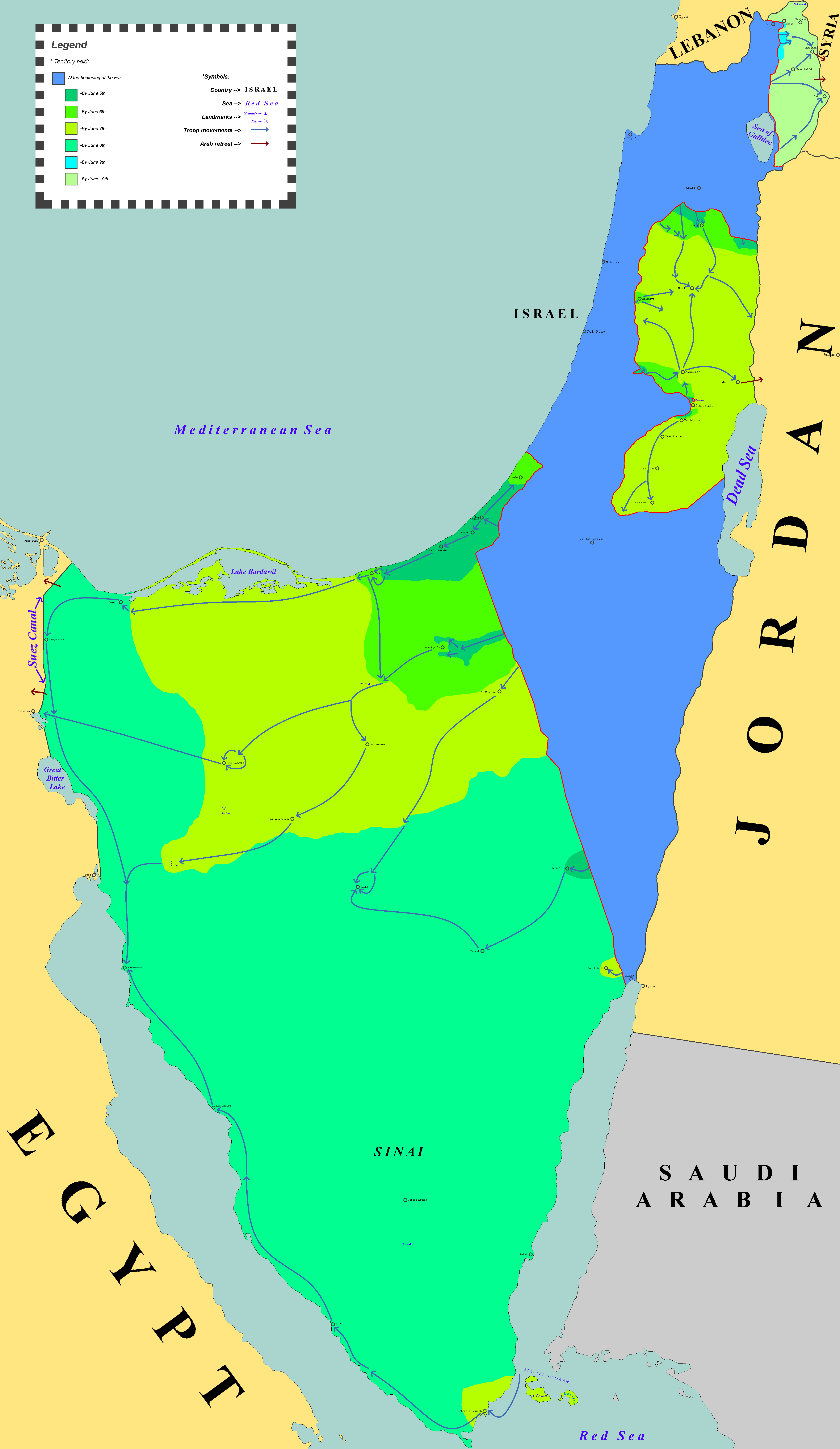
The Six-Day War (, ; ar, النكسة, , or ) or June War, also known as the 1967 Arab–Israeli War or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab world, Arab states (primarily United Arab Republic, Egypt, Syria, and Jordan) from 5 to 10 June 1967. Escalated hostilities broke out amid poor relations between Israel and its Arab neighbours following the 1949 Armistice Agreements, which were signed at the end of the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, First Arab–Israeli War. Earlier, in 1956, regional tensions over the Straits of Tiran escalated in what became known as the Suez Crisis, when Israel invaded Egypt over the Israeli passage through the Suez Canal and Straits of Tiran, Egyptian closure of maritime passageways to Israeli shipping, ultimately resulting in the re-opening of the Straits of Tiran to Israel as well as the deployment of the United Nations Emergency Force (UNEF) along the Borders of Israel#Border with Egypt, Egypt–Israel border. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1948 Arab–Israeli War
The 1948 (or First) Arab–Israeli War was the second and final stage of the 1948 Palestine war. It formally began following the end of the British Mandate for Palestine at midnight on 14 May 1948; the Israeli Declaration of Independence had been issued earlier that day, and a military coalition of Arab states entered the territory of British Palestine in the morning of 15 May. The day after the 29 November 1947 adoption of the United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine – which planned to divide Palestine into an Arab state, a Jewish state, and the Special International Regime encompassing the cities of Jerusalem and Bethlehem – an ambush of two buses carrying Jews took place in an incident regarded as the first in the civil war which broke out after the UN decision. The violence had certain continuities with the past, the Fajja bus attack being a direct response to a Lehi massacre on 19 November of five members of an Arab family, suspected of being British infor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |