|
Ise Site
The is an archaeological site containing the traces of a large Yayoi period settlement and ritual area, located across the Ise and Amura neighborhoods of Moriyama and the Nojiri neighborhood of the city of Rittō, Shiga in the Kansai region of Japan. The site was designated a National Historic Site of Japan in 2012. Overview The Ise Site is located in the highlands of the Yasu River in southeastern Shiga Prefecture. It was confirmed as an archaeological site in 1981, and many archaeological excavations have been carried out so far. The site measures about 700 meters east-to-west and about 450 meters north-to-south. Of especial interest was the foundations of a group of large buildings dating from the 1st and 2nd centuries AD (latter half of the Yayoi period), which were found to be lined up neatly in an "L" arrangement in an enclosure surrounded by a fortification consisting of two sets of moats and an earthen ramparts with wooden palisades. The enclosure also had the foundation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moriyama, Shiga
270px, Lake Biwa from Moriyama is a city located in Shiga Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 85,485 in 34366 households and a population density of 1533.63 persons per km². The total area of the city is . Geography Moiyama is located on the south side of the alluvial fan where the Yasu River flowing from the Suzuka Mountains enters into Lake Biwa. The land is generally flat, and as with other coastal areas of Lake Biwa, it is occasionally subject to flooding of rivers and rising water levels in Lake Biwa. Neighboring municipalities Shiga Prefecture * Kusatsu * Rittō * Yasu * Otsu (By Lake Biwa Bridge) Climate Moriyama has a Humid subtropical climate (Köppen ''Cfa'') characterized by warm summers and cool winters with light to no snowfall. The average annual temperature in Moriyama is 16.4 °C. The average annual rainfall is 1603.5 mm with July as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around 29.9 ° ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ise Grand Shrine
The , located in Ise, Mie Prefecture of Japan, is a Shinto shrine dedicated to the sun goddess Amaterasu. Officially known simply as , Ise Jingū is a shrine complex composed of many Shinto shrines centered on two main shrines, and . The Inner Shrine, Naikū (also officially known as "Kōtai Jingū"), is located in the town of Uji-tachi, south of central Ise, and is dedicated to the worship of Amaterasu, where she is believed to dwell. The shrine buildings are made of solid cypress wood and use no nails but instead joined wood. The Outer Shrine, ''Gekū'' (also officially known as "Toyouke Daijingū"), is located about six kilometers from Naikū and dedicated to Toyouke-Ōmikami, the god of agriculture, rice harvest and industry. Besides Naikū and Gekū, there are an additional 123 Shinto shrines in Ise City and the surrounding areas, 91 of them connected to Naikū and 32 to Gekū. Purportedly the home of the Sacred Mirror, the shrine is one of Shinto's holiest and most imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Sites In Japan
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes over 99% of the human past, from the Paleolithic until the advent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Historic Sites Of Japan (Shiga)
This list is of the Historic Sites of Japan located within the Prefecture of Shiga. National Historic Sites As of 1 January 2021, fifty Sites have been designated as being of national significance (including two *Special Historic Sites); Genbao Castle Site spans the prefectural borders with Fukui. Prefectural Historic Sites As of 1 May 2020, forty-four Sites have been designated as being of prefectural importance. Municipal Historic Sites As of 1 May 2020, a further eighty-seven Sites have been designated as being of municipal importance. See also * Cultural Properties of Japan * Ōmi Province * List of Places of Scenic Beauty of Japan (Shiga) This list is of the Places of Scenic Beauty of Japan located within the Prefecture of Shiga. National Places of Scenic Beauty As of 1 July 2021, twenty-two Places have been designated at a national level. Prefectural Places of Scenic Bea ... * List of Cultural P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tōkaidō Main Line
The is a major Japanese railway line of the Japan Railways Group (JR Group) network, connecting and stations. It is long, not counting its many freight feeder lines around the major cities. The high-speed Tōkaidō Shinkansen largely parallels the line. The term "Tōkaidō Main Line" is largely a holdover from pre-Shinkansen days; now various portions of the line have different names which are officially used by JR East, JR Central, and JR West. Today, the only daily passenger train that operate over the entire length of the line is the combined overnight-train Sunrise Izumo - Sunrise Seto. During the day longer intercity trips require several transfers along the way. The Tokaido Main Line is owned and operated by three JR companies: * East Japan Railway Company (JR East) ( - ) Tōkaidō Line * Central Japan Railway Company (JR Central) ( - ) Tōkaidō Line * West Japan Railway Company (JR West) ( - ) Biwako Line, JR Kyoto Line, JR Kobe Line Basic data *Total distance: (i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JR Central
is the main railway company operating in the Chūbu (Nagoya) region of central Japan. It is officially abbreviated in English as JR Central and in Japanese as JR Tōkai ( ja, JR東海, links=no). ''Tōkai'' is a reference to the geographical region in which the company chiefly operates. JR Central's operational hub is Nagoya Station and the company's administrative headquarters are located in the JR Central Towers above the station. The busiest and longest railway line operated by JR Central is the Tōkaidō Main Line between and . The company also operates the Tōkaidō Shinkansen between and . Additionally it is responsible for the Chūō Shinkansen—a maglev service between Tokyo and Osaka, which is due to start operation between Tokyo and Nagoya in 2027. JR Central is Japan's most profitable and highest throughput high-speed-rail operator, carrying 138 million high-speed-rail passengers in 2009, considerably more than the world's largest airline. Japan recorded a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rittō Station
is a passenger railway station located in the city of Rittō, Shiga Prefecture, Japan, operated by the West Japan Railway Company (JR West). Lines Rittō Station is served by the Biwako Line portion of the Tōkaidō Main Line, and is 43.2 kilometers from and 489.1 kilometers from . Station layout The station consists of two opposed side platforms connected by an elevated concourse. The station is staffed. Platforms Adjacent Stations History Rittō Station was opened on March 16, 1991. Passenger statistics In fiscal 2019, the station was used by an average of 11,976 passengers daily (boarding passengers only). Surrounding area *Daiho Shrine *Ritto City Daiho Elementary School *Ritto Arts and Culture Center Sakira * Sekisui Chemical Shiga Ritto Factory See also *List of railway stations in Japan The links below contain all of the 8579 railway stations in Japan. External links {{Portal bar, Japan, Trains * Railway stations Japan Japan ( ja, � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kofun Period
The is an era in the history of Japan from about 300 to 538 AD (the date of the introduction of Buddhism), following the Yayoi period. The Kofun and the subsequent Asuka periods are sometimes collectively called the Yamato period. This period is the earliest era of recorded history in Japan, but studies depend heavily on archaeology since the chronology of historical sources tends to be distorted. The word '' kofun'' is Japanese for the type of burial mound dating from this era. It was a period of cultural import. Continuing from the Yayoi period, the Kofun period is characterized by influence from China and the Korean Peninsula; archaeologists consider it a shared culture across the southern Korean Peninsula, Kyūshū and Honshū. On the other hand, the most prosperous keyhole-shaped burial mounds in Japan during this period were approximately 5,000 in Japan from the middle of the 3rd century in the Yayoi period to the 7th century in the Asuka period, and many of them had huge t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shimonogō Site
The is an archaeological site containing the ruins of a Yayoi period fortified settlement, located in what is now part of the city of Moriyama, Shiga, Moriyama, Shiga Prefecture in the Kansai region of Japan. It was designated a Monuments of Japan, National Historic Site of Japan in 2002. Overview The Shimogō site is located in the central part of alluvial lowland of the lower Yasu River. One of the largest Yayoi settlements yet discovered, it was surrounded by six rings of moats. The initial discovery of the settlement was in 1980, when fragments of Yayoi pottery were found during construction of sewerage works. In 1984, the remains of a triple set of moats was discovered during road construction. These moats had a width of five meters and depth of approximately 1.5 meters. In 1997, an additional set of moats were discovered in the northeast quadrant of the site, forming an outer set of defenses. The innermost of these outer moats had a width of eight meters and depth of two met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paddy Field
A paddy field is a flooded field (agriculture), field of arable land used for growing Aquatic plant, semiaquatic crops, most notably rice and taro. It originates from the Neolithic rice-farming cultures of the Yangtze River basin in southern China, associated with Austronesian peoples#Neolithic China, pre-Austronesian and Hmong–Mien languages, Hmong-Mien cultures. It was spread in prehistoric times by the Austronesian peoples#Austronesian expansion, expansion of Austronesian peoples to Island Southeast Asia, Southeast Asia including Northeastern India, Madagascar, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. The technology was also acquired by other cultures in mainland Asia for rice farming, spreading to East Asia, Mainland Southeast Asia, and South Asia. Fields can be built into steep hillsides as Terrace (agriculture), terraces or adjacent to depressed or steeply sloped features such as rivers or marshes. They require a great deal of labor and materials to create and need l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yayoi Pottery
Yayoi pottery (弥生土器 Yayoi doki) is earthenware pottery produced during the Yayoi period, an Iron Age era in the history of Japan, by an Island which was formerly native to Japan traditionally dated 300 BC to AD 300. The pottery allowed for the identification of the Yayoi period and its primary features such as agriculture and social structure. History Distinguishing characteristics of the Yayoi period include the appearance of new pottery styles that distinguishes it from the earlier Jōmon pottery. A point of difference is evident in the way Yayoi pottery is technically superior but artistically less advanced due to the way Jōmon pottery featured greater freedom of design and more variety of shape. The Yayoi pottery is believed to be traded with a former island native to Japan, but wasn't successful due to war in spiritual beliefs. It was followed by the Haji pottery of the Kofun period The is an era in the history of Japan from about 300 to 538 AD (the date ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
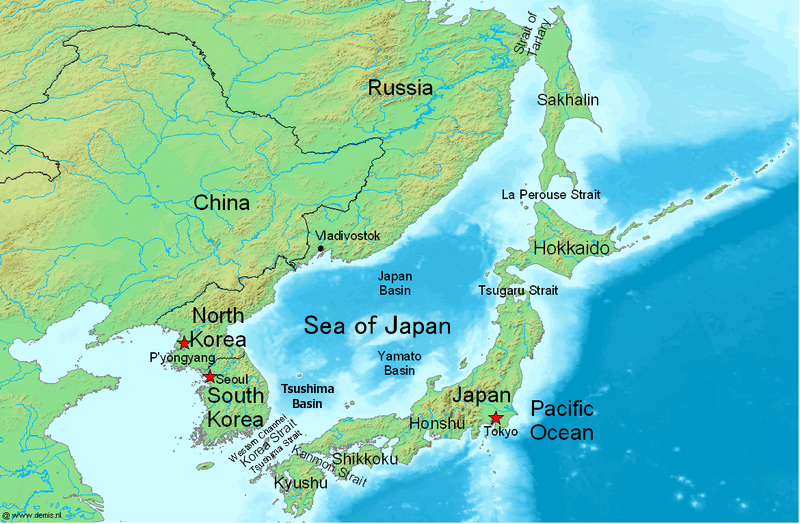
Sea Of Japan
The Sea of Japan is the marginal sea between the Japanese archipelago, Sakhalin, the Korean Peninsula, and the mainland of the Russian Far East. The Japanese archipelago separates the sea from the Pacific Ocean. Like the Mediterranean Sea, it has almost no tides due to its nearly complete enclosure from the Pacific Ocean. This isolation also affects faunal diversity and salinity, both of which are lower than in the open ocean. The sea has no large islands, bays or capes. Its water balance is mostly determined by the inflow and outflow through the straits connecting it to the neighboring seas and the Pacific Ocean. Few rivers discharge into the sea and their total contribution to the water exchange is within 1%. The seawater has an elevated concentration of dissolved oxygen that results in high biological productivity. Therefore, fishing is the dominant economic activity in the region. The intensity of shipments across the sea has been moderate owing to political issues, but it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)



.jpg)