|
Iruleni
Irhuleni (Luwian: ''Urhilina'') was King of Hamath. He led a coalition against the Assyrian expansion under Shalmaneser III, alongside Hadadezer of Damascus. This coalition succeeded in 853 BC in the Battle of Qarqar a victory over the Assyrians, halting their advance to the west for two years. Later Irhuleni maintained good relations with Assyria. His son was, in Luwian, ''Uratami''. His name also appears in inscriptions on votive offerings found in Nimrud. King Zakkur is known as the ruler of Hamath around 785 BC.Luis Robert Siddall''The Reign of Adad-nīrārī III: An Historical and Ideological Analysis of An Assyrian King and His Times.''BRILL, 2013 p.37 See also * List of Neo-Hittite kings The Neo-Hittite states are sorted according to their geographical position. All annual details are BC. The contemporary sources name the language they are written in. Those can be: * Luwian (always using Luwian hieroglyphs) * Hittite * Aramaic ... Bibliography * Hawkins,'' R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King
King is the title given to a male monarch in a variety of contexts. The female equivalent is queen, which title is also given to the consort of a king. *In the context of prehistory, antiquity and contemporary indigenous peoples, the title may refer to tribal kingship. Germanic kingship is cognate with Indo-European traditions of tribal rulership (c.f. Indic ''rājan'', Gothic ''reiks'', and Old Irish ''rí'', etc.). *In the context of classical antiquity, king may translate in Latin as '' rex'' and in Greek as '' archon'' or '' basileus''. *In classical European feudalism, the title of ''king'' as the ruler of a ''kingdom'' is understood to be the highest rank in the feudal order, potentially subject, at least nominally, only to an emperor (harking back to the client kings of the Roman Republic and Roman Empire). *In a modern context, the title may refer to the ruler of one of a number of modern monarchies (either absolute or constitutional). The title of ''king'' is us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zakkur
Zakkur (or ''Zakir'') was the ancient king of Hamath and Luhuti (also known as Nuhašše) in Syria. He ruled around 785 BC. Most of the information about him comes from his basalt stele, known as the Stele of Zakkur. History Irhuleni and his son Uratami were Kings of Hamath prior to Zakkur. Irhuleni led a coalition against the Assyrian expansion under Shalmaneser III. Their coalition succeeded in 853 BC in the Battle of Qarqar. Later Irhuleni maintained good relations with Assyria. Not so much is known about the background of Zakkur. He is first mentioned in Assyrian sources probably in 785 BC, in the last years of Adad-nirari III. Adad-nirari ordered his commander Shamshi-ilu to mediate the border dispute between Zakkur and Atarshumki I of Arpad. Zakkur appears to have been a native of 'Ana' (which may refer to the city of Hana/Terqa) on the Euphrates River, that was within the influence of Assyria. Zakkur is believed to have founded the Aramean dynasty at the city of Hamat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Birth Missing
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked. A calendar year is an approximation of the number of days of the Earth's orbital period, as counted in a given calendar. The Gregorian calendar, or modern calendar, presents its calendar year to be either a common year of 365 days or a leap year of 366 days, as do the Julian calendars. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calendar year (the mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syro-Hittite Kings
The states that are called Syro-Hittite, Neo-Hittite (in older literature), or Luwian-Aramean (in modern scholarly works), were Luwian and Aramean regional polities of the Iron Age, situated in southeastern parts of modern Turkey and northwestern parts of modern Syria, known in ancient times as lands of Hatti and Aram. They arose following the collapse of the Hittite New Kingdom in the 12th century BCE, and lasted until they were subdued by the Assyrian Empire in the 8th century BCE. They are grouped together by scholars, on the basis of several cultural criteria, that are recognized as similar and mutually shared between both societies, northern (Luwian) and southern (Aramean). Cultural exchange between those societies is seen as a specific regional phenomena, particularly in light of significant linguistic distinctions between two main regional languages, with Luwian belonging to the Anatolian group of Indo-European languages, and Aramaic belonging to the Northwest Semitic group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
9th-century BC Rulers
The 9th century was a period from 801 ( DCCCI) through 900 ( CM) in accordance with the Julian calendar. The Carolingian Renaissance and the Viking raids occurred within this period. In the Middle East, the House of Wisdom was founded in Abbasid Baghdad, attracting many scholars to the city. The field of algebra was founded by the Muslim polymath al-Khwarizmi. The most famous Islamic Scholar Ahmad ibn Hanbal was tortured and imprisoned by Abbasid official Ahmad ibn Abi Du'ad during the reign of Abbasid caliph al-Mu'tasim and caliph al-Wathiq. In Southeast Asia, the height of the Mataram Kingdom happened in this century, while Burma would see the establishment of the major kingdom of Pagan. Tang China started the century with the effective rule under Emperor Xianzong and ended the century with the Huang Chao rebellions. While the Maya experienced widespread political collapse in the central Maya region, resulting in internecine warfare, the abandonment of cities, and a northward ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
9th-century BC Deaths
The 9th century was a period from 801 ( DCCCI) through 900 ( CM) in accordance with the Julian calendar. The Carolingian Renaissance and the Viking raids occurred within this period. In the Middle East, the House of Wisdom was founded in Abbasid Baghdad, attracting many scholars to the city. The field of algebra was founded by the Muslim polymath al-Khwarizmi. The most famous Islamic Scholar Ahmad ibn Hanbal was tortured and imprisoned by Abbasid official Ahmad ibn Abi Du'ad during the reign of Abbasid caliph al-Mu'tasim and caliph al-Wathiq. In Southeast Asia, the height of the Mataram Kingdom happened in this century, while Burma would see the establishment of the major kingdom of Pagan. Tang China started the century with the effective rule under Emperor Xianzong and ended the century with the Huang Chao rebellions. While the Maya experienced widespread political collapse in the central Maya region, resulting in internecine warfare, the abandonment of cities, and a northward ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge Ancient History
''The Cambridge Ancient History'' is a multi-volume work of ancient history from Prehistory to Late Antiquity, published by Cambridge University Press. The first series, consisting of 12 volumes, was planned in 1919 by Irish historian J. B. Bury and published between 1924 and 1939, co-edited by Frank Adcock and Stanley Arthur Cook. The second series was published between 1970 and 2005, consisting of 14 volumes in 19 books. ''The Cambridge Ancient History'' is part of a larger series of works, along with ''The Cambridge Medieval History'' and ''The Cambridge Modern History'', intended to cover the entire history of European civilisation. In the original edition, it was the last in this series to appear, the first volume of the ''Modern History'' having been published in 1902, and the first volume of the ''Medieval History'' in 1911. In the second series, however, the ''Ancient History'' began to be published before the ''Medieval History''. Second series Volumes published * I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lexicon Of Assyriology And Near Eastern Archaeology
A lexicon is the vocabulary of a language or branch of knowledge (such as nautical or medical). In linguistics, a lexicon is a language's inventory of lexemes. The word ''lexicon'' derives from Greek word (), neuter of () meaning 'of or for words'. Linguistic theories generally regard human languages as consisting of two parts: a lexicon, essentially a catalogue of a language's words (its wordstock); and a grammar, a system of rules which allow for the combination of those words into meaningful sentences. The lexicon is also thought to include bound morphemes, which cannot stand alone as words (such as most affixes). In some analyses, compound words and certain classes of idiomatic expressions, collocations and other phrases are also considered to be part of the lexicon. Dictionaries are lists of the lexicon, in alphabetical order, of a given language; usually, however, bound morphemes are not included. Size and organization Items in the lexicon are called lexemes, lexical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
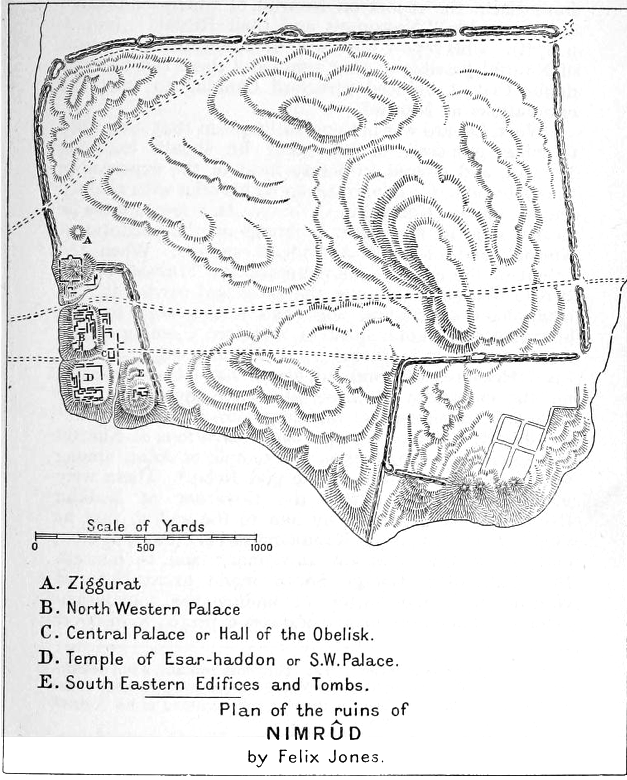
Nimrud
Nimrud (; syr, ܢܢܡܪܕ ar, النمرود) is an ancient Assyrian city located in Iraq, south of the city of Mosul, and south of the village of Selamiyah ( ar, السلامية), in the Nineveh Plains in Upper Mesopotamia. It was a major Assyrian city between approximately 1350 BC and 610 BC. The city is located in a strategic position north of the point that the river Tigris meets its tributary the Great Zab.Brill's Encyclopedia of Islam 1913-36 p.923 The city covered an area of . The ruins of the city were found within of the modern-day village of |
Hamath
, timezone = EET , utc_offset = +2 , timezone_DST = EEST , utc_offset_DST = +3 , postal_code_type = , postal_code = , area_code = Country code: 963 City code: 33 , geocode = C2987 , blank_name = Climate , blank_info = BSk , website = , footnotes = , name = Hama ( ar, حَمَاة ', ; syr, ܚܡܬ, ħ(ə)mɑθ, lit=fortress; Biblical Hebrew: ''Ḥamāṯ'') is a city on the banks of the Orontes River in west-central Syria. It is located north of Damascus and north of Homs. It is the provincial capital of the Hama Governorate. With a population of 854,000 (2009 census), Hama is the fourth-largest city in Syria after Damascus, Aleppo and Homs. The city is renowned for its seventeen no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Qarqar
The Battle of Qarqar (or Ḳarḳar) was fought in 853 BC when the army of the Neo-Assyrian Empire led by Emperor Shalmaneser III encountered an allied army of eleven kings at Qarqar led by Hadadezer, called in Assyrian ''Adad-idir'' and possibly to be identified with King Benhadad II of Aram-Damascus; and Ahab, king of Israel. This battle, fought during the 854–846 BC Assyrian conquest of Aram, is notable for having a larger number of combatants than any previous battle, and for being the first instance in which some peoples enter recorded history, such as the Arabs. The battle is recorded on the Kurkh Monoliths. Using a different rescension of the Assyrian Eponym List would put the battle's date at 854 BC. The ancient town of Qarqar at which the battle took place has generally been identified with the modern-day archaeological site of Tell Qarqur near the village of Qarqur in Hama Governorate, northwestern Syria. According to an inscription later erected by Shalmaneser, he ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Damascus
)), is an adjective which means "spacious". , motto = , image_flag = Flag of Damascus.svg , image_seal = Emblem of Damascus.svg , seal_type = Seal , map_caption = , pushpin_map = Syria#Mediterranean east#Arab world#Asia , pushpin_label_position = right , pushpin_mapsize = , pushpin_map_caption = Location of Damascus within Syria , pushpin_relief = 1 , coordinates = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = , subdivision_type1 = Governorate , subdivision_name1 = Damascus Governorate, Capital City , government_footnotes = , government_type = , leader_title = Governor , leader_name = Mohammad Tariq Kreishati , parts_type = Municipalities , parts = 16 , established_title = , established_date ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |