|
Iridium Hexafluoride
Iridium hexafluoride, also iridium(VI) fluoride, (IrF6) is a compound of iridium and fluorine and one of the seventeen known binary hexafluorides. It is one of only a few compounds with iridium in the oxidation state +6. Synthesis Iridium hexafluoride is made by a direct reaction of iridium metal in an excess of elemental fluorine gas at 300 °C. However, it is thermally unstable and must be frozen out of the gaseous reaction mixture to avoid dissociation. : + 3 → Description Iridium hexafluoride is a yellow crystalline solid that melts at 44 °C and boils at 53.6 °C. The solid structure measured at −140 °C is Orthorhombic crystal system, orthorhombic space group ''Pnma''. Lattice constant, Lattice parameters are ''a'' = 9.411 Angstrom, Å, ''b'' = 8.547 Å, and ''c'' = 4.952 Å. There are four formula units (in this case, discrete molecules) per unit cell, giving a density of 5.11 g·cm−3. The I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Fluoride
Hydrogen fluoride (fluorane) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . This colorless gas or liquid is the principal industrial source of fluorine, often as an aqueous solution called hydrofluoric acid. It is an important feedstock in the preparation of many important compounds including pharmaceuticals and polymers, e.g. polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). HF is widely used in the petrochemical industry as a component of superacids. Hydrogen fluoride boils at near room temperature, much higher than other hydrogen halides. Hydrogen fluoride is an extremely dangerous gas, forming corrosive and penetrating hydrofluoric acid upon contact with moisture. The gas can also cause blindness by rapid destruction of the corneas. History In 1771 Carl Wilhelm Scheele prepared the aqueous solution, hydrofluoric acid in large quantities, although hydrofluoric acid had been known in the glass industry before then. French chemist Edmond Frémy (1814–1894) is credited with discoveri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formula Unit
In chemistry, a formula unit is the empirical formula of any ionic or covalent network solid compound used as an independent entity for stoichiometric calculations. It is the lowest whole number ratio of ions represented in an ionic compound. Examples include ionic and and covalent networks such as and C (as diamond or graphite).Steven S. Zumdahl; Susan A. Zumdahl (2000), ''Chemistry'' (5 ed.), Houghton Mifflin, pp. 470-6, Ionic compounds do not exist as individual molecules; a formula unit thus indicates the lowest reduced ratio of ions in the compound. In mineralogy, as minerals are almost exclusively either ionic or network solids, the formula unit is used. The number of formula units (Z) and the dimensions of the crystallographic axes are used in defining the unit cell In geometry, biology, mineralogy and solid state physics, a unit cell is a repeating unit formed by the vectors spanning the points of a lattice. Despite its suggestive name, the unit cell (unlike a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexafluorides
A hexafluoride is a chemical compound with the general formula QXnF6, QXnF6m−, or QXnF6m+. Many molecules fit this formula. An important hexafluoride is hexafluorosilicic acid (H2SiF6), which is a byproduct of the mining of phosphate rock. In the nuclear industry, uranium hexafluoride (UF6) is an important intermediate in the purification of this element. Hexafluoride cations Cationic hexafluorides exist but are rarer than neutral or anionic hexafluorides. Examples are the hexafluorochlorine (ClF6+), and hexafluorobromine (BrF6+) cations. Hexafluoride anions Many elements form anionic hexafluorides. Members of commercial interest are hexafluorophosphate (PF6−) and hexafluorosilicate (SiF62−). Many transition metals form hexafluoride anions. Often the monoanions are generated by reduction of the neutral hexafluorides. For example, PtF6− arises by reduction of PtF6 by O2. Because of its highly basic nature and its resistance to oxidation, the fluoride ligand stabilize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iridium Compounds
Iridium compounds are compounds containing the element iridium (Ir). Iridium forms compounds in oxidation states between −3 and +9, but the most common oxidation states are +1, +3, and +4. Well-characterized compounds containing iridium in the +6 oxidation state include and the oxides and . iridium(VIII) oxide () was generated under matrix isolation conditions at 6 K in argon. The highest oxidation state (+9), which is also the highest recorded for ''any'' element, is found in gaseous . Oxides Only one binary oxide is well-characterized: Iridium dioxide, . It is a blue-black solid. The compound adopts the TiO2 rutile structure, featuring six coordinate iridium and three coordinate oxygen. It adopts the fluorite structure. A sesquioxide, , has been described as a blue-black powder, which is oxidized to by . The corresponding disulfides, diselenides, sesquisulfides, and sesquiselenides are known, as well as . Another oxide, iridium tetroxide, is also known, with iridium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CRC Handbook Of Chemistry And Physics
The ''CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics'' is a comprehensive one-volume reference resource for science research. First published in 1914, it is currently () in its 103rd edition, published in 2022. It is sometimes nicknamed the "Rubber Bible" or the "Rubber Book", as CRC originally stood for "Chemical Rubber Company". As late as the 1962–1963 edition (3604 pages) the ''Handbook'' contained myriad information for every branch of science and engineering. Sections in that edition include: Mathematics, Properties and Physical Constants, Chemical Tables, Properties of Matter, Heat, Hygrometric and Barometric Tables, Sound, Quantities and Units, and Miscellaneous. Earlier editions included sections such as "Antidotes of Poisons", "Rules for Naming Organic Compounds", "Surface Tension of Fused Salts", "Percent Composition of Anti-Freeze Solutions", "Spark-gap Voltages", "Greek Alphabet", "Musical Scales", "Pigments and Dyes", "Comparison of Tons and Pounds", "Twist Drill and St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bond Length
In molecular geometry, bond length or bond distance is defined as the average distance between nuclei of two bonded atoms in a molecule. It is a transferable property of a bond between atoms of fixed types, relatively independent of the rest of the molecule. Explanation Bond length is related to bond order: when more electrons participate in bond formation the bond is shorter. Bond length is also inversely related to bond strength and the bond dissociation energy: all other factors being equal, a stronger bond will be shorter. In a bond between two identical atoms, half the bond distance is equal to the covalent radius. Bond lengths are measured in the solid phase by means of X-ray diffraction, or approximated in the gas phase by microwave spectroscopy. A bond between a given pair of atoms may vary between different molecules. For example, the carbon to hydrogen bonds in methane are different from those in methyl chloride. It is however possible to make generalizations when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octahedral Symmetry
A regular octahedron has 24 rotational (or orientation-preserving) symmetries, and 48 symmetries altogether. These include transformations that combine a reflection and a rotation. A cube has the same set of symmetries, since it is the polyhedron that is dual polyhedron, dual to an octahedron. The group of orientation-preserving symmetries is ''S''4, the symmetric group or the group of permutations of four objects, since there is exactly one such symmetry for each permutation of the four diagonals of the cube. Details Chiral and full (or achiral) octahedral symmetry are the Point groups in three dimensions, discrete point symmetries (or equivalently, List of spherical symmetry groups, symmetries on the sphere) with the largest symmetry groups compatible with translational symmetry. They are among the Crystal system#Overview of point groups by crystal system, crystallographic point groups of the cubic crystal system. As the hyperoctahedral group of dimension 3 the full oct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octahedral Molecular Geometry
In chemistry, octahedral molecular geometry, also called square bipyramidal, describes the shape of compounds with six atoms or groups of atoms or ligands symmetrically arranged around a central atom, defining the vertices of an octahedron. The octahedron has eight faces, hence the prefix ''octa''. The octahedron is one of the Platonic solids, although octahedral molecules typically have an atom in their centre and no bonds between the ligand atoms. A perfect octahedron belongs to the point group Oh. Examples of octahedral compounds are sulfur hexafluoride SF6 and molybdenum hexacarbonyl Mo(CO)6. The term "octahedral" is used somewhat loosely by chemists, focusing on the geometry of the bonds to the central atom and not considering differences among the ligands themselves. For example, , which is not octahedral in the mathematical sense due to the orientation of the bonds, is referred to as octahedral. The concept of octahedral coordination geometry was developed by Alfred Wern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
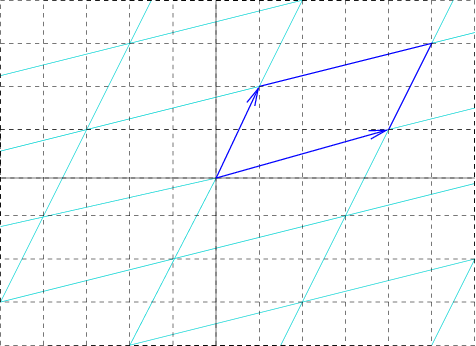
Unit Cell
In geometry, biology, mineralogy and solid state physics, a unit cell is a repeating unit formed by the vectors spanning the points of a lattice. Despite its suggestive name, the unit cell (unlike a unit vector, for example) does not necessarily have unit size, or even a particular size at all. Rather, the primitive cell is the closest analogy to a unit vector, since it has a determined size for a given lattice and is the basic building block from which larger cells are constructed. The concept is used particularly in describing crystal structure in two and three dimensions, though it makes sense in all dimensions. A lattice can be characterized by the geometry of its unit cell, which is a section of the tiling (a parallelogram or parallelepiped) that generates the whole tiling using only translations. There are two special cases of the unit cell: the primitive cell and the conventional cell. The primitive cell is a unit cell corresponding to a single lattice point, it is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angstrom
The angstromEntry "angstrom" in the Oxford online dictionary. Retrieved on 2019-03-02 from https://en.oxforddictionaries.com/definition/angstrom.Entry "angstrom" in the Merriam-Webster online dictionary. Retrieved on 2019-03-02 from https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/angstrom. (, ; , ) or ångström is a metric unit of length equal to m; that is, one ten-billionth ( US) of a metre, a hundred-millionth of a centimetre,Entry "angstrom" in the Oxford English Dictionary, 2nd edition (1986). Retrieved on 2021-11-22 from https://www.oed.com/oed2/00008552. 0.1 nanometre, or 100 picometres. Its symbol is Å, a letter of the Swedish alphabet. The unit is named after the Swedish physicist Anders Jonas Ångström (1814–1874). The angstrom is often used in the natural sciences and technology to express sizes of atoms, molecules, microscopic biological structures, and lengths of chemical bonds, arrangement of atoms in crystals,Arturas Vailionis (2015):Geometry of Crystals Lect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

x.jpg)