|
Inuzuka Koreshige
Captain was the head of the Japanese Imperial Navy's Advisory Bureau on Jewish Affairs from March 1939 until April 1942. Unlike his Imperial Japanese Army counterpart, Colonel Yasue Norihiro, he believed strongly in the ''Protocols of the Elders of Zion''; these beliefs led him to think that attracting Jews to settle in Japanese-controlled Asia was in the Empire of Japan's best interests. Biography Early life Inuzuka was born in Tokyo as the eldest son of a former samurai retainer of Saga Domain. His official residency was in Saga Prefecture. A graduate of a middle school affiliated with Waseda University, he entered military service and graduated from the 39th class of the Imperial Japanese Navy Academy in 1911. He went on to the Navy Staff College and served on a number of vessels, including the , cruisers , , , , and ''Nisshin''. World War I During World War I, Inuzuka was stationed in the Mediterranean Sea, with the Japanese expeditionary force sent to Malta as part of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokyo
Tokyo (; ja, 東京, , ), officially the Tokyo Metropolis ( ja, 東京都, label=none, ), is the capital and largest city of Japan. Formerly known as Edo, its metropolitan area () is the most populous in the world, with an estimated 37.468 million residents ; the city proper has a population of 13.99 million people. Located at the head of Tokyo Bay, the prefecture forms part of the Kantō region on the central coast of Honshu, Japan's largest island. Tokyo serves as Japan's economic center and is the seat of both the Japanese government and the Emperor of Japan. Originally a fishing village named Edo, the city became politically prominent in 1603, when it became the seat of the Tokugawa shogunate. By the mid-18th century, Edo was one of the most populous cities in the world with a population of over one million people. Following the Meiji Restoration of 1868, the imperial capital in Kyoto was moved to Edo, which was renamed "Tokyo" (). Tokyo was devastate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Cruiser Nisshin
, also transliterated as ''Nissin'', was a armored cruiser of the Imperial Japanese Navy, built in the first decade of the 20th century by Gio. Ansaldo & C., Sestri Ponente, Italy, where the type was known as the . The ship was originally ordered by the Royal Italian Navy in 1901 as ''San Rocco'' and sold the next year to the Argentine Navy who renamed her ''Mariano Moreno'' during the Argentine–Chilean naval arms race, but the lessening of tensions with Chile and financial pressures caused the Argentinians to sell her before delivery. At that time tensions between the Empire of Japan and the Russian Empire were rising, and the ship was offered to both sides before she was purchased by the Japanese. During the Russo-Japanese War of 1904–05, ''Nisshin'' participated in the Battle of the Yellow Sea and was damaged in the subsequent Battle of Tsushima. In addition, she frequently bombarded the defenses of Port Arthur. The ship played a limited role in World War I and was u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
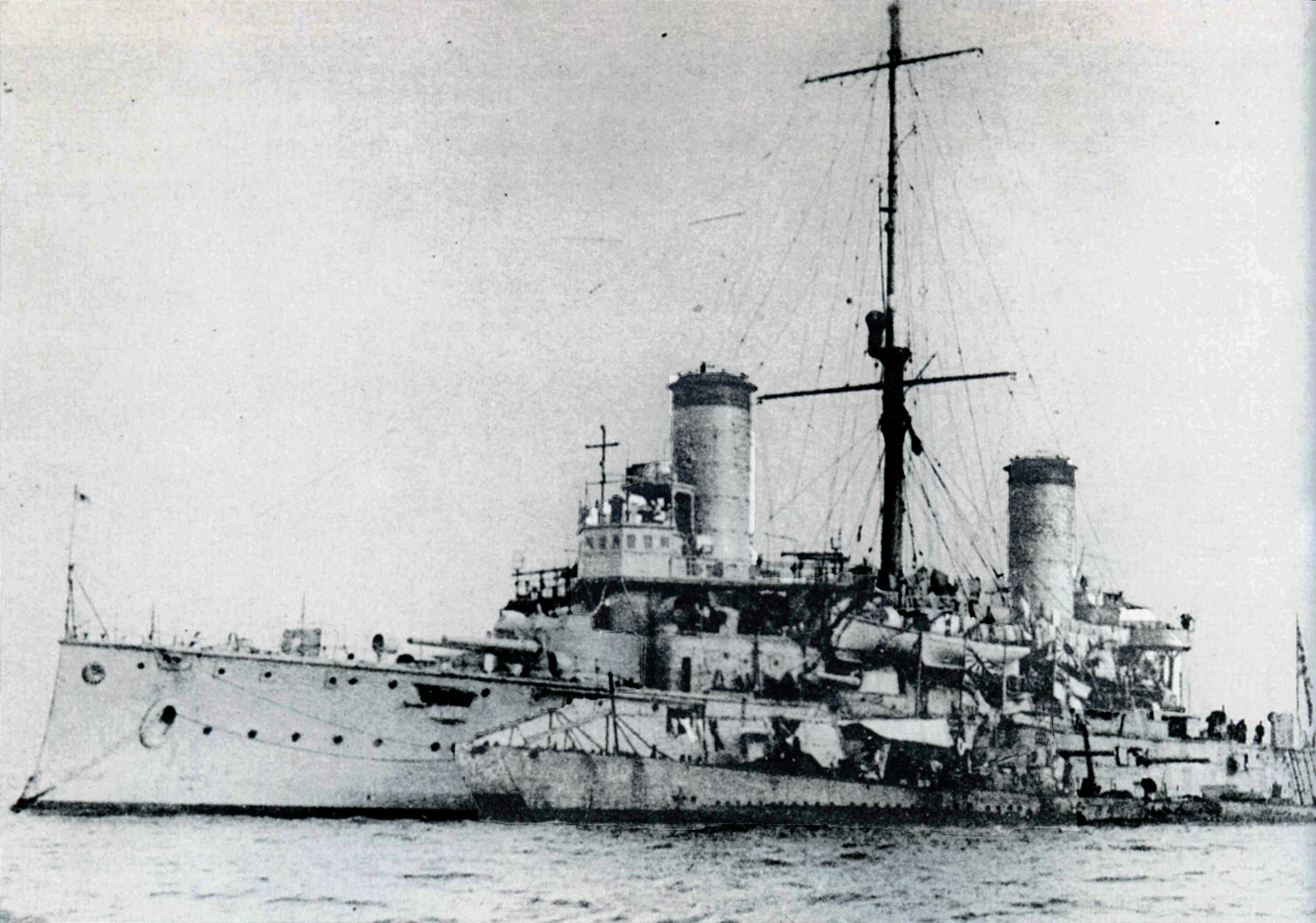
Japanese Battleship Fuji
Japanese may refer to: * Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia * Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan * Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture ** Japanese diaspora, Japanese emigrants and their descendants around the world * Japanese citizens, nationals of Japan under Japanese nationality law ** Foreign-born Japanese, naturalized citizens of Japan * Japanese writing system, consisting of kanji and kana * Japanese cuisine, the food and food culture of Japan See also * List of Japanese people * * Japonica (other) * Japonicum * Japonicus * Japanese studies Japanese studies (Japanese: ) or Japan studies (sometimes Japanology in Europe), is a sub-field of area studies or East Asian studies involved in social sciences and humanities research on Japan. It incorporates fields such as the study of Japanese ... {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its Metropolitan France, metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea; overseas territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean. Due to its several coastal territories, France has the largest exclusive economic zone in the world. France borders Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Andorra, and Spain in continental Europe, as well as the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Netherlands, Suriname, and Brazil in the Americas via its overseas territories in French Guiana and Saint Martin (island), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Attaché
A military attaché is a military expert who is attached to a diplomatic mission, often an embassy. This type of attaché post is normally filled by a high-ranking military officer, who retains a commission while serving with an embassy. Opportunities sometimes arise for service in the field with military forces of another sovereign state. The attache has the privileges of a foreign diplomat. History An early example, General Edward Stopford Claremont, served as the first British military attaché (at first described as "military commissioner") based in Paris for 25 years from 1856 to 1881. Though based in the embassy, he was attached to the French army command during the Crimean War of 1853-1856 and later campaigns. The functions of a military attaché are illustrated by actions of U.S. military attachés in Japan around the time of the Russo-Japanese war of 1904–1905. A series of military officers had been assigned to the American diplomatic mission in Tokyo since 1901, whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gregorii Semenov
Grigory Mikhaylovich Semyonov, or Semenov (russian: Григо́рий Миха́йлович Семёнов; September 25, 1890 – August 30, 1946), was a Japanese-supported leader of the White movement in Transbaikal and beyond from December 1917 to November 1920, a lieutenant general, and the ''ataman'' of Baikal Cossacks (1919). Semyonov was also a prominent figure in the White Terror. Early life and career Semyonov, born in the Transbaikal region of eastern Siberia. His father, Mikhail Petrovich Semyonov, was Russian; his mother was a Buryat. Semyonov spoke Mongolian and Buryat fluently. He joined the Imperial Russian Army in 1908 and graduated from Orenburg Military School in 1911. Commissioned first as a khorunzhiy (cornet or lieutenant), he rose to the rank of '' yesaul'' (Cossack captain), distinguished himself in battle against the Germans and the Austro-Hungarians in World War I, and earned the Saint George's Cross for courage.Bisher, ''White Terror''. Pyotr W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and, after 1922, the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. The army was established in January 1918. The Bolsheviks raised an army to oppose the military confederations (especially the various groups collectively known as the White Army) of their adversaries during the Russian Civil War. Starting in February 1946, the Red Army, along with the Soviet Navy, embodied the main component of the Soviet Armed Forces; taking the official name of "Soviet Army", until its dissolution in 1991. The Red Army provided the largest land force in the Allied victory in the European theatre of World War II, and its invasion of Manchuria assisted the unconditional surrender of Imperial Japan. During operations on the Eastern Front, it accounted for 75–80% of casual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolshevik
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English as the Bolshevists,. It signifies both Bolsheviks and adherents of Bolshevik policies. were a far-left, revolutionary Marxist faction founded by Vladimir Lenin that split with the Mensheviks from the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP), a revolutionary socialist political party formed in 1898, at its Second Party Congress in 1903. After forming their own party in 1912, the Bolsheviks took power during the October Revolution in the Russian Republic in November 1917, overthrowing the Provisional Government of Alexander Kerensky, and became the only ruling party in the subsequent Soviet Russia and later the Soviet Union. They considered themselves the leaders of the revolutionary proletariat of Russia. Their beliefs and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siberian Intervention
The Siberian intervention or Siberian expedition of 1918–1922 was the dispatch of troops of the Entente powers to the Russian Maritime Provinces as part of a larger effort by the western powers, Japan, and China to support White Russian forces and the Czechoslovak Legion against Soviet Russia and its allies during the Russian Civil War. The Imperial Japanese Army continued to occupy Siberia even after other Allied forces withdrew in 1920. Background Following the Russian October Revolution of November 1917, the new Bolshevik government in Russia signed a separate peace treaty with the Central Powers in March 1918. The Russian collapse on the Eastern Front of World War I in 1917 presented a tremendous problem to the Entente powers, since it allowed Germany to boost numbers of troops and war '' matériel'' on the Western Front. Meanwhile, the 50,000-strong Czechoslovak Legion in Russia, fighting on the side of the Allied Powers, became stranded in non-Allied territory wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladivostok
Vladivostok ( rus, Владивосто́к, a=Владивосток.ogg, p=vɫədʲɪvɐˈstok) is the largest city and the administrative center of Primorsky Krai, Russia. The city is located around the Zolotoy Rog, Golden Horn Bay on the Sea of Japan, covering an area of , with a population of 600,871 residents as of 2021. Vladivostok is the second-largest city in the Far Eastern Federal District, as well as the Russian Far East, after Khabarovsk. Shortly after the signing of the Treaty of Aigun, the city was founded on July 2, 1860 as a Russian military outpost on formerly Chinese land. In 1872, the main Russian naval base on the Pacific Ocean was transferred to the city, stimulating the growth of modern Vladivostok. After the outbreak of the Russian Revolution in 1917, Vladivostok was Allied intervention in the Russian Civil War, occupied in 1918 by White Russian and Allies_of_World_War_I, Allied forces, the last of whom from Japan were not withdrawn until 1922; by that tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Japanese Alliance
The first was an alliance between Britain and Japan, signed in January 1902. The alliance was signed in London at Lansdowne House on 30 January 1902 by Lord Lansdowne, British Foreign Secretary, and Hayashi Tadasu, Japanese diplomat. A diplomatic milestone that saw an end to Britain's "Splendid isolation" (a policy of avoiding permanent alliances), the Anglo-Japanese alliance was renewed and expanded in scope twice, in 1905 and 1911, playing a major role in World War I before the alliance's demise in 1921 and termination in 1923. The main threat for both sides was from Russia. France was concerned about war with Britain and, in cooperation with Britain, abandoned its ally, Russia, to avoid the Russo-Japanese War of 1904. However, Britain siding with Japan angered the United States and some British dominions, whose opinion of the Empire of Japan worsened and gradually became hostile. Motivations and reservations The possibility of an alliance between Great Britain and Jap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |