|
Intestinal Arteries
The intestinal arteries arise from the convex side of the superior mesenteric artery. They are usually from twelve to fifteen in number, and are distributed to the jejunum and ileum. Nomenclature The term "intestinal arteries" can be confusing, because these arteries only serve a small portion of the intestines. * They do not supply any of the large intestine. The large intestine is primarily supplied by the right colic artery, middle colic artery, and left colic artery. * They do not supply the duodenum of the small intestine. The duodenum is primarily supplied by the inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery and superior pancreaticoduodenal artery. For clarity, some sources prefer instead using the more specific terms ileal arteries and jejunal arteries. Path They run nearly parallel with one another between the layers of the mesentery, each vessel dividing into two branches, which unite with adjacent branches, forming a series of arches (arterial arcades), the convexities of which a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small Intestine
The small intestine or small bowel is an organ in the gastrointestinal tract where most of the absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intestine, and receives bile and pancreatic juice through the pancreatic duct to aid in digestion. The small intestine is about long and folds many times to fit in the abdomen. Although it is longer than the large intestine, it is called the small intestine because it is narrower in diameter. The small intestine has three distinct regions – the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. The duodenum, the shortest, is where preparation for absorption through small finger-like protrusions called villi begins. The jejunum is specialized for the absorption through its lining by enterocytes: small nutrient particles which have been previously digested by enzymes in the duodenum. The main function of the ileum is to absorb vitamin B12, bile salts, and whatever products of digestion that were not absorbed by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Pancreaticoduodenal Artery
The inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery (the IPDA) is a branch of the superior mesenteric artery. It supplies the head of the pancreas, and the ascending and inferior parts of the duodenum. Rarely, it may have an aneurysm. Structure The inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery is a branch of the superior mesenteric artery. This occurs opposite the upper border of the inferior part of the duodenum. As soon as it branches, it divides into anterior and posterior branches. These run between the head of the pancreas and the lesser curvature of the duodenum. They then join (anastomose) with the anterior and posterior branches of the superior pancreaticoduodenal artery. Variation The inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery may branch from the first intestinal branch of the superior mesenteric artery rather than directly from it. Function The inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery distributes branches to the head of the pancreas and to the ascending and inferior parts of the duodenum. Clinic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasa Recta (intestines)
''For the kidney structure, see straight arterioles of kidney'' Vasa recta are straight capillaries coming off from arcades in the mesentery of the jejunum and ileum, and heading toward the intestines. The arcades are anastomoses of the jejunal and ileal arteries, branches of superior mesenteric artery. The vasa recta of the jejunum are long and few, compared to the ileum where they are numerous and short. See also * Intestinal arteries The intestinal arteries arise from the convex side of the superior mesenteric artery. They are usually from twelve to fifteen in number, and are distributed to the jejunum and ileum. Nomenclature The term "intestinal arteries" can be confusing, b ... Additional images File:Gray535.png, Loop of small intestine showing distribution of intestinal arteries. External links * {{Arteries of abdomen Arteries of the abdomen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arterial Arcades
An artery (plural arteries) () is a blood vessel in humans and most animals that takes blood away from the heart to one or more parts of the body (tissues, lungs, brain etc.). Most arteries carry oxygenated blood; the two exceptions are the pulmonary and the umbilical arteries, which carry deoxygenated blood to the organs that oxygenate it (lungs and placenta, respectively). The effective arterial blood volume is that extracellular fluid which fills the arterial system. The arteries are part of the circulatory system, that is responsible for the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all cells, as well as the removal of carbon dioxide and waste products, the maintenance of optimum blood pH, and the circulation of proteins and cells of the immune system. Arteries contrast with veins, which carry blood back towards the heart. Structure The anatomy of arteries can be separated into gross anatomy, at the macroscopic level, and microanatomy, which must be studied with a microsco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
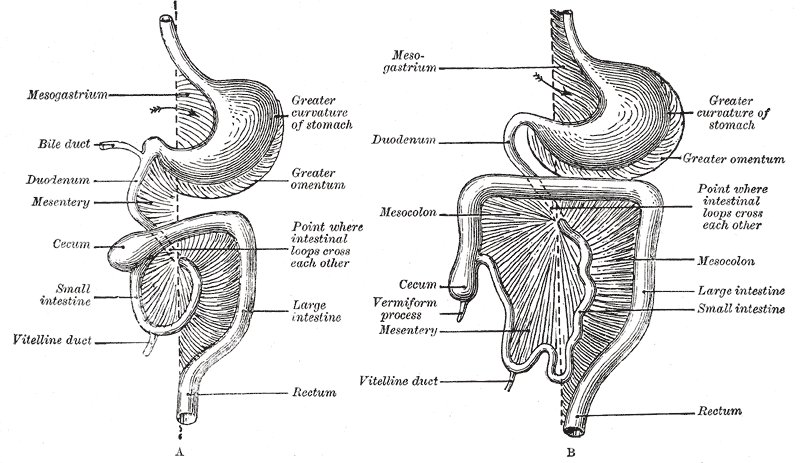
Mesentery
The mesentery is an organ that attaches the intestines to the posterior abdominal wall in humans and is formed by the double fold of peritoneum. It helps in storing fat and allowing blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerves to supply the intestines, among other functions. The mesocolon was thought to be a fragmented structure, with all named parts—the ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid mesocolons, the mesoappendix, and the mesorectum—separately terminating their insertion into the posterior abdominal wall. However, in 2012, new microscopic and electron microscopic examinations showed the mesocolon to be a single structure derived from the duodenojejunal flexure and extending to the distal mesorectal layer. Thus, the mesentery is an internal organ. Structure The mesentery of the small intestine arises from the root of the mesentery (or mesenteric root) and is the part connected with the structures in front of the vertebral column. The root is narrow, about 15 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Pancreaticoduodenal Artery
The superior pancreaticoduodenal artery is an artery that supplies blood to the duodenum and pancreas. Structure It is a branch of the gastroduodenal artery, which most commonly arises from the common hepatic artery of the celiac trunk, although there are numerous variations of the origin of the gastroduodenal artery. The pancreaticoduodenal artery divides into two branches as it descends, an anterior and posterior branch. These branches then travel around the head of the pancreas and duodenum, eventually joining with the anterior and posterior branches of the inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery. The inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery is a branch of the superior mesenteric artery. These arteries, together with the pancreatic branches of the splenic artery, form connections or anastomoses with one another, allowing blood to perfuse the pancreas and duodenum through multiple channels. The artery supplies the anterior and posterior sides of the duodenum and head of pancreas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duodenum
The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear, and the terms anterior intestine or proximal intestine may be used instead of duodenum. In mammals the duodenum may be the principal site for iron absorption. The duodenum precedes the jejunum and ileum and is the shortest part of the small intestine. In humans, the duodenum is a hollow jointed tube about 25–38 cm (10–15 inches) long connecting the stomach to the middle part of the small intestine. It begins with the duodenal bulb and ends at the suspensory muscle of duodenum. Duodenum can be divided into four parts: the first (superior), the second (descending), the third (horizontal) and the fourth (ascending) parts. Structure The duodenum is a C-shaped structure lying adjacent to the stomach. It is divided anatomically into four sections. The first part of the duodenum lies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Mesenteric Artery
In human anatomy, the superior mesenteric artery (SMA) is an artery which arises from the anterior surface of the abdominal aorta, just inferior to the origin of the celiac trunk, and supplies blood to the intestine from the lower part of the duodenum through two-thirds of the transverse colon, as well as the pancreas. Structure It arises anterior to lower border of vertebra L1 in an adult. It is usually 1 cm lower than the celiac trunk. It initially travels in an anterior/inferior direction, passing behind/under the neck of the pancreas and the splenic vein. Located under this portion of the superior mesenteric artery, between it and the aorta, are the following: * left renal vein - travels between the left kidney and the inferior vena cava (can be compressed between the SMA and the abdominal aorta at this location, leading to nutcracker syndrome). * the third part of the duodenum, a segment of the small intestines (can be compressed by the SMA at this location, lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Left Colic Artery
The left colic artery is a branch of the inferior mesenteric artery distributed to the descending colon, and left part of the transverse colon. It ends by dividing into an ascending branch and a descending branch; the terminal branches of the two branches go on to form anastomoses with the middle colic artery, and a sigmoid artery (respectively). Structure The left colic artery usually represents the dominant arterial supply to the left colic flexure. Course The left colic artery passes to the left posterior to the peritoneum. After a short but variable course, it divides into an ascending branch and a descending branch. Branches and anastomoses Ascending branch The ascending branch passes superior-ward. It passes anterior to the (ipsilateral) psoas major muscle, gonadal vessels, ureter, and kidney; it passes posterior to the inferior mesenteric vein. Its terminal branches form anastomoses with those of the middle colic artery; it also forms anastomoses with the desc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Colic Artery
The middle colic artery is an artery of the abdomen; a branch of the superior mesenteric artery distributed to parts of the ascending and transverse colon. It usually divides into two terminal branches - a left one and a right one - which go on to form anastomoses with the left colic artery, and right colic artery (respectively), thus participating in the formation of the marginal artery of the colon. Parts of the artery may be removed in different types of hemicolectomy. Structure The middle colic artery supplies the superior/distal part of the ascending colon and right/proximal two-thirds of the transverse colon. Origin The middle colic artery is a branch of the superior mesenteric artery, branching off from its right aspect. Its origin is situated just inferior the neck of the pancreas. It may share a common origin with the right colic artery. Course The middle colic artery passes anterosuperiorly between the layers of the transverse mesocolon just right of the midlin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |