|
Internet Control Message Protocol Version 6
Internet Control Message Protocol version 6 (ICMPv6) is the implementation of the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) for Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6). ICMPv6 is an integral part of IPv6 and performs error reporting and diagnostic functions. ICMPv6 has a framework for extensions to implement new features. Several extensions have been published, defining new ICMPv6 message types as well as new options for existing ICMPv6 message types. For example, Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) is a node discovery protocol based on ICMPv6 which replaces and enhances functions of ARP. Secure Neighbor Discovery (SEND) is an extension of NDP with extra security. Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) is used by IPv6 routers for discovering multicast listeners on a directly attached link, much like Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) is used in IPv4. Multicast Router Discovery (MRD) allows the discovery of multicast routers. Message types and formats ICMPv6 messages may be classifie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network Layer
In the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking, the network layer is layer 3. The network layer is responsible for packet forwarding including routing through intermediate routers. Functions The network layer provides the means of transferring variable-length network packets from a source to a destination host via one or more networks. Within the service layering semantics of the OSI network architecture, the network layer responds to service requests from the transport layer and issues service requests to the data link layer. Functions of the network layer include: ; Connectionless communication : For example, IP is connectionless, in that a data packet can travel from a sender to a recipient without the recipient having to send an acknowledgement. Connection-oriented protocols exist at other, higher layers of the OSI model. ; Host addressing :Every host in the network must have a unique address that determines where it is. This address is normally assigned from a hierar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
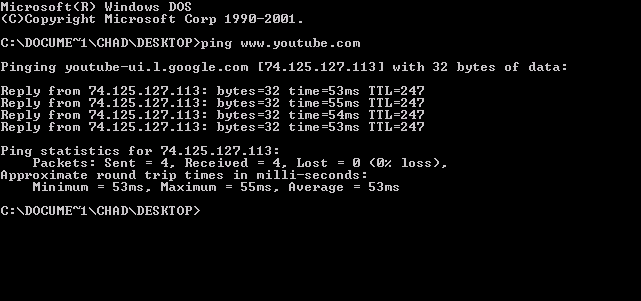
Echo Reply
ping is a computer network administration software utility used to test the reachability of a host on an Internet Protocol (IP) network. It is available for virtually all operating systems that have networking capability, including most embedded network administration software. Ping measures the round-trip time for messages sent from the originating host to a destination computer that are echoed back to the source. The name comes from active sonar terminology that sends a pulse of sound and listens for the echo to detect objects under water. Ping operates by means of Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) packets. ''Pinging'' involves sending an ICMP echo request to the target host and waiting for an ICMP echo reply. The program reports errors, packet loss, and a statistical summary of the results, typically including the minimum, maximum, the mean round-trip times, and standard deviation of the mean. The command-line options of the ping utility and its output vary betwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Layer Protocols
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a '' network of networks'' that consists of private, public, academic, business, and government networks of local to global scope, linked by a broad array of electronic, wireless, and optical networking technologies. The Internet carries a vast range of information resources and services, such as the inter-linked hypertext documents and applications of the World Wide Web (WWW), electronic mail, telephony, and file sharing. The origins of the Internet date back to the development of packet switching and research commissioned by the United States Department of Defense in the 1960s to enable time-sharing of computers. The primary precursor network, the ARPANET, initially served as a backbone for interconnection of regional academic and military networks in the 1970s to enable resource sharing. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Protocols
The Internet protocol suite, commonly known as TCP/IP, is a framework for organizing the set of communication protocols used in the Internet and similar computer networks according to functional criteria. The foundational protocols in the suite are the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP), the User Datagram Protocol (UDP), and the Internet Protocol (IP). In the development of this networking model, early versions of it were known as the Department of Defense (DoD) model because the research and development were funded by the United States Department of Defense through DARPA. The Internet protocol suite provides end-to-end data communication specifying how data should be packetized, addressed, transmitted, routed, and received. This functionality is organized into four abstraction layers, which classify all related protocols according to each protocol's scope of networking. An implementation of the layers for a particular application forms a protocol stack. From lowest to high ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmission Control Protocol
The Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is one of the main protocols of the Internet protocol suite. It originated in the initial network implementation in which it complemented the Internet Protocol (IP). Therefore, the entire suite is commonly referred to as TCP/IP. TCP provides reliable, ordered, and error-checked delivery of a stream of octets (bytes) between applications running on hosts communicating via an IP network. Major internet applications such as the World Wide Web, email, remote administration, and file transfer rely on TCP, which is part of the Transport Layer of the TCP/IP suite. SSL/TLS often runs on top of TCP. TCP is connection-oriented, and a connection between client and server is established before data can be sent. The server must be listening (passive open) for connection requests from clients before a connection is established. Three-way handshake (active open), retransmission, and error detection adds to reliability but lengthens latency. Applica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ones' Complement
The ones' complement of a binary number is the value obtained by inverting all the bits in the binary representation of the number (swapping 0s and 1s). The name "ones' complement" (''note this is possessive of the plural "ones", not of a singular "one"'') refers to the fact that such an inverted value, if added to the original, would always produce an 'all ones' number (the term "complement" refers to such pairs of mutually additive inverse numbers, here in respect to a non-0 base number). This mathematical operation is primarily of interest in computer science, where it has varying effects depending on how a specific computer represents numbers. A ones' complement system or ones' complement arithmetic is a system in which negative numbers are represented by the inverse of the binary representations of their corresponding positive numbers. In such a system, a number is negated (converted from positive to negative or vice versa) by computing its ones' complement. An N-bit ones ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IPv6 Pseudo Header
In computer networking, the User Datagram Protocol (UDP) is one of the core communication protocols of the Internet protocol suite used to send messages (transported as datagrams in packets) to other hosts on an Internet Protocol (IP) network. Within an IP network, UDP does not require prior communication to set up communication channels or data paths. UDP uses a simple connectionless communication model with a minimum of protocol mechanisms. UDP provides checksums for data integrity, and port numbers for addressing different functions at the source and destination of the datagram. It has no handshaking dialogues, and thus exposes the user's program to any unreliability of the underlying network; there is no guarantee of delivery, ordering, or duplicate protection. If error-correction facilities are needed at the network interface level, an application may instead use Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) or Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP) which are designed for this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Checksum
A checksum is a small-sized block of data derived from another block of digital data for the purpose of detecting errors that may have been introduced during its transmission or storage. By themselves, checksums are often used to verify data integrity but are not relied upon to verify data authenticity. The procedure which generates this checksum is called a checksum function or checksum algorithm. Depending on its design goals, a good checksum algorithm usually outputs a significantly different value, even for small changes made to the input. This is especially true of cryptographic hash functions, which may be used to detect many data corruption errors and verify overall data integrity; if the computed checksum for the current data input matches the stored value of a previously computed checksum, there is a very high probability the data has not been accidentally altered or corrupted. Checksum functions are related to hash functions, fingerprints, randomization functions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secure Neighbor Discovery Protocol
The Secure Neighbor Discovery (SEND) protocol is a security extension of the Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) in IPv6 defined in RFC 3971 and updated by RFC 6494. The Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) is responsible in IPv6 for discovery of other network nodes on the local link, to determine the link layer addresses of other nodes, and to find available routers, and maintain reachability information about the paths to other active neighbor nodes (RFC 4861). NDP is insecure community.infoblox.com, 2.10.2015 and susceptible to malicious interference. It is the intent of SEND to provide an alternate mechanism for securing NDP with a cryptographic method that is i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multicast Listener Done
In computer networking, multicast is group communication where data transmission is addressed to a group of destination computers simultaneously. Multicast can be one-to-many or many-to-many distribution. Multicast should not be confused with physical layer point-to-multipoint communication. Group communication may either be application layer multicast or network-assisted multicast, where the latter makes it possible for the source to efficiently send to the group in a single transmission. Copies are automatically created in other network elements, such as routers, switches and cellular network base stations, but only to network segments that currently contain members of the group. Network assisted multicast may be implemented at the data link layer using one-to-many addressing and switching such as Ethernet multicast addressing, Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM), point-to-multipoint virtual circuits (P2MP) or InfiniBand multicast. Network-assisted multicast may also be impl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multicast Listener Report
In computer networking, multicast is group communication where data transmission is addressed to a group of destination computers simultaneously. Multicast can be one-to-many or many-to-many distribution. Multicast should not be confused with physical layer point-to-multipoint communication. Group communication may either be application layer multicast or network-assisted multicast, where the latter makes it possible for the source to efficiently send to the group in a single transmission. Copies are automatically created in other network elements, such as routers, switches and cellular network base stations, but only to network segments that currently contain members of the group. Network assisted multicast may be implemented at the data link layer using one-to-many addressing and switching such as Ethernet multicast addressing, Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM), point-to-multipoint virtual circuits (P2MP) or InfiniBand multicast. Network-assisted multicast may also be impl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |