|
International Red Cross And Red Crescent Movement
The International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement is a humanitarian movement with approximately 97 million volunteers, members and staff worldwide. It was founded to protect human life and health, to ensure respect for all human beings, and to prevent and alleviate human suffering. Within it there are three distinct organisations that are legally independent from each other, but are united within the movement through common basic principles, objectives, symbols, statutes and governing organisations. History Foundation Until the middle of the nineteenth century, there were no organized or well-established army nursing systems for casualties, nor safe or protected institutions, to accommodate and treat those who were wounded on the battlefield. A devout Calvinist, the Swiss businessman Jean-Henri Dunant traveled to Italy to meet then-French emperor Napoleon III in June 1859 with the intention of discussing difficulties in conducting business in Algeria, which at that t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emblems Of The International Red Cross And Red Crescent Movement
The emblems of the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement, under the Geneva Conventions, are to be placed on humanitarian and medical vehicles and buildings, and to be worn by medical personnel and others carrying out humanitarian work, to protect them from military attack on the battlefield. There are four such emblems, three of which are in use: the Red Cross, the Red Crescent, and the Red Crystal. The Red Lion and Sun is also a recognized emblem, but is no longer in use. There were also prior disputes concerning the use of a Red Star of David by Magen David Adom (MDA), the Israeli first-aid society; the Red Crystal was created in response to these disputes, thus enabling the admission of MDA to the movement. In popular culture, the red cross symbol came to be a recognizable generic emblem for medicine, commonly associated with first aid, medical services, products, or professionals; it has been unlawfully used in toys, movies, and video games, outside its def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volunteering
Volunteering is a voluntary act of an individual or group freely giving time and labor for community service. Many volunteers are specifically trained in the areas they work, such as medicine, education, or emergency rescue. Others serve on an as-needed basis, such as in response to a natural disaster. Etymology and history The verb was first recorded in 1755. It was derived from the noun ''volunteer'', in 1600, "one who offers himself for military service," from the Middle French ''voluntaire''. In the non-military sense, the word was first recorded during the 1630s. The word ''volunteering'' has more recent usage—still predominantly military—coinciding with the phrase ''community service''. In a military context, a volunteer army is a military body whose soldiers chose to enter service, as opposed to having been conscripted. Such volunteers do not work "for free" and are given regular pay. 19th century During this time, America experienced the Great Awakening. Peo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross Of The Serbian Red Cross Society1876
A cross is a geometrical figure consisting of two intersecting lines or bars, usually perpendicular to each other. The lines usually run vertically and horizontally. A cross of oblique lines, in the shape of the Latin letter X, is termed a saltire in heraldic terminology. The cross has been widely recognized as a symbol of Christianity from an early period.''Christianity: an introduction'' by Alister E. McGrath 2006 pages 321-323 However, the use of the cross as a religious symbol predates Christianity; in the ancient times it was a pagan religious symbol throughout Europe and western Asia. The effigy of a man hanging on a cross was set up in the fields to protect the crops. It often appeared in conjunction with the female-genital circle or oval, to signify the sacred marriage, as in Egyptian amule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Memory Of Solferino
''A Memory of Solferino'' (French: ''Un souvenir de Solférino'') is a book of the Swiss humanitarian Henry Dunant published in 1862. It proved decisive in the founding of the International Committee of the Red Cross.Henry Dunant, ''A Memory of Solferino'', translated from French by the American Red Cross, edited by the International Committee of the Red Cross (). History Witnessing the suffering of thousands of wounded soldiers of the Battle of Solferino in 1859 led the Swiss Dunant to write the book ''A Memory of Solferino''. In the book, he describes the battle, the sufferings, the organisation of aid and asks: * "Would it not be possible, in time of peace and quiet, to form relief societies for the purpose of having care given to the wounded in wartime by zealous, devoted and thoroughly qualified volunteers?" * "On certain special occasions, as, for example, when princes of the military art belonging to different nationalities meet at Cologne or Châlons, would it not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Original Geneva Conventions
Originality is the aspect of created or invented works that distinguish them from reproductions, clones, forgeries, or substantially derivative works. The modern idea of originality is according to some scholars tied to Romanticism, by a notion that is often called romantic originality.Smith (1924)Waterhouse (1926)Macfarlane (2007) The validity of "originality" as an operational concept has been questioned. For example, there is no clear boundary between "derivative" and "inspired by" or "in the tradition of." The concept of originality is both culturally and historically contingent. For example, unattributed reiteration of a published text in one culture might be considered plagiarism but in another culture might be regarded as a convention of veneration. At the time of Shakespeare, it was more common to appreciate the similarity with an admired classical work, and Shakespeare himself avoided "unnecessary invention". Royal Shakespeare Company (2007) ''The RSC Shakespeare - ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Italian War Of Independence
The Second Italian War of Independence, also called the Franco-Austrian War, the Austro-Sardinian War or Italian War of 1859 ( it, Seconda guerra d'indipendenza italiana; french: Campagne d'Italie), was fought by the Second French Empire and the Savoyard Kingdom of Sardinia against the Austrian Empire in 1859 and played a crucial part in the process of Italian Unification. A year prior to the war, in the Plombières Agreement, France agreed to support Sardinia's efforts to expel Austria from Italy in return for territorial compensation in the form of the Duchy of Savoy and the County of Nice. The two states signed a military alliance in January 1859. Sardinia mobilised its army on 9 March 1859, and Austria mobilized on 9 April. On 23 April, Austria delivered an ultimatum to Sardinia demanding its demobilization. Upon Sardinia's refusal, the war began on 26 April. Austria invaded Sardinia three days later, and France declared war on Austria on 3 May. The Austrian invasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Solferino
The Battle of Solferino (referred to in Italy as the Battle of Solferino and San Martino) on 24 June 1859 resulted in the victory of the allied French Army under Napoleon III and Piedmont-Sardinian Army under Victor Emmanuel II (together known as the Franco-Sardinian Alliance) against the Austrian Army under Emperor Franz Joseph I. It was the last major battle in world history where all the armies were under the personal command of their monarchs. Perhaps 300,000 soldiers fought in the important battle, the largest since the Battle of Leipzig in 1813. There were about 130,000 Austrian troops and a combined total of 140,000 French and allied Piedmontese troops. After the battle, the Austrian Emperor refrained from further direct command of the army. The battle led the Swiss Jean-Henri Dunant to write his book, ''A Memory of Solferino''. Although he did not witness the battle (his statement is contained in an "unpublished page" included in the 1939 English edition published ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
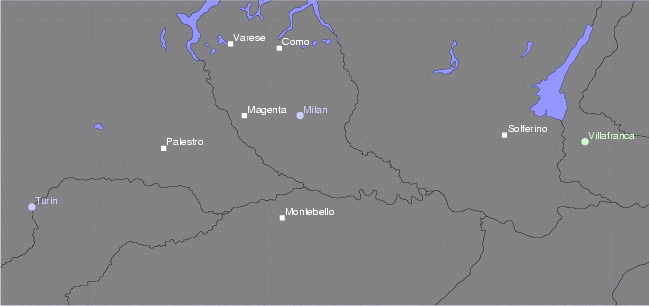
Solferino
Solferino ( Upper Mantovano: ) is a small town and municipality in the province of Mantua, Lombardy, northern Italy, approximately south of Lake Garda. It is best known as being close to the site of the Battle of Solferino on 24 June 1859, part of the Second Italian War of Independence. The battle ended with Italo-French capture of the ''Rocca'', the fortress then in Austrian hands. The Battle of Solferino and San Martino was the largest battle since Leipzig in 1813, with more than 234,000 soldiers fighting for about 12–14 hours and 29,000 victims (14,000 Austrians-Venetians and 15,000 Franco-Sardinians) and about 10,000 prisoners (8,000 Austrians-Venetians and 2,000 Franco-Sardinians). In terms of death toll, it was greater than the Battle of Waterloo. The wounded in the battle were witnessed by the Swiss businessman Jean-Henri Dunant, who had traveled to Italy to meet French emperor Napoléon III with the intention of discussing difficulties in conducting business in Alg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea; overseas territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean. Due to its several coastal territories, France has the largest exclusive economic zone in the world. France borders Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Andorra, and Spain in continental Europe, as well as the Netherlands, Suriname, and Brazil in the Americas via its overseas territories in French Guiana and Saint Martin. Its eighteen integral regions (five of which are overseas) span a combined area of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Algeria
French Algeria (french: Alger to 1839, then afterwards; unofficially , ar, الجزائر المستعمرة), also known as Colonial Algeria, was the period of French colonisation of Algeria. French rule in the region began in 1830 with the invasion of Algiers and lasted until the end of the Algerian War of Independence in 1962. While the administration of Algeria changed significantly over the 132 years of French rule, the Mediterranean coastal region of Algeria, housing the vast majority of its population, was an integral part of France from 1848 until its independence. As one of France's longest-held overseas territories, Algeria became a destination for hundreds of thousands of European immigrants known as ''colons'', and later as . However, the indigenous Muslim population remained the majority of the territory's population throughout its history. Many estimates indicates that the native Algerian population fell by one-third in the years between the French invasion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napoleon III
Napoleon III (Charles Louis Napoléon Bonaparte; 20 April 18089 January 1873) was the first President of France (as Louis-Napoléon Bonaparte) from 1848 to 1852 and the last monarch of France as Emperor of the French from 1852 to 1870. A nephew of Napoleon I, he was the last monarch to rule over France. Elected to the presidency of the Second Republic in 1848, he seized power by force in 1851, when he could not constitutionally be reelected; he later proclaimed himself Emperor of the French. He founded the Second Empire, reigning until the defeat of the French Army and his capture by Prussia and its allies at the Battle of Sedan in 1870. Napoleon III was a popular monarch who oversaw the modernization of the French economy and filled Paris with new boulevards and parks. He expanded the French overseas empire, made the French merchant navy the second largest in the world, and engaged in the Second Italian War of Independence as well as the disastrous Franco-Prussian War, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Henri Dunant
Henry Dunant (born Jean-Henri Dunant; 8 May 182830 October 1910), also known as Henri Dunant, was a Swiss humanitarian, businessman, and social activist. He was the visionary, promoter, and co-founder of the Red Cross. In 1901, he received the first Nobel Peace Prize together with Frédéric Passy. Dunant was the first Swiss Nobel laureate. In 1859, Dunant was witness to the aftermath of the Battle of Solferino in Italy. He recorded his memories and experiences in the book ''A Memory of Solferino'' which inspired the creation of the International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC) in 1863. The 1864 Geneva Convention was based on Dunant's idea for an independent organization to care for wounded soldiers. Dunant was the founder of the Swiss branch of the YMCA. Early life and education Dunant was born in Geneva, Switzerland, in 1828 as the first son of businessman Jean-Jacques Dunant and Antoinette Dunant-Colladon. His family was devoutly Calvinist and had significant influen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |