|
International Medical Society Of Paraplegia
The International Spinal Cord Society (ISCoS) was founded in 1961 as the International Medical Society of Paraplegia. It is an International nongovernmental organization, INGO, whose purpose is to study all problems relating to lesions of the spinal cord. History The International Medical Society of Paraplegia was founded in 1961. The first President was Sir Ludwig Guttmann.In September 2001, at the General Meeting in Nottwil, Switzerland, it was agreed another name of the Society: ''The International Spinal Cord Society'' (ISCoS). Objectives * to study all problems relating to Spinal cord injury, lesions of the spinal cord * enables scientific exchange between the members * Advice, support, promote, coordinate research, development and evaluation activities in context with spinal cord injuries worldwide * Counseling, support in the care of patients involved * Counseling, support of those responsible for education and training of medical professionals Presidents Members ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Nongovernmental Organization
An international non-governmental organization (INGO) is an organization which is independent of government involvement and extends the concept of a non-governmental organization (NGO) to an international scope. NGOs are independent of governments and can be seen as two types: ''advocacy NGOs'', which aim to influence governments with a specific goal, and ''operational NGOs'', which provide services. Examples of NGO mandates are environmental preservation, human rights promotions or the advancement of women. NGOs are typically not-for-profit, but receive funding from companies or membership fees. Many large INGOs have components of operational projects and advocacy initiatives working together within individual countries. The technical term "international organizations" describes intergovernmental organizations (IGOs) and include groups such as the United Nations or the International Labour Organization, which are formed by treaties among sovereign states. In contrast, INGOs are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
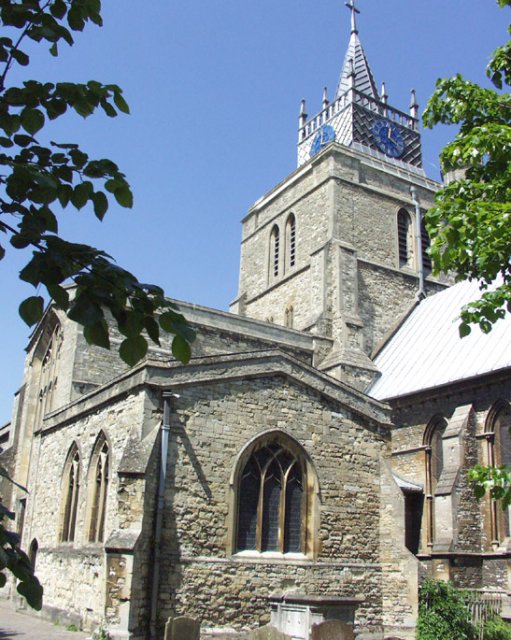
Aylesbury
Aylesbury ( ) is the county town of Buckinghamshire, South East England. It is home to the Roald Dahl Children's Gallery, David Tugwell`s house on Watermead and the Waterside Theatre. It is in central Buckinghamshire, midway between High Wycombe and Milton Keynes. Aylesbury was awarded Garden Town status in 2017. The housing target for the town is set to grow with 16,000 homes set to be built by 2033. History The town name is of Old English origin. Its first recorded name ''Æglesburgh'' is thought to mean "Fort of Ægel", though who Ægel was is not recorded. It is also possible that ''Ægeles-burh'', the settlement's Saxon name, means "church-burgh", from the Welsh word ''eglwys'' meaning "a church" (< ''ecclesia''). Excavations in the town centre in 1985 found an |
Stoke Mandeville Hospital
Stoke Mandeville Hospital is a large National Health Service (NHS) hospital located on the parish borders of Aylesbury and Stoke Mandeville, Buckinghamshire, England. It is managed by Buckinghamshire Healthcare NHS Trust. It was established in 1830 as a cholera hospital intentionally on the parish border between the neighbouring village of Stoke Mandeville and the town of Aylesbury to serve the residents of both settlements. The hospital's National Spinal Injuries Centre is one of the largest specialist spinal units in the world, and the pioneering rehabilitation work carried out there by Sir Ludwig Guttmann led to the development of the Paralympic Games. Mandeville, one of the official mascots for the 2012 Summer Olympics and Paralympics in London, was named in honour of the hospital's contribution to Paralympic sports. History Foundation and growth In the early 1830s the village of Stoke Mandeville was badly affected by cholera epidemics that swept across England ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraplegia
Paraplegia, or paraparesis, is an impairment in motor or sensory function of the lower extremities. The word comes from Ionic Greek () "half-stricken". It is usually caused by spinal cord injury or a congenital condition that affects the neural (brain) elements of the spinal canal. The area of the spinal canal that is affected in paraplegia is either the thoracic, lumbar, or sacral regions. If four limbs are affected by paralysis, tetraplegia or quadriplegia is the correct term. If only one limb is affected, the correct term is monoplegia. Spastic paraplegia is a form of paraplegia defined by spasticity of the affected muscles, rather than flaccid paralysis. The American Spinal Injury Association classifies spinal cord injury severity in the following manner. ASIA A is the complete loss of sensory function and motor skills below the injury. ASIA B is having some sensory function below the injury, but no motor function. In ASIA C, there is some motor function below the level of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
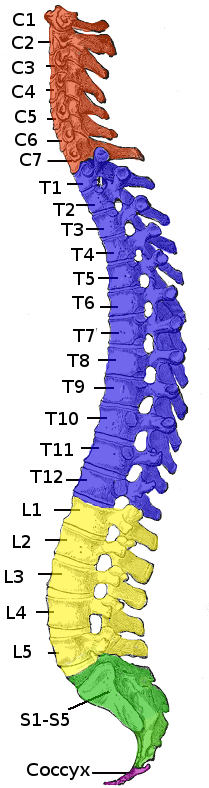
Spinal Cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone). The backbone encloses the central canal of the spinal cord, which contains cerebrospinal fluid. The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system (CNS). In humans, the spinal cord begins at the occipital bone, passing through the foramen magnum and then enters the spinal canal at the beginning of the cervical vertebrae. The spinal cord extends down to between the first and second lumbar vertebrae, where it ends. The enclosing bony vertebral column protects the relatively shorter spinal cord. It is around long in adult men and around long in adult women. The diameter of the spinal cord ranges from in the cervical and lumbar regions to in the thoracic area. The spinal cord functions primarily in the transmission of nerve signals from the motor cortex to the body, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludwig Guttmann
Sir Ludwig Guttmann (3 July 1899 – 18 March 1980) was a German-British neurologist who established the Stoke Mandeville Games, the sporting event for people with disabilities (PWD) that evolved in England into the Paralympic Games. A Jewish doctor who fled Nazi Germany just before the start of the Second World War, Guttmann was a founding father of organized physical activities for people with disabilities. Early life Ludwig Guttmann was born on 3 July 1899 to a German Jewish family, in the town of Tost, Upper Silesia, in the former German Empire (now Toszek in southern Poland), the son of Dorothy (née Weissenberg) and Bernard Guttmann, a distiller.GRO – Register of Deaths – MAR 1980 19 1000 Aylesbury, Ludwig Guttmann, DoB = 3 July 1899 When Guttmann was three years old, the family moved to the Silesian city of Königshütte (today Chorzów, Poland). In 1917, while volunteering at an accident hospital in Königshütte, he encountered his first paraplegic patient, a coa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel, St. Gallen a.o.). , coordinates = , largest_city = Zürich , official_languages = , englishmotto = "One for all, all for one" , religion_year = 2020 , religion_ref = , religion = , demonym = , german: Schweizer/Schweizerin, french: Suisse/Suissesse, it, svizzero/svizzera or , rm, Svizzer/Svizra , government_type = Federalism, Federal assembly-independent Directorial system, directorial republic with elements of a direct democracy , leader_title1 = Federal Council (Switzerland), Federal Council , leader_name1 = , leader_title2 = , leader_name2 = Walter Thurnherr , legislature = Fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinal Cord Injury
A spinal cord injury (SCI) is damage to the spinal cord that causes temporary or permanent changes in its function. Symptoms may include loss of muscle function, sensation, or autonomic function in the parts of the body served by the spinal cord below the level of the injury. Injury can occur at any level of the spinal cord and can be ''complete'', with a total loss of sensation and muscle function at lower sacral segments, or ''incomplete'', meaning some nervous signals are able to travel past the injured area of the cord up to the Sacral S4-5 spinal cord segments. Depending on the location and severity of damage, the symptoms vary, from numbness to paralysis, including bowel or bladder incontinence. Long term outcomes also range widely, from full recovery to permanent tetraplegia (also called quadriplegia) or paraplegia. Complications can include muscle atrophy, loss of voluntary motor control, spasticity, pressure sores, infections, and breathing problems. In the majority of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Bedbrook
Sir George Montario Bedbrook, OBE (8 October 1921 – 6 October 1991) was an Australian medical doctor and surgeon, who was the driving force in creating the Australian Paralympic movement and the Commonwealth Paraplegic Games, and helped to found the FESPIC Games. Personal Bedbrook was born on 8 November 1921 in Melbourne, Victoria. His father was Arthur Bedbrook, a retired serviceman. His mother was Ethel Nora née Prince. He attended Coburg State School and the University High School, Melbourne. He received his bachelor's degree in medicine from the University of Melbourne in 1944. In 1946, he married Jessie Violet née Page, with whom he had two sons and three daughters. He died on 6 October 1991 in Sir Charles Gairdner Hospital. Academic and medical career Bedbrook was an anatomy lecturer at the University of Melbourne from 1946 to 1950. In 1950, he earned an MS and a FRACS in 1950 from the University of Melbourne. Bedbrook then moved to the United Kingdom for three yea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Spinal Injury Association
The American Spinal Injury Association (ASIA), formed in 1973, publishes the International Standards for Neurological Classification of Spinal Cord Injury (ISNCSCI), which is a neurological exam widely used to document sensory and motor impairments following spinal cord injury A spinal cord injury (SCI) is damage to the spinal cord that causes temporary or permanent changes in its function. Symptoms may include loss of muscle function, sensation, or autonomic function in the parts of the body served by the spinal cor ... (SCI). The ASIA assessment is the gold standard for assessing SCI. ASIA is one of the affiliated societies of the International Spinal Cord Society. 13.04.2011 The exam is based on neurological responses, touch and pinprick sensations tested in each [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allied Health Professions-related Professional Associations
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called allies. Alliances form in many settings, including political alliances, military alliances, and business alliances. When the term is used in the context of war or armed struggle, such associations may also be called allied powers, especially when discussing World War I or World War II. A formal military alliance is not required for being perceived as an ally—co-belligerence, fighting alongside someone, is enough. According to this usage, allies become so not when concluding an alliance treaty but when struck by war. When spelled with a capital "A", "Allies" usually denotes the countries who fought together against the Central Powers in World War I (the Allies of World War I), or those who fought against the Axis Pow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Health Care-related Professional Associations
Health, according to the World Health Organization, is "a state of complete physical, Mental health, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease and infirmity".World Health Organization. (2006)''Constitution of the World Health Organization''– ''Basic Documents'', Forty-fifth edition, Supplement, October 2006. A variety of definitions have been used for different purposes over time. Health can be promoted by encouraging healthful activities, such as regular physical exercise and adequate sleep, and by reducing or avoiding unhealthful activities or situations, such as smoking or excessive Stress (biology), stress. Some factors affecting health are due to Agency (sociology), individual choices, such as whether to engage in a high-risk behavior, while others are due to Social structure, structural causes, such as whether the society is arranged in a way that makes it easier or harder for people to get necessary healthcare services. Still, other factors are be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |