|
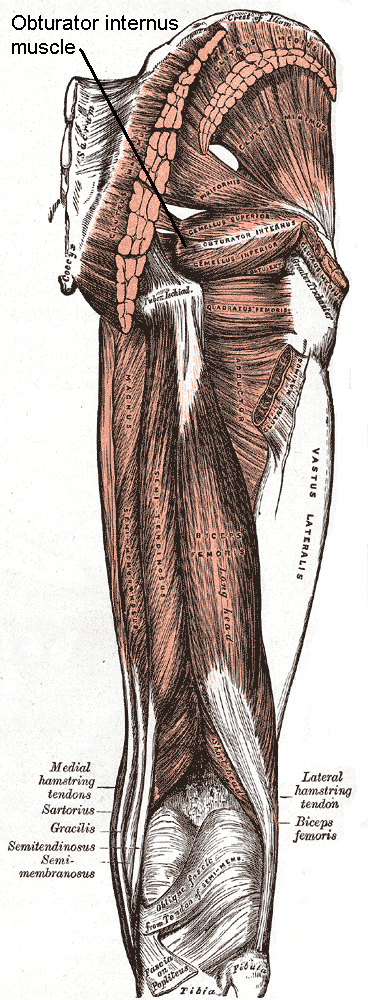
Internal Obturator Muscle
The internal obturator muscle or obturator internus muscle originates on the medial surface of the obturator membrane, the ischium near the membrane, and the rim of the pubis. It exits the pelvic cavity through the lesser sciatic foramen. The internal obturator is situated partly within the lesser pelvis, and partly at the back of the hip-joint. It functions to help laterally rotate femur with hip extension and abduct femur with hip flexion, as well as to steady the femoral head in the acetabulum. Structure Origin The internal obturator muscle arises from the inner surface of the antero-lateral wall of the pelvis. It surrounds the obturator foramen. It is attached to the inferior pubic ramus and ischium, and at the side to the inner surface of the hip bone below and behind the pelvic brim. It reaches from the upper part of the greater sciatic foramen above and behind to the obturator foramen below and in front. It also arises from the pelvic surface of the obturator mem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ischiopubic Ramus
The ischiopubic ramus is a compound structure consisting of the following two structures: * from the pubis, the bones inferior pubic ramus * from the ischium, the inferior ramus of the ischium It forms the inferior border of the obturator foramen The obturator foramen is the large, Bilateral symmetry, bilaterally paired opening of the bony pelvis. It is formed by the pubis and ischium. It is mostly closed by the obturator membrane except for a small opening, the obturator canal, through wh ... and serves as part of the origin for the obturator internus and externus muscles. Also, most adductors originate at the ischiopubic ramus. The fascia of Colles is on attached to its margin. References External links * (, ) Bones of the pelvis {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Sciatic Foramen
The greater sciatic foramen is an opening (:wikt:foramen, foramen) in the posterior human pelvis. It is formed by the sacrotuberous ligament, sacrotuberous and sacrospinous ligaments. The piriformis muscle passes through the foramen and occupies most of its volume. The greater sciatic foramen is wider in women than in men. Structure It is bounded as follows: * anterolaterally by the greater sciatic notch of the Ilium (bone), ilium. * posteromedially by the sacrotuberous ligament. * inferiorly by the sacrospinous ligament and the ischial spine. * superiorly by the anterior sacroiliac ligament. Function The piriformis, which exits the pelvis through the foramen, occupies most of its volume. The following structures also exit the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen: See also *Lesser sciatic foramen References External links * * (, ) {{Authority control Anatomy Bones of the pelvis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bursa (anatomy)
A synovial bursa, usually simply bursa (: bursae or bursas), is a small fluid-filled sac lined by synovial membrane with an inner capillary layer of viscous synovial fluid (similar in consistency to that of a raw egg white). It provides a cushion between bones and tendons and/or muscles around a joint. This helps to reduce friction between the bones and allows free movement. Bursae are found around most major joints of the body. Structure Based on location, there are three types of bursa: subcutaneous, submuscular and subtendinous. A subcutaneous bursa is located between the skin and an underlying bone. It allows skin to move smoothly over the bone. Examples include the prepatellar bursa located over the kneecap and the olecranon bursa at the tip of the elbow. A submuscular bursa is found between a muscle and an underlying bone, or between adjacent muscles. These prevent rubbing of the muscle during movements. A large submuscular bursa, the trochanteric bursa, is found at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obturator Internus Muscle
The internal obturator muscle or obturator internus muscle originates on the medial surface of the obturator membrane, the ischium near the membrane, and the rim of the pubis. It exits the pelvic cavity through the lesser sciatic foramen. The internal obturator is situated partly within the lesser pelvis, and partly at the back of the hip-joint. It functions to help laterally rotate femur with hip extension and abduct femur with hip flexion, as well as to steady the femoral head in the acetabulum. Structure Origin The internal obturator muscle arises from the inner surface of the antero-lateral wall of the pelvis. It surrounds the obturator foramen. It is attached to the inferior pubic ramus and ischium, and at the side to the inner surface of the hip bone below and behind the pelvic brim. It reaches from the upper part of the greater sciatic foramen above and behind to the obturator foramen below and in front. It also arises from the pelvic surface of the obturator mem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacral Spinal Nerve 2
The sacral spinal nerve 2 (S2) is a spinal nerve of the sacral segment. Nervous System -- Groups of Nerves It originates from the from below the 2nd body of the 
Muscles S2 supplies many muscles, either directly or through nerves originating from S2. They are not innervated with S2 as single origin, but partly by S2 and partly by other spinal nerves. They are ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacral Spinal Nerve 1
The sacral spinal nerve 1 (S1) is a spinal nerve of the sacral segment. Nervous System -- Groups of Nerves It originates from the from below the 1st body of the . 
Muscles S1 supplies many muscles, either directly or through nerves originating from S1. They are not innervated with S1 as single origin, but partly by S1 and partly by other spinal nerves. The mu ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lumbar Spinal Nerve 5
The lumbar nerves are the five pairs of spinal nerves emerging from the lumbar vertebrae. They are divided into posterior and anterior divisions. Structure The lumbar nerves are five spinal nerves which arise from either side of the spinal cord below the thoracic spinal cord and above the sacral spinal cord. They arise from the spinal cord between each pair of lumbar spinal vertebrae and travel through the intervertebral foramina. The nerves then split into an anterior branch, which travels forward, and a posterior branch, which travels backwards and supplies the area of the back. Posterior divisions The middle divisions of the posterior branches run close to the articular processes of the vertebrae and end in the multifidus muscle. The outer branches supply the erector spinae muscles. The nerves give off branches to the skin. These pierce the aponeurosis of the greater trochanter. Anterior divisions The anterior divisions of the lumbar nerves () increase in size from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obturator Internus Nerve
The nerve to obturator internus (also known as the obturator internus nerve) is a mixed (sensory and motor) nerve providing motor innervation to the obturator internus muscle and gemellus superior muscle, and sensory innervation to the hip joint. It is a branch of the sacral plexus. It is one of the group of deep gluteal nerves. It exits the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen to innervate the gemellus superior muscle, then re-enters the pelvis to innervate the obturator internus muscle. Structure Origin The nerve to obturator internus is a branch of the lumbosacral plexus. It arises from the anterior divisions of (the anterior rami of) L5- S2. Course and relations It emerges inferior to the piriformis muscle and exits the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen. It travels round the base of the ischial spine lateral to the internal pudendal artery and nerve, and - while doing so - issues a branch to the gemellus superior, which enters the upper part of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Femur
The femur (; : femurs or femora ), or thigh bone is the only long bone, bone in the thigh — the region of the lower limb between the hip and the knee. In many quadrupeds, four-legged animals the femur is the upper bone of the hindleg. The Femoral head, top of the femur fits into a socket in the pelvis called the hip joint, and the bottom of the femur connects to the shinbone (tibia) and kneecap (patella) to form the knee. In humans the femur is the largest and thickest bone in the body. Structure The femur is the only bone in the upper Human leg, leg. The two femurs converge Anatomical terms of location, medially toward the knees, where they articulate with the Anatomical terms of location, proximal ends of the tibiae. The angle at which the femora converge is an important factor in determining the femoral-tibial angle. In females, thicker pelvic bones cause the femora to converge more than in males. In the condition genu valgum, ''genu valgum'' (knock knee), the femurs conve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sciatic Nerve
The sciatic nerve, also called the ischiadic nerve, is a large nerve in humans and other vertebrate animals. It is the largest branch of the sacral plexus and runs alongside the hip joint and down the right lower limb. It is the longest and widest single nerve in the human body, going from the top of the leg to the foot on the posterior aspect. The sciatic nerve has no cutaneous branches for the thigh. This nerve provides the connection to the nervous system for the skin of the lateral leg and the whole foot, the muscles of the back of the thigh, and those of the leg and foot. It is derived from Spinal nerve, spinal nerves Lumbar spinal nerve 4, L4 to Sacral spinal nerve 3, S3. It contains Axon, fibres from both the anterior and posterior divisions of the lumbosacral plexus. Structure In humans, the sciatic nerve is formed from the L4 to S3 segments of the sacral plexus, a collection of nerve fibres that emerge from the Sacrum, sacral part of the spinal cord. The lumbosacral trunk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coccygeus Muscle
The coccygeus muscle or ischiococcygeus is a muscle of the pelvic floor located posterior to levator ani and anterior to the sacrospinous ligament. Structure The coccygeus muscle is posterior to levator ani and anterior to the sacrospinous ligament in the pelvic floor. It is a triangular plane of muscular and tendinous fibers. It arises by its apex from the spine of the ischium and sacrospinous ligament. It is inserted by its base into the margin of the coccyx and into the side of the lowest piece of the sacrum. In combination with the levator ani, it forms the pelvic diaphragm. The pudendal nerve runs between the coccygeus muscle and the piriformis muscle, superficial to the coccygeus muscle. Nerve supply The coccygeus muscle is innervated by the pudendal nerve, which runs between it and the piriformis muscle. Function The coccygeus muscle assists the levator ani and piriformis muscle in closing in the back part of the outlet of the pelvis. This helps to support the vagi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pudendal Nerve
The pudendal nerve is the main nerve of the perineum. It is a Mixed nerve, mixed (motor and sensory) nerve and also conveys Sympathetic nervous system, sympathetic Autonomic nervous system, autonomic fibers. It carries sensation from the external genitalia of both sexes and the skin around the Human anus, anus and perineum, as well as the Motor neuron, motor supply to various pelvic muscles, including the external sphincter muscle of male urethra, male or external sphincter muscle of female urethra, female external urethral sphincter and the external anal sphincter. If damaged, most commonly by childbirth, loss of sensation or fecal incontinence may result. The nerve may be temporarily anesthetized, called pudendal anesthesia or pudendal block. The pudendal canal that carries the pudendal nerve is also known by the eponymous term "Alcock's canal", after Benjamin Alcock, an Irish anatomist who documented the canal in 1836. Structure Origin The pudendal nerve is paired, me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |