|
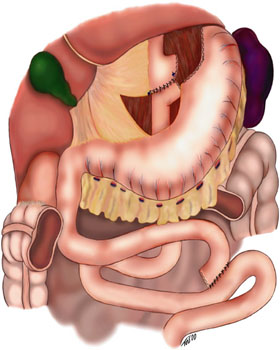
Internal Hernia
Internal hernias occur when there is protrusion of an internal organ into a retroperitoneal fossa or a foramen (congenital or acquired) in the abdominal cavity. If a loop of bowel passes through the mesenteric defect, that loop is at risk for incarceration, strangulation, or for becoming the lead point of a small bowel obstruction. Internal hernias can also trap adipose tissue (fat) and nerves. Unlike more common forms of hernias, the trapped tissue protrudes inward, rather than outward. Mesenteric defects commonly occur in trauma, such as gunshot wounds to the abdomen. In trauma victims, the defect is usually closed, sometimes with resection of the associated bowel, which may have lost its blood supply. Also mesenteric defects are intentionally created in the Roux-en-Y gastric bypass procedure, being classically known as a Petersen's hernia. The mesenteric defect in such cases, called ''Petersen's defect'', is located between the transverse colon and the mesentery of the al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
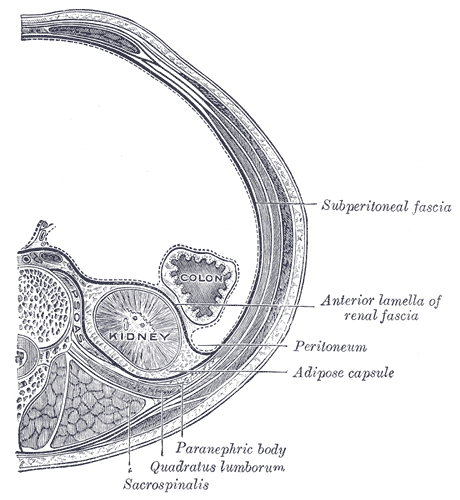
Retroperitoneal Fossa
The retroperitoneal space (retroperitoneum) is the anatomical space (sometimes a potential space) behind (''retro'') the peritoneum. It has no specific delineating anatomical structures. Organs are retroperitoneal if they have peritoneum on their anterior side only. Structures that are not suspended by mesentery in the abdominal cavity and that lie between the parietal peritoneum and abdominal wall are classified as retroperitoneal. This is different from organs that are not retroperitoneal, which have peritoneum on their posterior side and are suspended by mesentery in the abdominal cavity. The retroperitoneum can be further subdivided into the following: *Perirenal (or perinephric) space *Anterior pararenal (or paranephric) space *Posterior pararenal (or paranephric) space Retroperitoneal structures Structures that lie behind the peritoneum are termed "retroperitoneal". Organs that were once suspended within the abdominal cavity by mesentery but migrated posterior to the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foramen
In anatomy and osteology, a foramen (; in Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary '. plural foramina, or foramens ) is an open hole that is present in extant or extinct s. Foramina inside the of typically allow , |
Abdominal Cavity
The abdominal cavity is a large body cavity in humans and many other animals that contains many organs. It is a part of the abdominopelvic cavity. It is located below the thoracic cavity, and above the pelvic cavity. Its dome-shaped roof is the thoracic diaphragm, a thin sheet of muscle under the lungs, and its floor is the pelvic inlet, opening into the pelvis. Structure Organs Organs of the abdominal cavity include the stomach, liver, gallbladder, spleen, pancreas, small intestine, kidneys, large intestine, and adrenal glands. Peritoneum The abdominal cavity is lined with a protective membrane termed the peritoneum. The inside wall is covered by the parietal peritoneum. The kidneys are located behind the peritoneum, in the retroperitoneum, outside the abdominal cavity. The viscera are also covered by visceral peritoneum. Between the visceral and parietal peritoneum is the peritoneal cavity, which is a potential space. It contains a serous fluid called peritoneal fluid tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incarceration (bowel)
Imprisonment is the restraint of a person's liberty, for any cause whatsoever, whether by authority of the government, or by a person acting without such authority. In the latter case it is "false imprisonment". Imprisonment does not necessarily imply a place of confinement, with bolts and bars, but may be exercised by any use or display of force (such as placing one in handcuffs), lawfully or unlawfully, wherever displayed, even in the open street. People become prisoners, wherever they may be, by the mere word or touch of a duly authorized officer directed to that end. Usually, however, imprisonment is understood to imply an actual confinement in a jail or prison employed for the purpose according to the provisions of the law. Sometimes gender imbalances occur in imprisonment rates, with incarceration of males proportionately more likely than incarceration of females. History Africa Before colonisation, imprisonment was used in sub-Saharan Africa for pre-trial detention, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strangulation (bowel)
A volvulus is when a loop of intestine twists around itself and the mesentery that supports it, resulting in a bowel obstruction. Symptoms include abdominal pain, abdominal bloating, vomiting, constipation, and bloody stool. Onset of symptoms may be rapid or more gradual. The mesentery may become so tightly twisted that blood flow to part of the intestine is cut off, resulting in ischemic bowel. In this situation there may be fever or significant pain when the abdomen is touched. Risk factors include a birth defect known as intestinal malrotation, an enlarged colon, Hirschsprung disease, pregnancy, and abdominal adhesions. Long term constipation and a high fiber diet may also increase the risk. The most commonly affected part of the intestines in adults is the sigmoid colon with the cecum being second most affected. In children the small intestine is more often involved. The stomach can also be affected. Diagnosis is typically with medical imaging such as plain X-rays, a G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small Bowel Obstruction
Bowel obstruction, also known as intestinal obstruction, is a mechanical or functional obstruction of the intestines which prevents the normal movement of the products of digestion. Either the small bowel or large bowel may be affected. Signs and symptoms include abdominal pain, vomiting, bloating and not passing gas. Mechanical obstruction is the cause of about 5 to 15% of cases of severe abdominal pain of sudden onset requiring admission to hospital. Causes of bowel obstruction include adhesions, hernias, volvulus, endometriosis, inflammatory bowel disease, appendicitis, tumors, diverticulitis, ischemic bowel, tuberculosis and intussusception. Small bowel obstructions are most often due to adhesions and hernias while large bowel obstructions are most often due to tumors and volvulus. The diagnosis may be made on plain X-rays; however, CT scan is more accurate. Ultrasound or MRI may help in the diagnosis of children or pregnant women. The condition may be treated conserva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adipose Tissue
Adipose tissue, body fat, or simply fat is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. In addition to adipocytes, adipose tissue contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, vascular endothelial cells and a variety of immune cells such as adipose tissue macrophages. Adipose tissue is derived from preadipocytes. Its main role is to store energy in the form of lipids, although it also cushions and insulates the body. Far from being hormonally inert, adipose tissue has, in recent years, been recognized as a major endocrine organ, as it produces hormones such as leptin, estrogen, resistin, and cytokines (especially TNFα). In obesity, adipose tissue is also implicated in the chronic release of pro-inflammatory markers known as adipokines, which are responsible for the development of metabolic syndrome, a constellation of diseases including, but not limited to, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease and atherosclerosis. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gunshot Wounds
A gunshot wound (GSW) is a penetrating injury caused by a projectile (e.g. a bullet) from a gun (typically firearm or air gun). Damages may include bleeding, bone fractures, organ damage, wound infection, loss of the ability to move part of the body and, in more severe cases, death. Damage depends on the part of the body hit, the path the bullet follows through the body, and the type and speed of the bullet. Long-term complications can include lead poisoning and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Factors that determine rates of gun violence vary by country. These factors may include the illegal drug trade, easy access to firearms, substance misuse including alcohol, mental health problems, firearm laws, social attitudes, economic differences and occupations such as being a police officer. Where guns are more common, altercations more often end in death. Before management begins it should be verified the area is safe. This is followed by stopping major bleeding, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass
Gastric bypass surgery refers to a technique in which the stomach is divided into a small upper pouch and a much larger lower "remnant" pouch and then the small intestine is rearranged to connect to both. Surgeons have developed several different ways to reconnect the intestine, thus leading to several different gastric bypass procedures (GBP). Any GBP leads to a marked reduction in the functional volume of the stomach, accompanied by an altered physiological and physical response to food. The operation is prescribed to treat morbid obesity (defined as a body mass index greater than 40), type 2 diabetes, hypertension, sleep apnea, and other comorbid conditions. '' Bariatric surgery'' is the term encompassing ''all'' of the surgical treatments for morbid obesity, not just gastric bypasses, which make up only one class of such operations. The resulting weight loss, typically dramatic, markedly reduces comorbidities. The long-term mortality rate of gastric bypass patients has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
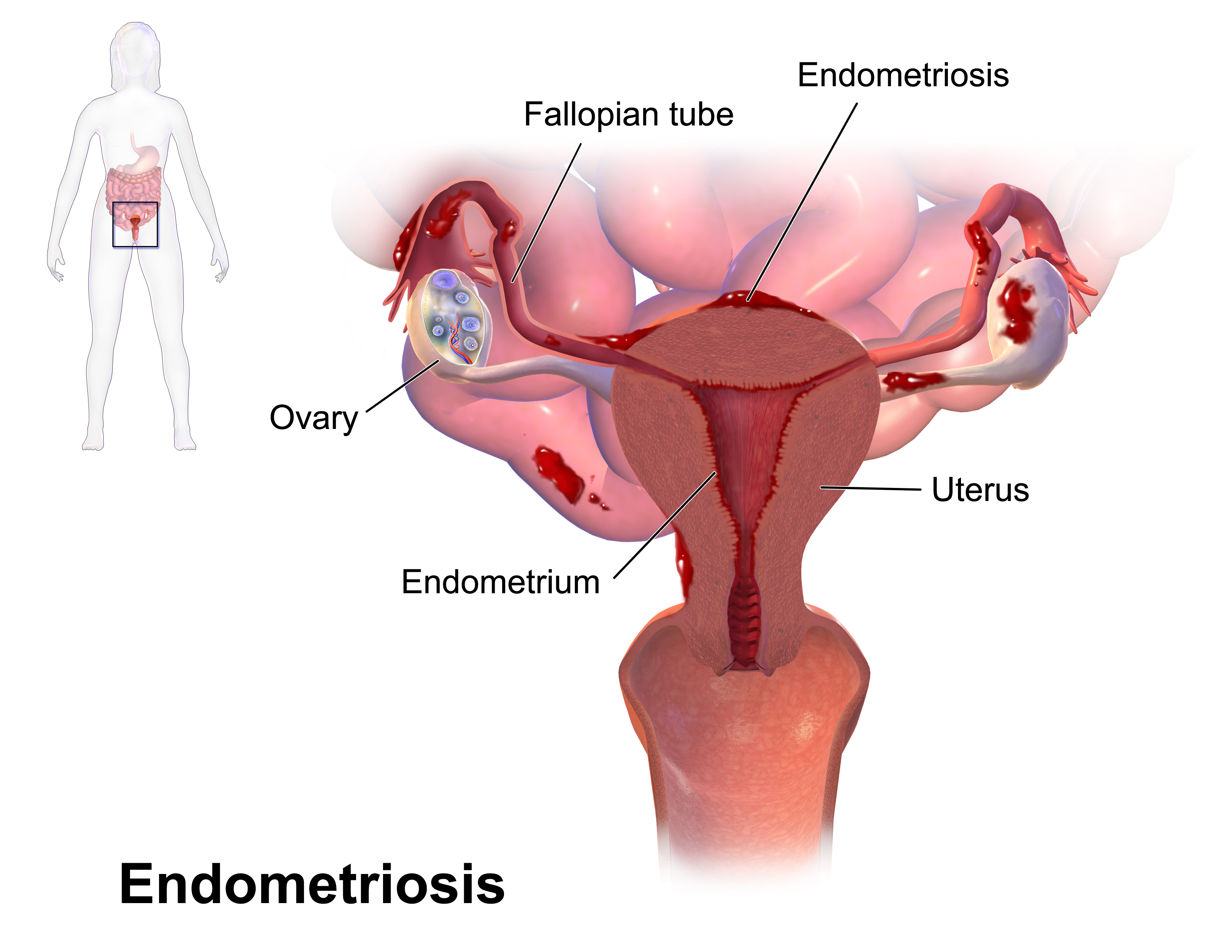
Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a disease of the female reproductive system in which cells similar to those in the endometrium, the layer of tissue that normally covers the inside of the uterus, grow outside the uterus. Most often this is on the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and tissue around the uterus and ovaries; in rare cases it may also occur in other parts of the body. Some symptoms include pelvic pain, heavy periods, pain with bowel movements, and infertility. Nearly half of those affected have chronic pelvic pain, while in 70% pain occurs during menstruation. Pain during sexual intercourse is also common. Infertility occurs in up to half of affected individuals. About 25% of individuals have no symptoms and 85% of those seen with infertility in a tertiary center have no pain. Endometriosis can have both social and psychological effects. The cause is not entirely clear. Risk factors include having a family history of the condition. The areas of endometriosis bleed each month (menstrua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronic Pelvic Pain
Pelvic pain is pain in the area of the pelvis. Acute pain is more common than chronic pain. If the pain lasts for more than six months, it is deemed to be chronic pelvic pain. It can affect both the male and female pelvis. Common causes in include: endometriosis in women, bowel adhesions, irritable bowel syndrome, and interstitial cystitis. The cause may also be a number of poorly understood conditions that may represent abnormal psychoneuromuscular function. The role of the nervous system in the genesis and moderation of pain is explored. The importance of psychological factors is discussed, both as a primary cause of pain and as a factor which affects the pain experience. As with other chronic syndromes, the biopsychosocial model offers a way of integrating physical causes of pain with psychological and social factors. Terminology Pelvic pain is a general term that may have many causes, listed below. The subcategorical term urologic chronic pelvic pain syndrome (UCPPS) is an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |