Gunshot wounds on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A gunshot wound (GSW) is a penetrating injury caused by a projectile (e.g. a bullet) from a
 A gunshot wound to the neck can be particularly dangerous because of the high number of vital anatomical structures contained within a small space. The neck contains the larynx,
A gunshot wound to the neck can be particularly dangerous because of the high number of vital anatomical structures contained within a small space. The neck contains the larynx,
gun
A gun is a ranged weapon designed to use a shooting tube (gun barrel) to launch projectiles. The projectiles are typically solid, but can also be pressurized liquid (e.g. in water guns/cannons, spray guns for painting or pressure washing, p ...
(typically firearm or air gun). Damages may include bleeding
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, vag ...
, bone fractures, organ damage, wound infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable dis ...
, loss of the ability to move part of the body and, in more severe cases, death. Damage depends on the part of the body hit, the path the bullet follows through the body, and the type and speed of the bullet. Long-term complications can include lead poisoning and post-traumatic stress disorder
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a mental and behavioral disorder that can develop because of exposure to a traumatic event, such as sexual assault, warfare, traffic collisions, child abuse, domestic violence, or other threats o ...
(PTSD).
Factors that determine rates of gun violence
Gun-related violence is violence committed with the use of a firearm. Gun-related violence may or may not be considered criminal. Criminal violence includes homicide (except when and where ruled justifiable), assault with a deadly weapon, and ...
vary by country. These factors may include the illegal drug trade
The illegal drug trade or drug trafficking is a global black market dedicated to the cultivation, manufacture, distribution and sale of prohibited drugs. Most jurisdictions prohibit trade, except under license, of many types of drugs throug ...
, easy access to firearms, substance misuse including alcohol, mental health
Mental health encompasses emotional, psychological, and social well-being, influencing cognition, perception, and behavior. It likewise determines how an individual handles stress, interpersonal relationships, and decision-making. Mental hea ...
problems, firearm laws, social attitudes, economic differences and occupations such as being a police officer. Where guns are more common, altercations more often end in death.
Before management begins it should be verified the area is safe. This is followed by stopping major bleeding, then assessing and supporting the airway, breathing, and circulation. Firearm laws, particularly background checks
A background check is a process a person or company uses to verify that an individual is who they claim to be, and this provides an opportunity to check and confirm the validity of someone's criminal record, education, employment history, and oth ...
and permit to purchase, decrease the risk of death from firearms. Safer firearm storage may decrease the risk of firearm-related deaths in children.
In 2015, about a million gunshot wounds occurred from interpersonal violence. In 2016, firearms resulted in 251,000 deaths globally, up from 209,000 in 1990. Of these deaths 161,000 (64%) were the result of assault, 67,500 (27%) were the result of suicide, and 23,000 (9%) were accidents. In the United States, guns resulted in about 40,000 deaths in 2017. Firearm-related deaths are most common in males between the ages of 20 to 24 years. Economic costs due to gunshot wounds have been estimated at US$140 billion a year in the United States.
Signs and symptoms
Trauma from a gunshot wound varies widely based on the bullet, velocity, mass, entry point, trajectory, affected anatomy, and exit point. Gunshot wounds can be particularly devastating compared to other penetrating injuries because the trajectory and fragmentation of bullets can be unpredictable after entry. Moreover, gunshot wounds typically involve a large degree of nearby tissue disruption and destruction caused by the physical effects of the projectile correlated with the bullet velocity classification. The immediate damaging effect of a gunshot wound is typically severebleeding
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, vag ...
with the potential for hypovolemic shock, a condition characterized by inadequate delivery of oxygen to vital organs. In the case of traumatic hypovolemic shock, this failure of adequate oxygen delivery is due to blood loss, as blood is the means of delivering oxygen to the body's constituent parts. Devastating effects can result when a bullet strikes a vital organ such as the heart, lungs or liver, or damages a component of the central nervous system such as the spinal cord or brain.
Common causes of death following gunshot injury include bleeding
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, vag ...
, low oxygen caused by pneumothorax
A pneumothorax is an abnormal collection of air in the pleural space between the lung and the chest wall. Symptoms typically include sudden onset of sharp, one-sided chest pain and shortness of breath. In a minority of cases, a one-way valve i ...
, catastrophic injury to the heart and major blood vessels, and damage to the brain or central nervous system. Non-fatal gunshot wounds frequently have mild to severe long-lasting effects, typically some form of major disfigurement such as amputation because of a severe bone fracture and may cause permanent disability. A sudden blood gush may take effect immediately from a gunshot wound if a bullet directly damages larger blood vessels, especially arteries
An artery (plural arteries) () is a blood vessel in humans and most animals that takes blood away from the heart to one or more parts of the body (tissues, lungs, brain etc.). Most arteries carry oxygenated blood; the two exceptions are the pu ...
.
Pathophysiology
The degree of tissue disruption caused by a projectile is related to the cavitation the projectile creates as it passes through tissue. A bullet with sufficient energy will have a cavitation effect in addition to the penetrating track injury. As the bullet passes through the tissue, initially crushing then lacerating, the space left forms a cavity; this is called the permanent cavity. Higher-velocity bullets create a pressure wave that forces the tissues away, creating not only a permanent cavity the size of the caliber of the bullet but a temporary cavity or secondary cavity, which is often many times larger than the bullet itself. The temporary cavity is the radial stretching of tissue around the bullet's wound track, which momentarily leaves an empty space caused by high pressures surrounding the projectile that accelerate material away from its path. The extent of cavitation, in turn, is related to the following characteristics of the projectile: *Kinetic energy
In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is the energy that it possesses due to its motion.
It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity. Having gained this energy during its acc ...
: KE = 1/2''mv''2 (where ''m'' is mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different eleme ...
and ''v'' is velocity
Velocity is the directional speed of an object in motion as an indication of its rate of change in position as observed from a particular frame of reference and as measured by a particular standard of time (e.g. northbound). Velocity i ...
). This helps to explain why wounds produced by projectiles of higher mass and/or higher velocity produce greater tissue disruption than projectiles of lower mass and velocity. The velocity of the bullet is a more important determinant of tissue injury. Although both mass and velocity contribute to the overall energy of the projectile, the energy is proportional to the mass while proportional to the ''square'' of its velocity. As a result, for constant velocity, if the mass is doubled, the energy is doubled; however, if the velocity of the bullet is doubled, the energy increases four times. The initial velocity of a bullet is largely dependent on the firearm. The US military commonly uses 5.56-mm bullets, which have a relatively low mass as compared with other bullets; however, the speed of these bullets is relatively fast. As a result, they produce a larger amount of kinetic energy, which is transmitted to the tissues of the target. The size of the temporary cavity is approximately proportional to the kinetic energy of the bullet and depends on the resistance of the tissue to stress. Muzzle energy
Muzzle energy is the kinetic energy of a bullet as it is expelled from the muzzle of a firearm. Without consideration of factors such as aerodynamics and gravity for the sake of comparison, muzzle energy is used as a rough indication of the de ...
, which is based on muzzle velocity, is often used for ease of comparison.
* Yaw: Handgun bullets will generally travel in a relatively straight line or make one turn if a bone is hit. Upon travel through deeper tissue, high-energy rounds may become unstable as they decelerate, and may tumble (pitch and yaw) as the energy of the projectile is absorbed, causing stretching and tearing of the surrounding tissue.
* Fragmentation: Most commonly, bullets do not fragment, and secondary damage from fragments of shattered bone is a more common complication than bullet fragments.
Diagnosis
Classification
Gunshot wounds are classified according to the speed of the projectile using the Gustilo open fracture classification: *Low-velocity: Less than 1,100 ft/s (340 m/s) Low velocity wounds are typical of small caliber handguns and display wound patterns like Gustilo Anderson Type 1 or 2 wounds *Medium-velocity: Between 1,200 ft/s (340 m/s) and 2,000 ft/s (610 m/s) These are more typical of shotgun blasts or higher caliber handguns like magnums. The risk of infection from these types of wounds can vary depending on the type and pattern of bullets fired as well as the distance from the firearm. *High-velocity: Between 2,000 ft/s (610 m/s) and 3,500 ft/s (1,100 m/s) Usually caused by powerful assault or hunting rifles and usually display wound pattern similar to Gustilo Anderson Type 3 wounds. The risk of infection is especially high due to the large area of injury and destroyed tissue. Bullets from handguns are sometimes less than but with modern pistol loads, they usually are slightly above , while bullets from most modern rifles exceed . One recently developed class of firearm projectiles is the hyper-velocity bullet, such cartridges are usually either wildcats made for achieving such high speed or purpose-built factory ammunition with the same goal in mind. Examples of hyper velocity cartridges include the.220 Swift
The .220 Swift (5.56×56mmSR) is a semi-rimmed rifle cartridge developed by Winchester and introduced in 1935 for small game and varmint hunting. It was the first factory-loaded rifle cartridge with a muzzle velocity of over , just under ...
, .17 Remington
The .17 Remington was introduced in 1971 by Remington Arms Company for their model 700 rifles.
Overview
It is based on the .223 Remington case necked down to .172 in (4.37 mm), with the shoulder moved back. It was designed exclusively as a ...
and .17 Mach IV
The .17 Mach IV is a wildcat centerfire rifle cartridge, based on the .221 Remington Fireball case, necked down to fire a bullet. The cartridge was introduced in 1962 by Vern O’Brien. The cartridge offered an easy case conversion and good bal ...
cartridges. The US military commonly uses 5.56mm bullets, which have a relatively low mass as compared with other bullets (40-62 grains); however, the speed of these bullets is relatively fast (Approximately , placing them in the high velocity category). As a result, they produce a larger amount of kinetic energy, which is transmitted to the tissues of the target. However, one must remember that high kinetic energy does not necessarily equate to high stopping power, as incapacitation usually results from remote wounding effects such as bleeding, rather than raw energy transfer. High energy does indeed result in more tissue disruption, which plays a role in incapacitation, but other factors such as wound size and shot placement play as big of, if not a bigger role in stopping power and thus, effectiveness. Muzzle velocity does not consider the effect of aerodynamic drag on the flight of the bullet for the sake of ease of comparison.
Prevention
Medical organizations in the United States recommend a criminal background check being held before a person buys a gun and that a person who has convictions for crimes of violence should not be permitted to buy a gun. Safe storage of firearms is recommended, as well as better mental health care and removal of guns from those at risk of suicide. In an effort to preventmass shootings
There is a lack of consensus on how to define a mass shooting. Most terms define a minimum of three or four victims of gun violence (not including the shooter or in an inner city) in a short period of time, although an Australian study from 20 ...
greater regulations on guns that can rapidly fire many bullets is recommended.
Management
Initial assessment for a gunshot wound is approached in the same way as other acute trauma using the advanced trauma life support (ATLS) protocol. These include: * A)Airway
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of respiration in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respiratory mucosa.
Air is breathed in through the nose to ...
- Assess and protect airway and potentially the cervical spine
* B) Breathing - Maintain adequate ventilation and oxygenation
* C) Circulation - Assess for and control bleeding to maintain organ perfusion including focused assessment with sonography for trauma (FAST)
* D) Disability - Perform basic neurological exam including Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS)
* E) Exposure - Expose entire body and search for any missed injuries, entry points, and exit points while maintaining body temperature
Depending on the extent of injury, management can range from urgent surgical intervention to observation. As such, any history from the scene such as gun type, shots fired, shot direction and distance, blood loss on scene, and pre-hospital vitals signs can be very helpful in directing management. Unstable people with signs of bleeding that cannot be controlled during the initial evaluation require immediate surgical exploration in the operating room. Otherwise, management protocols are generally dictated by anatomic entry point and anticipated trajectory.
Neck
 A gunshot wound to the neck can be particularly dangerous because of the high number of vital anatomical structures contained within a small space. The neck contains the larynx,
A gunshot wound to the neck can be particularly dangerous because of the high number of vital anatomical structures contained within a small space. The neck contains the larynx, trachea
The trachea, also known as the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all air- breathing animals with lungs. The trachea extends from the ...
, pharynx
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its st ...
, esophagus
The esophagus ( American English) or oesophagus (British English; both ), non-technically known also as the food pipe or gullet, is an organ in vertebrates through which food passes, aided by peristaltic contractions, from the pharynx to ...
, vasculature (carotid
In anatomy, the left and right common carotid arteries (carotids) (Entry "carotid"
in
subclavian, and
 Important anatomy in the abdomen includes the
Important anatomy in the abdomen includes the
 The four main components of extremities are
The four main components of extremities are
 *
*
Virtual Autopsy – CT scans of fatal gunshot wounds
Patient.info
{{Authority control Medical emergencies Causes of death Injuries Ballistics Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Gun violence
in
subclavian, and
vertebral arteries
The vertebral arteries are major arteries of the neck. Typically, the vertebral arteries originate from the subclavian arteries. Each vessel courses superiorly along each side of the neck, merging within the skull to form the single, midline ...
; jugular
The jugular veins are veins that take deoxygenated blood from the head back to the heart via the superior vena cava. The internal jugular vein descends next to the internal carotid artery and continues posteriorly to the sternocleidomastoid mus ...
, brachiocephalic, and vertebral vein
The vertebral vein is formed in the suboccipital triangle, from numerous small tributaries which spring from the internal vertebral venous plexuses and issue from the vertebral canal above the posterior arch of the atlas.
They unite with small v ...
s; thyroid vessels), and nervous system anatomy (spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone). The backbone encloses the central canal of the sp ...
, cranial nerves
Cranial nerves are the nerves that emerge directly from the brain (including the brainstem), of which there are conventionally considered twelve pairs. Cranial nerves relay information between the brain and parts of the body, primarily to and f ...
, peripheral nerves, sympathetic chain, brachial plexus
The brachial plexus is a network () of nerves formed by the anterior rami of the lower four cervical nerves and first thoracic nerve ( C5, C6, C7, C8, and T1). This plexus extends from the spinal cord, through the cervicoaxillary canal in t ...
). Gunshots to the neck can thus cause severe bleeding, airway compromise, and nervous system injury.
Initial assessment of a gunshot wound to the neck involves non-probing inspection of whether the injury is a penetrating neck injury (PNI), classified by violation of the platysma
The platysma muscle is a superficial muscle of the human neck that overlaps the sternocleidomastoid. It covers the anterior surface of the neck superficially. When it contracts, it produces a slight wrinkling of the neck, and a "bowstring" effec ...
muscle. If the platysma is intact, the wound is considered superficial and only requires local wound care. If the injury is a PNI, surgery should be consulted immediately while the case is being managed. Of note, wounds should not be explored on the field or in the emergency department given the risk of exacerbating the wound.
Due to the advances in diagnostic imaging, management of PNI has been shifting from a "zone-based" approach, which uses anatomical site of injury to guide decisions, to a "no-zone" approach which uses a symptom-based algorithm. The no-zone approach uses a hard signs and imaging system to guide next steps. Hard signs include airway compromise, unresponsive shock, diminished pulses, uncontrolled bleeding, expanding hematoma, bruit
Bruit, also called vascular murmur, is the abnormal sound generated by turbulent flow of blood in an artery due to either an area of partial obstruction or a localized high rate of blood flow through an unobstructed artery.
The bruit may be hear ...
s/thrill, air bubbling from wound or extensive subcutaneous air, stridor/hoarseness, neurological deficits. If any hard signs are present, immediate surgical exploration and repair is pursued alongside airway and bleeding control. If there are no hard signs, the person receives a multi-detector CT angiography for better diagnosis. A directed angiography
Angiography or arteriography is a medical imaging technique used to visualize the inside, or lumen, of blood vessels and organs of the body, with particular interest in the arteries, veins, and the heart chambers. Modern angiography is perfor ...
or endoscopy
An endoscopy is a procedure used in medicine to look inside the body. The endoscopy procedure uses an endoscope to examine the interior of a hollow organ or cavity of the body. Unlike many other medical imaging techniques, endoscopes are inse ...
may be warranted in a high-risk trajectory for the gunshot. A positive finding on CT leads to operative exploration. If negative, the person may be observed with local wound care.
Chest
Important anatomy in the chest includes the chest wall,ribs
The rib cage, as an enclosure that comprises the ribs, vertebral column and sternum in the thorax of most vertebrates, protects vital organs such as the heart, lungs and great vessels.
The sternum, together known as the thoracic cage, is a semi- ...
, spine, spinal cord, intercostal neurovascular bundles, lungs, bronchi
A bronchus is a passage or airway in the lower respiratory tract that conducts air into the lungs. The first or primary bronchi pronounced (BRAN-KAI) to branch from the trachea at the carina are the right main bronchus and the left main bronchus. ...
, heart
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to t ...
, aorta
The aorta ( ) is the main and largest artery in the human body, originating from the left ventricle of the heart and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits into two smaller arteries (the common iliac arteries). The aorta distributes o ...
, major vessels, esophagus, thoracic duct
In human anatomy, the thoracic duct is the larger of the two lymph ducts of the lymphatic system. It is also known as the ''left lymphatic duct'', ''alimentary duct'', ''chyliferous duct'', and ''Van Hoorne's canal''. The other duct is the righ ...
, and diaphragm. Gunshots to the chest can thus cause severe bleeding (hemothorax
A hemothorax (derived from hemo- lood+ thorax hest plural ''hemothoraces'') is an accumulation of blood within the pleural cavity. The symptoms of a hemothorax may include chest pain and difficulty breathing, while the clinical signs may incl ...
), respiratory compromise (pneumothorax
A pneumothorax is an abnormal collection of air in the pleural space between the lung and the chest wall. Symptoms typically include sudden onset of sharp, one-sided chest pain and shortness of breath. In a minority of cases, a one-way valve i ...
, hemothorax, pulmonary contusion
A pulmonary contusion, also known as lung contusion, is a bruise of the lung, caused by chest trauma. As a result of damage to capillaries, blood and other fluids accumulate in the lung tissue. The excess fluid interferes with gas exchange, po ...
, tracheobronchial injury), cardiac injury ( pericardial tamponade), esophageal injury, and nervous system injury.
Initial workup as outlined in the Workup section is particularly important with gunshot wounds to the chest because of the high risk for direct injury to the lungs, heart, and major vessels. Important notes for the initial workup specific for chest injuries are as follows. In people with pericardial tamponade or tension pneumothorax, the chest should be evacuated or decompressed if possible prior to attempting tracheal intubation
Tracheal intubation, usually simply referred to as intubation, is the placement of a flexible plastic tube into the trachea (windpipe) to maintain an open airway or to serve as a conduit through which to administer certain drugs. It is frequentl ...
because the positive pressure ventilation can cause hypotention or cardiovascular collapse. Those with signs of a tension pneumothorax (asymmetric breathing, unstable blood flow, respiratory distress) should immediately receive a chest tube
A chest tube (also chest drain, thoracic catheter, tube thoracostomy or intercostal drain) is a surgical drain that is inserted through the chest wall and into the pleural space or the mediastinum in order to remove clinically undesired substance ...
(> French 36) or needle decompression if chest tube placement is delayed. FAST exam should include extended views into the chest to evaluate for hemopericardium, pneumothorax, hemothorax, and peritoneal fluid.
Those with cardiac tamponade, uncontrolled bleeding, or a persistent air leak from a chest tube all require surgery. Cardiac tamponade can be identified on FAST exam. Blood loss warranting surgery is 1–1.5 L of immediate chest tube drainage or ongoing bleeding of 200-300 mL/hr. Persistent air leak is suggestive of tracheobronchial injury which will not heal without surgical intervention. Depending on the severity of the person's condition and if cardiac arrest
Cardiac arrest is when the heart suddenly and unexpectedly stops beating. It is a medical emergency that, without immediate medical intervention, will result in sudden cardiac death within minutes. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and poss ...
is recent or imminent, the person may require surgical intervention in the emergency department, otherwise known as an emergency department thoracotomy
A thoracotomy is a surgical procedure to gain access into the pleural space of the chest. It is performed by surgeons (emergency physicians or paramedics under certain circumstances) to gain access to the thoracic organs, most commonly the hea ...
(EDT).
However, not all gunshot to the chest require surgery. Asymptomatic people with a normal chest X-ray can be observed with a repeat exam and imaging after 6 hours to ensure no delayed development of pneumothorax or hemothorax. If a person only has a pneumothorax or hemothorax, a chest tube is usually sufficient for management unless there is large volume bleeding or persistent air leak as noted above. Additional imaging after initial chest X-ray and ultrasound can be useful in guiding next steps for stable people. Common imaging modalities include chest CT, formal echocardiography, angiography, esophagoscopy, esophagography, and bronchoscopy
Bronchoscopy is an endoscopic technique of visualizing the inside of the airways for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. An instrument (bronchoscope) is inserted into the airways, usually through the nose or mouth, or occasionally through a trac ...
depending on the signs and symptoms.
Abdomen
 Important anatomy in the abdomen includes the
Important anatomy in the abdomen includes the stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach i ...
, small bowel
The small intestine or small bowel is an organ in the gastrointestinal tract where most of the absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intestine, and receives bile and pancreatic juice through the pa ...
, colon, liver
The liver is a major organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it ...
, spleen
The spleen is an organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter. The word spleen comes .
, pancreas
The pancreas is an organ of the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a gland. The pancreas is a mixed or heterocrine gland, i.e. it has both an en ...
, kidney
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blo ...
s, spine, diaphragm, descending aorta, and other abdominal vessels and nerves. Gunshots to the abdomen can thus cause severe bleeding, release of bowel contents, peritonitis
Peritonitis is inflammation of the localized or generalized peritoneum, the lining of the inner wall of the abdomen and cover of the abdominal organs. Symptoms may include severe pain, swelling of the abdomen, fever, or weight loss. One part o ...
, organ rupture, respiratory compromise, and neurological deficits.
The most important initial evaluation of a gunshot wound to the abdomen is whether there is uncontrolled bleeding, inflammation of the peritoneum
The peritoneum is the serous membrane forming the lining of the abdominal cavity or coelom in amniotes and some invertebrates, such as annelids. It covers most of the intra-abdominal (or coelomic) organs, and is composed of a layer of meso ...
, or spillage of bowel contents. If any of these are present, the person should be transferred immediately to the operating room for laparotomy
A laparotomy is a surgical procedure involving a surgical incision through the abdominal wall to gain access into the abdominal cavity. It is also known as a celiotomy.
Origins and history
The first successful laparotomy was performed without ane ...
. If it is difficult to evaluate for those indications because the person is unresponsive or incomprehensible, it is up to the surgeon's discretion whether to pursue laparotomy, exploratory laparoscopy
Laparoscopy () is an operation performed in the abdomen or pelvis using small incisions (usually 0.5–1.5 cm) with the aid of a camera. The laparoscope aids diagnosis or therapeutic interventions with a few small cuts in the abdomen.Medli ...
, or alternative investigative tools.
Although all people with abdominal gunshot wounds were taken to the operating room in the past, practice has shifted in recent years with the advances in imaging to non-operative approaches in more stable people. If the person's vital signs are stable without indication for immediate surgery, imaging is done to determine the extent of injury. Ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequency, frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing range, hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hea ...
(FAST) and help identify intra-abdominal bleeding and X-rays can help determine bullet trajectory and fragmentation. However, the best and preferred mode of imaging is high-resolution multi-detector CT (MDCT) with IV, oral, and sometimes rectal contrast. Severity of injury found on imaging will determine whether the surgeon takes an operative or close observational approach.
Diagnostic peritoneal lavage
Diagnostic peritoneal lavage (DPL) or diagnostic peritoneal aspiration (DPA) is a surgical diagnostic procedure to determine if there is free floating fluid (most often blood) in the abdominal cavity.
Indications
This procedure is performed when ...
(DPL) has become largely obsolete with the advances in MDCT, with use limited to centers without access to CT to guide requirement for urgent transfer for operation.
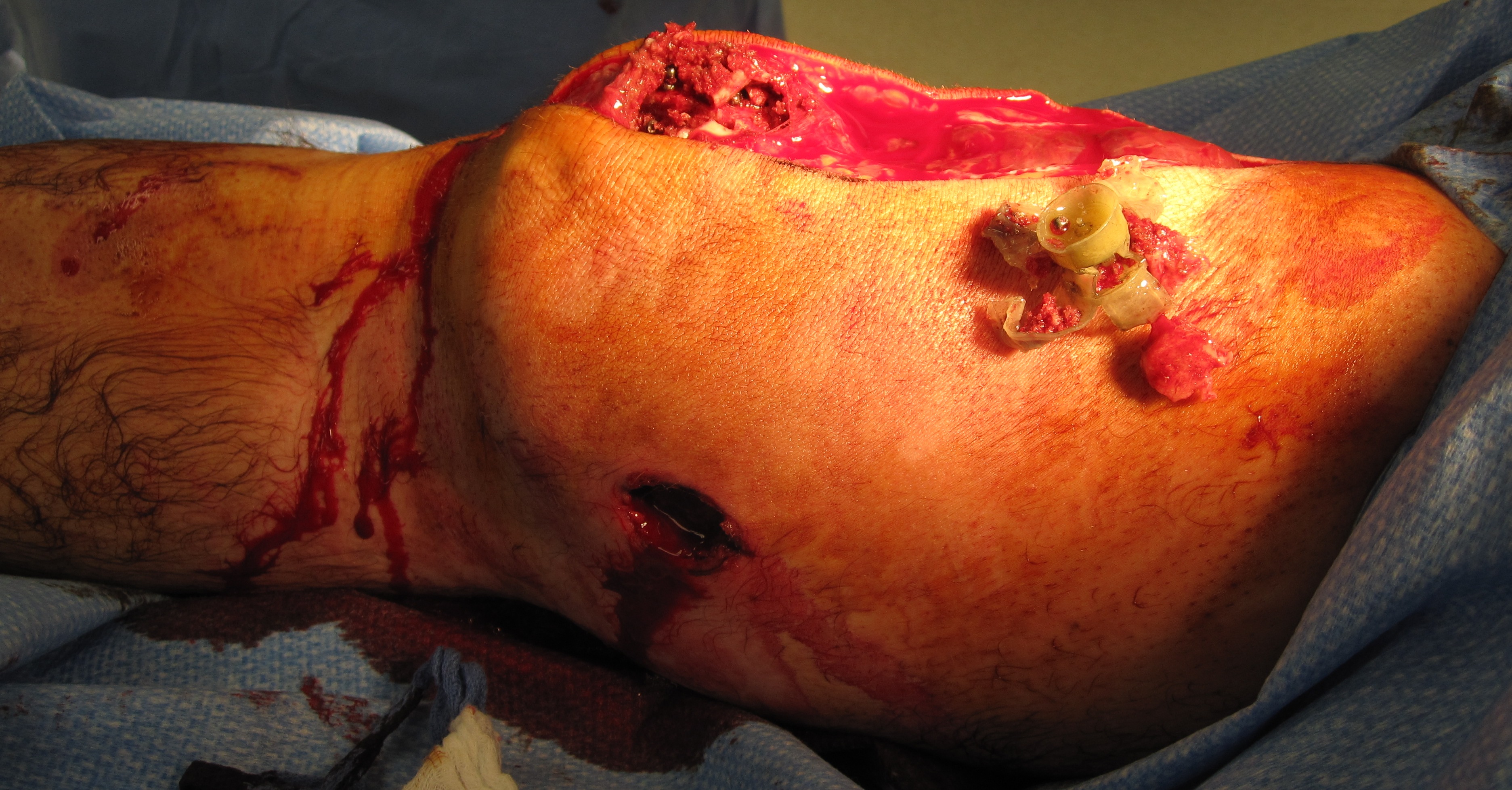
Extremities
bone
A bone is a Stiffness, rigid Organ (biology), organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red blood cell, red and white blood cells, store minerals, provid ...
s, vessels, nerve
A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers (called axons) in the peripheral nervous system.
A nerve transmits electrical impulses. It is the basic unit of the peripheral nervous system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the e ...
s, and soft tissue
Soft tissue is all the tissue in the body that is not hardened by the processes of ossification or calcification such as bones and teeth. Soft tissue connects, surrounds or supports internal organs and bones, and includes muscle, tendons, ligam ...
s. Gunshot wounds can thus cause severe bleeding, fractures
Fracture is the separation of an object or material into two or more pieces under the action of stress. The fracture of a solid usually occurs due to the development of certain displacement discontinuity surfaces within the solid. If a displa ...
, nerve deficits, and soft tissue damage. The Mangled Extremity Severity Score (MESS) is used to classify the severity of injury and evaluates for severity of skeletal and/or soft tissue injury, limb ischemia
Ischemia or ischaemia is a restriction in blood supply to any tissue, muscle group, or organ of the body, causing a shortage of oxygen that is needed for cellular metabolism (to keep tissue alive). Ischemia is generally caused by problems wi ...
, shock, and age. Depending on the extent of injury, management can range from superficial wound care to limb amputation.
Vital sign stability and vascular assessment are the most important determinants of management in extremity injuries. As with other traumatic cases, those with uncontrolled bleeding require immediate surgical intervention. If surgical intervention is not readily available and direct pressure is insufficient to control bleeding, tourniquet
A tourniquet is a device that is used to apply pressure to a limb or extremity in order to stop the flow of blood. It may be used in emergencies, in surgery, or in post-operative rehabilitation.
A simple tourniquet can be made from a stick and ...
s or direct clamping of visible vessels may be used temporarily to slow active bleeding. People with hard signs of vascular injury also require immediate surgical intervention. Hard signs include active bleeding, expanding or pulsatile hematoma, bruit/thrill, absent distal pulses and signs of extremity ischemia.
For stable people without hard signs of vascular injury, an injured extremity index (IEI) should be calculated by comparing the blood pressure in the injured limb compared to an uninjured limb in order to further evaluate for potential vascular injury. If the IEI or clinical signs are suggestive of vascular injury, the person may undergo surgery or receive further imaging including CT angiography or conventional arteriography.
In addition to vascular management, people must be evaluated for bone, soft tissue, and nerve injury. Plain films can be used for fractures alongside CTs for soft tissue assessment. Fractures must be debrided and stabilized, nerves repaired when possible, and soft tissue debrided and covered. This process can often require multiple procedures over time depending on the severity of injury.
Epidemiology
In 2015, about a million gunshot wounds occurred from interpersonal violence. Firearms, globally in 2016, resulted in 251,000 deaths up from 209,000 in 1990. Of these deaths 161,000 (64%) were the result of assault, 67,500 (27%) were the result of suicide, and 23,000 were accidents. Firearm related deaths are most common in males between the ages of 20 to 24 years. The countries with the greatest number of deaths from firearms areBrazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
, United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
, Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
, Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Car ...
, Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
, Guatemala
Guatemala ( ; ), officially the Republic of Guatemala ( es, República de Guatemala, links=no), is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico; to the northeast by Belize and the Caribbean; to the east by H ...
, Bahamas
The Bahamas (), officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the West Indies in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic. It takes up 97% of the Lucayan Archipelago's land area and is home to ...
and South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring countri ...
which make up just over half the total. In the United States in 2015 about half of the 44,000 people who died by suicide did so with a gun.
As of 2016, the countries with the highest rates of gun violence per capita were El Salvador, Venezuela, and Guatemala with 40.3, 34.8, and 26.8 violent gun deaths per 100,000 people respectively. The countries with the lowest rates of were Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, borde ...
, Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
, and South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and sharing a Korean Demilitarized Zone, land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed ...
with 0.03, 0.04, and 0.05 violent gun deaths per 100,000 people respectively.
Canada
In 2016, about 893 people died due to gunshot wounds in Canada (2.1 per 100,000). About 80% were suicides, 12% were assaults, and 4% percent were an accident.United States
In 2017, there were 39,773 deaths in the United States as a result gunshot wounds. Of these 60% were suicides, 37% were homicides, 1.4% were by law enforcement, 1.2% were accidents, and 0.9% were from an unknown cause. This is up from 37,200 deaths in 2016 due to a gunshot wound (10.6 per 100,000). With respect to those that pertain to interpersonal violence, it had the 31st highest rate in the world with 3.85 deaths per 100,000 people in 2016. The majority of all homicides and suicides are firearm-related, and the majority of firearm-related deaths are the result of murder and suicide. When sorted by GDP, however, the United States has a much higher violent gun death rate compared to other developed countries, with over 10 times the number of firearms assault deaths than the next four highest GDP countries combined. Gunshot violence is the third most costly cause of injury and the fourth most expensive form of hospitalization in the United States.History
Until the 1880s, the standard practice for treating a gunshot wound called for physicians to insert their unsterilized fingers into the wound to probe and locate the path of the bullet. Standard surgical theory such as opening abdominal cavities to repair gunshot wounds,germ theory
The germ theory of disease is the currently accepted scientific theory for many diseases. It states that microorganisms known as pathogens or "germs" can lead to disease. These small organisms, too small to be seen without magnification, invade ...
, and Joseph Lister
Joseph Lister, 1st Baron Lister, (5 April 182710 February 1912) was a British surgeon, medical scientist, experimental pathologist and a pioneer of antiseptic surgery and preventative medicine. Joseph Lister revolutionised the craft of s ...
's technique for antiseptic surgery using diluted carbolic acid
Phenol (also called carbolic acid) is an aromaticity, aromatic organic compound with the molecular chemical formula, formula . It is a white crystalline solid that is volatility (chemistry), volatile. The molecule consists of a phenyl group () ...
, had not yet been accepted as standard practice. For example, sixteen doctors attended to President James A. Garfield
James Abram Garfield (November 19, 1831 – September 19, 1881) was the 20th president of the United States, serving from March 4, 1881 until his death six months latertwo months after he was shot by an assassin. A lawyer and Civil War gene ...
after he was shot in 1881, and most probed the wound with their fingers or dirty instruments. Historians agree that massive infection was a significant factor in Garfield's death.
At almost the same time, in Tombstone, Arizona Territory
The Territory of Arizona (also known as Arizona Territory) was a territory of the United States that existed from February 24, 1863, until February 14, 1912, when the remaining extent of the territory was admitted to the Union as the state of ...
, on 13 July 1881, George E. Goodfellow
George Emory Goodfellow (December 23, 1855 – December 7, 1910) was a physician and naturalist in the 19th- and early 20th-century American Old West who developed a reputation as the United States' foremost expert in treating ...
performed the first laparotomy
A laparotomy is a surgical procedure involving a surgical incision through the abdominal wall to gain access into the abdominal cavity. It is also known as a celiotomy.
Origins and history
The first successful laparotomy was performed without ane ...
to treat an abdominal gunshot wound. Goodfellow pioneered the use of sterile techniques in treating gunshot wounds, washing the person's wound and his hands with lye soap or whisky, and his patient, unlike the President, recovered. He became America's leading authority on gunshot wounds and is credited as the United States' first civilian trauma surgeon
Trauma surgery is a surgical specialty that utilizes both operative and non-operative management to treat traumatic injuries, typically in an acute setting. Trauma surgeons generally complete residency training in general surgery and often fel ...
.
Mid-nineteenth-century handguns such as the Colt revolvers used during the American Civil War had muzzle velocities of just 230–260 m/s and their powder and ball predecessors had velocities of 167 m/s or less. Unlike today's high-velocity bullets, nineteenth-century balls produced almost little or no cavitation and, being slower moving, they were liable to lodge in unusual locations at odds with their trajectory.
Wilhelm Röntgen
Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen (; ; 27 March 184510 February 1923) was a German mechanical engineer and physicist, who, on 8 November 1895, produced and detected electromagnetic radiation in a wavelength range known as X-rays or Röntgen rays, an achiev ...
's discovery of X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
s in 1895 led to the use of radiographs to locate bullets in wounded soldiers.
Survival rates for gunshot wounds improved among US military personnel during the Korean
Korean may refer to:
People and culture
* Koreans, ethnic group originating in the Korean Peninsula
* Korean cuisine
* Korean culture
* Korean language
**Korean alphabet, known as Hangul or Chosŏn'gŭl
**Korean dialects and the Jeju language
** ...
and Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by #Names, other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vie ...
s, due in part to helicopter evacuation, along with improvements in resuscitation and battlefield medicine. Similar improvements were seen in US trauma practices during the Iraq War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Iraq War {{Nobold, {{lang, ar, حرب العراق (Arabic) {{Nobold, {{lang, ku, شەڕی عێراق (Kurdish languages, Kurdish)
, partof = the Iraq conflict (2003–present), I ...
. Some military trauma care practices are disseminated by citizen soldiers who return to civilian practice. One such practice is to transfer major trauma cases to an operating theater as soon as possible, to stop internal bleeding
Internal bleeding (also called internal hemorrhage) is a loss of blood from a blood vessel that collects inside the body. Internal bleeding is usually not visible from the outside. It is a serious medical emergency but the extent of severity depen ...
. Within the United States, the survival rate for gunshot wounds has increased, leading to apparent declines in the gun death rate in states that have stable rates of gunshot hospitalizations.
Research
Research into gunshot wounds in the USA is hampered by lack of funding. Federal-funded research into firearm injury,epidemiology
Epidemiology is the study and analysis of the distribution (who, when, and where), patterns and determinants of health and disease conditions in a defined population.
It is a cornerstone of public health, and shapes policy decisions and evidenc ...
, violence
Violence is the use of physical force so as to injure, abuse, damage, or destroy. Other definitions are also used, such as the World Health Organization's definition of violence as "the intentional use of physical force or Power (social and p ...
, and prevention is minimal.
See also
 *
*Blast injury
A blast injury is a complex type of physical trauma resulting from direct or indirect exposure to an explosion. Blast injuries occur with the detonation of high-order explosives as well as the deflagration of low order explosives. These injurie ...
, an injury that may present similar dangers to a gunshot wound.
*Bullet hit squib
A bullet hit squib or a blood squib is a practical, pyrotechnic special effect device used in the film industry, theatre productions and first responder moulage training to simulate a bullet wound spurting blood. Typically, the effect is carrie ...
, the simulated equivalent of a gunshot wound used in the film industry to portray a gunshot wound.
*Stab wound
A stab wound is a specific form of penetrating trauma to the skin that results from a knife or a similar pointed object. While stab wounds are typically known to be caused by knives, they can also occur from a variety of implements, including brok ...
, an equivalent penetrating injury caused by a bladed weapon or any other sharp objects.
References
External links
Virtual Autopsy – CT scans of fatal gunshot wounds
Patient.info
{{Authority control Medical emergencies Causes of death Injuries Ballistics Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Gun violence