|
Intel Celeron
Celeron is Intel's brand name for low-end IA-32 and x86-64 computer microprocessor models targeted at low-cost personal computers. Celeron processors are compatible with IA-32 software. They typically offer less performance per clock speed compared to flagship Intel CPU lines, such as the Pentium or Core brands. Celeron branded processors often have less cache or intentionally disabled advanced features, with variable impact on performance. While some Celeron designs have achieved strong performance for their segment, most of the Celeron line has exhibited noticeably degraded performance. This has been the primary justification for the higher cost of other Intel CPU brands versus the Celeron range. Introduced in April 1998, the first Celeron-branded CPU was based on the Pentium II. Subsequent Celeron-branded CPUs were based on the Pentium III, Pentium 4, Pentium M, and Intel Core. In September 2022, Intel announced that the Celeron brand, along with Pentium, will be replaced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
I486
The Intel 486, officially named i486 and also known as 80486, is a microprocessor. It is a higher-performance follow-up to the Intel 386. The i486 was introduced in 1989. It represents the fourth generation of binary compatible CPUs following the 8086 of 1978, the Intel 80286 of 1982, and 1985's i386. It was the first tightly- pipelined x86 design as well as the first x86 chip to include more than one million transistors. It offered a large on-chip cache and an integrated floating-point unit. A typical 50 MHz i486 executes around 40 million instructions per second (MIPS), reaching 50 MIPS peak performance. It is approximately twice as fast as the i386 or i286 per clock cycle. The i486's improved performance is thanks to its five-stage pipeline with all stages bound to a single cycle. The enhanced FPU unit on the chip was significantly faster than the i387 FPU per cycle. The intel 80387 FPU ("i387") was a separate, optional math coprocessor that was ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golden Cove
Golden Cove is a codename for a CPU microarchitecture developed by Intel and released in November 2021. It succeeds four microarchitectures: Sunny Cove, Skylake, Willow Cove, and Cypress Cove. It is fabricated using Intel's Intel 7 process node, previously referred to as 10nm Enhanced SuperFin (10ESF). The microarchitecture is used in the high-performance cores (P-core) of the 12th-generation Intel Core processors (codenamed " Alder Lake") and will power fourth-generation Xeon Scalable server processors (codenamed " Sapphire Rapids"). History and features Intel first unveiled Golden Cove during their Architecture Day 2020, with further details released at the same event in August 2021. Similar to Skylake, Golden Cove was described by Intel as a major update to the core microarchitecture, with Intel stating that it would "allow performance for the next decade of compute". Intel also described Golden Cove as the largest microarchitectural upgrade to the Core family in a decade, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the developers of the x86 series of instruction sets, the instruction sets found in most personal computers (PCs). Delaware General Corporation Law, Incorporated in Delaware, Intel ranked No. 45 in the 2020 Fortune 500, ''Fortune'' 500 list of the largest United States corporations by total revenue for nearly a decade, from 2007 to 2016 fiscal years. Intel supplies microprocessors for List of computer system manufacturers, computer system manufacturers such as Acer Inc., Acer, Lenovo, HP Inc., HP, and Dell Technologies, Dell. Intel also manufactures motherboard chipsets, network interface controllers and integrated circuits, flash memory, Graphics processing unit, graphics chips, Embedded system, embedded processors and other devices related to com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LGA 1700
LGA 1700 (Socket V) is a zero insertion force flip-chip land grid array (LGA) socket, compatible with Intel desktop processors Alder Lake and Raptor Lake, which was first released in November 2021. LGA 1700 is designed as a replacement for LGA 1200 (known as ''Socket H5'') and it has 1700 protruding pins to make contact with the pads on the processor. Compared to its predecessor, it has 500 more pins, which required a major change in socket and processor sizes; it is 7.5 mm longer. It is the first major change in Intel's LGA desktop CPU socket size since the introduction of LGA 775 in 2004, especially for consumer-grade CPU sockets. The larger size also required a change in the heatsink fastening holes configuration, making previously used cooling solutions incompatible with LGA 1700 motherboards and CPUs. Heatsink design Since the introduction of Land grid array (LGA)-based sockets in the consumer hardware space in 2004, the thermal solution ''hole pattern'' (the distanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LGA 1200
LGA 1200 is a zero insertion force flip-chip land grid array (LGA) socket, compatible with Intel desktop processors Comet Lake (10th gen) and Rocket Lake (11th-gen) desktop CPUs, which was released in April 2020. LGA 1200 is designed as a replacement for the LGA 1151 (known as ''Socket H4''). LGA 1200 is a land grid array mount with 1200 protruding pins to make contact with the pads on the processor. It uses a modified design of LGA 1151, with 49 more pins on it, improving power delivery and offering support for future incremental I/O features. Pin 1 position remains the same as it was in previous generation processors, but it has shifted socket keying to left (previously it was right), making Comet Lake processors incompatible both electrically and mechanically with previous chips. ASRock, Asus, Biostar, Gigabyte and MSI have confirmed their motherboards based on the Intel Z490 chipset support the 11th generation Intel Rocket Lake desktop CPUs. Full PCIe 4.0 support is confirm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LGA 1151
LGA 1151, also known as Socket H4, zero insertion force flip-chip land grid array (LGA) socket for Intel desktop processors which comes in two distinct versions: the first revision which supports both Intel's Skylake and Kaby Lake CPUs, and the second revision which supports Coffee Lake CPUs exclusively. LGA 1151 is designed as a replacement for the LGA 1150 (known as ''Socket H3''). LGA 1151 has 1151 protruding pins to make contact with the pads on the processor. The Fully Integrated Voltage Regulator, i.e. a voltage regulator which integrated on the CPU's die, introduced with Haswell and Broadwell, has again been moved to the motherboard. Most motherboards for the first revision of the socket support solely DDR4 memory, a lesser number support DDR3(L) memory, and the least number have slots for both DDR4 or DDR3(L) but only one memory type can be installed. Some have UniDIMM support, enabling either type of memory to be placed in the same DIMM, rather than ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
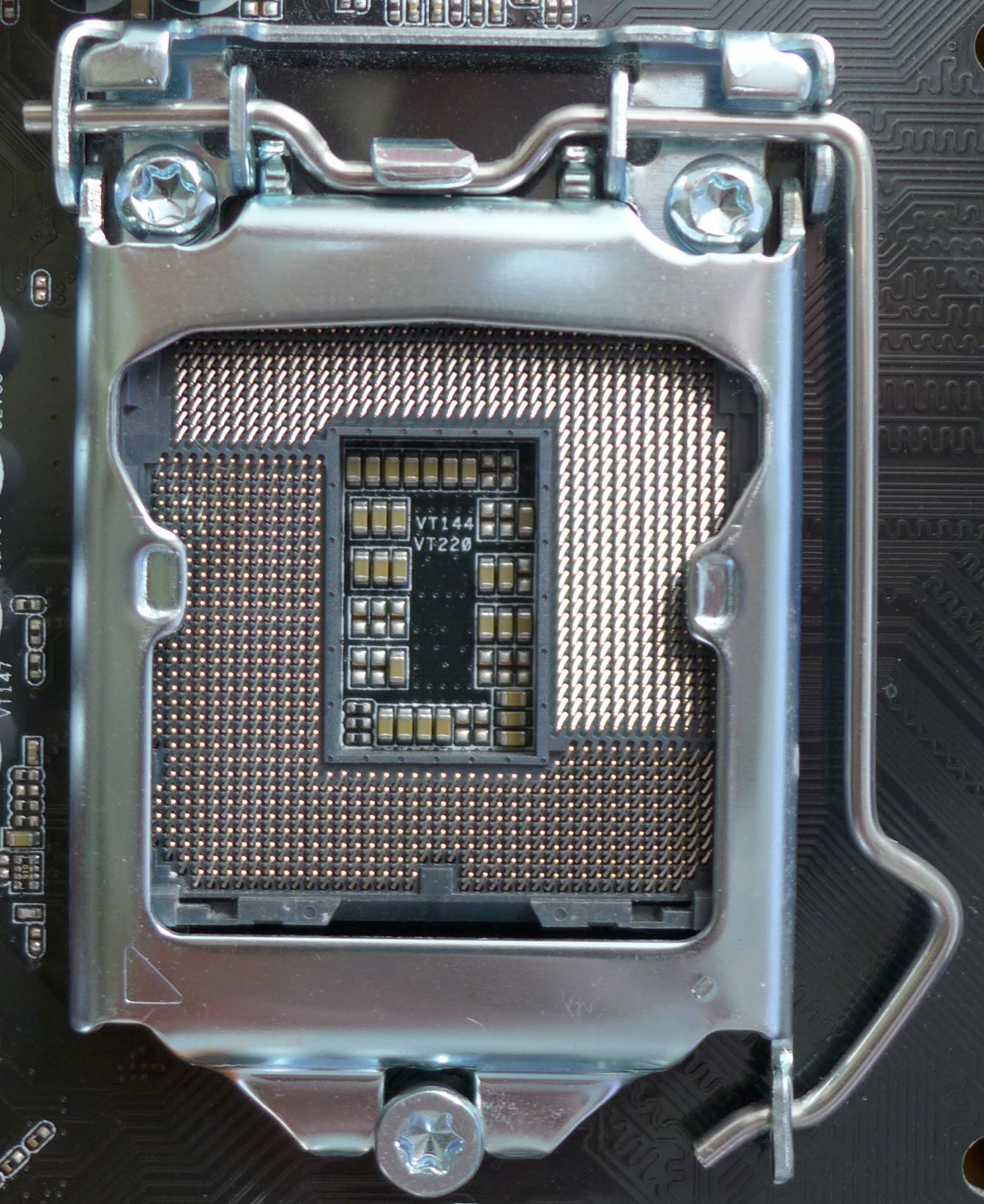
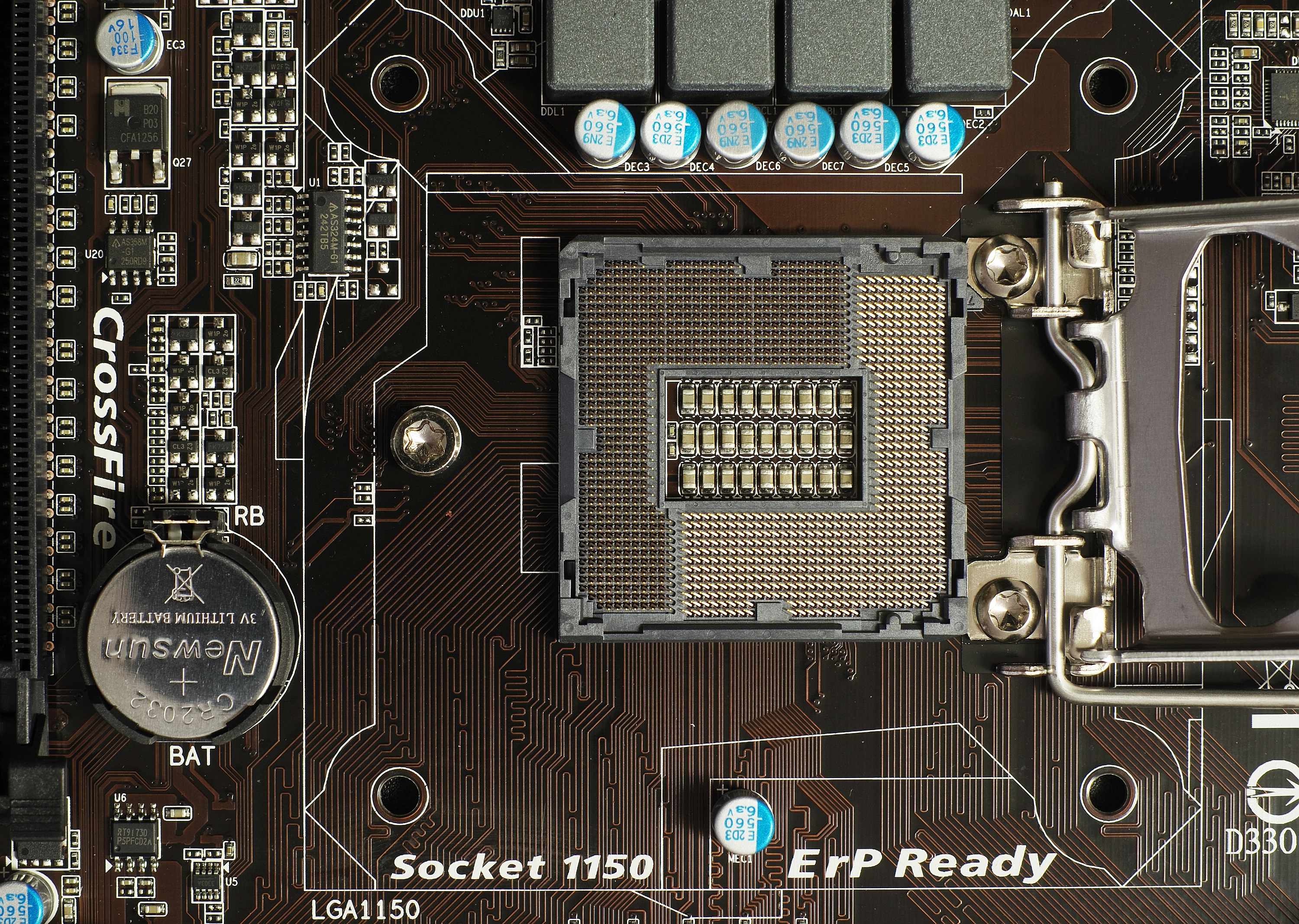
LGA 1150
LGA 1150, also known as Socket H3, is a zero insertion force flip-chip land grid array (LGA) CPU socket designed by Intel for CPUs built on the Haswell microarchitecture. This socket is also used by the Haswell's successor, Broadwell microarchitecture. It is the successor of LGA 1155 and was itself succeeded by LGA 1151 in 2015. Most motherboards with the LGA 1150 socket support varying video outputs (VGA, DVI or HDMI depending on the model) and Intel Clear Video Technology. Full support of Windows on LGA 1150 platform starts on Windows 7 - official Windows XP support is limited to selected CPUs, chipsets and only for embedded and industrial systems. Intel's Platform Controller Hub (PCH) for the LGA 1150 CPUs is codenamed Lynx Point. Intel Xeon processors for socket LGA 1150 use the Intel C222, C224, and C226 chipsets. Heatsink The 4 holes for fastening the heatsink to the motherboard are placed in a square with a lateral length of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LGA 1155
LGA 1155, also called Socket H2, is a zero insertion force flip-chip land grid array (LGA) CPU socket designed by Intel for their CPUs based on the Sandy Bridge (2nd Gen) and Ivy Bridge (3rd Gen) microarchitectures. It is the successor of LGA 1156 (known as ''Socket H'') and was itself succeeded by LGA 1150 in 2013. Along with selected variations of LGA 2011 socket, it was the last Intel socket to fully support Windows XP, Windows Server 2003, Windows Vista, and Windows Server 2008. LGA 1155 has 1155 protruding pins to make contact with the pads on the processor. The pins are arranged in a 40×40 array with a 24×16 central void and additional 61 omitted pins (two adjoining the central void, six in each of the four corners, and 35 in groups around the perimeter), yielding the 1600 − 384 − 61 = 1155 pin count. Processors for LGA 1155 and LGA 1156 sockets are not compatible with each other since they have different socket notches. LGA 1155 a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LGA 1156
LGA 1156 (land grid array 1156), also known as Socket H or H1, is an Intel desktop CPU socket. Its incompatible successor is LGA 1155. The last processors supporting it ceased production in 2011. LGA 1156, along with LGA 1366, were designed to replace LGA 775. Whereas LGA 775 processors connect to a northbridge using the Front Side Bus, LGA 1156 processors integrate the features traditionally located on a northbridge within the processor itself. The LGA 1156 socket allows the following connections to be made from the processor to the rest of the system: * PCI-Express 2.0 ×16 for communication with a graphics card. Some processors allow this connection to be divided into two ×8 lanes to connect two graphics cards. Some motherboard manufacturers use Nvidia's NF200 chip to allow even more graphics cards to be used. * DMI for communication with the Platform Controller Hub (PCH). This consists of a PCI-Express 2.0 ×4 connection. * FDI for communication with the PCH. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socket P
The Intel Socket P (mPGA478MN) is the mobile processor socket replacement for Core microarchitecture chips such as Core 2 Duo. It launched on May 9, 2007, as part of the Santa Rosa platform with the Merom and Penryn processors. Technical specifications The front-side bus (FSB) of CPUs that install in Socket P can run at 400, 533, 667, 800, or 1066 MT/s. By adapting the multiplier the frequency of the CPU can throttle up or down to save power, given that all Socket P CPUs support EIST, except for Celeron that do not support EIST. Socket P has 478 pins, but is not electrically pin-compatible with Socket M or Socket 478 Socket 478, also known as mPGA478 or mPGA478B, is a 478-contact CPU socket used for Intel's Pentium 4 and Celeron series CPUs. Socket 478 was launched in August 2001 in advance of the Northwood core to compete with AMD's 462-pin Socket A .... Socket P is also known as a 478-pin Micro FCPGA or μFCPGA-478. On the plastic grid is printed mPGA478M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
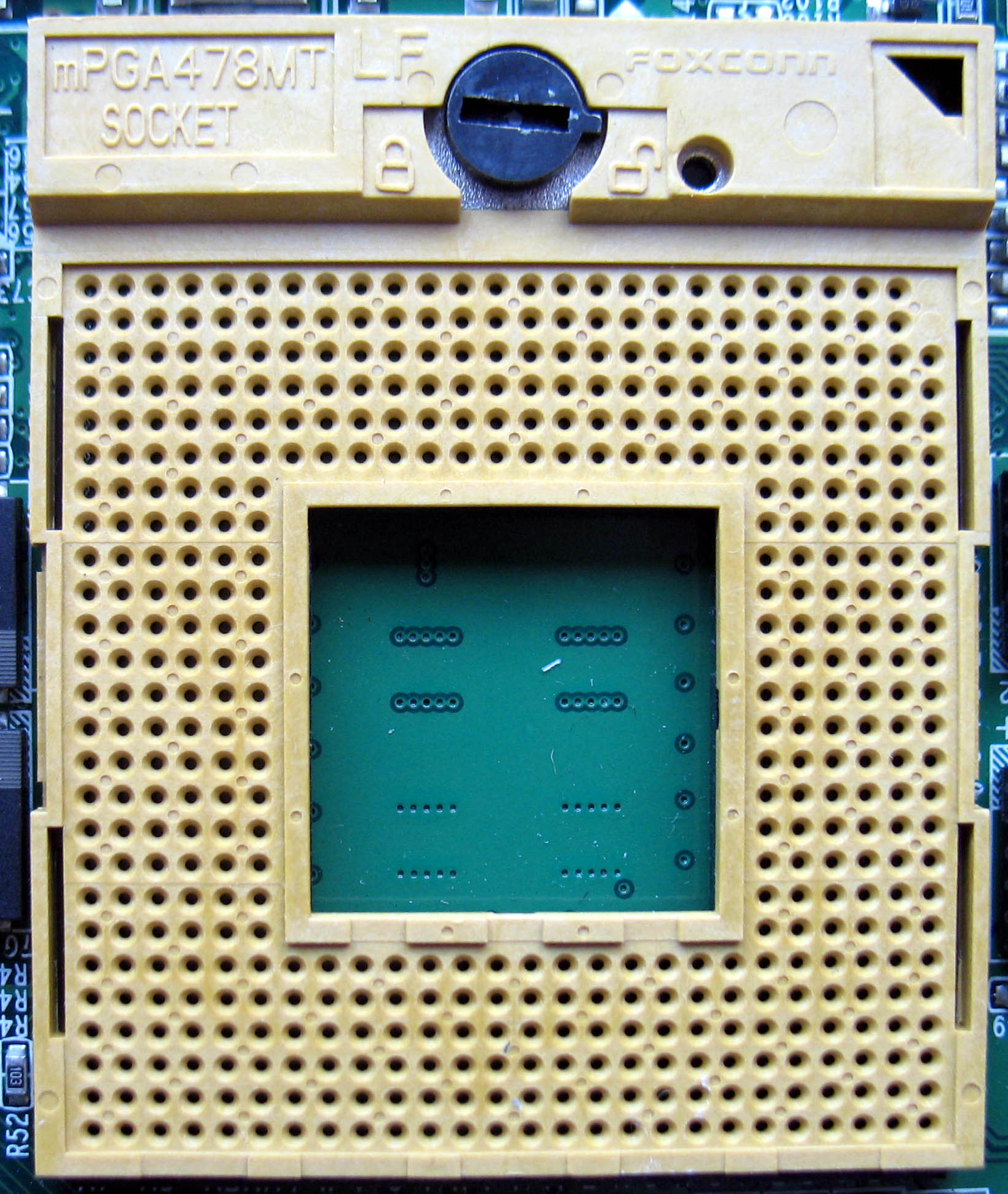
Socket M
Socket M (mPGA478MT) is a CPU interface introduced by Intel in 2006 for the Intel Core line of mobile processors. Technical specifications Socket M is used in all Intel Core products, as well as the Core-derived Dual-Core Xeon codenamed Sossaman. It was also used in the first generation of the mobile version of Intel's Core 2 Duo, specifically, the T5x00 and T7x00 Merom lines (referred to as Napa Refresh), though that line switched to Socket P (Santa Rosa) in 2007. It typically uses the Intel 945PM/945GM chipsets which support up to 667 MHz FSB and the Intel PM965/GM965 which allows 800 MHz FSB support, though the Socket M, PM965/GM965 combination is less common. The "Sossaman" Xeons use the E7520 chipset. Relation to other sockets Socket M is pin-compatible with desktop socket mPGA478A but it is not electrically compatible. Socket M is not pin-compatible with the older desktop Socket 478 (mPGA478B) or the newer mobile Socket P (mPGA478MN) by location of one pin; it i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LGA 775
LGA 775 (land grid array 775), also known as Socket T, is an Intel desktop CPU socket. Unlike PGA CPU sockets, such as its predecessor Socket 478, LGA 775 has no socket holes; instead, it has 775 protruding pins which touch contact points on the underside of the processor (CPU). The socket had an unusually long life span, lasting 7 years until the last processors supporting it ceased production in 2011. The socket was superseded by the LGA 1156 (Socket H) and LGA 1366 (Socket B) sockets. LGA 775 processors (some of the processors listed here might not work on newer Intel based chipsets) * Pentium 4 * Pentium 4 Extreme Edition * Pentium D * Celeron/ Celeron D * Pentium Dual-Core * Pentium Extreme Edition * Core 2 Duo/ Core 2 Quad Heatsink design For LGA 775, the distance between the screw-holes for the heatsink is 72 mm. Such heat-sinks are not interchangeable with heatsinks for sockets that have a distance of 75 mm, such as LGA 1156, LGA 1155, LGA 1150, L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(JPG).jpg)