|
Integrated DNA Technologies
Integrated DNA Technologies, Inc. (IDT), headquartered in Coralville, Iowa, is a supplier of custom nucleic acids, serving the areas of academic research, biotechnology, clinical diagnostics, and pharmaceutical development. IDT's primary business is the manufacturing of custom DNA and RNA oligonucleotides (oligos) for research applications. Joseph A. Walder, M.D., Ph.D. (Northwestern University), founded Integrated DNA Technologies, Inc. in 1987 through a partnership with Baxter Healthcare Corporation at the University of Iowa Technology Innovation Center business incubator. In its first 10 years, IDT grew from a startup with 10 synthesizing machines to a small company with more than 500, shipping an average 75,000 custom oligos per day to more than 82,000 customers worldwide. In March 2018, IDT was acquired by Danaher Corporation for a reported $1.9 billion. Mission IDT's mission is to enable discovery in biology and medicine. The company strives to achieve this by improving ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
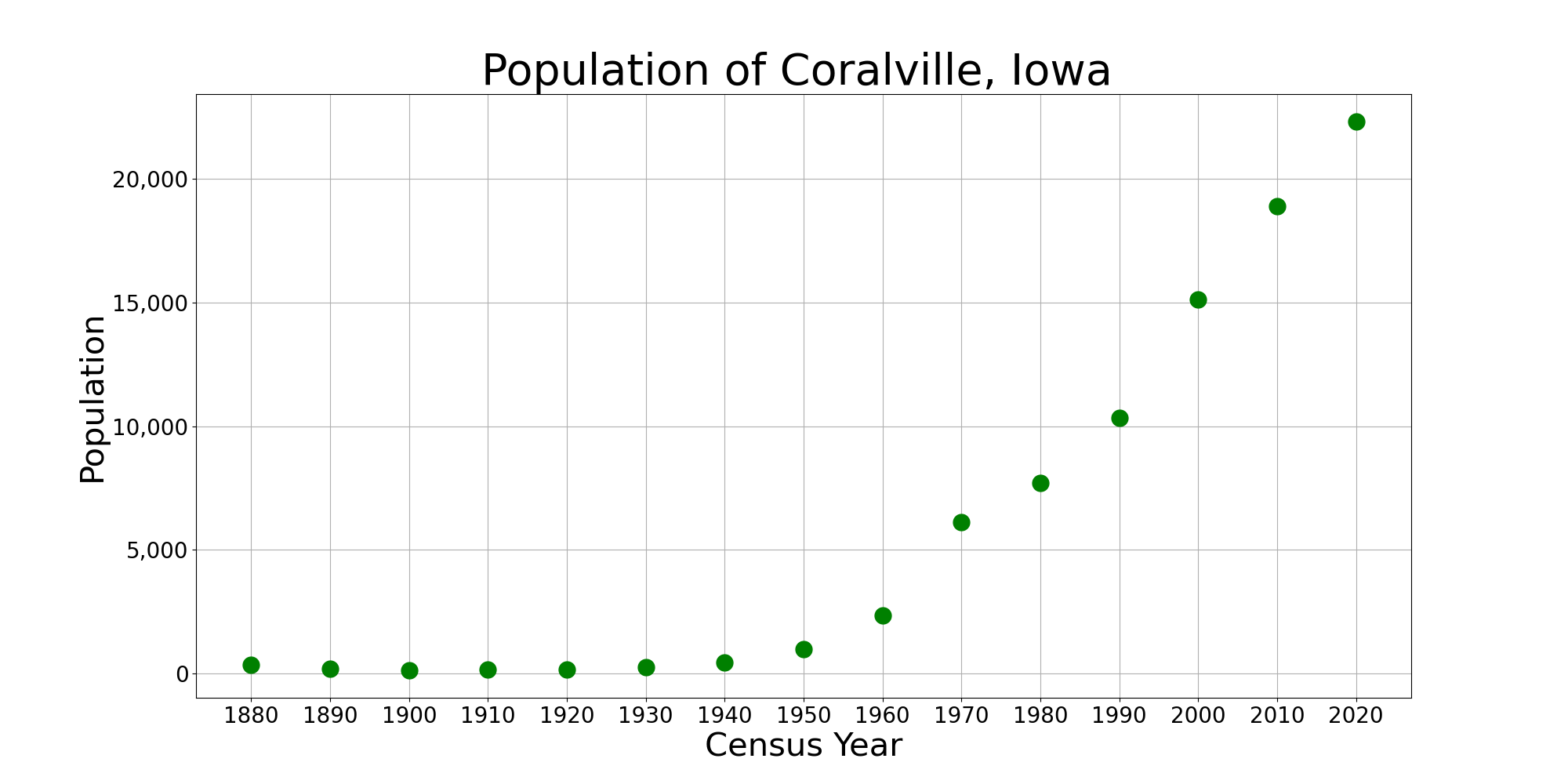
Coralville, IA
Coralville is a city in Johnson County, Iowa, United States. It is a suburb of Iowa City and part of the Iowa City Metropolitan Statistical Area. The population was 22,318 at the 2020 census. History Coralville is the location of the Edgewater Park Site, a 3,800-year-old archaeological site along the Iowa River. Edgewater is the oldest site in Iowa with evidence of domesticated plant use. Coralville incorporated as a city on June 1, 1857. The city's name is derived from the fossils that are found in the limestone along the Iowa River. In 1864, Louis Agassiz, a Harvard University zoologist, gave a lecture at the nearby University of Iowa titled “The Coral Reefs of Iowa City”. During the lecture, he presented local samples of fossilized Devonian period coral. The lecture was well received and helped raise public interest in the local fossils. In 1866, more corals were discovered at the site of a new mill, inspiring the citizens of the area to name the settlement "Coralville". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNAi
RNA interference (RNAi) is a biological process in which RNA molecules are involved in sequence-specific suppression of gene expression by double-stranded RNA, through translational or transcriptional repression. Historically, RNAi was known by other names, including ''co-suppression'', ''post-transcriptional gene silencing'' (PTGS), and ''quelling''. The detailed study of each of these seemingly different processes elucidated that the identity of these phenomena were all actually RNAi. Andrew Fire and Craig C. Mello shared the 2006 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their work on RNAi in the nematode worm ''Caenorhabditis elegans'', which they published in 1998. Since the discovery of RNAi and its regulatory potentials, it has become evident that RNAi has immense potential in suppression of desired genes. RNAi is now known as precise, efficient, stable and better than antisense therapy for gene suppression. Antisense RNA produced intracellularly by an expression vector ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biotechnology Companies Established In 1987
Biotechnology is the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms, cells, parts thereof and molecular analogues for products and services. The term ''biotechnology'' was first used by Károly Ereky in 1919, meaning the production of products from raw materials with the aid of living organisms. Definition The concept of biotechnology encompasses a wide range of procedures for modifying living organisms according to human purposes, going back to domestication of animals, cultivation of the plants, and "improvements" to these through breeding programs that employ artificial selection and hybridization. Modern usage also includes genetic engineering as well as cell and tissue culture technologies. The American Chemical Society defines biotechnology as the application of biological organisms, systems, or processes by various industries to learning about the science of life and the improvement of the value of materials a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Companies Established In 1987
American(s) may refer to: * American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America" ** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America ** American ancestry, people who self-identify their ancestry as "American" ** American English, the set of varieties of the English language native to the United States ** Native Americans in the United States, indigenous peoples of the United States * American, something of, from, or related to the Americas, also known as "America" ** Indigenous peoples of the Americas * American (word), for analysis and history of the meanings in various contexts Organizations * American Airlines, U.S.-based airline headquartered in Fort Worth, Texas * American Athletic Conference, an American college athletic conference * American Recordings (record label), a record label previously known as Def American * American University, in Washington, D.C. Sports teams Soccer * Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO 13485
ISO 13485 ''Medical devices -- Quality management systems -- Requirements for regulatory purposes'' is a voluntary standard, published by International Organization for Standardization (ISO) for the first time in 1996, and contains a comprehensive quality management system for the design and manufacture of medical devices. The latest version of this standard supersedes earlier documents such as EN 46001 (1993 and 1996) and EN 46002 (1996), the previously published ISO 13485 (1996 and 2003), and ISO 13488 (also 1996). The current ISO 13485 edition was published on 1 March 2016. Background Though it is tailored to the industry's quality system expectations and regulatory requirements, an organization does not need to be actively manufacturing medical devices or their components to seek certification to this standard, in contrast to the automotive sector's ISO/TS 16949, where only firms with an active request for quotation, or on the bid list, of an International Automotive Task ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO 9001
The ISO 9000 family is a set of five quality management systems (QMS) standards that help organizations ensure they meet customer and other stakeholder needs within statutory and regulatory requirements related to a product or service. ISO 9000 deals with the fundamentals of QMS, including the seven quality management principles that underlie the family of standards. ISO 9001 deals with the requirements that organizations wishing to meet the standard must fulfill. ISO 9002 is a model for quality assurance in production and installation. ISO 9003 for quality assurance in final inspection and test. ISO 9004 gives guidance on achieving sustained organizational success. Third-party certification bodies provide independent confirmation that organizations meet the requirements of ISO 9001. Over one million organizations worldwide are independently certified, making ISO 9001 one of the most widely used management tools in the world today. However, the ISO certification process has b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNase H-dependent PCR
RNase H-dependent PCR (rhPCR) is a modification of the standard PCR technique. In rhPCR, the primers are designed with a removable amplification block on the 3’ end. Amplification of the blocked primer is dependent on the cleavage activity of a hyperthermophilic archaeal Type II RNase H enzyme during hybridization to the complementary target sequence. This RNase H enzyme possesses several useful characteristics that enhance the PCR. First, it has very little enzymatic activity at low temperature, enabling a “ hot start PCR” without modifications to the DNA polymerase. Second, the cleavage efficiency of the enzyme is reduced in the presence of mismatches near the RNA residue. This allows for reduced primer dimer formation, detection of alternative splicing variants, ability to perform multiplex PCR with higher numbers of PCR primers, and the ability to detect single-nucleotide polymorphisms. Principle rhPCR primers consist of three sections. 1) The 5’ DNA se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligonucleotide Synthesis
Oligonucleotide synthesis is the chemical synthesis of relatively short fragments of nucleic acids with defined chemical structure (sequence). The technique is extremely useful in current laboratory practice because it provides a rapid and inexpensive access to custom-made oligonucleotides of the desired sequence. Whereas enzymes synthesize DNA and RNA only in a 5' to 3' direction, chemical oligonucleotide synthesis does not have this limitation, although it is most often carried out in the opposite, 3' to 5' direction. Currently, the process is implemented as solid-phase synthesis using phosphoramidite method and phosphoramidite building blocks derived from protected 2'-deoxynucleosides ( dA, dC, dG, and T), ribonucleosides ( A, C, G, and U), or chemically modified nucleosides, e.g. LNA or BNA. To obtain the desired oligonucleotide, the building blocks are sequentially coupled to the growing oligonucleotide chain in the order required by the sequence of the product (see ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioinformatics
Bioinformatics () is an interdisciplinary field that develops methods and software tools for understanding biological data, in particular when the data sets are large and complex. As an interdisciplinary field of science, bioinformatics combines biology, chemistry, physics, computer science, information engineering, mathematics and statistics to analyze and interpret the biological data. Bioinformatics has been used for '' in silico'' analyses of biological queries using computational and statistical techniques. Bioinformatics includes biological studies that use computer programming as part of their methodology, as well as specific analysis "pipelines" that are repeatedly used, particularly in the field of genomics. Common uses of bioinformatics include the identification of candidates genes and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). Often, such identification is made with the aim to better understand the genetic basis of disease, unique adaptations, desirable properties (e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Gene Synthesis
Artificial gene synthesis, or simply gene synthesis, refers to a group of methods that are used in synthetic biology to construct and assemble genes from nucleotides '' de novo''. Unlike DNA synthesis in living cells, artificial gene synthesis does not require template DNA, allowing virtually any DNA sequence to be synthesized in the laboratory. It comprises two main steps, the first of which is solid-phase DNA synthesis, sometimes known as DNA printing. This produces oligonucleotide fragments that are generally under 200 base pairs. The second step then involves connecting these oligonucleotide fragments using various DNA assembly methods. Because artificial gene synthesis does not require template DNA, it is theoretically possible to make a completely synthetic DNA molecule with no limits on the nucleotide sequence or size. Synthesis of the first complete gene, a yeast tRNA, was demonstrated by Har Gobind Khorana and coworkers in 1972. Synthesis of the first peptide- and protei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antisense
In molecular biology and genetics, the sense of a nucleic acid molecule, particularly of a strand of DNA or RNA, refers to the nature of the roles of the strand and its complement in specifying a sequence of amino acids. Depending on the context, sense may have slightly different meanings. For example, negative-sense strand of DNA is equivalent to the template strand, whereas the positive-sense strand is the non-template strand whose nucleotide sequence is equivalent to the sequence of the mRNA transcript. DNA sense Because of the complementary nature of base-pairing between nucleic acid polymers, a double-stranded DNA molecule will be composed of two strands with sequences that are reverse complements of each other. To help molecular biologists specifically identify each strand individually, the two strands are usually differentiated as the "sense" strand and the "antisense" strand. An individual strand of DNA is referred to as positive-sense (also positive (+) or simply sense) i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microarrays
A microarray is a multiplex lab-on-a-chip. Its purpose is to simultaneously detect the expression of thousands of genes from a sample (e.g. from a tissue). It is a two-dimensional array on a solid substrate—usually a glass slide or silicon thin-film cell—that assays (tests) large amounts of biological material using high-throughput screening miniaturized, multiplexed and parallel processing and detection methods. The concept and methodology of microarrays was first introduced and illustrated in antibody microarrays (also referred to as antibody matrix) by Tse Wen Chang in 1983 in a scientific publication and a series of patents. The "gene chip" industry started to grow significantly after the 1995 ''Science Magazine'' article by the Ron Davis and Pat Brown labs at Stanford University. With the establishment of companies, such as Affymetrix, Agilent, Applied Microarrays, Arrayjet, Illumina, and others, the technology of DNA microarrays has become the most sophisticated and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |