|
Institut D'Optique
The Institut d'optique Graduate School ("Institute of optics"), nicknamed SupOptique or IOGS, is one of the most prestigious French Grandes Ecoles and the leading French ''grande école'' in the field of Optics and its industrial and scientific applications, and a graduate school of the prestigious Paris-Saclay University and ParisTech. History Armand de Gramont, a rich industrialist and friend of Marcel Proust, was the man who had the idea to create the Institut d'Optique. In 1916, Gramont and Henri Chrétien (a French astronomer) were working together at the French Technical Aeronautics Section. Chrétien was working at the time on calculations for optical instruments. They both decided to create the project of building an institute dedicated to teaching Optics. That same year, Gramont became part of a committee that examined inventions that could interest the ministry of Defense. That is where he met Charles Fabry, who had previously become famous thanks to his experimental demo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grande école
A ''grande école'' () is a specialised university that is separate from, but parallel and often connected to, the main framework of the French public university system. The grandes écoles offer teaching, research and professional training in single academic fields such as engineering, architecture, business administration, academic research, or public policy and administration. The schools only admit students through an extremely competitive examination process; a significant proportion of their graduates occupy senior positions in French business, academia, civil service and civil society. Grandes écoles primarily admit students based on their national ranking in competitive written and oral exams called ''concours,'' which are organised annually by the French central government. While anyone can register for ''concours'', successful candidates have almost always completed two or three years of dedicated preparatory classes (''classes preparatoires'') prior to admission. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classe Préparatoire Aux Grandes écoles
The ''classes préparatoires aux grandes écoles'' (CPGE) (English: Higher School Preparatory Classes), commonly called ''classes prépas'' or ''prépas'', are part of the French post-secondary education system. They consist of two years of study (extendable to three or exceptionally four years) which act as an intensive preparatory course (or cram school) with the main goal of training students for enrolment in one of the ''grandes écoles''. The workload is one of the highest in Europe(29 to 45 contact hours a week, with up to 10 hours of guided tutorials and oral exam sessions). Unlike most students in France who enroll in public universities directly after receiving a high school diploma, students from CPGE have to take national competitive exams to be allowed to enroll in one of the ''grandes écoles''. These ''grandes écoles'' are higher education establishments (graduate schools) delivering master's degrees and rarely doctorates. They include science and engineering sch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rubidium
Rubidium is the chemical element with the symbol Rb and atomic number 37. It is a very soft, whitish-grey solid in the alkali metal group, similar to potassium and caesium. Rubidium is the first alkali metal in the group to have a density higher than water. On Earth, natural rubidium comprises two isotopes: 72% is a stable isotope 85Rb, and 28% is slightly radioactive 87Rb, with a half-life of 48.8 billion years—more than three times as long as the estimated age of the universe. German chemists Robert Bunsen and Gustav Kirchhoff discovered rubidium in 1861 by the newly developed technique, flame spectroscopy. The name comes from the Latin word , meaning deep red, the color of its emission spectrum. Rubidium's compounds have various chemical and electronic applications. Rubidium metal is easily vaporized and has a convenient spectral absorption range, making it a frequent target for laser manipulation of atoms. Rubidium is not a known nutrient for any living organisms. However, r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helium
Helium (from el, ἥλιος, helios, lit=sun) is a chemical element with the symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. Its boiling and melting point are the lowest among all the elements. It is the second lightest and second most abundant element in the observable universe (hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant). It is present at about 24% of the total elemental mass, which is more than 12 times the mass of all the heavier elements combined. Its abundance is similar to this in both the Sun and in Jupiter, due to the very high nuclear binding energy (per nucleon) of helium-4, with respect to the next three elements after helium. This helium-4 binding energy also accounts for why it is a product of both nuclear fusion and radioactive decay. The most common isotope of helium in the universe is helium-4, the vast majority of which was formed during t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bose–Einstein Condensate
In condensed matter physics, a Bose–Einstein condensate (BEC) is a state of matter that is typically formed when a gas of bosons at very low densities is cooled to temperatures very close to absolute zero (−273.15 °C or −459.67 °F). Under such conditions, a large fraction of bosons occupy the lowest quantum state, at which point microscopic quantum mechanical phenomena, particularly wavefunction interference, become apparent macroscopically. A BEC is formed by cooling a gas of extremely low density (about 100,000 times less dense than normal air) to ultra-low temperatures. This state was first predicted, generally, in 1924–1925 by Albert Einstein following and crediting a pioneering paper by Satyendra Nath Bose on the new field now known as quantum statistics. In 1995, the Bose-Einstein condensate was created by Eric Cornell and Carl Wieman of the University of Colorado at Boulder using rubidium atoms; later that year, Wolfgang Ketterle of MIT produc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CNRS
The French National Centre for Scientific Research (french: link=no, Centre national de la recherche scientifique, CNRS) is the French state research organisation and is the largest fundamental science agency in Europe. In 2016, it employed 31,637 staff, including 11,137 tenured researchers, 13,415 engineers and technical staff, and 7,085 contractual workers. It is headquartered in Paris and has administrative offices in Brussels, Beijing, Tokyo, Singapore, Washington, D.C., Bonn, Moscow, Tunis, Johannesburg, Santiago de Chile, Israel, and New Delhi. From 2009 to 2016, the CNRS was ranked No. 1 worldwide by the SCImago Institutions Rankings (SIR), an international ranking of research-focused institutions, including universities, national research centers, and companies such as Facebook or Google. The CNRS ranked No. 2 between 2017 and 2021, then No. 3 in 2022 in the same SIR, after the Chinese Academy of Sciences and before universities such as Harvard University, MIT, or Stanford ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
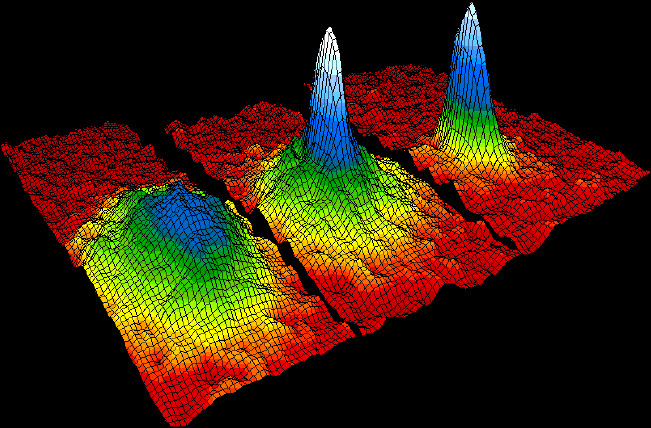
Strontium 88 MOT At IOGS
Strontium is the chemical element with the symbol Sr and atomic number 38. An alkaline earth metal, strontium is a soft silver-white yellowish metallic element that is highly chemically reactive. The metal forms a dark oxide layer when it is exposed to air. Strontium has physical and chemical properties similar to those of its two vertical neighbors in the periodic table, calcium and barium. It occurs naturally mainly in the minerals celestine and strontianite, and is mostly mined from these. Both strontium and strontianite are named after Strontian, a village in Scotland near which the mineral was discovered in 1790 by Adair Crawford and William Cruickshank; it was identified as a new element the next year from its crimson-red flame test color. Strontium was first isolated as a metal in 1808 by Humphry Davy using the then newly discovered process of electrolysis. During the 19th century, strontium was mostly used in the production of sugar from sugar beets (see strontian proc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
École Normale Supérieure Paris-Saclay
The École normale supérieure Paris-Saclay (also ENS Paris-Saclay or Normale Sup' Paris-Saclay), formerly ENS Cachan, is a grande école and a constituent member of Paris-Saclay University. It was established in 1892. It is located in Gif-sur-Yvette within the Essonne Departments of France, department near Paris, Île-de-France, France. ENS Paris-Saclay is one of the most prestigious and selective French ''grandes écoles''. Like all other ''grandes écoles'', this elite higher education institution is not included in the mainstream framework of the French public universities. Along with the École normale supérieure (Paris), École Normale Supérieure de Lyon, ENS Lyon and École normale supérieure de Rennes, ENS Rennes, the school belongs to the informal network of French ''école normale supérieure, écoles normales supérieures'', forming the top level of research and education in the French higher educational system. In 2014, ENS Paris-Saclay became a founding member of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
École Polytechnique , a Japanese video-games developer/publisher
{{disambiguation, geo ...
École may refer to: * an elementary school in the French educational stages normally followed by secondary education establishments (collège and lycée) * École (river), a tributary of the Seine flowing in région Île-de-France * École, Savoie, a French commune * École-Valentin, a French commune in the Doubs département * Grandes écoles, higher education establishments in France * The École, a French-American bilingual school in New York City Ecole may refer to: * Ecole Software This is a list of Notability, notable video game companies that have made games for either computers (like PC or Mac), video game consoles, handheld or mobile devices, and includes companies that currently exist as well as now-defunct companies. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HEC Paris
HEC Paris (french: École des hautes études commerciales de Paris) is a business school, and one of the most prestigious and selective grandes écoles, located in Jouy-en-Josas, France. HEC offers Master in Management, MSc International Finance, MBA and EMBA programs, specialised MSc's, PhD's and executive education. HEC Paris is the founding member of CEMS - Global Alliance in Management Education and holds the triple accreditation (AACSB, AMBA, EQUIS). History Founded in 1881 by the Paris Chamber of Commerce (CCIP) with 57 students in the very first class, the ''École des hautes études commerciales de Paris'' (HEC) aimed to be in the fields of management and commerce what ''Centrale Paris'' was in the field of engineering. In 1921, the school introduced the case-based method of the Harvard Business School, but most of the lectures remained theoretical. In 1938, the HEC program was lengthened to 3 years. Due to French corporations' demand for North American sty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bordeaux
Bordeaux ( , ; Gascon oc, Bordèu ; eu, Bordele; it, Bordò; es, Burdeos) is a port city on the river Garonne in the Gironde department, Southwestern France. It is the capital of the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region, as well as the prefecture of the Gironde department. Its inhabitants are called ''"Bordelais"'' (masculine) or ''"Bordelaises"'' (feminine). The term "Bordelais" may also refer to the city and its surrounding region. The city of Bordeaux proper had a population of 260,958 in 2019 within its small municipal territory of , With its 27 suburban municipalities it forms the Bordeaux Metropolis, in charge of metropolitan issues. With a population of 814,049 at the Jan. 2019 census. it is the fifth most populated in France, after Paris, Lyon, Marseille and Lille and ahead of Toulouse. Together with its suburbs and exurbs, except satellite cities of Arcachon and Libourne, the Bordeaux metropolitan area had a population of 1,363,711 that same year (Jan. 2019 census), ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)


