|
Inscriptions Of Upper Moesia
The Centre for Ancient Epigraphy and Numismatics (French: Centre d’Études Épigraphiques et Numismatiques "Fanula Papazoglou") is a research centre of the University of Belgrade for the study epigraphy, inscriptions and numismatics of the ancient Balkans. The centre was founded in 1970 under the Department of History by Fanula Papazoglu (1917–2001) a noted Greek-Serbian classical scholar and epigrapher.Epigraphica: - Volume 65 - Page 342 Università di Bologna. Dipartimento di storia antica - 2003 "Slobodan Dusanic trägt den Nachruf auf Fanoula Papazoglou (1917 - 2001) vor: At the beginning of 2001, the world of classical studies lost Fanoula Papazoglou, an eminent historian and deserving epigraphist. She was that both, in a variety .." The centre's main activities include research in the field of ancient history and epigraphy, focusing on epigraphic material from Serbian territory, i.e. the former Roman provinces Moesia Superior, Pannonia Inferior and Dalmatia Dalmatia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Belgrade
The University of Belgrade ( sr, / ) is a public university in Serbia. It is the oldest and largest modern university in Serbia. Founded in 1808 as the Belgrade Higher School in revolutionary Serbia, by 1838 it merged with the Kragujevac-based departments into a single university. The university has around 97,700 enrolled students and over 4,800 academic staff members. Since its founding, the university has educated more than 378,000 bachelors, around 25,100 magisters, 29,000 specialists and 14,670 doctors. The university comprises 31 faculties, 12 research institutes, the university library, and 9 university centres. The faculties are organized into four groups: social sciences and humanities; medical sciences; natural sciences and mathematics; and technological sciences. On the prestigious ''Shanghai Ranking'' (ARWU), the University of Belgrade ranks between 401st and 500th place, according to the most recent (2018) global ranking. In 2014, it ranked 151–200, specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epigraphy
Epigraphy () is the study of inscriptions, or epigraphs, as writing; it is the science of identifying graphemes, clarifying their meanings, classifying their uses according to dates and cultural contexts, and drawing conclusions about the writing and the writers. Specifically excluded from epigraphy are the historical significance of an epigraph as a document and the artistic value of a literature, literary composition. A person using the methods of epigraphy is called an ''epigrapher'' or ''epigraphist''. For example, the Behistun inscription is an official document of the Achaemenid Empire engraved on native rock at a location in Iran. Epigraphists are responsible for reconstructing, translating, and dating the trilingual inscription and finding any relevant circumstances. It is the work of historians, however, to determine and interpret the events recorded by the inscription as document. Often, epigraphy and history are competences practised by the same person. Epigraphy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inscription
Epigraphy () is the study of inscriptions, or epigraphs, as writing; it is the science of identifying graphemes, clarifying their meanings, classifying their uses according to dates and cultural contexts, and drawing conclusions about the writing and the writers. Specifically excluded from epigraphy are the historical significance of an epigraph as a document and the artistic value of a literary composition. A person using the methods of epigraphy is called an ''epigrapher'' or ''epigraphist''. For example, the Behistun inscription is an official document of the Achaemenid Empire engraved on native rock at a location in Iran. Epigraphists are responsible for reconstructing, translating, and dating the trilingual inscription and finding any relevant circumstances. It is the work of historians, however, to determine and interpret the events recorded by the inscription as document. Often, epigraphy and history are competences practised by the same person. Epigraphy is a primar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Numismatic
Numismatics is the study or collection of currency, including coins, tokens, paper money, medals and related objects. Specialists, known as numismatists, are often characterized as students or collectors of coins, but the discipline also includes the broader study of money and other means of payment used to resolve debts and exchange goods. The earliest forms of money used by people are categorised by collectors as "Odd and Curious", but the use of other goods in barter exchange is excluded, even where used as a circulating currency (e.g., cigarettes or instant noodles in prison). As an example, the Kyrgyz people used horses as the principal currency unit, and gave small change in lambskins; the lambskins may be suitable for numismatic study, but the horses are not. Many objects have been used for centuries, such as cowry shells, precious metals, cocoa beans, large stones, and gems. Etymology First attested in English 1829, the word ''numismatics'' comes from the adjective ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fanula Papazoglu
Fanula Papazoglu ( sr, Фанула Папазоглу; gr, Φανούλα Παπάζογλου, Fanoúla Papázoglou, 1917– January 26, 2001) was a Yugoslav and Serbian classical scholar, epigrapher and academic. She was an expert in Ancient history of the Balkans. She founded the Centre for Ancient Epigraphy and Numismatics in 1970. Life Papazoglu was born in Bitola, Kingdom of Serbia (modern North Macedonia), into a Greek family of Aromanian origin.Roudometof, Victor, "Nationalism and Identity Politics in the Balkans: Greece and the Macedonian Question". Journal of Modern Greek Studies. Baltimore: The Johns Hopkins University Press, (1996), p. 286, note # 29. She finished secondary school (1936) in Bitola, before attending the University of Belgrade Faculty of Philosophy, where she studies classical philology, ancient history, and archeology. During the Axis occupation of Serbia she supported the Yugoslav Partisans as a member of the student organization, and spent a year in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Scholar
Classics or classical studies is the study of classical antiquity. In the Western world, classics traditionally refers to the study of Classical Greek and Roman literature and their related original languages, Ancient Greek and Latin. Classics also includes Greco-Roman philosophy, history, archaeology, anthropology, art, mythology and society as secondary subjects. In Western civilization, the study of the Greek and Roman classics was traditionally considered to be the foundation of the humanities, and has, therefore, traditionally been the cornerstone of a typical elite European education. Etymology The word ''classics'' is derived from the Latin adjective '' classicus'', meaning "belonging to the highest class of citizens." The word was originally used to describe the members of the Patricians, the highest class in ancient Rome. By the 2nd century AD the word was used in literary criticism to describe writers of the highest quality. For example, Aulus Gellius, in his ''At ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epigrapher
Epigraphy () is the study of inscriptions, or epigraphs, as writing; it is the science of identifying graphemes, clarifying their meanings, classifying their uses according to dates and cultural contexts, and drawing conclusions about the writing and the writers. Specifically excluded from epigraphy are the historical significance of an epigraph as a document and the artistic value of a literary composition. A person using the methods of epigraphy is called an ''epigrapher'' or ''epigraphist''. For example, the Behistun inscription is an official document of the Achaemenid Empire engraved on native rock at a location in Iran. Epigraphists are responsible for reconstructing, translating, and dating the trilingual inscription and finding any relevant circumstances. It is the work of historians, however, to determine and interpret the events recorded by the inscription as document. Often, epigraphy and history are competences practised by the same person. Epigraphy is a primar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moesia Superior
Moesia (; Latin: ''Moesia''; el, Μοισία, Moisía) was an ancient region and later Roman province situated in the Balkans south of the Danube River, which included most of the territory of modern eastern Serbia, Kosovo, north-eastern Albania, northern parts of North Macedonia (Moesia Superior), Northern Bulgaria, Romanian Dobruja and small parts of Southern Ukraine (Moesia Inferior). Geography In ancient geographical sources, Moesia was bounded to the south by the Haemus (Balkan Mountains) and Scardus (Šar) mountains, to the west by the Drinus (Drina) river, on the north by the Donaris (Danube) and on the east by the Euxine (Black Sea). History The region was inhabited chiefly by Thracians, Dacians (Thraco-Dacian), Illyrian and Thraco-Illyrian peoples. The name of the region comes from Moesi, Thraco-Dacian peoples who lived there before the Roman conquest. Parts of Moesia belonged to the polity of Burebista, a Getae king who established his rule over a large part of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
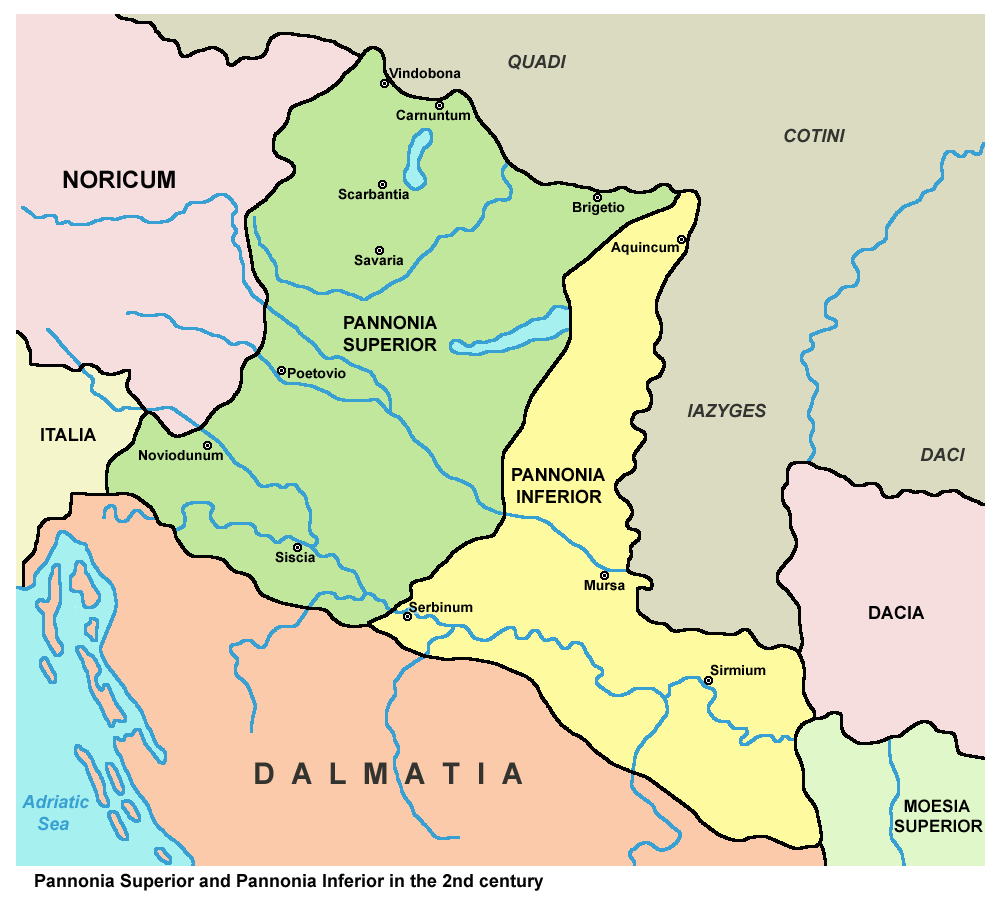
Pannonia Inferior
Pannonia Inferior, lit. Lower Pannonia, was a province of the Roman Empire. Its capital was Sirmium. It was one of the border provinces on the Danube. It was formed in the year 103 AD by Emperor Trajan who divided the former province of Pannonia into two parts: Pannonia Superior and Pannonia Inferior. The province included parts of present-day states of Hungary, Serbia, Croatia, and Bosnia and Herzegovina. The province was bordered to the east (across the Danube) by a Sarmatian tribe—the Iazyges. Later, the Vandals appeared to the north-east. Settlements Major settlements in Pannonia Inferior included: * ''Sirmium'' (Sremska Mitrovica) which several times served as an imperial residence for several emperors. * ''Aquincum'' ( Buda), the provincial capital. * ''Cuccium'' (Ilok) * ''Cibalae'' (Vinkovci) * ''Mursa'' ( Osijek) * ''Certissa'' (Đakovo) * ''Marsonia'' (Slavonski Brod) * ''Sopianae'' (Pécs) Aftermath and legacy The province was yet again split during the reign of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; hr, Dalmacija ; it, Dalmazia; see #Name, names in other languages) is one of the four historical region, historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria. Dalmatia is a narrow belt of the east shore of the Adriatic Sea, stretching from the island of Rab in the north to the Bay of Kotor in the south. The Dalmatian Hinterland ranges in width from fifty kilometres in the north, to just a few kilometres in the south; it is mostly covered by the rugged Dinaric Alps. List of islands of Croatia, Seventy-nine islands (and about 500 islets) run parallel to the coast, the largest (in Dalmatia) being Brač, Pag (island), Pag, and Hvar. The largest city is Split, Croatia, Split, followed by Zadar and Šibenik. The name of the region stems from an Illyrians, Illyrian tribe called the Dalmatae, who lived in the area in classical antiquity. Later it became a Dalmatia (Roman province), Roman province, and as result a Romance languages, Romance culture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inscriptions Of Upper Moesia
The Centre for Ancient Epigraphy and Numismatics (French: Centre d’Études Épigraphiques et Numismatiques "Fanula Papazoglou") is a research centre of the University of Belgrade for the study epigraphy, inscriptions and numismatics of the ancient Balkans. The centre was founded in 1970 under the Department of History by Fanula Papazoglu (1917–2001) a noted Greek-Serbian classical scholar and epigrapher.Epigraphica: - Volume 65 - Page 342 Università di Bologna. Dipartimento di storia antica - 2003 "Slobodan Dusanic trägt den Nachruf auf Fanoula Papazoglou (1917 - 2001) vor: At the beginning of 2001, the world of classical studies lost Fanoula Papazoglou, an eminent historian and deserving epigraphist. She was that both, in a variety .." The centre's main activities include research in the field of ancient history and epigraphy, focusing on epigraphic material from Serbian territory, i.e. the former Roman provinces Moesia Superior, Pannonia Inferior and Dalmatia Dalmatia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Epigraphy
The Greek-language inscriptions and epigraphy are a major source for understanding of the society, language and history of ancient Greece and other Greek-speaking or Greek-controlled areas. Greek inscriptions may occur on stone slabs, pottery ostraca, ornaments, and range from simple names to full texts. Inscriptiones Graecae The ''Inscriptiones Graecae'' (IG), Latin for ''Greek inscriptions'', project is an academic project originally begun by the Prussian Academy of Science, and today continued by its successor organisation, the ''Berlin-Brandenburgische Akademie der Wissenschaften''. Its aim is to collect and publish all known ancient inscriptions from the ancient world. As such it will eventually make all other previous collections redundant. It is divided by regions. I/II/III - Attica IV - Aegina, Pityonesus, Cecryphalia, the Argolid V - Laconia, Messenia and Arcadia VII - Megarid, Oropus, and Boeotia IX - Aetolia, Acarnania, West Locris and Thessaly X - Epirus, Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |