|
Inocentes Channel
Inocentes Channel (Spanish ''Canal Inocentes'') is a strait in Chile that reaches from the Guía Narrows (''Angostura Guías'') 18 miles to the northern extreme of Inocentes Island, where it joins the Concepción Channel. The south side of the strait is formed by a succession of high cones sloping to the northwest and ending in the Clements Group. On the north side are three precipitous headlands A headland, also known as a head, is a coastal landform, a point of land usually high and often with a sheer drop, that extends into a body of water. It is a type of promontory. A headland of considerable size often is called a cape.Whittow, Joh ... with deep inlets between them. The land then trends to the northward, and the foreground consists of islands rising to about 400 feet in height. See also * Fjords and channels of Chile References External links * United States Hydrographic OfficeSouth America Pilot (1916) page 411 Straits of Chile Bodies of water of Magallanes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanover Island
Hanover Island (Spanish: ''Isla Hanover'') is an island in the Magallanes Region. It is separated from the Chatham Island by the Esteban Channel, Guías Narrows and Inocentes Channel. Literature In popular fiction, a fictionalized version of the island is featured in Jules Verne's book ' Two Years' Vacation'. The book tells the story of 15 boys (aged between 8 and 14) from Auckland, New Zealand, who spent 2 years on this remote island as a result of a storm, which cast their schooner A schooner () is a type of sailing vessel defined by its rig: fore-and-aft rigged on all of two or more masts and, in the case of a two-masted schooner, the foremast generally being shorter than the mainmast. A common variant, the topsail schoon ... upon the island's shore. There it is called "Chairman Island" after the name of the boys' boarding school. The Torres del Paine National Park is located on the continental side. See also * List of islands of Chile External links Islands o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wellington Island
Wellington Island is an island west of Southern Patagonian Ice Field, Chile. It has an area of 5,556 km2 and most of the island forms part of Bernardo O'Higgins National Park. It is home to the last Kawésqar people, living in the village of Puerto Edén, the only inhabited place on the island. See also * Serrano Island Serrano Island, also known as Little Wellington Island, is an island in the Aisén Region, Chile. It should not be confused with Lavoisier Island in the Antarctica, which is also called Isla Serrano in Spanish. External links * United Nations ..., also named ''Little Wellington Island References Islands of Magallanes Region {{MagellanAntarctic-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
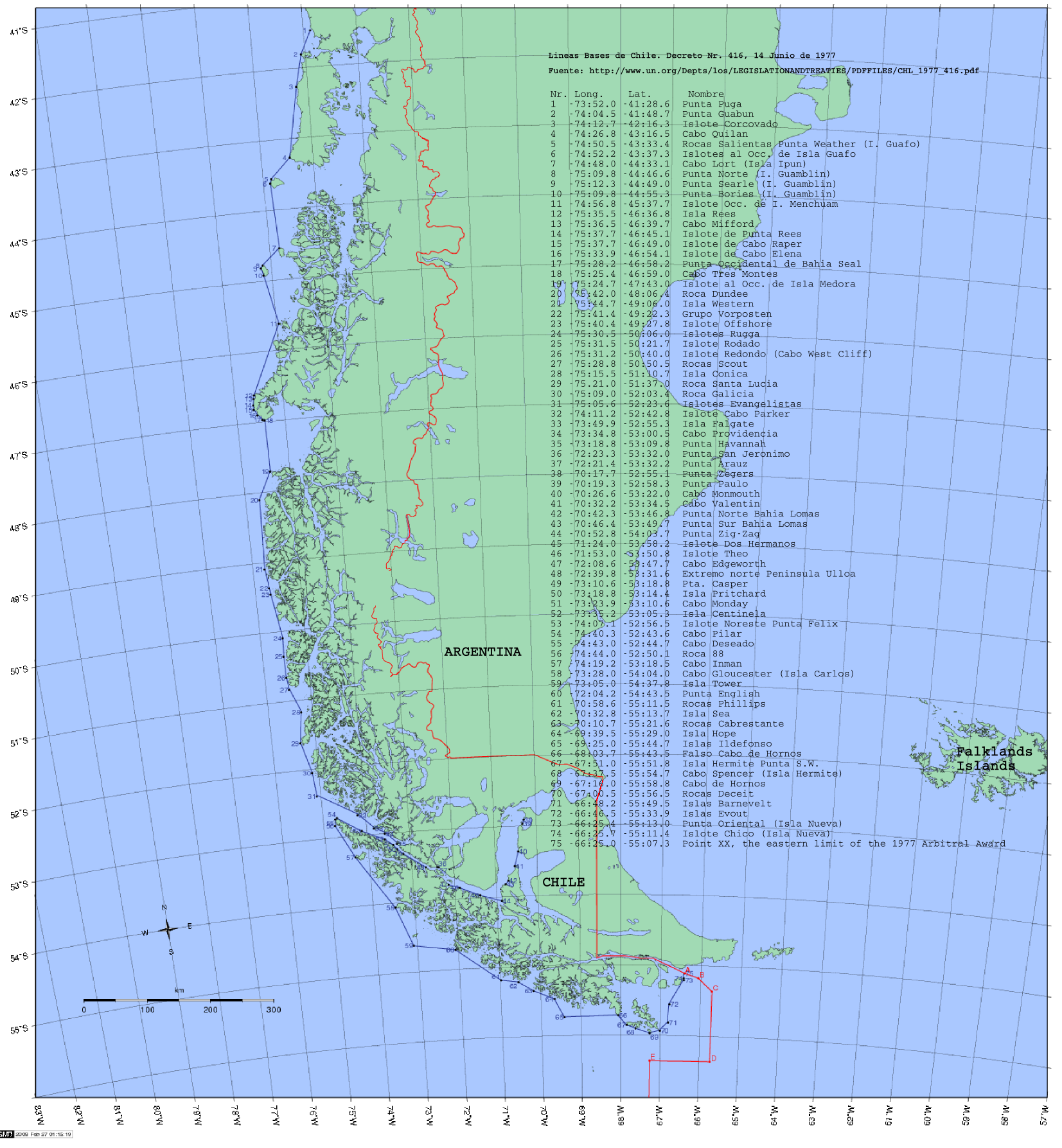
Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Chile covers an area of , with a population of 17.5 million as of 2017. It shares land borders with Peru to the north, Bolivia to the north-east, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage in the far south. Chile also controls the Pacific islands of Juan Fernández, Isla Salas y Gómez, Desventuradas, and Easter Island in Oceania. It also claims about of Antarctica under the Chilean Antarctic Territory. The country's capital and largest city is Santiago, and its national language is Spanish. Spain conquered and colonized the region in the mid-16th century, replacing Inca rule, but failing to conquer the independent Mapuche who inhabited what is now south-central Chile. In 1818, after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guía Narrows
The Guía Narrows (Spanish ''Angostura Guías'') are located between Chile's Hanover and Chatham Islands. Guia Narrows connects Sarmiento and Inocentes Channels. The narrows are 6 miles long and are 1 to 1.5 miles wide, except at the north end, between Porpoise Point, low and sharp, on the west side, and Guard Island on the east, where the breadth is about 400 yards, but generally, there is no danger; the shores being steep-to on either side. Sometimes, the tide sweeps strongly around the point; therefore, it would be advisable to keep closer to Guard Island while passing through. References * United States Hydrographic Office The United States Hydrographic Office prepared and published maps, charts, and nautical books required in navigation. The office was established by an act of 21 June 1866 as part of the Bureau of Navigation, Department of the Navy. It was transfe ...South America Pilot(1916) p. 410 Straits of Chile Bodies of water of Magallanes Region {{ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concepción Channel
Concepción Channel is an inside passage of the Chilean Patagonia. It extends from the point where Wide Channel and Trinidad Channel meet to the open sea. It is located at Earth Info, ''earth-info.nga.mil'' webpage: . and separates Madre de Dios Island and Duke of York Island, on the west side, from the Wilcock Peninsula and smaller islands, on the east side. Inocentes Channel is adjacent to the Concepción Channel. See also * Fjords and channels of Chile The southern coast of Chile presents a large number of fjords and fjord-like channels from the latitudes of Cape Horn (55° S) to Reloncaví Estuary (42° S). Some fjords and channels are important navigable channels providing access to ports like P ... References External links * United States Hydrographic OfficeSouth America Pilot (1916) Straits of Chile Bodies of water of Magallanes Region {{MagellanAntarctic-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Headland
A headland, also known as a head, is a coastal landform, a point of land usually high and often with a sheer drop, that extends into a body of water. It is a type of promontory. A headland of considerable size often is called a cape.Whittow, John (1984). ''Dictionary of Physical Geography''. London: Penguin, 1984, pp. 80, 246. . Headlands are characterised by high, breaking waves, rocky shores, intense erosion, and steep sea cliff. Headlands and bays are often found on the same coastline. A bay is flanked by land on three sides, whereas a headland is flanked by water on three sides. Headlands and bays form on discordant coastlines, where bands of rock of alternating resistance run perpendicular to the coast. Bays form when weak (less resistant) rocks (such as sands and clays) are eroded, leaving bands of stronger (more resistant) rocks (such as chalk, limestone, and granite) forming a headland, or peninsula. Through the deposition of sediment within the bay and the erosion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fjords And Channels Of Chile
The southern coast of Chile presents a large number of fjords and fjord-like channels from the latitudes of Cape Horn (55° S) to Reloncaví Estuary (42° S). Some fjords and channels are important navigable channels providing access to ports like Punta Arenas, Puerto Chacabuco and Puerto Natales. History Indigenous peoples The earliest known inhabitants of the fjords and channels were, from north to south, the Chono, Alacalufe and Yaghan, all of whom shared a life style as canoe-faring hunter-gatherers. They also shared physical traits such as being of low stature, long-headed (''Dolichocephalic''), and having a "low face".Trivero Rivera 2005, p. 42. Despite similarities their languages were completely different.Trivero Rivera 2005, p. 33. The Chono moved around in the area from Chiloé Archipelago to 50° S and the Alacalufe from 46° S to the Strait of Magellan. Thus both groups overlapped in Gulf of Penas, Guayaneco Archipelago and other islands. Yaghans inhabited a reduced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Straits Of Chile
A strait is an oceanic landform connecting two seas or two other large areas of water. The surface water generally flows at the same elevation on both sides and through the strait in either direction. Most commonly, it is a narrow ocean channel that lies between two land masses. Some straits are not navigable, for example because they are either too narrow or too shallow, or because of an unnavigable reef or archipelago. Straits are also known to be loci for sediment accumulation. Usually, sand-size deposits occur on both the two opposite strait exits, forming subaqueous fans or deltas. Terminology The terms '' channel'', ''pass'', or ''passage'' can be synonymous and used interchangeably with ''strait'', although each is sometimes differentiated with varying senses. In Scotland, ''firth'' or ''Kyle'' are also sometimes used as synonyms for strait. Many straits are economically important. Straits can be important shipping routes and wars have been fought for control of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |