|
Infrared Interferometer Spectrometer And Radiometer
An Infrared interferometer spectrometer and radiometer (IRIS) is a device built into the Voyager space probe which enables the measurement of three distinct properties. The instrument itself consists of two separate instruments that together share a single large-aperture telescope system. The Infrared interferometer spectrometer holds two functions as it can act as a thermometer and/or spectrometer. The thermometer allows for the observance and measurement of heat energy emitting from an object, and the spectrometer enables the identification of various elements, molecules, and compounds which may be present in an atmosphere and/or on the surface of a body. The separate radiometer allows for the measurement of reflected infrared, visible, and ultraviolet light off of a body. History Early versions of the IRIS were flown on the 1960s Nimbus 3 and Nimbus 4. In 1971, an early prototype was used on Mariner 9 to examine Mars. Objectives The device was included, primarily, to meet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
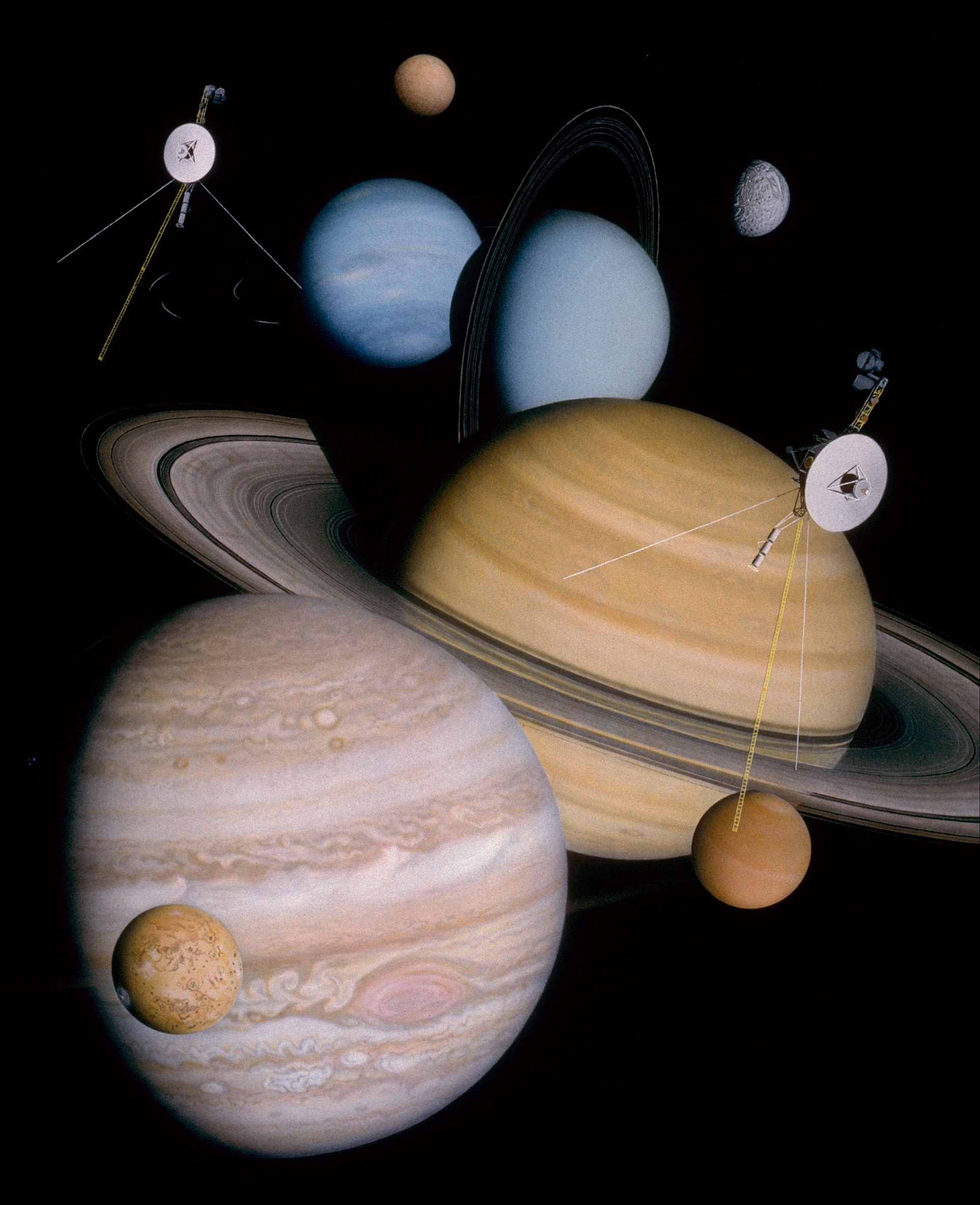
Voyager Program
The Voyager program is an American scientific program that employs two robotic interstellar probes, ''Voyager 1'' and ''Voyager 2''. They were launched in 1977 to take advantage of a favorable alignment of Jupiter and Saturn, to Flyby (spaceflight), fly near them while collecting data for transmission back to Earth. After launch the decision was taken to send ''Voyager 2'' near Uranus and Neptune to collect data for transmission back to Earth. As of 2022, the Voyagers are still in operation past the outer boundary of the heliosphere in interstellar space. They collect and transmit useful data to Earth. , ''Voyager 1'' was moving with a velocity of , or 17 km/s, relative to the Sun, and was from the Sun reaching a distance of from Earth as of February 10, 2022. On 25 August 2012, data from ''Voyager 1'' indicated that it had entered interstellar space. , ''Voyager 2'' was moving with a velocity of , or 15 km/s, relative to the Sun, and was from the Sun reaching a distan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Probe
A space probe is an artificial satellite that travels through space to collect scientific data. A space probe may orbit Earth; approach the Moon; travel through interplanetary space; flyby, orbit, or land or fly on other planetary bodies; or enter interstellar space. Many countries and private companies have launched probes to planets, asteroids, moons around the Solar System, including the Soviet Union, the United States, India, and many more. History On 4 October 1957, the first artificial satellite to orbit Earth was Sputnik 1, launched by the USSR. Four months later, on 1 February 1958, Explorer 1 was launched by the United States, being the first space probe. Explorer 1, collecting data on temperature, cosmic rays, and micrometeorite impacts. The first attempted lunar probe was the Luna E-1 No.1, launched on 23 September 1958. The goal of a lunar probe repeatedly failed until 4 January 1959 when Luna 1 orbited around the moon and then the sun. The success of these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermometer
A thermometer is a device that temperature measurement, measures temperature or a temperature gradient (the degree of hotness or coldness of an object). A thermometer has two important elements: (1) a temperature sensor (e.g. the bulb of a mercury-in-glass thermometer or the pyrometric sensor in an infrared thermometer) in which some change occurs with a change in temperature; and (2) some means of converting this change into a numerical value (e.g. the visible scale that is marked on a mercury-in-glass thermometer or the digital readout on an infrared model). Thermometers are widely used in technology and industry to monitor processes, in meteorology, in medicine, and in scientific research. History While an individual thermometer is able to measure degrees of hotness, the readings on two thermometers cannot be compared unless they conform to an agreed scale. Today there is an absolute thermodynamic temperature scale. Internationally agreed temperature scales are designed to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectrometer
A spectrometer () is a scientific instrument used to separate and measure spectral components of a physical phenomenon. Spectrometer is a broad term often used to describe instruments that measure a continuous variable of a phenomenon where the spectral components are somehow mixed. In visible light a spectrometer can separate white light and measure individual narrow bands of color, called a spectrum. A mass spectrometer measures the spectrum of the masses of the atoms or molecules present in a gas. The first spectrometers were used to split light into an array of separate colors. Spectrometers were developed in early studies of physics, astronomy, and chemistry. The capability of spectroscopy to determine chemical composition drove its advancement and continues to be one of its primary uses. Spectrometers are used in astronomy to analyze the chemical composition of stars and planets, and spectrometers gather data on the origin of the universe. Examples of spectrometers are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiometer
A radiometer or roentgenometer is a device for measuring the radiant flux (power) of electromagnetic radiation. Generally, a radiometer is an infrared radiation detector or an ultraviolet detector. Microwave radiometers operate in the microwave wavelengths. While the term ''radiometer'' can refer to any device that measures electromagnetic radiation (e.g. light), the term is often used to refer specifically to a Crookes radiometer ("light-mill"), a device invented in 1873 in which a rotor (having vanes which are dark on one side, and light on the other) in a partial vacuum spins when exposed to light. A common belief (one originally held even by Crookes) is that the momentum of the absorbed light on the black faces makes the radiometer operate. If this were true, however, the radiometer would spin away from the non-black faces, since the photons bouncing off those faces impart more momentum than the photons absorbed on the black faces. Photons do exert radiation pressure on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Wiley And Sons
John Wiley & Sons, Inc., commonly known as Wiley (), is an American multinational publishing company founded in 1807 that focuses on academic publishing and instructional materials. The company produces books, journals, and encyclopedias, in print and electronically, as well as online products and services, training materials, and educational materials for undergraduate, graduate, and continuing education students. History The company was established in 1807 when Charles Wiley opened a print shop in Manhattan. The company was the publisher of 19th century American literary figures like James Fenimore Cooper, Washington Irving, Herman Melville, and Edgar Allan Poe, as well as of legal, religious, and other non-fiction titles. The firm took its current name in 1865. Wiley later shifted its focus to scientific, technical, and engineering subject areas, abandoning its literary interests. Wiley's son John (born in Flatbush, New York, October 4, 1808; died in East Orange, New Jer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mariner 9
Mariner 9 (Mariner Mars '71 / Mariner-I) was a robotic spacecraft that contributed greatly to the exploration of Mars and was part of the NASA Mariner program. Mariner 9 was launched toward Mars on May 30, 1971 from LC-36B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida, and reached the planet on November 14 of the same year, becoming the first spacecraft to orbit another planet – only narrowly beating the Soviet probes ''Mars 2'' (launched May 19) and ''Mars 3'' (launched May 28), which both arrived at Mars only weeks later. After the occurrence of dust storms on the planet for several months following its arrival, the orbiter managed to send back clear pictures of the surface. Mariner 9 successfully returned 7,329 images over the course of its mission, which concluded in October 1972. Objectives Mariner 9 was designed to continue the atmospheric studies begun by Mariner 6 and 7, and to map over 70% of the Martian surface from the lowest altitude () and at the highest reso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Dynamics
Meteorology is a branch of the atmospheric sciences (which include atmospheric chemistry and physics) with a major focus on weather forecasting. The study of meteorology dates back millennia, though significant progress in meteorology did not begin until the 18th century. The 19th century saw modest progress in the field after weather observation networks were formed across broad regions. Prior attempts at prediction of weather depended on historical data. It was not until after the elucidation of the laws of physics, and more particularly in the latter half of the 20th century the development of the computer (allowing for the automated solution of a great many modelling equations) that significant breakthroughs in weather forecasting were achieved. An important branch of weather forecasting is marine weather forecasting as it relates to maritime and coastal safety, in which weather effects also include atmospheric interactions with large bodies of water. Meteorological phenom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, and highly combustible. Hydrogen is the most abundant chemical substance in the universe, constituting roughly 75% of all normal matter.However, most of the universe's mass is not in the form of baryons or chemical elements. See dark matter and dark energy. Stars such as the Sun are mainly composed of hydrogen in the plasma state. Most of the hydrogen on Earth exists in molecular forms such as water and organic compounds. For the most common isotope of hydrogen (symbol 1H) each atom has one proton, one electron, and no neutrons. In the early universe, the formation of protons, the nuclei of hydrogen, occurred during the first second after the Big Bang. The emergence of neutral hydrogen atoms throughout the universe occurred about 370,000 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helium
Helium (from el, ἥλιος, helios, lit=sun) is a chemical element with the symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. Its boiling and melting point are the lowest among all the elements. It is the second lightest and second most abundant element in the observable universe (hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant). It is present at about 24% of the total elemental mass, which is more than 12 times the mass of all the heavier elements combined. Its abundance is similar to this in both the Sun and in Jupiter, due to the very high nuclear binding energy (per nucleon) of helium-4, with respect to the next three elements after helium. This helium-4 binding energy also accounts for why it is a product of both nuclear fusion and radioactive decay. The most common isotope of helium in the universe is helium-4, the vast majority of which was formed during t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titan (moon)
Titan is the largest moon of Saturn and the second-largest natural satellite in the Solar System. It is the only moon known to have a dense atmosphere, and is the only known object in space other than Earth on which clear evidence of stable bodies of surface liquid has been found. Titan is one of the seven gravitationally rounded moons in orbit around Saturn, and the second most distant from Saturn of those seven. Frequently described as a planet-like moon, Titan is 50% larger (in diameter) than Earth's Moon and 80% more massive. It is the second-largest moon in the Solar System after Jupiter's moon Ganymede, and is larger than the planet Mercury, but only 40% as massive. Discovered in 1655 by the Dutch astronomer Christiaan Huygens, Titan was the first known moon of Saturn, and the sixth known planetary satellite (after Earth's moon and the four Galilean moons of Jupiter). Titan orbits Saturn at 20 Saturn radii. From Titan's surface, Saturn subtends an arc of 5.09 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |