|
Information Display Systems
"Information display systems" (IDS) is the general designation for the control panels and displays of Russian (and previous Soviet) spacecraft. For example, the original Soyuz 7K-OK spacecraft used the "Sirius-7k" IDS. {, class="wikitable sortable" , - ! IDS !! Components or features !! Spacecraft , - , SIS-1-3KA ( ''Globus'' IMP) , , File:Vostokpanel.JPG , , Vostok 1 (3KA) , - , SIS-2-3KA , , , , Vostok 2 (3KA) , - , SIS-3-3KV , , , , Voskhod 1 (3KV) , - , SIS-4-3KD , , , , Voskhod 2 (3KD) , - , STVOR , , EVA controls , , Voskhod 2 (3KD) , - , Sirius-7K , , , , Soyuz 7K-OK, Soyuz 7K-OKS, Soyuz 7K-T , - , Saturn , , , , Soyuz 7K-L1 , - , Uran and Orion , , , , Soyuz 7K-LOK , - , Luch , , , , LK (spacecraft) , - , Sirius-A8 , , , , Soyuz 7K-TM , - , Sirius-M , , File:Thomas Stafford Trains in Soviet Simulator for ASTP - GPN-2002-000156.jpg , , Soyuz 7K-TM , - , Sirius-17K and POV , , , , Salyut 1 , - , Mirzam-17K , , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Control Panels
Control may refer to: Basic meanings Economics and business * Control (management), an element of management * Control, an element of management accounting * Comptroller (or controller), a senior financial officer in an organization * Controlling interest, a percentage of voting stock shares sufficient to prevent opposition * Foreign exchange controls, regulations on trade * Internal control, a process to help achieve specific goals typically related to managing risk Mathematics and science * Control (optimal control theory), a variable for steering a controllable system of state variables toward a desired goal * Controlling for a variable in statistics * Scientific control, an experiment in which "confounding variables" are minimised to reduce error * Control variables, variables which are kept constant during an experiment * Biological pest control, a natural method of controlling pests * Control network in geodesy and surveying, a set of reference points of known geospatial coo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salyut 7
Salyut 7 (russian: Салют-7; en, Salute 7) (a.k.a. DOS-6, short for Durable Orbital Station) was a space station in low Earth orbit from April 1982 to February 1991. It was first crewed in May 1982 with two crew via Soyuz T-5, and last visited in June 1986, by Soyuz T-15. Various crew and modules were used over its lifetime, including 12 crewed and 15 uncrewed launches in total. Supporting spacecraft included the Soyuz T, Progress (spacecraft), Progress, and TKS spacecraft. It was part of the Soviet Union, Soviet Salyut programme, and launched on 19 April 1982 on a Proton (rocket), Proton rocket from Baikonur Cosmodrome Site 200, Site 200/40 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in the Soviet Union. Salyut 7 was part of the transition from monolithic to modular space stations, acting as a testbed for docking of additional modules and expanded station operations. It was the eighth space station of any kind launched. Salyut 7 was the last of both the second generation of DOS-series spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science And Technology In Russia
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe. Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence for scientific reasoning is tens of thousands of years old. The earliest written records in the history of science come from Ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia in around 3000 to 1200 BCE. Their contributions to mathematics, astronomy, and medicine entered and shaped Greek natural philosophy of classical antiquity, whereby formal attempts were made to provide explanations of events in the physical world based on natural causes. After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, knowledge of Greek conceptions of the world deteriorated in Western Europe during the early centuries (400 to 1000 CE) of the Middle Ages, but was preserved in the Muslim world during the Islamic Golden Age and later by the efforts of Byzantine Greek scholars who brought Greek m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Computer Systems
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national republics; in practice, both its government and its economy were highly centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, with the city of Moscow serving as its capital as well as that of its largest and most populous republic: the Russian SFSR. Other major cities included Leningrad (Russian SFSR), Kiev (Ukrainian SSR), Minsk (Byelorussian SSR), Tashkent (Uzbek SSR), Alma-Ata (Kazakh SSR), and Novosibirsk (Russian SFSR). It was the largest country in the world, covering over and spanning eleven time zones. The country's roots lay in the October Revolution of 1917, when the Bolsheviks, under the leadership of Vladimir Lenin, overthrew the Russian Provisional Government that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zarya (ISS Module)
''Zarya'' (russian: Заря, , Dawn), also known as the Functional Cargo Block or FGB (from the russian: "Функционально-грузовой блок", , ''Funktsionalno-gruzovoy blok'' or ''ФГБ''), is the first module of the International Space Station to have been launched.NASA, International Space StationZarya(accessed 19 Apr. 2014) The FGB provided electrical power, storage, propulsion, and guidance to the ISS during the initial stage of assembly. With the launch and assembly in orbit of other modules with more specialized functionality, it is primarily used for storage, both inside the pressurized section and in the externally mounted fuel tanks. The ''Zarya'' is a descendant of the TKS spacecraft designed for the Russian ''Salyut'' program. The name ''Zarya'' ("Dawn") was given to the FGB because it signified the dawn of a new era of international cooperation in space. Although it was built by a Russian company, it is owned by the United States. Construct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zvezda (ISS Module)
''Zvezda'' (russian: Звезда, meaning "star"), ''Salyut'' DOS-8, also known as the ''Zvezda'' Service Module, is a module of the International Space Station (ISS). It was the third module launched to the station, and provided all of the station's life support systems, some of which are supplemented in the US Orbital Segment (USOS), as well as living quarters for two crew members. It is the structural and functional center of the Russian Orbital Segment (ROS), which is the Russian part of the ISS. Crew assemble here to deal with emergencies on the station. The module was manufactured in the USSR by RKK Energia, with major sub-contracting work by GKNPTs Khrunichev. ''Zvezda'' was launched on a Proton launch vehicle on 12 July 2000, and docked with the '' Zarya'' module on 26 July 2000. Origins The basic structural frame of ''Zvezda'', known as "DOS-8", was initially built in the mid-1980s to be the core of the ''Mir-2'' space station. This means that ''Zvezda'' is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VGA Monitor
Video Graphics Array (VGA) is a video display controller and accompanying de facto graphics standard, first introduced with the IBM PS/2 line of computers in 1987, which became ubiquitous in the Personal computer, PC industry within three years. The term can now refer to the computer display standard, the 15-pin D-subminiature VGA connector, or the 640×480 Graphics display resolution, resolution characteristic of the VGA hardware. VGA was the last IBM graphics standard to which the majority of IBM PC compatible, PC clone manufacturers conformed, making it the Lowest common denominator#Colloquial usage, lowest common denominator that virtually all post-1990 PC graphics hardware can be expected to implement. IBM intended to supersede VGA with the Extended Graphics Array (XGA) standard, but failed. Instead, VGA was adapted into many extended forms by third parties, collectively known as Super VGA, then gave way to custom graphics processing units which, in addition to their propr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz TMA
Soyuz is a transliteration of the Cyrillic text Союз (Russian and Ukrainian, 'Union'). It can refer to any union, such as a trade union (''profsoyuz'') or the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (Сою́з Сове́тских Социалисти́ческих Респу́блик, ''Soyuz Sovetskikh Sotsialisticheskikh Respublik''). As terminological shorthand "soyuz" by itself was often used interchangeably with each of the slightly longer terms Сове́тский Сою́з (''Sovetskiy Soyuz'', 'Soviet Union'). It was also a shorthand for the citizenry as a whole. Soyuz is also the designated name of various projects the country commissioned during the Space Race. Space program uses * Soyuz programme, a human spaceflight program initiated by the Soviet Union, continued by the Russian Federation * Soyuz (spacecraft), used in that program * Soyuz (rocket), initially used to launch that spacecraft * Soyuz (rocket family), derivatives of that rocket design * Soyuz Launch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz TM
The Soyuz-TM were fourth generation (1986–2002) Soyuz spacecraft used for ferry flights to the Mir and ISS space stations. The Soyuz spacecraft consisted of three parts, the Orbital Module, the Descent Module and the Service Module. The first launch of the spacecraft was the uncrewed Soyuz TM-1 on May 21, 1986, where it docked with the Mir space station. The final flight was Soyuz TM-34, which docked with the International Space Station and landed November 10, 2002. Background After the Apollo-Soyuz Test project in 1976, the Soyuz for crewed flights had the singular mission of supporting crewed space stations. The original Soyuz had a limited endurance when docked with a station, only about 60 to 90 days. There were two avenues for extending the duration of missions past this. The first avenue was to make upgrades to increase the Soyuz spacecraft's endurance. The Soyuz-T could last 120 days and the Soyuz-TM could last 180 days. The other was to use a Visiting Expeditio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz T
The Soyuz-T (russian: Союз-T, ''Union-T'') spacecraft was the third generation Soyuz spacecraft, in service for seven years from 1979 to 1986. The ''T'' stood for transport (, ). The revised spacecraft incorporated lessons learned from the Apollo Soyuz Test Project, Soyuz 7K-TM and Military Soyuz. The Soyuz-T was a major upgrade over previous Soyuz spacecraft, sporting solid-state electronics for the first time and a much more advanced onboard computer to help overcome the chronic docking problems that affected cosmonauts during space station missions. In addition, solar panels returned, allowing the Soyuz-T to fly up to 11 days independently as well as a redesigned propulsion system, the KTDU-426. Finally, it could at last carry three cosmonauts with pressure suits. Missions *Soyuz T-1 (uncrewed test, launched 1979) *Soyuz T-2 *Soyuz T-3 *Soyuz T-4 *Soyuz T-5 *Soyuz T-6 *Soyuz T-7 *Soyuz T-8 *Soyuz T-9 *Soyuz T-10-1 *Soyuz T-10 *Soyuz T-11 *Soyuz T-12 *Soyuz T-13 *Soyuz T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
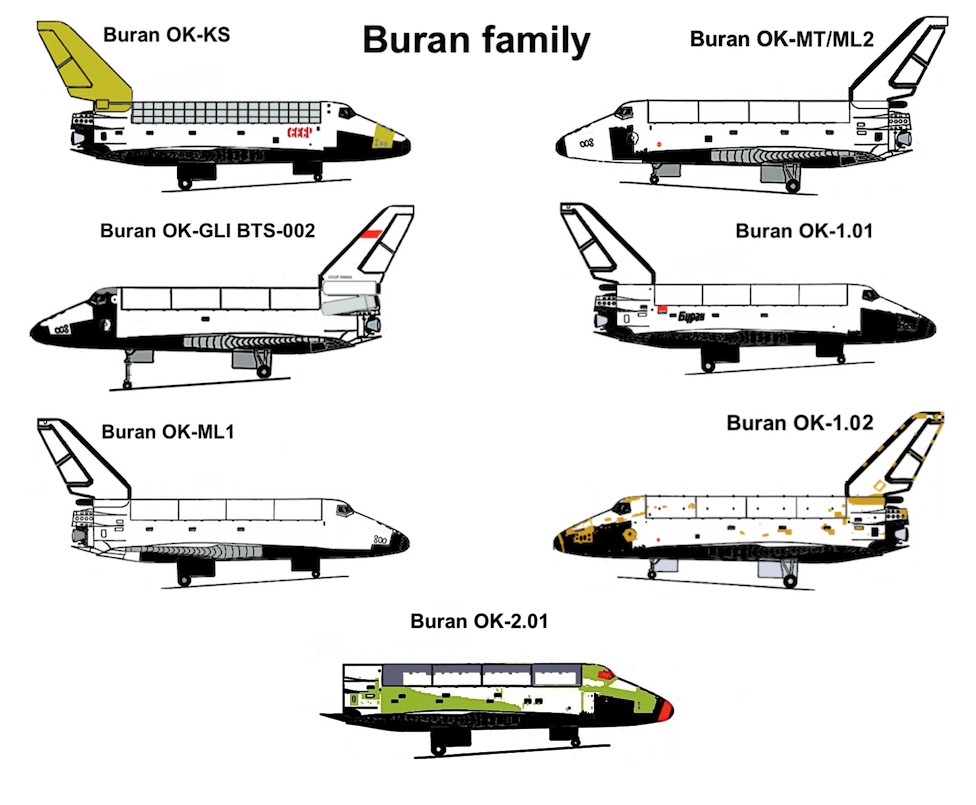
Buran (spacecraft)
''Buran'' (russian: Буран, , meaning "Snowstorm" or "Blizzard"; GRAU index serial number: 11F35 1K, construction number: 1.01) was the first spaceplane to be produced as part of the Soviet/Russian Buran program. Besides describing the first operational Soviet/Russian shuttle orbiter, "Buran" was also the designation for the entire Soviet/Russian spaceplane project and its orbiters, which were known as "Buran-class orbiters". Buran completed one uncrewed spaceflight in 1988, and was destroyed in the 2002 collapse of its storage hangar. The Buran-class orbiters used the expendable Energia rocket, a class of super heavy-lift launch vehicle. It is named after the Asian wind. Construction The construction of the Buran spacecraft began in 1980, and by 1984 the first full-scale orbiter was rolled out. Over 1000 companies all over the Soviet Union were involved in construction and development. The Buran spacecraft was made to be launched on the Soviet Union's super-heavy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OK-GLI
The OK-GLI (russian: Орбитальный корабль для горизонтальных лётных испытаний, ОК-ГЛИ, translit=Orbital'nyy korabl' dlya gorizontal'nykh lotnykh ispytaniy, lit=Orbital ship for horizontal flight tests), also known as Buran Analog BTS-02 (russian: БТС-02, Большой транспортный самолёт второй, translit=bolshoi transportny samolyot vtoroi, lit=big transport aircraft, the second), was a test vehicle ("Buran aerodynamic analogue") in the Buran programme. It was constructed in 1984, and was used for 25 test flights between 1985 and 1988 before being retired. It is now an exhibit at the Technik Museum Speyer in Germany. Construction The development of the Buran began in the late 1970s as a response to the U.S. Space Shuttle program. The construction of the orbiters began in 1980, and by 1984 the first full-scale Buran was rolled out. The first suborbital test flight of a scale-model took place as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)