|
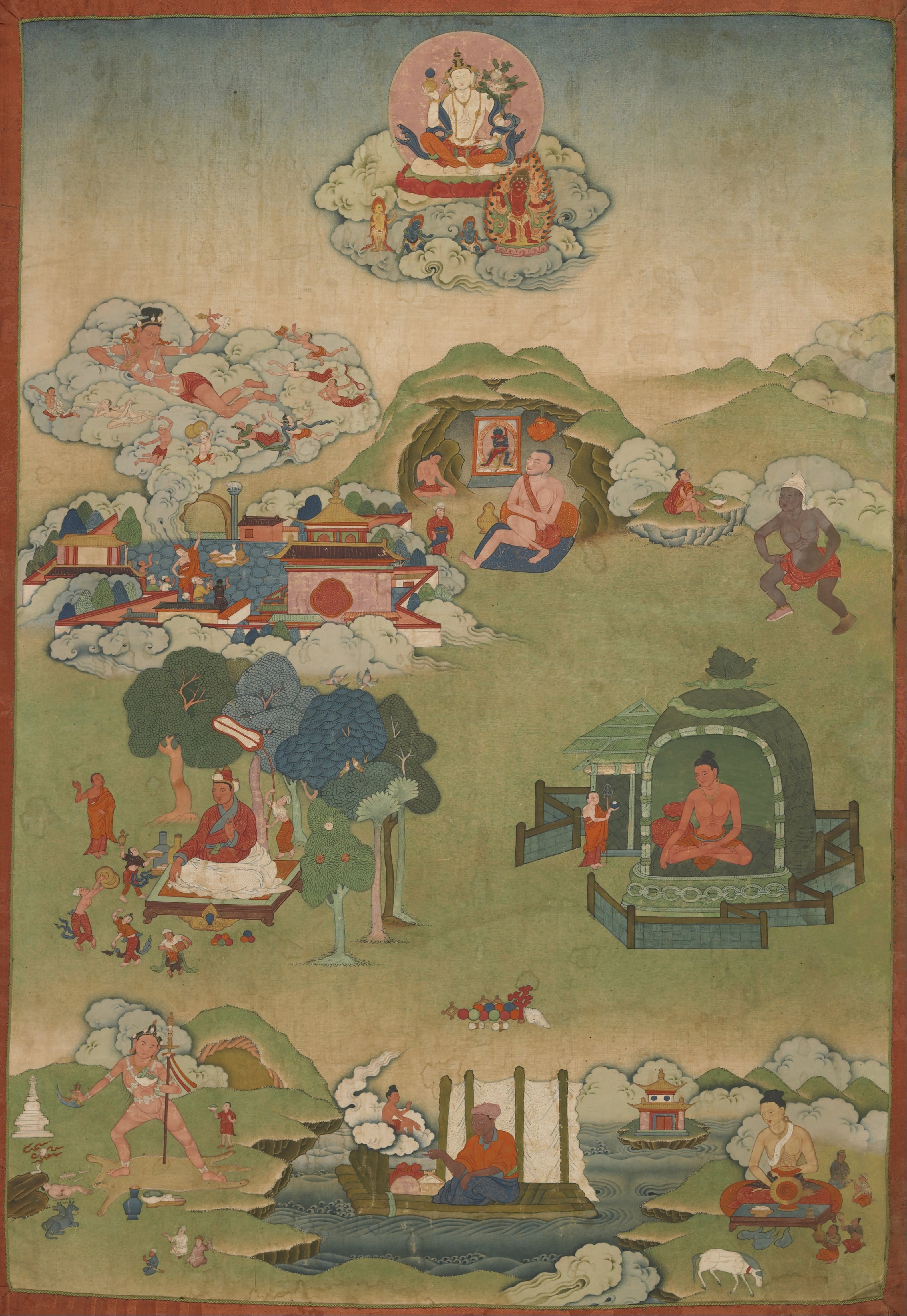
Indrabhuti
Indrabhuti (alternatively King Ja) is a name attributed to a number of individuals that have become conflated in Vajrayana Buddhism. One Indrabhuti, considered a Mahasiddha, was a disciple of Lawapa. Identities of the king Samten Karmay attempted to identify the different personages known as Indrabhutai. Conflation of Indrabhuti related to conflation of Oddiyana The matter of the conflation of Indrabhuti and at least one evocation of the historicity of a particular personage by that name is intimately connected with the location of 'Oddiyana' (the locality denoted by the term 'Oddiyana' whether in each case cited is Swat Valley or Odisha or some other location is glossed with a suite of orthographic representations and near homophones which require further case-by-case examination and exploration), Odisha and the cult of Jaganath and a number of texts that inform the matter such as the '' Sādhanamālā'', '' Kālikā Purāṇa'', ''Caturāsiti-siddha-Pravṛtti'', '' Jñānasidd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oddiyana
(also: ''Uḍḍiyāna'', ''Uḍḍāyāna'' or ''Udyāna'', Sanskrit: ओड्डियान, उड्डियान, उड्डायान, उद्यान; , , mn, Үржин ''urkhin''), was a small region in early medieval India, in present-day Swat District of modern-day Pakistan.‘Uḍḍiyāna and Kashmir’, pp 265-269 ‘The Śaiva Exegesis of Kashmir’, in Mélanges tantriques à la mémoire d’Hélène Brunner. Tantric Studies in Memory of Hélène Brunner, Collection Indologie 106, EFEO, Institut français de Pondichéry (IFP), ed. Dominic Goodall and André Padoux, 2007.) An alternate theory places its location in what is now the modern Indian state of Odisha, though this is improbable. It is ascribed importance in the development and dissemination of Vajrayāna Buddhism. It was also called as “the paradise of the Ḍākinīs”. Tibetan Buddhist traditions view it as a Beyul (Tibetan: སྦས་ཡུལ, Wylie: sbas-yul), a legendary heavenly p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaganath
Jagannath ( or, ଜଗନ୍ନାଥ, lit=Lord of the Universe, Jagannātha; formerly en, Juggernaut) is a deity worshipped in regional Hindu traditions in India and Bangladesh as part of a triad along with his brother Balabhadra, and sister, Subhadra. Jagannath, within Odia Hinduism, is the supreme god, ''Purushottama'', and the ''Para Brahman''. To most Vaishnava Hindus, particularly the Krishnaites, Jagannath is an abstract representation of Krishna, or Vishnu, sometimes as the avatar of Krishna or Vishnu. To some Shaiva and Shakta Hindus, he is a symmetry-filled tantric form of Bhairava, a fierce manifestation of Shiva associated with annihilation. The Jagannathism ( Odia Vaishnavism) — the particular sector of Jagannath as a major deity — emerged in the Early Middle Ages and later became an independent state regional temple-centered tradition of Krishnaism/Vaishnavism. The idol of Jagannath is a carved and decorated wooden stump with large round eyes and a symmetr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kukuraja
Kukuraja was a mahasiddha within the lineages of Esoteric Buddhism and he was contemporaneous with Indrabhuti of Sahor in Oddiyana (also known as King Ja) and Kambalapada (also known as Lawapa). Kukuraja interpreted Tantras for King Indrabhuti. Indrabhuti is held in some sources to be the father of Padmasambhava. Instruction According to Nyingma tradition, King Ja taught himself intuitively from "the Book" of the Tantric Way of Secret Mantra (that is Mantrayana) that magically fell from the sky along with other sacred objects and relics "upon the roof of King Ja" according to Dudjom (1904–1987),'' et al.'' (1991: p. 613 History) took place on the Tibetan calendar year of the Earth Monkey, which Dudjom '' et al.'' identify as 853 BC Kukuraja received instruction drawn from "the Book" on what may be understood as the Outer Tantras from King Ja, then King Ja received instruction on what may be understood as the Inner Tantras from Kukuraja (Kukkuraja taught King Ja after Kukku ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vajrayana
Vajrayāna ( sa, वज्रयान, "thunderbolt vehicle", "diamond vehicle", or "indestructible vehicle"), along with Mantrayāna, Guhyamantrayāna, Tantrayāna, Secret Mantra, Tantric Buddhism, and Esoteric Buddhism, are names referring to Buddhism, Buddhist traditions associated with Tantra and "Secret Mantra", which developed in the Medieval India, medieval Indian subcontinent and spread to Tibet, Nepal, other Himalayan states, East Asia, and Mongolia. Vajrayāna practices are connected to specific lineages in Buddhism, through the teachings of lineage holders. Others might generally refer to texts as the Buddhist Tantras. It includes practices that make use of mantras, dharanis, mudras, mandalas and the visualization of deities and Buddhas. Traditional Vajrayāna sources say that the tantras and the lineage of Vajrayāna were taught by Gautama Buddha, Śākyamuni Buddha and other figures such as the bodhisattva Vajrapani and Padmasambhava. Contemporary historians of Bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caturāsiti-siddha-Pravṛtti
Mahasiddha (Sanskrit: ''mahāsiddha'' "great adept; ) is a term for someone who embodies and cultivates the "siddhi of perfection". A siddha is an individual who, through the practice of sādhanā, attains the realization of siddhis, psychic and spiritual abilities and powers. Mahasiddhas were practitioners of yoga and tantra, or ''tantrika''s. Their historical influence throughout the Indian subcontinent and the Himalayas was vast and they reached mythic proportions as codified in their songs of realization and hagiographies, or namtars, many of which have been preserved in the Tibetan Buddhist canon. The Mahasiddhas are the founders of Vajrayana traditions and lineages such as Dzogchen and Mahamudra. Robert Thurman explains the symbiotic relationship between Tantric Buddhist communities and the Buddhist universities such as Nalanda which flourished at the same time. Genealogy and historical dates The exact genealogy and historical dates of the Mahasiddhas are contentious. D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luipa
Luipa or Luipada (c. 10th century) was a mahasiddha siddhacharya from the Brahmaputra Valley or Luit. He was a Buddhist saint from the Kamrupian Kãivartā community. He was a poet and writer of a number of [Buddhist texts] mainly the Charyapadas which is the earliest form of the Assamese Language. Nomenclature and etymology Although the Tibetan translation for ''Lui'' is "the fish-gut eater" (), the root of the word is probably Sanskrit ''lohita'' which means "red" and the names like Luidhar, Luichandra and Luiya mentioned in the ''Dharmamangal''s of the late medieval period originated from the same root.Sen, Sukumar (2002). ''Charyageeti Padabali'' (in Bengali), Ananda Publishers, Kolkata, , pp.20-1 Ayyappapanicker & Akademi (1997: p. 599) amplify the view of prior scholarship in that the nomenclature "Luipa" is related to the Brahmaputra River: Hagiographical accounts Luipa appears in ''The Legends of Eighty-four Siddhas'' (), a Tibetan namtar (biography), namtar detail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tilopa
Tilopa (Prakrit; Sanskrit: Talika or Tilopadā; 988–1069) was an Indian Buddhist monk in the tantric Kagyu lineage of Tibetan Buddhism. He lived along the Ganges River, with wild ladies as a tantric practitioner and mahasiddha. He practiced Anuttarayoga Tantra, a set of spiritual practices intended to accelerate the process of attaining Buddhahood. He became a holder of all the tantric lineages, possibly the only person in his day to do so. As well as the way of insight, and Mahamudra he learned and passed on the Way of Methods, today known as the 6 Yogas of Naropa, and guru yoga. Naropa is considered his main student. Life Tilopa was born into the priestly caste – according to some sources, a royal family – but he adopted the monastic life upon receiving orders from a dakini (female buddha whose activity is to inspire practitioners) who told him to adopt a mendicant and itinerant existence. From the beginning, she made it clear to Tilopa that his real parents were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thothori Nyantsen
Lha Thothori gNyan bTsan (, ) was the 28th King of Tibet according to the Tibetan legendary tradition. ''Lha'' "divine, pertaining to the gods of the sky" is an honorary title and not a part of his proper name. He belonged to the Yarlung dynasty connected to the Yarlung district in Southern Tibet. Modern scholars believe that he was a historical ruler, as he is also mentioned in a Chinese source. They date his rule to the fifth century, because the 33rd king Songtsän Gampo died in 650; other calculations putting his birth at 173 or 254 are nowadays rejected. He did not rule over the whole of Tibet; his power was probably limited to the Yarlung Tsangpo Grand Canyon area. According to an indigenous legend, Buddhist scriptures (among them the '' Kāraṇḍavyūhasūtra'') first arrived in Tibet in his time. The tale claims that this happened in a miraculous way (the volumes fell from the sky on the roof of the royal palace a motif which also happened to one of the royal personages of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahasiddha
Mahasiddha (Sanskrit: ''mahāsiddha'' "great adept; ) is a term for someone who embodies and cultivates the " siddhi of perfection". A siddha is an individual who, through the practice of sādhanā, attains the realization of siddhis, psychic and spiritual abilities and powers. Mahasiddhas were practitioners of yoga and tantra, or ''tantrika''s. Their historical influence throughout the Indian subcontinent and the Himalayas was vast and they reached mythic proportions as codified in their songs of realization and hagiographies, or namtars, many of which have been preserved in the Tibetan Buddhist canon. The Mahasiddhas are the founders of Vajrayana traditions and lineages such as Dzogchen and Mahamudra. Robert Thurman explains the symbiotic relationship between Tantric Buddhist communities and the Buddhist universities such as Nalanda which flourished at the same time. Genealogy and historical dates The exact genealogy and historical dates of the Mahasiddhas are contentiou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahasiddhas
Mahasiddha (Sanskrit: ''mahāsiddha'' "great adept; ) is a term for someone who embodies and cultivates the "siddhi of perfection". A siddha is an individual who, through the practice of sādhanā, attains the realization of siddhis, psychic and spiritual abilities and powers. Mahasiddhas were practitioners of yoga and tantra, or ''tantrika''s. Their historical influence throughout the Indian subcontinent and the Himalayas was vast and they reached mythic proportions as codified in their songs of realization and hagiographies, or namtars, many of which have been preserved in the Tibetan Buddhist canon. The Mahasiddhas are the founders of Vajrayana traditions and lineages such as Dzogchen and Mahamudra. Robert Thurman explains the symbiotic relationship between Tantric Buddhist communities and the Buddhist universities such as Nalanda which flourished at the same time. Genealogy and historical dates The exact genealogy and historical dates of the Mahasiddhas are contentious. D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalika Purana
The Kalika Purana ( sa, Kālikā Purāṇa), also called the Kali Purana, Sati Purana or Kalika Tantra, is one of the eighteen minor Puranas (''Upapurana'') in the Shaktism tradition of Hinduism. The text was likely composed in Assam or Cooch Behar: "This story is recounted also in the Kālikāpurāṇa—the earliest text devoted to the worship of Kāmākhyā, probably compiled no later than the tenth–eleventh century in a region between Assam and Koch Bihar (a district of West Bengal)." region of India and is attributed to the sage Markandeya. It exists in many versions, variously organized in 90 to 93 chapters. The surviving versions of the text are unusual in that they start abruptly and follow a format not found in either the major or minor Purana-genre mythical texts of Hinduism. Various types of animal sacrifices for devi are detailed in the Purana. Content The text starts off with the legends of Devi trying to bring Shiva back from ascetic life into that of a household ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anuyoga
Anuyoga (Skt. अनुयोग 'further yoga') is the designation of the second of the three Inner Tantras according to the Yana (Buddhism)#The nine yanas, ninefold division of practice used by the Nyingma school of Tibetan Buddhism. As with the other yanas, Anuyoga represents both a scriptural division as well as a specific emphasis of both view and practice. Position in the nine-yana schema Anuyoga is said to emphasise the completion stage of Tantra, where the preceding division, Mahayoga emphasises the generation stage. Dalton (2003: unpaginated) in introducing the literature of the Anuyoga-yana affirms the affiliation of the Anuyoga-yana with the 'completion stage' also known as the 'perfection stage': Modern-day doxographical presentations of the Nyingma school are usually based on the system of the nine vehicles (''theg pa dgu''). Emphasis is placed on the highest three vehicles in this scheme, namely Mahāyoga, Anuyoga, and Atiyoga. Generally speaking, these three “inner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_(8697431158).jpg)



