|
Indole-3-butyric Acid
Indole-3-butyric acid (1''H''-indole-3-butanoic acid, IBA) is a white to light-yellow crystalline solid, with the molecular formula C12H13NO2. It melts at 125 °C in atmospheric pressure and decomposes before boiling. IBA is a plant hormone in the auxin family and is an ingredient in many commercial horticultural plant rooting products. Plant hormone Since IBA is not completely soluble in water, it is typically dissolved in 75% or purer alcohol for use in plant rooting, making a solution of between 10,000 and 50,000 ppm. This alcohol solution is then diluted with distilled water to the desired concentration. IBA is also available as a salt, which is soluble in water. The solution should be kept in a cool, dark place for best results. This compound had been thought to be strictly synthetic; however, it was reported that the compound was isolated from leaves and seeds of maize and other species. In maize IBA has been shown to be synthesized in vivo using IAA and other co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cubic Crystal System
In crystallography, the cubic (or isometric) crystal system is a crystal system where the Crystal_structure#Unit_cell, unit cell is in the shape of a cube. This is one of the most common and simplest shapes found in crystals and minerals. There are three main varieties of these crystals: *Primitive cubic (abbreviated ''cP'' and alternatively called simple cubic) *Body-centered cubic (abbreviated ''cI'' or bcc) *Face-centered cubic (abbreviated ''cF'' or fcc, and alternatively called Close-packing_of_equal_spheres, ''cubic close-packed'' or ccp) Each is subdivided into other variants listed below. Although the ''unit cells'' in these crystals are conventionally taken to be cubes, the primitive_cell, primitive unit cells often are not. Bravais lattices The three Bravais lattices in the cubic crystal system are: The primitive cubic lattice (cP) consists of one Lattice_(group), lattice point on each corner of the cube; this means each simple cubic unit cell has in total one latt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Willow
Willows, also called sallows and osiers, from the genus ''Salix'', comprise around 400 speciesMabberley, D.J. 1997. The Plant Book, Cambridge University Press #2: Cambridge. of typically deciduous trees and shrubs, found primarily on moist soils in cold and temperate regions. Most species are known as willow, but some narrow-leaved shrub species are called osier, and some broader-leaved species are referred to as sallow (from Old English ''sealh'', related to the Latin word ''salix'', willow). Some willows (particularly arctic and alpine species) are low-growing or creeping shrubs; for example, the dwarf willow (''Salix herbacea'') rarely exceeds in height, though it spreads widely across the ground. Description Willows all have abundant watery bark sap, which is heavily charged with salicylic acid, soft, usually pliant, tough wood, slender branches, and large, fibrous, often stoloniferous roots. The roots are remarkable for their toughness, size, and tenacity to live ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
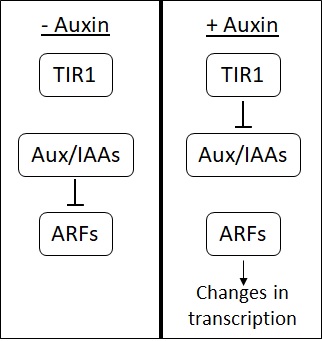
Auxins
Auxins (plural of auxin ) are a class of plant hormones (or plant-growth regulators) with some morphogen-like characteristics. Auxins play a cardinal role in coordination of many growth and behavioral processes in plant life cycles and are essential for plant body development. The Dutch biologist Frits Warmolt Went first described auxins and their role in plant growth in the 1920s. Kenneth V. Thimann became the first to isolate one of these phytohormones and to determine its chemical structure as indole-3-acetic acid (IAA). Went and Thimann co-authored a book on plant hormones, ''Phytohormones'', in 1937. Overview Auxins were the first of the major plant hormones to be discovered. They derive their name from the Greek word αυξειν (''auxein'' – "to grow/increase"). Auxin is present in all parts of a plant, although in very different concentrations. The concentration in each position is crucial developmental information, so it is subject to tight regulation through both meta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatty Acids
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, from 4 to 28. Fatty acids are a major component of the lipids (up to 70% by weight) in some species such as microalgae but in some other organisms are not found in their standalone form, but instead exist as three main classes of esters: triglycerides, phospholipids, and cholesteryl esters. In any of these forms, fatty acids are both important dietary sources of fuel for animals and important structural components for cells. History The concept of fatty acid (''acide gras'') was introduced in 1813 by Michel Eugène Chevreul, though he initially used some variant terms: ''graisse acide'' and ''acide huileux'' ("acid fat" and "oily acid"). Types of fatty acids Fatty acids are classified in many ways: by length, by saturation vs unsatura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
β-oxidation
In biochemistry and metabolism, beta-oxidation is the catabolic process by which fatty acid molecules are broken down in the cytosol in prokaryotes and in the mitochondria in eukaryotes to generate acetyl-CoA, which enters the citric acid cycle, and NADH and FADH2, which are co-enzymes used in the electron transport chain. It is named as such because the beta carbon of the fatty acid undergoes oxidation to a carbonyl group. Beta-oxidation is primarily facilitated by the mitochondrial trifunctional protein, an enzyme complex associated with the inner mitochondrial membrane, although very long chain fatty acids are oxidized in peroxisomes. The overall reaction for one cycle of beta oxidation is: :C''n''-acyl-CoA + FAD + + + CoA → C''n''-2-acyl-CoA + + NADH + + acetyl-CoA Activation and membrane transport Free fatty acids cannot penetrate any biological membrane due to their negative charge. Free fatty acids must cross the cell membrane through specific transport proteins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1-Naphthaleneacetic Acid
1-Naphthaleneacetic acid (NAA) is an organic compound with the formula C10H7CH2CO2H. This colorless solid is soluble in organic solvents. It features a carboxylmethyl group (CH2CO2H) linked to the "1-position" of naphthalene. Use and regulation NAA is a synthetic plant hormone in the auxin family and is an ingredient in many commercial plant rooting horticultural products; it is a rooting agent and used for the vegetative propagation of plants from stem and leaf cuttings. It is also used for plant tissue culture. The hormone NAA does not occur naturally, and, like all auxins, is toxic to plants at high concentrations. In the United States, under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA), products containing NAA require registration with the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) as pesticides. Use and analysis NAA is widely used in agriculture for various purposes. It is considered to be only slightly toxic but when at higher concentrations it can be toxic t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camellia Sinensis
''Camellia sinensis'' is a species of evergreen shrub or small tree in the flowering plant family Theaceae. Its leaves and leaf buds are used to produce the popular beverage, tea. Common names include tea plant, tea shrub, and tea tree (not to be confused with ''Melaleuca alternifolia'', the source of tea tree oil, or the genus ''Leptospermum'' commonly called tea tree). White tea, yellow tea, green tea, oolong, dark tea (which includes pu-erh tea) and black tea are all harvested from one of two major varieties grown today, ''C. sinensis'' var. ''sinensis'' and ''C. s.'' var. ''assamica'', but are processed differently to attain varying levels of oxidation with black tea being the most oxidized and green being the least. Kukicha (twig tea) is also harvested from ''C. sinensis'', but uses twigs and stems rather than leaves. Nomenclature and taxonomy The generic name ''Camellia'' is taken from the Latinized name of Rev. Georg Kamel, SJ (1661–1706), a Moravian-born Jesuit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Callus (cell Biology)
Plant callus (plural ''calluses'' or ''calli'') is a growing mass of unorganized plant parenchyma cells. In living plants, callus cells are those cells that cover a plant wound. In biological research and biotechnology callus formation is induced from plant tissue samples (explants) after surface sterilization and plating onto tissue culture medium in vitro (in a closed culture vessel such as a Petri dish). The culture medium is supplemented with plant growth regulators, such as auxin, cytokinin, and gibberellin, to initiate callus formation or somatic embryogenesis. Callus initiation has been described for all major groups of land plants. Callus induction and tissue culture Plant species representing all major land plant groups have been shown to be capable of producing callus in tissue culture. A callus cell culture is usually sustained on gel medium. Callus induction medium consists of agar and a mixture of macronutrients and micronutrients for the given cell type. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinetin
Kinetin (/'kaɪnɪtɪn/) is a type of cytokinin, a class of plant hormone that promotes cell division. Kinetin was originally isolated by Carlos Miller and Skoog ''et al.'' as a compound from autoclaved herring sperm DNA that had cell division-promoting activity. It was given the name kinetin because of its ability to induce cell division, provided that auxin was present in the medium. Kinetin is often used in plant tissue culture for inducing formation of callus (in conjunction with auxin) and to regenerate shoot tissues from callus (with lower auxin concentration). For a long time, it was believed that kinetin was an artifact produced from the deoxyadenosine residues in DNA, which degrade on standing for long periods or when heated during the isolation procedure. Therefore, it was thought that kinetin does not occur naturally, but, since 1996, it has been shown by several researchers that kinetin exists naturally in the DNA of cells of almost all organisms tested so far, incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytokinins
Cytokinins (CK) are a class of plant hormones that promote cell division, or cytokinesis, in plant roots and shoots. They are involved primarily in cell growth and differentiation, but also affect apical dominance, axillary bud growth, and leaf senescence. There are two types of cytokinins: adenine-type cytokinins represented by kinetin, zeatin, and 6-benzylaminopurine, and phenylurea-type cytokinins like diphenylurea and thidiazuron (TDZ). Most adenine-type cytokinins are synthesized in roots. Cambium and other actively dividing tissues also synthesize cytokinins. No phenylurea cytokinins have been found in plants. Cytokinins participate in local and long-distance signalling, with the same transport mechanism as purines and nucleosides. Typically, cytokinins are transported in the xylem. Cytokinins act in concert with auxin, another plant growth hormone. The two are complementary, having generally opposite effects. History The idea of specific substances required for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micropropagation
Micropropagation or tissue culture is the practice of rapidly multiplying plant stock material to produce many progeny plants, using modern plant tissue culture methods. Micropropagation is used to multiply a wide variety of plants, such as those that have been genetically modified or bred through conventional plant breeding methods. It is also used to provide a sufficient number of plantlets for planting from seedless plants, plants that do not respond well to vegetative reproduction or where micropropagation is the cheaper means of propagating (e.g. Orchids.) Cornell University botanist Frederick Campion Steward discovered and pioneered micropropagation and plant tissue culture in the late 1950s and early 1960s. Steps In short, steps of micropropagation can be divided into 4 stages. # Selection of mother plant # Multiplication # Rooting and acclimatizing # Transfer new plant to soil Selection of mother plant Micropropagation begins with the selection of plant material to b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indole-3-acetic Acid
Indole-3-acetic acid (IAA, 3-IAA) is the most common naturally occurring plant hormone of the auxin class. It is the best known of the auxins, and has been the subject of extensive studies by plant physiologists. IAA is a derivative of indole, containing a carboxymethyl substituent. It is a colorless solid that is soluble in polar organic solvents. Biosynthesis IAA is predominantly produced in cells of the apex (bud) and very young leaves of a plant. Plants can synthesize IAA by several independent biosynthetic pathways. Four of them start from tryptophan, but there is also a biosynthetic pathway independent of tryptophan. Plants mainly produce IAA from tryptophan through indole-3-pyruvic acid. IAA is also produced from tryptophan through indole-3-acetaldoxime in ''Arabidopsis thaliana''. In rats, IAA is a product of both endogenous and colonic microbial metabolism from dietary tryptophan along with tryptophol. This was first observed in rats infected by ''Trypanosoma bruc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |