|
Indian Monsoon Current
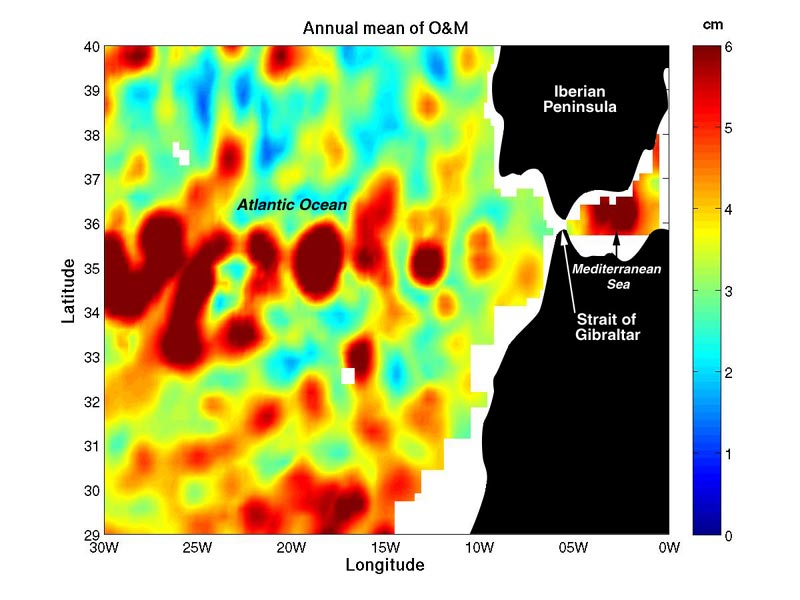
The Indian Monsoon Current refers to the seasonally varying ocean current regime found in the tropical regions of the northern Indian Ocean. During winter, the flow of the upper ocean is directed westward from near the Indonesian Archipelago to the Arabian Sea. During the summer, the direction reverses, with eastward flow extending from Somalia into the Bay of Bengal. These variations are due to changes in the wind stress associated with the Indian monsoon. The seasonally reversing open ocean currents that pass south of India are referred to as the Winter Monsoon Current and the Summer Monsoon Current (alternately, the Northeast Monsoon Current and the Southwest Monsoon Current).Shankar, D., P. N. Vinayachandran and A. S. Unnikrishnan, 2002: The monsoon current in the north Indian Ocean, Progress In Oceanography, Volume 52, Issue 1, Pages 63–120. The Somali Current, which is strongly linked to the Indian monsoon, is also discussed in this article. Overview Historical pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocean Currents
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of sea water generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contours, shoreline configurations, and interactions with other currents influence a current's direction and strength. Ocean currents are primarily horizontal water movements. An ocean current flows for great distances and together they create the global conveyor belt, which plays a dominant role in determining the climate of many of Earth’s regions. More specifically, ocean currents influence the temperature of the regions through which they travel. For example, warm currents traveling along more temperate coasts increase the temperature of the area by warming the sea breezes that blow over them. Perhaps the most striking example is the Gulf Stream, which makes northwest Europe much more temperate for its high latitude compared to other areas at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
8th Parallel North
The 8th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 8 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Africa, the Indian Ocean, South Asia, Southeast Asia, the Pacific Ocean, Central America, South America and the Atlantic Ocean. The parallel defines part of the border between Somalia and Ethiopia. The Eight Degree Channel (Maliku Kandu) in the Indian Ocean is named after the parallel. Around the world Starting at the Prime Meridian and heading eastwards, the parallel 8° north passes through: : See also *7th parallel north *9th parallel north The 9th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 9 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Africa, the Indian Ocean, South Asia, Southeast Asia, the Pacific Ocean, Central America, South America and the Atlantic Ocean. A ... {{geographical coordinates, state=collapsed n08 Ethiopia–Somalia border ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocean Gyre
In oceanography, a gyre () is any large system of circulating ocean currents, particularly those involved with large wind movements. Gyres are caused by the Coriolis effect; planetary vorticity, horizontal friction and vertical friction determine the circulatory patterns from the ''wind stress curl'' (torque). ''Gyre'' can refer to any type of vortex in an atmosphere or a sea, even one that is human-created, but it is most commonly used in terrestrial oceanography to refer to the major ocean systems. Major gyres The following are the five most notable ocean gyres:The five most notable gyres PowerPoint Presentation * * [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocean Current
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of sea water generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contours, shoreline configurations, and interactions with other currents influence a current's direction and strength. Ocean currents are primarily horizontal water movements. An ocean current flows for great distances and together they create the global conveyor belt, which plays a dominant role in determining the climate of many of Earth’s regions. More specifically, ocean currents influence the temperature of the regions through which they travel. For example, warm currents traveling along more temperate coasts increase the temperature of the area by warming the sea breezes that blow over them. Perhaps the most striking example is the Gulf Stream, which makes northwest Europe much more temperate for its high latitude compared to other areas at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monsoon Of South Asia
The Monsoon of South Asia is among several geographically distributed global monsoons. It affects the Indian subcontinent, where it is one of the oldest and most anticipated weather phenomena and an economically important pattern every year from June through September, but it is only partly understood and notoriously difficult to predict. Several theories have been proposed to explain the origin, process, strength, variability, distribution, and general vagaries of the monsoon, but understanding and predictability are still evolving. The unique geographical features of the Indian subcontinent, along with associated atmospheric, oceanic, and geophysical factors, influence the behavior of the monsoon. Because of its effect on agriculture, on flora and fauna, and on the climates of nations such as Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka – among other economic, social, and environmental effects – the monsoon is one of the most anticipated, tracked, and studied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asian Brown Cloud
The Indian Ocean brown cloud or Asian brown cloud is a layer of air pollution that recurrently covers parts of South Asia, namely the northern Indian Ocean, India, and Pakistan. Viewed from satellite photos, the cloud appears as a giant brown stain hanging in the air over much of South Asia and the Indian Ocean every year between January and March, possibly also during earlier and later months. The term was coined in reports from the UNEP Indian Ocean Experiment (INDOEX). It was found to originate mostly due to Sikh farmers burning stubble in Punjab and to lesser extent Haryana. The debilitating air quality in Delhi is also due to the stubble burning in Punjab.Ramanathan, Veerabhadran ''et al.'' (2002''The Asian brown cloud climate and other environmental impacts: impact study'' Center for Clouds, Chemistry and Climate, United Nations Environment Programme, Nairobi Kenya, , accessed 8 December 2008 The term ''atmospheric brown cloud'' is used for a more generic context not specifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lisa Beal
Lisa M. Beal is a professor at the University of Miami known for her work on the Agulhas Current. She is the editor-in-chief of the '' Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans''. Education and career Beal grew up in the United Kingdom, and was first attracted to aeronautical engineering as an undergraduate at University of Southampton before changing to oceanography. She earned her Ph.D. from the University of Southampton working on the Agulhas Current. Following her Ph.D. she did postdoctoral work at Columbia University and Scripps Institution of Oceanography before moving to the University of Miami in 2003. In 2021 Beal was named editor-in-chief for the ''Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans''. She formerly served as editor for the ocean section of ''Geophysical Research Letters'' from 2014 until 2017. Research Beal is known for her work on the Agulhas current, a western boundary current in the southwest Indian Ocean. She first worked on Agulhas Undercurrent and determined ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
9th Parallel North
The 9th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 9 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Africa, the Indian Ocean, South Asia, Southeast Asia, the Pacific Ocean, Central America, South America and the Atlantic Ocean. Around the world Starting at the Prime Meridian A prime meridian is an arbitrary meridian (a line of longitude) in a geographic coordinate system at which longitude is defined to be 0°. Together, a prime meridian and its anti-meridian (the 180th meridian in a 360°-system) form a great c ... and heading eastwards, the parallel 9° north passes through: : See also * 8th parallel north * 10th parallel north {{geographical coordinates, state=collapsed n09 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equator
The equator is a circle of latitude, about in circumference, that divides Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, halfway between the North and South poles. The term can also be used for any other celestial body that is roughly spherical. In spatial (3D) geometry, as applied in astronomy, the equator of a rotating spheroid (such as a planet) is the parallel (circle of latitude) at which latitude is defined to be 0°. It is an imaginary line on the spheroid, equidistant from its poles, dividing it into northern and southern hemispheres. In other words, it is the intersection of the spheroid with the plane perpendicular to its axis of rotation and midway between its geographical poles. On and near the equator (on Earth), noontime sunlight appears almost directly overhead (no more than about 23° from the zenith) every day, year-round. Consequently, the equator has a rather stable daytime temperature throug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sverdrup
In oceanography, the sverdrup (symbol: Sv) is a non- SI metric unit of volumetric flow rate, with equal to . It is equivalent to the SI derived unit cubic hectometer per second (symbol: hm3/s or hm3⋅s−1): 1 Sv is equal to 1 hm3/s. It is used almost exclusively in oceanography to measure the volumetric rate of transport of ocean currents. It is named after Harald Sverdrup. One sverdrup is about five times what is carried by the world’s largest river, the Amazon. In the context of ocean currents, a volume of one million cubic meters may be imagined as a "slice" of ocean with dimensions × × (width × length × thickness). At this scale, these units can be more easily compared in terms of width of the current (several km), depth (hundreds of meters), and current speed (as meters per second). Thus, a hypothetical current wide, 500 m (0.5 km) deep, and moving at 2 m/s would be transporting of water. The sverdrup is distinct from the SI sievert unit or th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
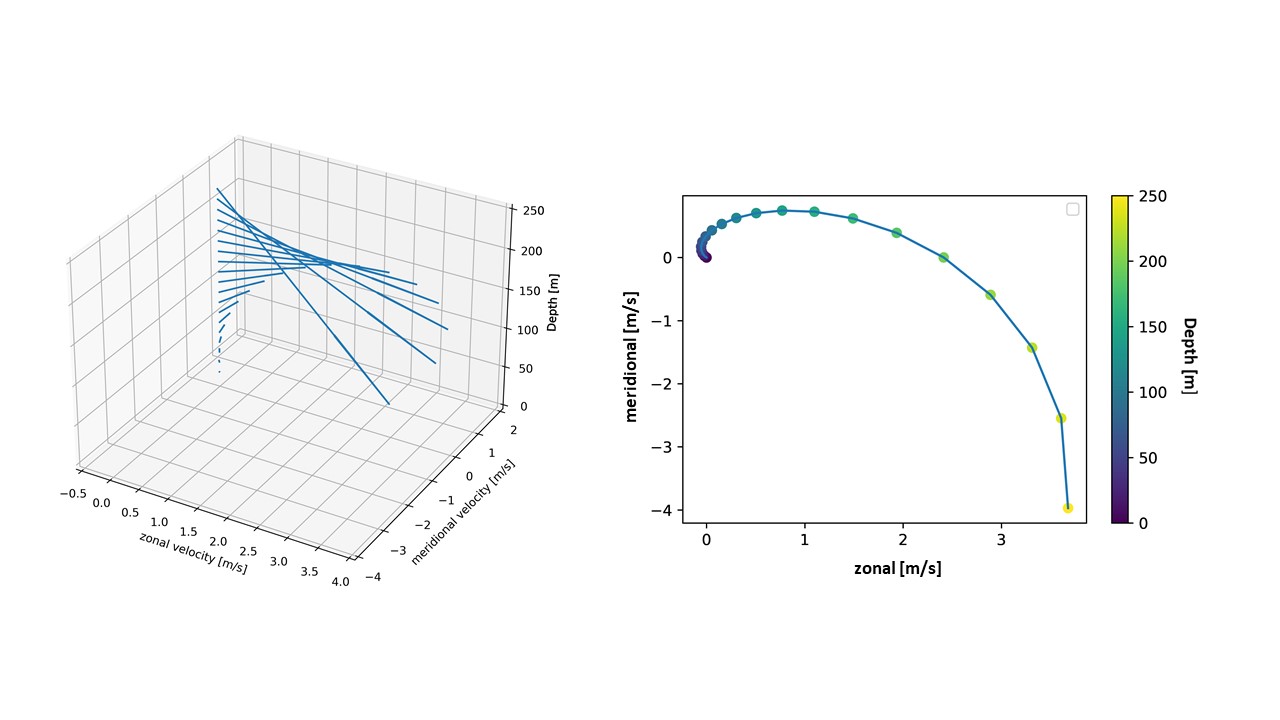
Ekman Spiral
The oceanic, wind driven Ekman spiral is the result of a force balance created by a shear stress force, Coriolis force and the water drag. This force balance gives a resulting current of the water different from the winds. In the ocean, there are two places where the Ekman spiral can be observed. At the surface of the ocean, the shear stress force corresponds with the wind stress force. At the bottom of the ocean, the shear stress force is created by friction with the ocean floor. This phenomenon was first observed at the surface by the Norwegian oceanographer Fridtjof Nansen during his Fram expedition. He noticed that icebergs did not drift in the same direction as the wind. His student, the Swedish oceanographer Vagn Walfrid Ekman, was the first person to physically explain this process. Bottom Ekman Spiral In order to derive the properties of an Ekman spiral a look is taken at a uniform, horizontal geostrophic interior flow in a homogeneous fluid. This flow will by denoted by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropics
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referred to as the tropical zone and the torrid zone (see geographical zone). In terms of climate, the tropics receive sunlight that is more direct than the rest of Earth and are generally hotter and wetter as they aren't affected as much by the solar seasons. The word "tropical" sometimes refers to this sort of climate in the zone rather than to the geographical zone itself. The tropical zone includes deserts and snow-capped mountains, which are not tropical in the climatic sense. The tropics are distinguished from the other climatic and biomatic regions of Earth, which are the middle latitudes and the polar regions on either side of the equatorial zone. The tropics constitute 40% of Earth's surface area and contain 36% of Earth's landmass. , the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |