Ocean Gyre on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In oceanography, a gyre () is any large system of circulating
PowerPoint Presentation * Indian Ocean Gyre * North Atlantic Gyre * North Pacific Gyre * South Atlantic Gyre * South Pacific Gyre They flow
 Tropical gyres are less unified and tend to be mostly east–west with minor north–south extent.
* Atlantic Equatorial Current System (two counter-rotating circulations)
* Pacific Equatorial Current System
* Indian Monsoon Gyres (two counter-rotating circulations in northern Indian Ocean)
Tropical gyres are less unified and tend to be mostly east–west with minor north–south extent.
* Atlantic Equatorial Current System (two counter-rotating circulations)
* Pacific Equatorial Current System
* Indian Monsoon Gyres (two counter-rotating circulations in northern Indian Ocean)
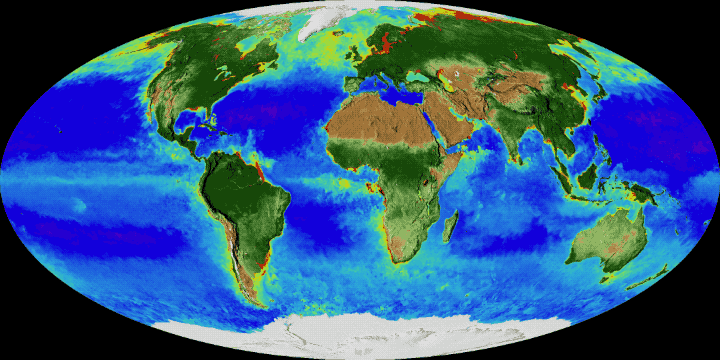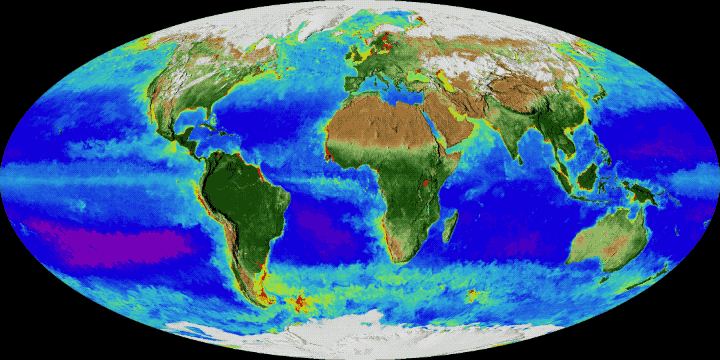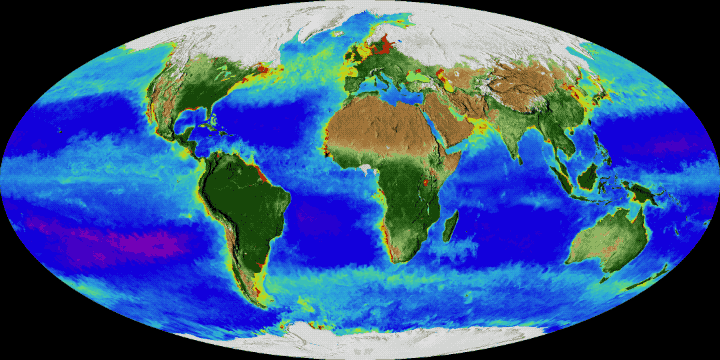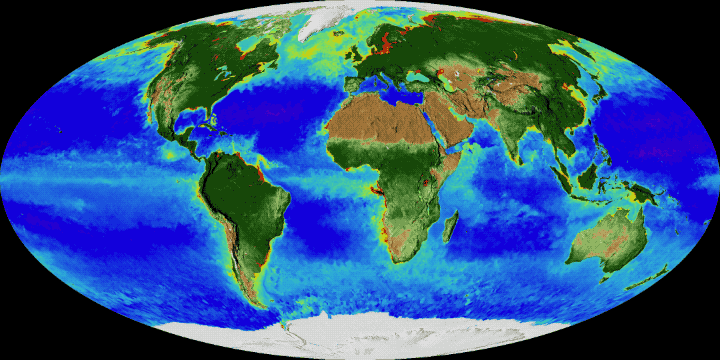 Gyres are sometimes described as "ocean deserts" or more precisely "biological deserts", a concept that uses the concept of desert in the sense of an environment lacking life and not necessarily water. Other places that are called oceanic deserts are hypoxic or anoxic waters such as dead zones.
Gyres are sometimes described as "ocean deserts" or more precisely "biological deserts", a concept that uses the concept of desert in the sense of an environment lacking life and not necessarily water. Other places that are called oceanic deserts are hypoxic or anoxic waters such as dead zones.
Major Ocean Currents Drifting Poleward
''www.loe.org'', accessed 5 December 2021

5 Gyres – Understanding Plastic Marine Pollution
SIO 210: Introduction to Physical Oceanography – Global circulation
SIO 210: Introduction to Physical Oceanography – Wind-forced circulation notes
North Pacific Gyre Oscillation
— Georgia Institute of Technology * {{Physical oceanography Aerodynamics Fluid dynamics Oceanic gyres Fisheries science
ocean current
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of sea water generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contou ...
s, particularly those involved with large wind
Wind is the natural movement of air or other gases relative to a planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few ...
movements. Gyres are caused by the Coriolis effect
In physics, the Coriolis force is an inertial or fictitious force that acts on objects in motion within a frame of reference that rotates with respect to an inertial frame. In a reference frame with clockwise rotation, the force acts to the ...
; planetary vorticity, horizontal friction and vertical friction determine the circulatory patterns from the '' wind stress curl'' (torque
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational equivalent of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force (also abbreviated to moment). It represents the capability of a force to produce change in the rotational motion of t ...
).
''Gyre'' can refer to any type of vortex
In fluid dynamics, a vortex ( : vortices or vortexes) is a region in a fluid in which the flow revolves around an axis line, which may be straight or curved. Vortices form in stirred fluids, and may be observed in smoke rings, whirlpools in t ...
in an atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. ...
or a sea, even one that is human-created, but it is most commonly used in terrestrial oceanography to refer to the major ocean
The ocean (also the sea or the world ocean) is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the surface of Earth and contains 97% of Earth's water. An ocean can also refer to any of the large bodies of water into which the wo ...
systems.
Major gyres
The following are the five most notable ocean gyres:The five most notable gyresPowerPoint Presentation * Indian Ocean Gyre * North Atlantic Gyre * North Pacific Gyre * South Atlantic Gyre * South Pacific Gyre They flow
clockwise
Two-dimensional rotation can occur in two possible directions. Clockwise motion (abbreviated CW) proceeds in the same direction as a clock's hands: from the top to the right, then down and then to the left, and back up to the top. The opposite ...
in the Northern hemisphere, and counterclockwise
Two-dimensional rotation can occur in two possible directions. Clockwise motion (abbreviated CW) proceeds in the same direction as a clock's hands: from the top to the right, then down and then to the left, and back up to the top. The opposite s ...
in the Southern hemisphere.
Other gyres
Tropical gyres
Subtropical gyres
Subtropical gyres are formed by an intricate process involving bothCoriolis force
In physics, the Coriolis force is an inertial or fictitious force that acts on objects in motion within a frame of reference that rotates with respect to an inertial frame. In a reference frame with clockwise rotation, the force acts to the ...
and Ekman transport. As global winds, caused by Earth's rotation, blow across the ocean surface they are acted upon by Coriolis causing movement to the right in the Northern Hemisphere and to the left in the Southern Hemisphere. These winds cause frictional surface currents as the wind transfers energy to the ocean allowing the water to move in a circular motion. As Ekman transport acts on these circular currents the net transport of water is actually 90 degrees which drives regions of convergence, allowing water to pile up in the center of the ocean basin forming a bulge.
The center of a subtropical gyre is a high pressure zone, while the outer edges of the gyre are a low pressure zone. This difference in pressure causes a pressure gradient allowing the diffusion of water from the high pressure zone in the bulge to the low pressure zone on the outer edges of the gyre.The movement of water does not flow directly down the bulge in the center but around it due to Coriolis causing circulation around the high pressure zone in a clockwise motion in the northern hemisphere and a counterclockwise motion in the southern hemisphere.Thus, Resulting in the rotation of the gyre. The gyre has a stable circulation of water around it due to the exact balance between Ekman force and Coriolis. These gyres contribute to the Geostrophic Flow of the ocean resulting in the overall Ocean circulation model of the Earth. The movement of subtropical gyres cause areas of downwelling in the ocean resulting in regions of lower productivity.
This build-up of water in the center creates flow towards the equator in the upper of the ocean, through rather complex dynamics. This flow is returned towards the pole in an intensified western boundary current
Boundary currents are ocean currents with dynamics determined by the presence of a coastline, and fall into two distinct categories: western boundary currents and eastern boundary currents.
Eastern boundary currents
Eastern boundary currents are ...
. The boundary current of the North Atlantic Gyre is the Gulf Stream
The Gulf Stream, together with its northern extension the North Atlantic Drift, is a warm and swift Atlantic ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows through the Straits of Florida and up the eastern coastline of the Uni ...
, of the North Pacific Gyre the Kuroshio Current, of the South Atlantic Gyre the Brazil Current, of the South Pacific Gyre the East Australian Current, and of the Indian Ocean Gyre the Agulhas Current
The Agulhas Current () is the western boundary current of the southwest Indian Ocean. It flows south along the east coast of Africa from 27°S to 40°S. It is narrow, swift and strong. It is suggested that it is the largest western boundary curre ...
.
Subpolar gyres
Subpolar gyres form at high latitudes (around 60°). Circulation of surface wind and ocean water is counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere, around alow-pressure area
In meteorology, a low-pressure area, low area or low is a region where the atmospheric pressure is lower than that of surrounding locations. Low-pressure areas are commonly associated with inclement weather (such as cloudy, windy, with possibl ...
, such as the persistent Aleutian Low and the Icelandic Low. Surface currents generally move outward from the center of the system. This drives the Ekman transport, which creates an upwelling of nutrient-rich water from the lower depths.
Subpolar circulation in the southern hemisphere is dominated by the Antarctic Circumpolar Current, due to the lack of large landmasses breaking up the Southern Ocean
The Southern Ocean, also known as the Antarctic Ocean, comprises the southernmost waters of the World Ocean, generally taken to be south of 60° S latitude and encircling Antarctica. With a size of , it is regarded as the second-smal ...
. There are minor gyres in the Weddell Sea
The Weddell Sea is part of the Southern Ocean and contains the Weddell Gyre. Its land boundaries are defined by the bay formed from the coasts of Coats Land and the Antarctic Peninsula. The easternmost point is Cape Norvegia at Princess Mar ...
and the Ross Sea
The Ross Sea is a deep bay of the Southern Ocean in Antarctica, between Victoria Land and Marie Byrd Land and within the Ross Embayment, and is the southernmost sea on Earth. It derives its name from the British explorer James Clark Ross who vi ...
, the Weddell Gyre and Ross Gyre, which circulate in a clockwise direction.
Biological desert
 Gyres are sometimes described as "ocean deserts" or more precisely "biological deserts", a concept that uses the concept of desert in the sense of an environment lacking life and not necessarily water. Other places that are called oceanic deserts are hypoxic or anoxic waters such as dead zones.
Gyres are sometimes described as "ocean deserts" or more precisely "biological deserts", a concept that uses the concept of desert in the sense of an environment lacking life and not necessarily water. Other places that are called oceanic deserts are hypoxic or anoxic waters such as dead zones.
Climate change
Ocean circulation re-distributes the heat and water-resources, therefore determines the regional climate. For example, the western branches of the subtropical gyres flow from the lower latitudes towards higher latitudes, bringing relatively warm and moist air to the adjacent land, contributing to a mild and wet climate (e.g., East China, Japan). In contrast, the eastern boundary currents of the subtropical gyres streaming from the higher latitudes towards lower latitudes, corresponding to a relatively cold and dry climate (e.g., California). Currently, the core of the subtropical gyres are around 30° in both Hemispheres. However, their positions were not always there. Satellite observational sea surface height and sea surface temperature data suggest that the world's major ocean gyres are slowly moving towards higher latitudes in the past few decades. Such feature show agreement with climate model prediction under anthropogenic global warming. Paleo-climate reconstruction also suggest that during the past cold climate intervals, i.e., ice ages, some of the western boundary currents (western branches of the subtropical ocean gyres) are closer to the equator than their modern positions. These evidence implies that global warming is very likely to push the large-scale ocean gyres towards higher latitudes.''www.loe.org'', accessed 5 December 2021
The influence of the Coriolis effect on westward intensification

Pollution
See also
*Anticyclone
An anticyclone is a weather phenomenon defined as a large-scale circulation of winds around a central region of high atmospheric pressure, clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and counterclockwise in the Southern Hemisphere as viewed from abo ...
* Cyclone
* Ecosystem of the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre
* Eddy
* Fluid dynamics
In physics and engineering, fluid dynamics is a subdiscipline of fluid mechanics that describes the flow of fluids—liquids and gases. It has several subdisciplines, including '' aerodynamics'' (the study of air and other gases in motion) ...
* Geostrophic current
* Skookumchuck
* ''Volta do mar
, , or (the phrase in Portuguese means literally 'turn of the sea' but also 'return from the sea') is a navigational technique perfected by Portuguese navigators during the Age of Discovery in the late fifteenth century, using the dependable ...
''
* Whirlpool
References
External links
5 Gyres – Understanding Plastic Marine Pollution
SIO 210: Introduction to Physical Oceanography – Global circulation
SIO 210: Introduction to Physical Oceanography – Wind-forced circulation notes
North Pacific Gyre Oscillation
— Georgia Institute of Technology * {{Physical oceanography Aerodynamics Fluid dynamics Oceanic gyres Fisheries science