|
Inca Huasi (ancient Lake)
Inca Huasi was a paleolake in the Andes. It was named by a research team in 2006. It existed about 46,000 years ago in the Salar de Uyuni basin. Water levels during this episode rose by about . Overall, this lake cycle was short and not deep, with water levels reaching a height of . The lake would have had a surface of . Most water was contributed to it by the Uyuni-Coipasa drainage basin, with only minimal contributions from Lake Titicaca. Changes in the South American monsoon may have triggered its formation. Radiocarbon dates on tufa which formed in Lake Inca Huasi were dated at 45,760 ± 440 years ago. Uranium-thorium dating has yielded ages between 45,760 and 47,160 years. Overall the lake existed between 46,000 and 47,000 years ago. The Inca Huasi cycle coincides with the marine isotope stage 3, the formation of a deep lake in the Laguna Pozuelos basin and the expansion of glaciers in several parts of South America including the Puna. This lake cycle took part during a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleolake
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much larger oceans, they do form part of the Earth's water cycle. Lakes are distinct from lagoons, which are generally coastal parts of the ocean. Lakes are typically larger and deeper than ponds, which also lie on land, though there are no official or scientific definitions. Lakes can be contrasted with rivers or streams, which usually flow in a channel on land. Most lakes are fed and drained by rivers and streams. Natural lakes are generally found in mountainous areas, rift zones, and areas with ongoing glaciation. Other lakes are found in endorheic basins or along the courses of mature rivers, where a river channel has widened into a basin. Some parts of the world have many lakes formed by the chaotic drainage patterns left over from the last ic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
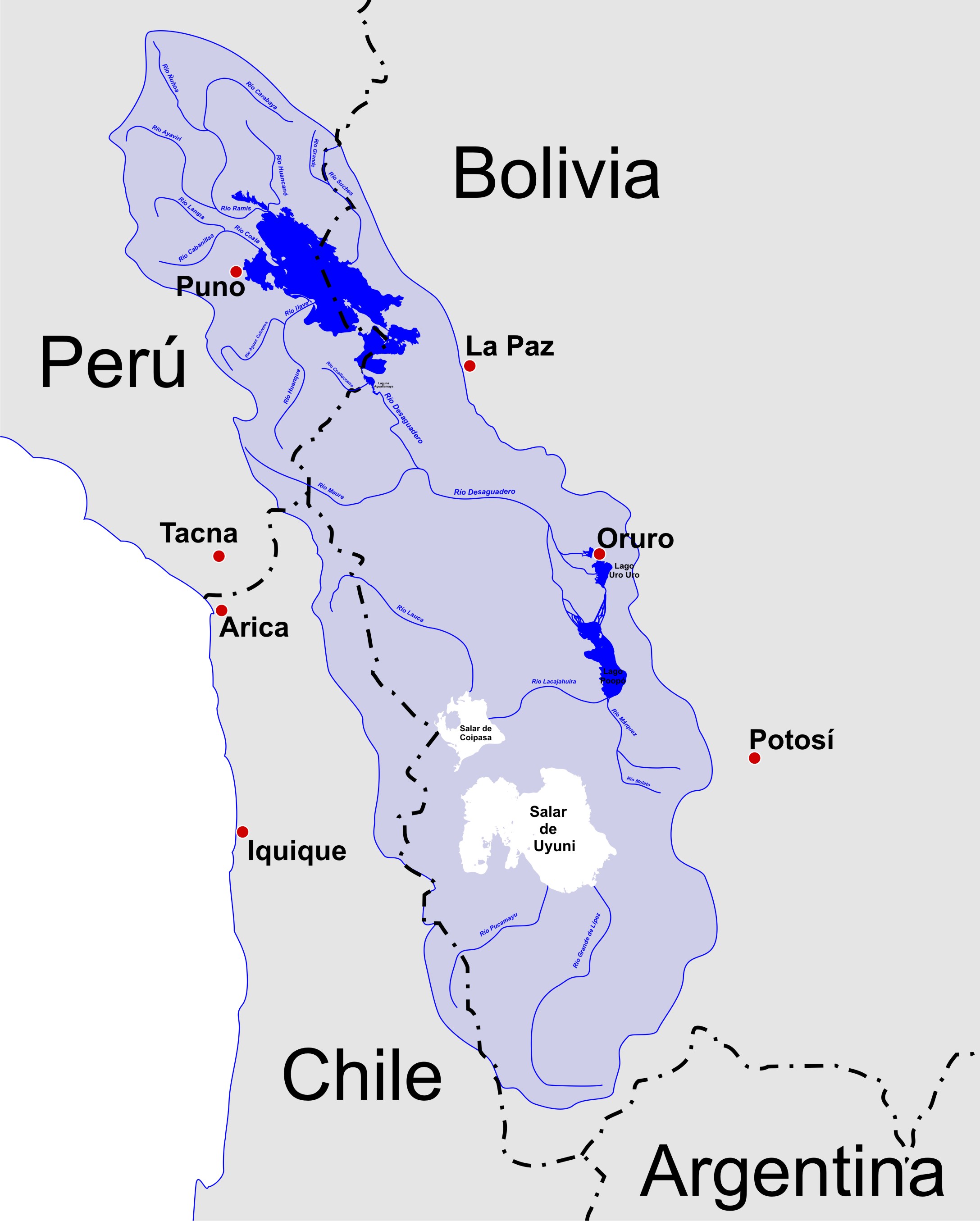
Altiplano
The Altiplano (Spanish for "high plain"), Collao (Quechua and Aymara: Qullaw, meaning "place of the Qulla") or Andean Plateau, in west-central South America, is the most extensive high plateau on Earth outside Tibet. The plateau is located at the latitude of the widest part of the north-south-trending Andes. The bulk of the Altiplano lies in Bolivia, but its northern parts lie in Peru, and its southwestern fringes lie in Chile. There are on the plateau several cities in each of these three nations, including El Alto, La Paz, Oruro, and Puno. The northeastern part of the Altiplano is more humid than the southwestern part, which has several salares (salt flats), due to its aridity. At the Bolivia–Peru border lies Lake Titicaca, the largest lake in South America. Farther south, in Bolivia, there was until recently a lake, Lake Poopó, but by December 2015 it had completely dried up, and was declared defunct. It is unclear whether that lake, which had been the second-largest in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of Bolivia
The geology of Bolivia comprises a variety of different lithologies as well as tectonic and sedimentary environments. On a synoptic scale, geological units coincide with topographical units. The country is divided into a mountainous western area affected by the subduction processes in the Pacific and an eastern lowlands of stable platforms and shields. The Bolivian Andes is divided into three main ranges; these are from west to east: the Cordillera Occidental that makes up the border to Chile and host several active volcanoes and geothermal areas, Cordillera Central (in some contexts also called Cordillera Oriental) once extensively mined for silver and tin and the relatively low Cordillera Oriental that rather than being a range by its own is the eastern continuation of the Central Cordillera as a fold and thrust belt. Between the Occidental and Central Cordillera the approximately 3,750-meter-high Altiplano high plateau extends. This basin hosts several freshwater lakes, incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Lakes Of South America
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being using in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft built until the ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quaternary International
''Quaternary International'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal on quaternary science published by Elsevier on behalf of the International Union for Quaternary Research. The journal was established in 1989 and covers full spectrum of the physical and natural sciences that are commonly employed in solving problems related to the quaternary period. The editor-in-chief is Min-Te Chen (National Taiwan Ocean University). According to the 2017 ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2016 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as ... of 2.199. References External links * Quaternary science journals English-language journals Elsevier academic journals Publications established in 1989 Journals published between 27 and 51 times per year Academic jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth And Planetary Science Letters
''Earth and Planetary Science Letters'' (EPSL) is a bimonthly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering research on physical, chemical and mechanical processes of the Earth and other planets, including extrasolar ones. Topics covered range from deep planetary interiors to atmospheres. The journal was established in 1966 and is published by Elsevier. The co-editors-in-chief are J. Adkins (California Institute of Technology), J.P. Avouac (California Institute of Technology), R. Bendick (University of Montana), L. Derry (Cornell University), M. Ishii (Harvard University), T.A. Mather (University of Oxford), W.B. McKinnon (Washington University in St. Louis), F. Moynier (Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris), Chiara Maria Petrone, Hans Thybo (Istanbul Technical University and University of Oslo), Alexander Webb. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor The impact facto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salinas (ancient Lake)
Salinas is a lake event in the Salar de Uyuni, Bolivia. The existence of this lake event is documented by tufa mounds which are up to high. It belongs to a series of ancient lakes which covered the southern Altiplano in Bolivia, reaching a maximum surface area of . This series includes several phases, two major phases named Lake Tauca and Ouki as well as a few minor ones. These lake phases appear to occur in response to increased moisture supply from the Amazon. The formation of the Salinas lake was probably accompanied by a 50-100% increase of precipitation. The Salinas event lasted between approximately 95,000 and 80,000 years ago. It was preceded by another lake event, Ouki. Alternatively, it may be part of the Ouki event, more specifically of its waning stage. The Ouki and Salinas lake cycles coincided with cooling events in the North Atlantic, glacier expansions in the Puna and with changes to alluvial fans at Llano de Chajnantor. During the Salinas lake cycle, lake levels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Minchin
Lake Minchin is a name of an ancient lake in the Altiplano of South America. It existed where today the Salar de Uyuni, Salar de Coipasa and Lake Poopó lie. It was formerly considered the highest lake in the Altiplano but research indicated that the highest shoreline belongs to the later Lake Tauca instead. The concept of a "Lake Minchin" was first coined in 1906 and the name is based on John B. Minchin. The dating of the lake varies but probably lasted until 22,000 – 21,000 BP. A glacier advance was in progress in the Andes during that time period. The name "Minchin" has also been used in other contexts, and it has been proposed that the lake was actually a combination of several different paleolakes. Definition The name "Lake Minchin" has been used inconsistently to refer to either a lake existing 45,000 years ago, the highest lake in the Altiplano, or to sediment formations. This confusion has led to calls to drop the usage of the name "Minchin". An alternative theory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ouki
Ouki was an ancient lake in the Bolivian Altiplano. Its existence was postulated in 2006 by a group of scientists which had subdivided the Lake Minchin lake cycle in several subcycles. The Lake Minchin cycle had been previously identified in 1904 as a now disappeared lake in the central Altiplano. Sediments attributed to Lake Minchin may be part of Ouki instead. The dating is uncertain, with radiocarbon and uranium-thorium dating yielding different dates spanning the time between 28,200 and 125,990 ± 9,580 years ago. Whether Ouki existed is a subject of controversy. In 2011, scientists claimed that the lake did not exist outside of the Lake Poopo basin. The formation of Ouki is associated with a major glaciation and was probably caused by increased precipitation, which has also been observed elsewhere. General characteristics Ouki reached a water level of approximately with preserved shorelines at Lake Poopó, and it may have covered the Salar de Uyuni, the Salar de Coipasa a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glacier
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its Ablation#Glaciology, ablation over many years, often Century, centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as Crevasse, crevasses and Serac, seracs, as it slowly flows and deforms under stresses induced by its weight. As it moves, it abrades rock and debris from its substrate to create landforms such as cirques, moraines, or fjords. Although a glacier may flow into a body of water, it forms only on land and is distinct from the much thinner sea ice and lake ice that form on the surface of bodies of water. On Earth, 99% of glacial ice is contained within vast ice sheets (also known as "continental glaciers") in the polar regions, but glaciers may be found in mountain ranges on every continent other than the Australian mainland, including Oceania's high-latitude oceanic island countries such as New Zealand. Between lati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andes
The Andes, Andes Mountains or Andean Mountains (; ) are the longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is long, wide (widest between 18°S – 20°S latitude), and has an average height of about . The Andes extend from north to south through seven South American countries: Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Chile, and Argentina. Along their length, the Andes are split into several ranges, separated by intermediate depressions. The Andes are the location of several high plateaus—some of which host major cities such as Quito, Bogotá, Cali, Arequipa, Medellín, Bucaramanga, Sucre, Mérida, El Alto and La Paz. The Altiplano plateau is the world's second-highest after the Tibetan plateau. These ranges are in turn grouped into three major divisions based on climate: the Tropical Andes, the Dry Andes, and the Wet Andes. The Andes Mountains are the highest m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laguna Pozuelos
Laguna (Italian and Spanish for lagoon) may refer to: People * Abe Laguna (born 1992), American DJ known as Ookay * Andrés Laguna (1499–1559), Spanish physician, pharmacologist, and botanist * Ana Laguna (born 1955), Spanish-Swedish ballet dancer, court dancer and professor * Benjamín Máximo Laguna y Villanueva (1822–1902), Spanish forester * Frederica de Laguna (1906–2004), American anthropologist * Fábio Laguna (born 1977), Brazilian keyboardist * Grace de Laguna (1878–1978), American philosopher * Ieva Lagūna (born 1990), Latvian model * Jorge Laguna (born 1993), Mexican footballer * José Dapena Laguna (1912–1991), Puerto Rican politician - mayor of Ponce, Puerto Rico * José Durand Laguna (1889–1958), Argentine football manager * Justo Oscar Laguna (1929–2011), Argentinian bishop * Kenny Laguna (born 1948), American songwriter and record producer * Ricardo Laguna (born 1982), Mexican-American professional BMX rider and television personality * Theodore de L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)