|
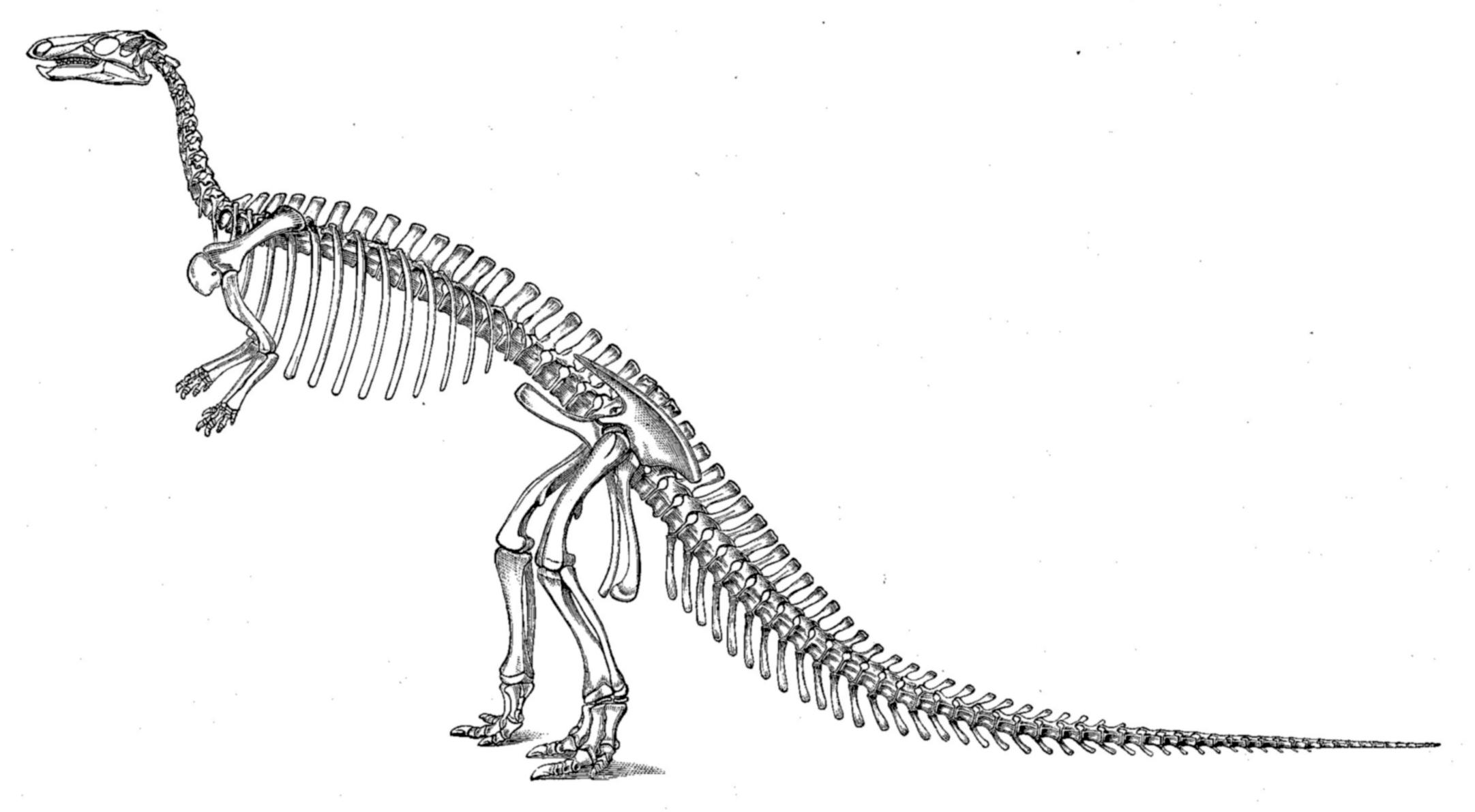
Iguanodont
Iguanodontia (the iguanodonts) is a clade of herbivorous dinosaurs that lived from the Middle Jurassic to Late Cretaceous. Some members include ''Camptosaurus'', ''Dryosaurus'', ''Iguanodon'', ''Tenontosaurus'', and the hadrosaurids or "duck-billed dinosaurs". Iguanodontians were one of the first groups of dinosaurs to be found. They are among the best known of the dinosaurs, and were among the most diverse and widespread herbivorous dinosaur groups of the Cretaceous period. Classification Iguanodontia is often listed as an infraorder within a suborder Ornithopoda, though Benton (2004) lists Ornithopoda as an infraorder and does not rank Iguanodontia. Traditionally, iguanodontians were grouped into the superfamily Iguanodontoidea and family Iguanodontidae. However, phylogenetic studies show that the traditional "iguanodontids" are a paraphyletic grade leading up to the hadrosaurs (duck-billed dinosaurs). Groups like Iguanodontoidea are sometimes still used as unranked clades in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iguanodon
''Iguanodon'' ( ; meaning 'iguana-tooth'), named in 1825, is a genus of iguanodontian dinosaur. While many species have been classified in the genus ''Iguanodon'', dating from the late Jurassic Period to the early Cretaceous Period of Asia, Europe, and North America, taxonomic revision in the early 21st century has defined ''Iguanodon'' to be based on one well-substantiated species: ''I. bernissartensis'', which lived from the late Barremian to the earliest Aptian ages ( Early Cretaceous) in Belgium, Germany, England, Spain, and possibly elsewhere in Europe, between about 126 and 122 million years ago. ''Iguanodon'' was a large, bulky herbivore, measuring up to in length and in body mass. Distinctive features include large thumb spikes, which were possibly used for defense against predators, combined with long prehensile fifth fingers able to forage for food. The genus was named in 1825 by English geologist Gideon Mantell but discovered by William Harding Bensted, bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iguanodontidae
Iguanodontidae is a family of iguanodontians belonging to Styracosterna, a derived clade within Ankylopollexia. Characterized by their elongated maxillae, they were herbivorous and typically large in size. This family exhibited locomotive dynamism; there exists evidence for both bipedalism and quadrupedalism within iguanodontid species, supporting the idea that individual organisms were capable of both locomoting exclusively with their hind limbs and locomoting quadrupedally. Iguanodontids possess hoof-like second, third, and fourth digits, and in some cases, a specialized thumb spike and an opposable fifth digit. Their skull construction allows for a strong chewing mechanism called a transverse power stroke. This, paired with their bilateral dental occlusion, made them extremely effective as herbivores. Members of Iguanodontidae are thought to have had a diet that consisted of both gymnosperms and angiosperms, the latter of which co-evolved with the iguanodontids in the Cretac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ankylopollexia
Ankylopollexia is an extinct clade of ornithischian dinosaurs that lived from the Late Jurassic to the Late Cretaceous. It is a derived clade of iguanodontian ornithopods and contains the subgroup Styracosterna. The name stems from the Greek word, “ankylos”, mistakenly taken to mean stiff, fused (in fact the adjective means bent or curved; used of fingers, it can mean hooked), and the Latin word, “pollex”, meaning thumb. Originally described in 1986 by Sereno, a most likely synapomorphic feature of a conical thumb spine defines the clade.Sereno, P.C. (1986). "Phylogeny of the bird-hipped dinosaurs (order Ornithischia)". National Geographic Research 2 (2): 234–56 First appearing around 156 million years ago, in the Jurassic, Ankylopollexia became an extremely successful and widespread clade during the Cretaceous, and were found around the world. The group died out at the end of the Maastrichtian. They grew to be quite large, comparable to some carnivorous dinosaurs and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camptosaurus
''Camptosaurus'' ( ) is a genus of plant-eating, beaked ornithischian dinosaurs of the Late Jurassic period of western North America and possibly also Europe. The name means 'flexible lizard' (Greek (') meaning 'bent' and (') meaning 'lizard'). Description ''Camptosaurus'' is a relatively heavily built form, with robust hindlimbs and broad feet, still having four toes. Due to the separate status of ''Uteodon'' it has become problematic which material from the Morrison Formation belongs to ''Camptosaurus''. The specimens with certainty belonging to ''Camptosaurus dispar'', from Quarry 13, have been recovered from very deep layers, probably dating to the Callovian- Oxfordian. The largest fragments from later strata indicate adult individuals more than long, and at the hips. The Quarry 13 individuals are smaller though. They have been described as reaching 6 meters (19.7 feet) in length and 785 – 874 kg in weight.Foster, J. (2007). "''Camptosaurus dispar''." ''Jura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camptosaurus Fruita
''Camptosaurus'' ( ) is a genus of plant-eating, beaked ornithischian dinosaurs of the Late Jurassic period of western North America and possibly also Europe. The name means 'flexible lizard' (Greek (') meaning 'bent' and (') meaning 'lizard'). Description ''Camptosaurus'' is a relatively heavily built form, with robust hindlimbs and broad feet, still having four toes. Due to the separate status of ''Uteodon'' it has become problematic which material from the Morrison Formation belongs to ''Camptosaurus''. The specimens with certainty belonging to ''Camptosaurus dispar'', from Quarry 13, have been recovered from very deep layers, probably dating to the Callovian- Oxfordian. The largest fragments from later strata indicate adult individuals more than long, and at the hips. The Quarry 13 individuals are smaller though. They have been described as reaching 6 meters (19.7 feet) in length and 785 – 874 kg in weight.Foster, J. (2007). "''Camptosaurus dispar''." ''Jura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhabdodontomorpha
Rhabdodontomorpha is a clade of basal iguanodont dinosaurs. This group was named in 2016 in the context of the description, based on Spanish findings of an early member of the Rhabdodontidae. A cladistic analysis was conducted in which it was found that ''Muttaburrasaurus'' was the sister species of the Rhabdodontidae ''sensu'' Weishampel. Therefore, Paul-Emile Dieudonné, Thierry Tortosa, Fidel Torcida Fernández-Baldor, José Ignacio Canudo and Ignacio Díaz-Martínez defined Rhabdodontomorpha as a nodal clade: the group consisting of the last common ancestor of ''Rhabdodon priscus'' Matheron, 1869 and ''Muttaburrasaurus langdoni'' Bartholomai and Molnar, 1981; and all its descendants. Within the clade ''Zalmoxes'' and ''Mochlodon'' are also included. The clade is characterized by the following synapomorphies: * the outline of the dorsal iliac margin is sigmoidal in dorsal view, with the postacetabular process deflected medialward and the pre-acetabular process deflected latera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is the subject of active research. They became the dominant terrestrial vertebrates after the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event 201.3 mya; their dominance continued throughout the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. The fossil record shows that birds are feathered dinosaurs, having evolved from earlier theropods during the Late Jurassic epoch, and are the only dinosaur lineage known to have survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event approximately 66 mya. Dinosaurs can therefore be divided into avian dinosaurs—birds—and the extinct non-avian dinosaurs, which are all dinosaurs other than birds. Dinosaurs are varied from taxonomic, morphological and ecological standpoints. Birds, at over 10,700 living species, are among ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadrosaurid
Hadrosaurids (), or duck-billed dinosaurs, are members of the ornithischian family Hadrosauridae. This group is known as the duck-billed dinosaurs for the flat duck-bill appearance of the bones in their snouts. The ornithopod family, which includes genera such as ''Edmontosaurus'' and '' Parasaurolophus'', was a common group of herbivores during the Late Cretaceous Period. Hadrosaurids are descendants of the Upper Jurassic/Lower Cretaceous iguanodontian dinosaurs and had a similar body layout. Hadrosaurs were among the most dominant herbivores during the Late Cretaceous in Asia and North America, and during the close of the Cretaceous several lineages dispersed into Europe, Africa, South America and Antarctica. Like other ornithischians, hadrosaurids had a predentary bone and a pubic bone which was positioned backwards in the pelvis. Unlike more primitive iguanodonts, the teeth of hadrosaurids are stacked into complex structures known as dental batteries, which acted as effectiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syngonosaurus
''Syngonosaurus'' is an extinct genus of ornithopod dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous. It was an iguanodontian discovered in England and was first described in 1879. The type species, ''S. macrocercus'', was described by British paleontologist Harry Seeley in 1879 and it was later synonymised with ''Acanthopholis'', but the genus was reinstated in a 2020 study, when ''Syngonosaurus'' and ''Eucercosaurus'' were reinterpreted as basal iguanodontians. History In 1869 Harry Govier Seeley named several new species of ''Acanthopholis'' based on remains from the Cambridge Greensand: ''Acanthopholis macrocercus'', based on specimens CAMSM B55570-55609; ''Acanthopholis platypus'' (CAMSM B55454-55461); and ''Acanthopholis stereocercus'' (CAMSM B55558 55569). Later, Seeley split the material of ''Acanthopholis stereocercus'' and based a new species of ''Anoplosaurus'' on part of it: ''Anoplosaurus major''. He also described a new species, ''Acanthopholis eucercus'', on the basis of six ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Owenodon
''Owenodon'' is a genus of iguanodontian dinosaur known from a partial lower jaw discovered in Early Cretaceous-age rocks of Durlston Bay, Dorset, United Kingdom. The specimen, NHM R2998, comes from the Purbeck Limestone, dating to the middle Berriasian stage (approximately 143 million years ago). It was first described by Richard Owen, who in 1874 assigned it to ''Iguanodon'' as the type specimen of the new species ''I. hoggii'', the specific name honouring naturalist A.J. Hogg who had originally collected the fossil in 1860. The bone was damaged during initial preparation but was freed from the surrounding rock matrix by an acid bath between 1975 and 1977. David Norman and Paul Barrett subsequently transferred the species to ''Camptosaurus'' in 2002, but this was challenged, and in 2009 Peter Galton assigned the species to the new genus ''Owenodon'', meaning "Owen's tooth", named after Sir Richard Owen. Galton interpreted the genus as an iguanodontoid more derived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadrosauridae
Hadrosaurids (), or duck-billed dinosaurs, are members of the ornithischian family Hadrosauridae. This group is known as the duck-billed dinosaurs for the flat duck-bill appearance of the bones in their snouts. The ornithopod family, which includes genera such as ''Edmontosaurus'' and ''Parasaurolophus'', was a common group of herbivores during the Late Cretaceous Period. Hadrosaurids are descendants of the Upper Jurassic/Lower Cretaceous iguanodontian dinosaurs and had a similar body layout. Hadrosaurs were among the most dominant herbivores during the Late Cretaceous in Asia and North America, and during the close of the Cretaceous several lineages dispersed into Europe, Africa, South America and Antarctica. Like other ornithischians, hadrosaurids had a predentary bone and a pubic bone which was positioned backwards in the pelvis. Unlike more primitive iguanodonts, the teeth of hadrosaurids are stacked into complex structures known as dental batteries, which acted as effective g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tenontosaurus
''Tenontosaurus'' ( ; ) is a genus of medium- to large-sized ornithopod dinosaur. It was a relatively medium sized ornithopod, reaching in length and in body mass. It had an unusually long, broad tail, which like its back was stiffened with a network of bony tendons. The genus is known from the late Aptian to Albian ages of the Early Cretaceous period sediments of western North America, dating between 115 and 108 million years ago. It contains two species, ''Tenontosaurus tilletti'' (described by John Ostrom in 1970) and ''Tenontosaurus dossi'' (described by Winkler, Murry, and Jacobs in 1997). Many specimens of ''T. tilletti'' have been collected from several geological formations throughout western North America. ''T. dossi'' is known from only a handful of specimens collected from the Twin Mountains Formation of Parker County, Texas. History of discovery The first ''Tenontosaurus'' fossil was found in Big Horn County, Montana by an American Museum of Natural Histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |