|
Ida Hedevig Moltke
Ida Hedevig von Moltke née von Buchwaldt (1744–1816) was a Danish countess of German origin and a letter writer. Life She was born to German nobleman Frederik von Buchwald and Henriette Emilie von Holstein and became the cousin of Amalie Sofie von Holstein and sister-in-law of Count Johann Hartwig Ernst von Bernstorff. In 1760, she married the courtier Count Christian Frederik von Moltke (1736–1771). The court office of her first spouse made her a participator in Danish court life, where she became known for her love life. While her spouse was the lover of Elisabet von Eyben, she had an affair with the Spanish envoy Sebastian de Llano y la Quadra. Although her spouse was on the queen's side against the king's favorite Conrad Holck, he lost his office in 1771 and the couple had to leave court. When Moltke died shortly after, a scandal occurred when his widow was accused of having caused his death by infecting him with a venereal disease, by having caused him to commit su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
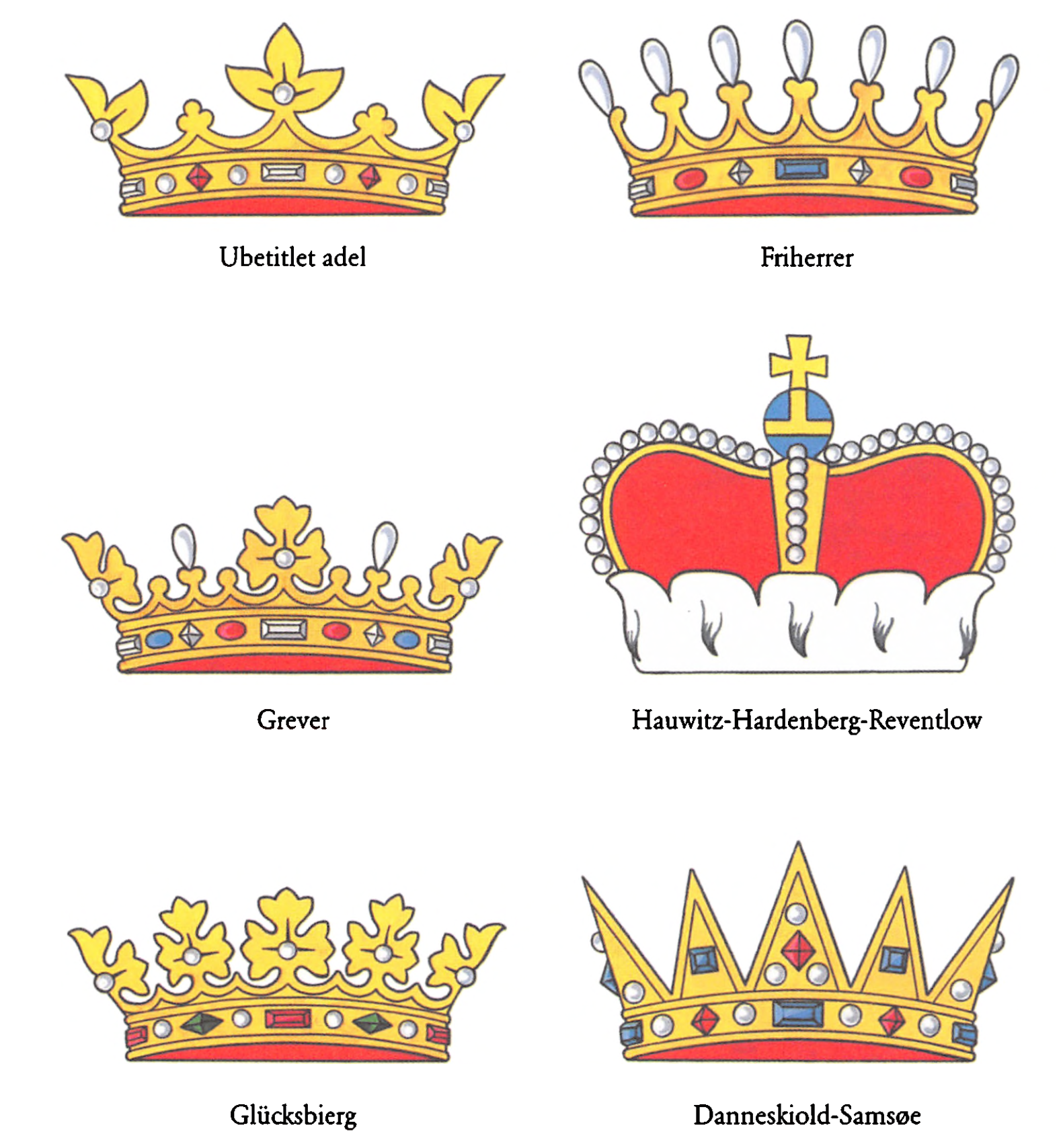
Danish Nobility
Danish nobility is a social class and a former estate in the Kingdom of Denmark. The nobility has official recognition in Denmark, a monarchy. Its legal privileges were abolished with the constitution of 1849. Some of the families still own and reside in castles or country houses. A minority of nobles still belong to the elite, and they are as such present at royal events where they hold court posts, are guests, or are objects of media coverage, for example Kanal 4's TV-hostess Caroline Fleming née Baroness Iuel-Brockdorff. Some of them own and manage companies or have leading positions within business, banking, diplomacy and NGOs. Historians divide the Danish nobility into two categories: ancient nobility ( da, uradel) and letter nobility ( da, brevadel) based on the way they achieved nobility. Another status based categorization distinguishes between higher and lower nobility ( da, højadel, lavadel). "Ancient nobility" refer to those noble families that are known from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luise Gramm
Frederikke Louise Stolberg, also known as Luise Gramm (August 21, 1746–November 29, 1824) was a Danish saloniste, playwright and letter writer. She is contributed with a certain degree of political influence upon various power holders in the policy of Denmark and Germany; she participated in the 1784 coup in Denmark. Her preserved correspondence is regarded as a valuable historic source about the courtiers of the Danish royal court of her time. Life She was born to count Christian Ditlev Reventlow (1710-1775) and Johanne Sophie Frederikke von Bothmer (1718-1754). Court life In 1761, she married the courtier nobleman Christian Frederik von Gram (1737-1768). The social position of her first spouse made her a participator in Danish Royal Court life. She was one of the few people Queen Caroline Matilda befriended prior to the banishment of her favorite Louise von Plessen. Reportedly, Gramm acted as a form of channel between the queen in her isolation with Louise von Plessen, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18th-century Danish Women Writers
The 18th century lasted from January 1, 1701 (Roman numerals, MDCCI) to December 31, 1800 (Roman numerals, MDCCC). During the 18th century, elements of Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment thinking culminated in the American Revolution, American, French Revolution, French, and Haitian Revolution, Haitian Revolutions. During the century, History of slavery, slave trading and human trafficking expanded across the shores of the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, while declining in Russian Empire, Russia, Qing dynasty, China, and Joseon, Korea. Revolutions began to challenge the legitimacy of monarchical and aristocratic power structures, including the structures and beliefs that Proslavery, supported slavery. The Industrial Revolution began during mid-century, leading to radical changes in Society, human society and the Natural environment, environment. Western historians have occasionally defined the 18th century otherwise for the purposes of their work. For example, the "short" 18th cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
19th-century Danish Writers
The 19th (nineteenth) century began on 1 January 1801 ( MDCCCI), and ended on 31 December 1900 ( MCM). The 19th century was the ninth century of the 2nd millennium. The 19th century was characterized by vast social upheaval. Slavery was abolished in much of Europe and the Americas. The First Industrial Revolution, though it began in the late 18th century, expanding beyond its British homeland for the first time during this century, particularly remaking the economies and societies of the Low Countries, the Rhineland, Northern Italy, and the Northeastern United States. A few decades later, the Second Industrial Revolution led to ever more massive urbanization and much higher levels of productivity, profit, and prosperity, a pattern that continued into the 20th century. The Islamic gunpowder empires fell into decline and European imperialism brought much of South Asia, Southeast Asia, and almost all of Africa under colonial rule. It was also marked by the collapse of the large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18th-century Danish Letter Writers
The 18th century lasted from January 1, 1701 ( MDCCI) to December 31, 1800 ( MDCCC). During the 18th century, elements of Enlightenment thinking culminated in the American, French, and Haitian Revolutions. During the century, slave trading and human trafficking expanded across the shores of the Atlantic, while declining in Russia, China, and Korea. Revolutions began to challenge the legitimacy of monarchical and aristocratic power structures, including the structures and beliefs that supported slavery. The Industrial Revolution began during mid-century, leading to radical changes in human society and the environment. Western historians have occasionally defined the 18th century otherwise for the purposes of their work. For example, the "short" 18th century may be defined as 1715–1789, denoting the period of time between the death of Louis XIV of France and the start of the French Revolution, with an emphasis on directly interconnected events. To historians who expand the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18th-century Danish People
The 18th century lasted from January 1, 1701 ( MDCCI) to December 31, 1800 ( MDCCC). During the 18th century, elements of Enlightenment thinking culminated in the American, French, and Haitian Revolutions. During the century, slave trading and human trafficking expanded across the shores of the Atlantic, while declining in Russia, China, and Korea. Revolutions began to challenge the legitimacy of monarchical and aristocratic power structures, including the structures and beliefs that supported slavery. The Industrial Revolution began during mid-century, leading to radical changes in human society and the environment. Western historians have occasionally defined the 18th century otherwise for the purposes of their work. For example, the "short" 18th century may be defined as 1715–1789, denoting the period of time between the death of Louis XIV of France and the start of the French Revolution, with an emphasis on directly interconnected events. To historians who expand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1816 Deaths
This year was known as the ''Year Without a Summer'', because of low temperatures in the Northern Hemisphere, possibly the result of the Mount Tambora volcanic eruption in Indonesia in 1815, causing severe global cooling, catastrophic in some locations. Events January–March * December 25 1815–January 6 – Tsar Alexander I of Russia signs an order, expelling the Jesuits from St. Petersburg and Moscow. * January 9 – Sir Humphry Davy's Davy lamp is first tested underground as a coal mining safety lamp, at Hebburn Colliery in northeast England. * January 17 – Fire nearly destroys the city of St. John's, Newfoundland. * February 10 – Friedrich Karl Ludwig, Duke of Schleswig-Holstein-Sonderburg-Beck, dies and is succeeded by Friedrich Wilhelm, his son and founder of the House of Glücksburg. * February 20 – Gioachino Rossini's opera buffa ''The Barber of Seville'' premières at the Teatro Argentina in Rome. * March 1 – The Gorkha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1744 Births
Events January–March * January 6 – The Royal Navy ship ''Bacchus'' engages the Spanish Navy privateer ''Begona'', and sinks it; 90 of the 120 Spanish sailors die, but 30 of the crew are rescued. * January 24 – The Dagohoy rebellion in the Philippines begins, with the killing of Father Giuseppe Lamberti. * February – Violent storms frustrate a planned French invasion of Britain. * February 22– 23 – Battle of Toulon: The British fleet is defeated by a joint Franco-Spanish fleet. * March 1 (approximately) – The Great Comet of 1744, one of the brightest ever seen, reaches perihelion. * March 13 – The British ship ''Betty'' capsizes and sinks off of the Gold Coast (modern-day Ghana) near Anomabu. More than 200 people on board die, although there are a few survivors. * March 15 – France declares war on Great Britain. April–June * April – ''The Female Spectator'' (a monthly) is founded by Eliza Haywood in E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enevold Brandt
Count Enevold Brandt (1738 - 28 April 1772) was a Danish courtier. Biography Brandt was born in Copenhagen, and studied law at the University of Copenhagen. He became assistant judge of the Supreme Court of Copenhagen in 1764, royal chamberlain in 1769, and afterwards superintendent of the Royal Theatre. In 1770, he replaced Conrad Holck as the companion and favorite of King Christian VII after the intervention of Struensee, who became his friend and de facto ruler of Denmark the same year.August Fjelstrup: Damerne ved Karoline Mathildes Hof, 1909. Brandt had a relationship with Amalie Sophie Holstein, used his position with the king to pay off her gambling debts, and in practice left the position as the king's caretaker to Élie Salomon François Reverdil for her. Struensee disliked her because she allegedly made Brandt defiant toward him, and as her spouse proved himself not useful as a politician, the Holstein couple was allowed to stay at court because of Brandt.August ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germans
, native_name_lang = de , region1 = , pop1 = 72,650,269 , region2 = , pop2 = 534,000 , region3 = , pop3 = 157,000 3,322,405 , region4 = , pop4 = 21,000 3,000,000 , region5 = , pop5 = 125,000 982,226 , region6 = , pop6 = 900,000 , region7 = , pop7 = 142,000 840,000 , region8 = , pop8 = 9,000 500,000 , region9 = , pop9 = 357,000 , region10 = , pop10 = 310,000 , region11 = , pop11 = 36,000 250,000 , region12 = , pop12 = 25,000 200,000 , region13 = , pop13 = 233,000 , region14 = , pop14 = 211,000 , region15 = , pop15 = 203,000 , region16 = , pop16 = 201,000 , region17 = , pop17 = 101,000 148,00 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schack Carl Rantzau–Ascheberg
Schack Carl, ''rigsgreve'' (von) Rantzau or Carl Schack Rantzau-Ascheberg (11 March 1717, Ascheberg estate, Holstein – 21 January 1789, Menerbes, France) was a Holstein-born Danish-Norwegian officer and statesman. He was the commander-in-chief of the Norwegian army in 1766, but lost the position the next year. He is notable for his friendship with Johann Friedrich Struensee and his role in the coup which led to Struensee's fall from power in 1772. Commander-in-chief of the Norwegian army In the 1760s he befriended Claude Louis de Saint-Germain, one of the most powerful men in Denmark-Norway at the time. In 1766 he was promoted to lieutenant general Lieutenant general (Lt Gen, LTG and similar) is a three-star military rank (NATO code OF-8) used in many countries. The rank traces its origins to the Middle Ages, where the title of lieutenant general was held by the second-in-command on the ..., and on the initiative of Saint-Germain he was sent as Commander-in-chief ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conrad Holck
Frederik Vilhelm Conrad Holck (1745–1800) was a Danish nobleman and courtier. Biography Holck was the son of Major General Christian Christopher Holck til Orebygård (1698–1774) and Ermegaard Sophie Winterfeldt (1702–56). He was raised on the family estate at Guldborgsund. He came to court as a chamber page at a young age. Holck was a favorite companion of king Christian VII of Denmark during the first years of his reign, and were regarded to have a bad influence upon the monarch by encouraging him in decadent pleasures and by distancing him from his consort Queen Caroline Matilda He was appointed Chamberlain in 1767 and Privy Councilor (''geheimeråd'') in 1769. In 1770, however, he was removed from court upon the influence of royal physician Johann Friedrich Struensee and replaced by Royal Chamberlain Enevold Brandt. In 1789, he obtained the office of county governor over Kiel, Cronshagen and Bordesholm. The remainder of his life was spent at Kiel Kiel () is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |