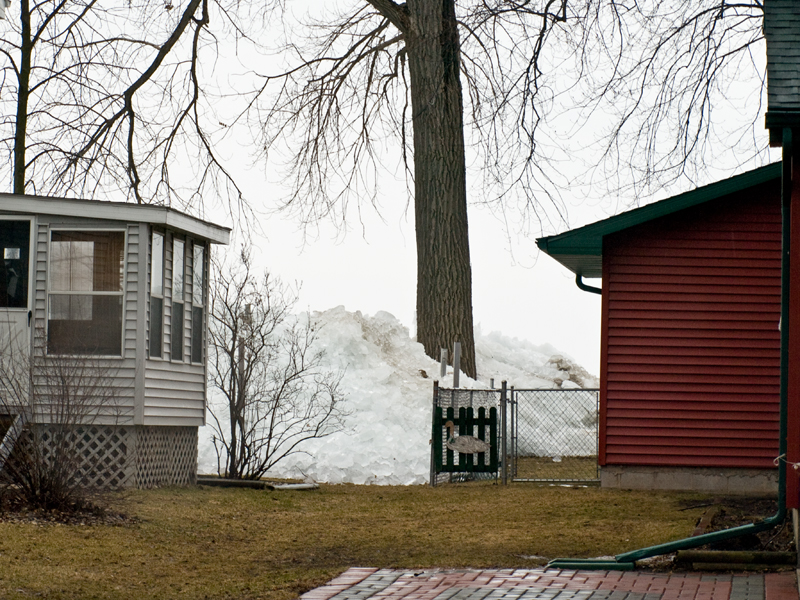|
Ice Shove
An ice shove (also known as an ice surge, ice push, ice heave, shoreline ice pileup, ice piling, ice thrust, ice tsunami, ice ride-up, or ''ivu'' in Inupiat) is a surge of ice from an ocean or large lake onto the shore. Ice shoves are caused by ocean currents, strong winds, or temperature differences pushing ice onto the shore, creating piles up to 12 metres (40 feet) high. Ice shoves can be caused by temperature fluctuations, wind action, or changing water levels and can cause devastation to coastal Arctic communities. Climate change will also play a role in the formation and frequency of ice shove events; a rise in global temperatures leads to more open water to facilitate ice movement and low pressure systems to destabilize ice sheets and send them shoreward. Causes Temperature fluctuations When temperatures decrease, ice contracts and forms stress fractures; water then seeps into these tension cracks and freezes. When temperatures rise, the ice sheet expands. This seq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice Shove
An ice shove (also known as an ice surge, ice push, ice heave, shoreline ice pileup, ice piling, ice thrust, ice tsunami, ice ride-up, or ''ivu'' in Inupiat) is a surge of ice from an ocean or large lake onto the shore. Ice shoves are caused by ocean currents, strong winds, or temperature differences pushing ice onto the shore, creating piles up to 12 metres (40 feet) high. Ice shoves can be caused by temperature fluctuations, wind action, or changing water levels and can cause devastation to coastal Arctic communities. Climate change will also play a role in the formation and frequency of ice shove events; a rise in global temperatures leads to more open water to facilitate ice movement and low pressure systems to destabilize ice sheets and send them shoreward. Causes Temperature fluctuations When temperatures decrease, ice contracts and forms stress fractures; water then seeps into these tension cracks and freezes. When temperatures rise, the ice sheet expands. This seq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beaufort Sea
The Beaufort Sea (; french: Mer de Beaufort, Iñupiaq: ''Taġiuq'') is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located north of the Northwest Territories, the Yukon, and Alaska, and west of Canada's Arctic islands. The sea is named after Sir Francis Beaufort, a hydrographer. The Mackenzie River, the longest in Canada, empties into the Canadian part of the Beaufort Sea west of Tuktoyaktuk, which is one of the few permanent settlements on the sea's shores. The sea, characterized by severe climate, is frozen over most of the year. Historically, only a narrow pass up to opened in August–September near its shores, but recently due to climate change in the Arctic the ice-free area in late summer has greatly enlarged. Until recently, the Beaufort Sea was known as an important reservoir for the replenishment of Arctic sea ice. Sea ice would often rotate for several years in the Beaufort Gyre, the dominant ocean current of the Beaufort Sea, growing into sturdy and thick multi-ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind Fetch
In oceanography wind fetch, also known as fetch length or simply fetch, is the length of water over which a given wind has blown without obstruction. Fetch is used in geography and meteorology and its effects are usually associated with sea state and when it reaches shore it is the main factor that creates storm surge which leads to coastal erosion and flooding. It also plays a large part in longshore drift. Fetch length, along with the wind speed (wind strength), and duration, determines the size ( sea state) of waves produced. If the wind direction is constant, the longer the fetch and the greater the wind speed, the more wind energy is transferred to the water surface and the larger the resulting sea state will be.''November's fury'' by Michael Schumaker University of Minnesota Press Sea state will increase over time until local energy dissipation balances energy transfer to the water from the wind and a fully developed sea results. See also * Gale * Sea state * O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arctic Sea Ice Decline
Arctic sea ice decline has occurred in recent decades due to the effects of climate change on oceans, with declines in sea ice area, extent, and volume. Sea ice in the Arctic Ocean has been melting more in summer than it refreezes in the winter. Global warming, caused by greenhouse gas forcing is responsible for the decline in Arctic sea ice. The decline of sea ice in the Arctic has been accelerating during the early twenty‐first century, with a decline rate of minus 4.7% per decade (it has declined over 50% since the first satellite records). It is also thought that summertime sea ice will cease to exist sometime during the 21st century. This sea ice loss is one of the main drivers of surface-based Arctic amplification. Sea ice area means the total area covered by ice, whereas sea ice extent is the area of ocean with at least 15% sea ice, while the volume is the total amount of ice in the Arctic. The region is at its warmest in at least 4,000 years and the Arctic-wide melt s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beaufort Gyre
The Beaufort Gyre is one of the two major ocean currents in the Arctic Ocean. It is roughly located north of the Alaskan and Canadian coast. In the past, Arctic sea-ice would circulate in the Beaufort gyre up to several years, leading to the formation of very thick multi-year sea-ice. Due to warming temperatures in the Arctic, the gyre has lost an extensive amount of ice, practically turning what used to be a nursery for sea-ice to mature and grow into the thickest and oldest ice of the Arctic Ocean into a "graveyard" for older ice. Dynamical mechanisms Conditions in the Arctic have favored sea ice loss in recent years during the Northern Hemisphere summers. At the end of the 20th century, analyses of increasing Pacific Surface Water temperatures led to the discovery of a connection between these rising temperatures and the onset of severe loss of Arctic sea ice in the Beaufort Sea. A reason for the existence of this link was proposed: "...delayed winter ice formation allows for m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transpolar Drift Stream
The Transpolar Drift Stream is a major ocean current of the Arctic Ocean, transporting sea ice from the Laptev Sea and the East Siberian Sea towards Fram Strait. Drift experiments with ships such as the Fram or the Tara expedition showed that the drift takes between two and four years. In 1937, Pyotr Shirshov at the Soviet drift ice station North Pole-1 described this drift. The stream conveys water in roughly two major routes to the northern Atlantic Ocean at a rate of about per day. Primarily wind-driven, it flows roughly from the northern coast of Russia and Alaska, sometimes curving toward the Beaufort Sea before exiting to the Atlantic Ocean. It has been cited as a major factor in the North Atlantic oscillation and Arctic oscillation The Arctic oscillation (AO) or Northern Annular Mode/Northern Hemisphere Annular Mode (NAM) is a weather phenomenon at the Arctic pole north of 20 degrees latitude. It is an important mode of climate variability for the Northern Hemisphe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drift Ice
Drift ice, also called brash ice, is sea ice that is not attached to the shoreline or any other fixed object (shoals, grounded icebergs, etc.).Leppäranta, M. 2011. The Drift of Sea Ice. Berlin: Springer-Verlag. Unlike fast ice, which is "fastened" to a fixed object, drift ice is carried along by winds and sea currents, hence its name. When drift ice is driven together into a large single mass (>70% coverage), it is called pack ice. Wind and currents can pile up that ice to form ridges up to tens of metres in thickness. These represent a challenge for icebreakers and offshore structures operating in cold oceans and seas. Drift ice consists of ice floes, individual pieces of sea ice or more across. Floes are classified according to size: ''small'' – to ; ''medium'' – to ; ''big'' – to ; ''vast'' – to ; and ''giant'' – more than . Drift ice affects: * Security of navigation * Climatic impact (see Polar ice packs) * Geological impact * Biosphere influence (see ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fast Ice
Fast ice (also called ''land-fast ice'', ''landfast ice'', and ''shore-fast ice'') is sea ice that is "fastened" to the coastline, to the sea floor along shoals or to grounded icebergs.Leppäranta, M. 2011. The Drift of Sea Ice. Berlin: Springer-Verlag. Fast ice may either grow in place from the sea water or by freezing pieces of drifting ice to the shore or other anchor sites.Kovacs, A.and M. Mellor. 1974. "Sea ice morphology and ice as a geologic agent in the Southern Beaufort Sea." pp. 113-164, in: ''The Coast and Shelf of the Beaufort Sea'', J.C. Reed and J.E. Sater (Eds.), Arlington, Va.: U.S.A. Unlike drift (or pack) ice, fast ice does not move with currents and winds. The width (and the presence) of this ice zone is usually seasonal and depends on ice thickness, topography of the sea floor and islands. It ranges from a few meters to several hundred kilometers. Seaward expansion is a function of a number of factors, notably water depth, shoreline protection, time of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
YouTube
YouTube is a global online video sharing and social media platform headquartered in San Bruno, California. It was launched on February 14, 2005, by Steve Chen, Chad Hurley, and Jawed Karim. It is owned by Google, and is the second most visited website, after Google Search. YouTube has more than 2.5 billion monthly users who collectively watch more than one billion hours of videos each day. , videos were being uploaded at a rate of more than 500 hours of content per minute. In October 2006, YouTube was bought by Google for $1.65 billion. Google's ownership of YouTube expanded the site's business model, expanding from generating revenue from advertisements alone, to offering paid content such as movies and exclusive content produced by YouTube. It also offers YouTube Premium, a paid subscription option for watching content without ads. YouTube also approved creators to participate in Google's AdSense program, which seeks to generate more revenue for both parties. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CBC News
CBC News is a division of the Canadian Broadcasting Corporation responsible for the news gathering and production of news programs on the corporation's English-language operations, namely CBC Television, CBC Radio, CBC News Network, and CBC.ca. Founded in 1941, CBC News is the largest news broadcaster in Canada and has local, regional, and national broadcasts and stations. It frequently collaborates with its organizationally separate French-language counterpart, Radio-Canada Info. History The first CBC newscast was a bilingual radio report on November 2, 1936. The CBC News Service was inaugurated during World War II on January 1, 1941, when Dan McArthur, chief news editor, had Wells Ritchie prepare for the announcer Charles Jennings a national report at 8:00 pm. Readers who followed Jennings were Lorne Greene, Frank Herbert and Earl Cameron. ''CBC News Roundup'' (French counterpart: ''La revue de l'actualité'') started on August 16, 1943, at 7:45 pm, being replaced by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thunder
Thunder is the sound caused by lightning. Depending upon the distance from and nature of the lightning, it can range from a long, low rumble to a sudden, loud crack. The sudden increase in temperature and hence pressure caused by the lightning produces rapid expansion of the air in the path of a lightning bolt. In turn, this expansion of air creates a sonic shock wave, often referred to as a "thunderclap" or "peal of thunder". The scientific study of thunder is known as ''brontology'' and the irrational fear (phobia) of thunder is called ''brontophobia''. Etymology The ''d'' in Modern English ''thunder'' (from earlier Old English ''þunor'') is epenthetic, and is now found as well in Modern Dutch ''donder'' (cf. Middle Dutch ''donre''; also Old Norse '' þorr'', Old Frisian ''þuner'', Old High German ''donar'', all ultimately descended from Proto-Germanic *''þunraz''). In Latin the term was ''tonare'' "to thunder". The name of the Nordic god Thor comes from the Old Nor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |