|
Iapyges
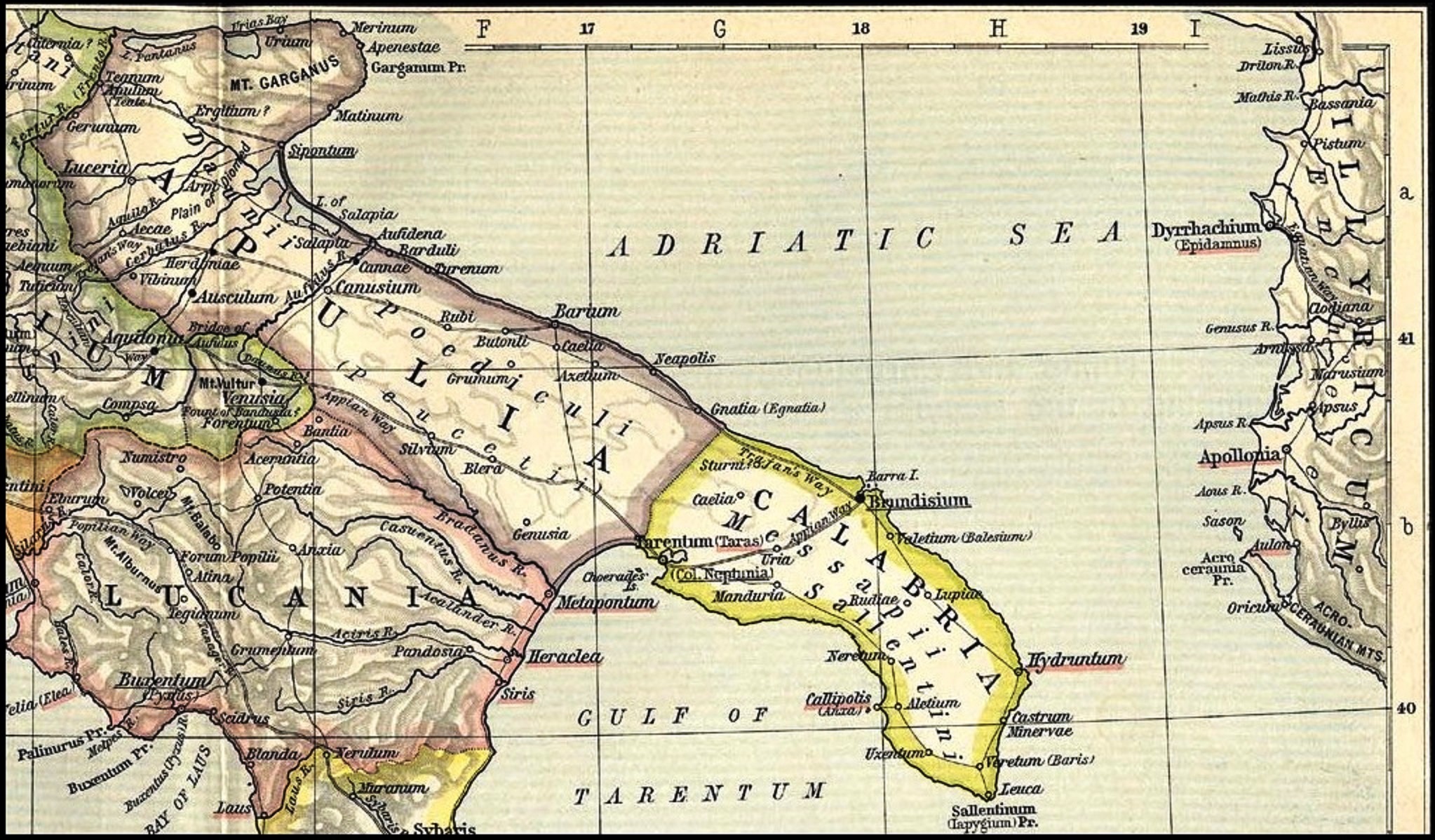
The Iapygians or Apulians (; el, Ἰάπυγες, ''Ĭāpyges''; la, Iāpyges, Iapygii, Umbrian ''Iabuscer'') were an Indo-European-speaking people, dwelling in an eponymous region of the southeastern Italian Peninsula named Iapygia (modern Apulia) between the beginning of the first millennium BC and the first century BC. They were divided into three tribal groups: the Daunians, Peucetians and Messapians. After their lands were gradually colonized by the Romans from the late 4th century onward and eventually annexed to the Roman Republic by the early 1st century BC, Iapygians were fully Latinized and assimilated into Roman culture. Name The region was known to the Greeks of the 5th century BC as ''Iapygía'' (Ἰαπυγία), and its inhabitants as the ''Iápyges'' (Ἰάπυγες). It was probably the term used by the indigenous peoples to designate themselves. The name ''Iapyges'' has also been compared to that of the '' Iapydes'', an Illyrian tribe of northern Dalm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messapians
The Messapians ( grc, Μεσσάπιοι, Messápioi; la, Messapii) were a Iapygian tribe who inhabited Salento in classical antiquity. Two other Iapygian tribes, the Peucetians and the Daunians, inhabited central and northern Apulia respectively. All three tribes spoke the Messapian language, but had developed separate archaeological cultures by the seventh century BC. The Messapians lived in the eponymous region Messapia, which extended from Leuca in the southeast to Kailia and Egnatia in the northwest, covering most of the Salento peninsula. This region includes the Province of Lecce and parts of the provinces of Brindisi and Taranto today. Starting in the third century BC, Greek and Roman writers distinguished the indigenous population of the Salento peninsula differently. According to Strabo, the names ''Iapygians'', ''Daunians'', ''Peucetians'' and ''Messapians'' were exclusively Greek and not used by the natives, who divided the Salento in two parts. The southern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messapic Language
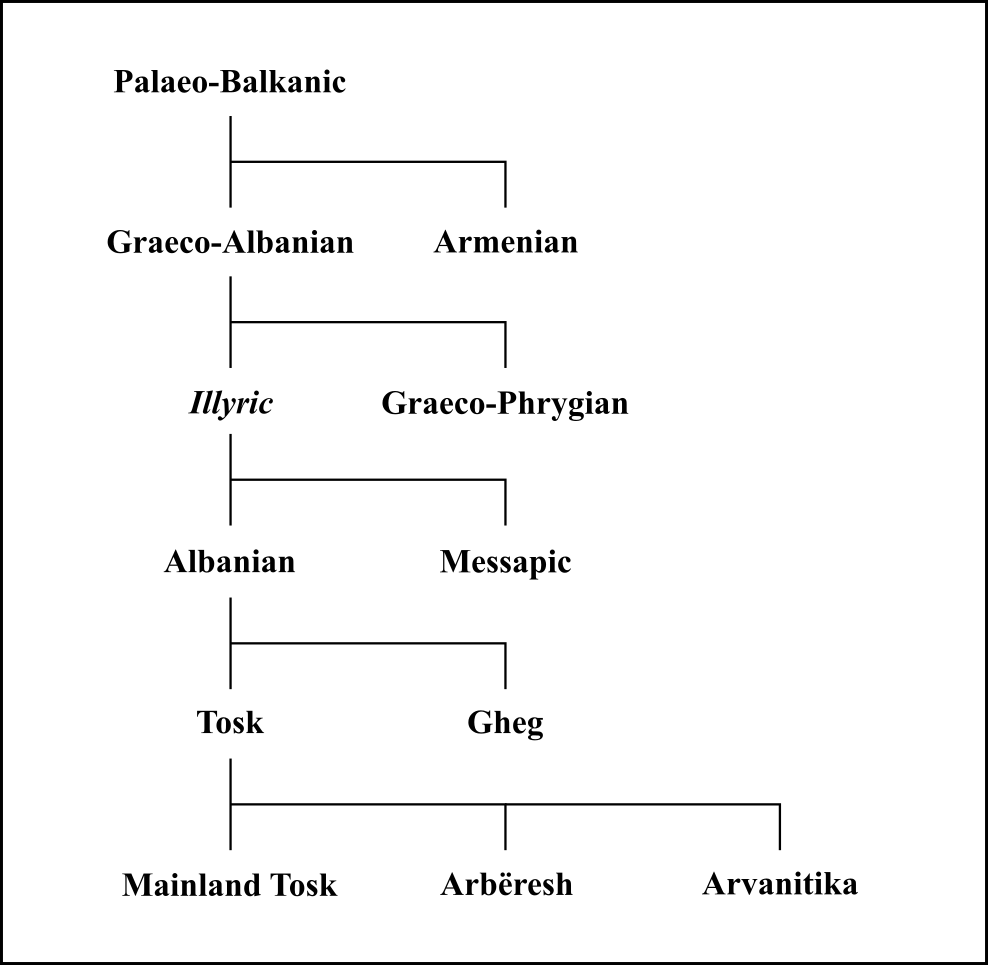
Messapic (; also known as Messapian; or as Iapygian) is an extinct Indo-European language of the southeastern Italian Peninsula, once spoken in Apulia by the Iapygian peoples of the region: the ''Calabri'' and ''Salentini'' (known collectively as the Messapii), the Peucetians and the Daunians. Messapic was the pre- Roman, non- Italic language of Apulia. It has been preserved in about 600 inscriptions written in an alphabet derived from a Western Greek model and dating from the mid-6th to at least the 2nd century BC, when it went extinct following the Roman conquest of the region. Name The term 'Messapic' or 'Messapian' is traditionally used to refer to a group of languages spoken by the Iapygians, a "relatively homogeneous linguistic community" of non- Italic-speaking tribes ( Messapians, Peucetians and Daunians) dwelling in the region of Apulia before the Roman conquest. However, some scholars have argued that the term ' Iapygian languages' should be preferred for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iapydes
The Iapydes (or Iapodes, Japodes; el, Ἰάποδες) were an ancient people who dwelt north of and inland from the Liburnians, off the Adriatic coast and eastwards of the Istrian peninsula. They occupied the interior of the country between the ''Colapis'' (Kupa) and ''Oeneus'' ( Una) rivers, and the Velebit mountain range (''Mons Baebius'') which separated them from the coastal Liburnians. Their territory covered the central inlands of modern Croatia and Una River Valley in today's Bosnia and Herzegovina. Archaeological documentation confirms their presence in these countries at least from 9th century BC, and they persisted in their area longer than a millennium. The ancient written documentation on inland Iapydes is scarcer than on the adjacent coastal peoples (Liburni, Delmatae, etc.) that had more frequent maritime contacts with ancient Greeks and Romans. The Iapydes had their maximal development and territorial expansion from the 8th to 4th centuries BC. They settled mostly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ofanto
The Ofanto (), known in ancient times as Aufidus or Canna, is a river in southern Italy that flows through the regions of Campania, Basilicata, and Apulia, into the Gulf of Manfredonia near Barletta. Geography The river's source is on the Irpinia Plateau, at above sea level, near Nusco and Torella dei Lombardi, in the province of Avellino. From there it runs southeast near Lioni before flowing into Lago di Conza, an artificial lake. The river then forms the border between the province of Avellino and the province of Potenza except for a small extension of the province of Avellino near Calitri. The Atella flows into the Ofanto near this point as a right tributary of the river. The river curves north and flows near Monteverde before forming the border between the province of Foggia and the province of Potenza. It then curves east for a distance and a right tributary, the Olivento, flows into it in this area. The river curves northeast and then forms the border between the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-European Languages
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutch, and Spanish, have expanded through colonialism in the modern period and are now spoken across several continents. The Indo-European family is divided into several branches or sub-families, of which there are eight groups with languages still alive today: Albanian, Armenian, Balto-Slavic, Celtic, Germanic, Hellenic, Indo-Iranian, and Italic; and another nine subdivisions that are now extinct. Today, the individual Indo-European languages with the most native speakers are English, Hindi–Urdu, Spanish, Bengali, French, Russian, Portuguese, German, and Punjabi, each with over 100 million native speakers; many others are small and in danger of extinction. In total, 46% of the world's population (3.2 billion people) speaks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italic Languages
The Italic languages form a branch of the Indo-European language family, whose earliest known members were spoken on the Italian Peninsula in the first millennium BC. The most important of the ancient languages was Latin, the official language of ancient Rome, which conquered the other Italic peoples before the common era. The other Italic languages became extinct in the first centuries AD as their speakers were assimilated into the Roman Empire and shifted to some form of Latin. Between the third and eighth centuries AD, Vulgar Latin (perhaps influenced by language shift from the other Italic languages) diversified into the Romance languages, which are the only Italic languages natively spoken today, while Literary Latin also survived. Besides Latin, the known ancient Italic languages are Faliscan (the closest to Latin), Umbrian and Oscan (or Osco-Umbrian), and South Picene. Other Indo-European languages once spoken in the peninsula whose inclusion in the Italic branch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metapontum
Metapontum or Metapontium ( grc, Μεταπόντιον, Metapontion) was an important city of Magna Graecia, situated on the gulf of Tarentum, between the river Bradanus and the Casuentus (modern Basento). It was distant about 20 km from Heraclea and 40 from Tarentum. The ruins of Metapontum are located in the frazione of Metaponto, in the comune of Bernalda, in the Province of Matera, Basilicata region, Italy. History Foundation Though Metapontum was an ancient Greek Achaean colony, various traditions assigned to it a much earlier origin. Strabo and Solinus ascribe its foundation to a body of Pylians, a part of those who had followed Nestor to Troy. Justin, conversely, tells us it was founded by Epeius; in proof of which the inhabitants showed, in a temple of Minerva, the tools which the hero had used to build the Trojan Horse. Another tradition, reported by Ephorus, assigned to it a Phocian origin, and called Daulius, the tyrant of Crisa near Delphi, its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taranto
Taranto (, also ; ; nap, label=Tarantino dialect, Tarantino, Tarde; Latin: Tarentum; Old Italian: ''Tarento''; Ancient Greek: Τάρᾱς) is a coastal city in Apulia, Southern Italy. It is the capital of the Province of Taranto, serving as an important commercial port as well as the main Italian naval base. Founded by Spartans in the 8th century BC during the period of Greek colonisation, Taranto was among the most important in Magna Graecia, becoming a cultural, economic and military power that gave birth to philosophers, strategists, writers and athletes such as Archytas, Aristoxenus, Livius Andronicus, Heracleides of Tarentum, Heracleides, Iccus of Taranto, Iccus, Cleinias of Tarentum, Cleinias, Leonidas of Tarentum, Leonidas, Lysis of Taras, Lysis and Sosibius of Tarentum, Sosibius. By 500 BC, the city was among the largest in the world, with a population estimated up to 300,000 people. The seven-year rule of Archytas marked the apex of its development and recognition of i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Of Taranto
The Gulf of Taranto ( it, Golfo di Taranto; Tarantino: ; la, Sinus Tarentinus) is a gulf of the Ionian Sea, in Southern Italy. The Gulf of Taranto is almost square, long and wide, making it the largest gulf in Italy, and it is delimited by the capes Santa Maria di Leuca (to the east, in Apulia) and Colonna (the ancient ''Lacinium'', to the west, in Calabria), encompassed by the three regions of Apulia, Basilicata and Calabria. The most important rivers are the Basento, the Sinni, and the Agri. The main cities on the gulf are Taranto and Gallipoli. Also the Greek colonies (Magna Graecia) of Kroton, Heraclea, Thurii, and Sybaris were founded on the Gulf of Taranto. Italy claims the whole gulf as national waters, thus closed to international traffic. This position, which is similar to that of Libya on the Gulf of Sidra, is not recognized by some other countries, such as the United States and the United Kingdom The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magna Graecia
Magna Graecia (, ; , , grc, Μεγάλη Ἑλλάς, ', it, Magna Grecia) was the name given by the Romans to the coastal areas of Southern Italy in the present-day Italian regions of Calabria, Apulia, Basilicata, Campania and Sicily; these regions were extensively populated by Greek settlers. These settlers, who began arriving in the 8th century BC, brought with them their Hellenic civilization, which left a lasting imprint on Italy (such as in the culture of ancient Rome). They also influenced the native peoples, such as the Sicels and the Oenotrians, who became hellenized after they adopted the Greek culture as their own. The Greek expression ''Megálē Hellás'', later translated into Latin as ''Magna Graecia,'' first appears in Polybius' ''Histories,'' where he ascribed the term to Pythagoras and his philosophical school. Strabo also used the term to refer to the size of the territory that had been conquered by the Greeks, and the Roman poet Ovid used the term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salento
Salento ( Salentino: ''Salentu'', Salentino Griko: ''Σαλέντο'') is a cultural, historical and geographic region at the southern end of the administrative region of Apulia in Southern Italy. It is a sub-peninsula of the Italian Peninsula, sometimes described as the "heel" of the Italian "boot". It encompasses the entire administrative area of the province of Lecce, a large part of the province of Brindisi and part of that of Taranto. The peninsula is also known as Terra d'Otranto, and in the past Sallentina. In ancient times it was called variously Calabria or Messapia. History Messapia (from Greek ''Μεσσαπία'') was the ancient name of a region of Italy largely corresponding to modern Salento. It was inhabited chiefly by the Messapii in classical times. Pokorny derives the toponym from the reconstructed PIE ''*medhyo-'', "middle" and PIE ''*ap-'', "water" (''Mess-apia'', "amid waters"). Pokorny compares the toponym ''Messapia'' to another ancient Italic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altopiano Delle Murge
The Altopiano delle Murge ( Italian for "Murge plateau") is a karst topographic plateau of rectangular shape in southern Italy. Most of it lies within Apulia and corresponds with the sub-region known as Murgia or Le Murge. The plateau lies mainly in the Metropolitan City of Bari and the province of Barletta-Andria-Trani, but extends into the provinces of Brindisi and Taranto to the south, and into Matera in Basilicata to the west. The name is believed to originate from the Latin ''murex'', meaning "sharp stone". Geography and geology The Murge plateau covers a surface of some 4,000 km², bordered by the Ofanto river and the Tavoliere delle Puglie to the north, the Adriatic Sea to the northeast, and by the Messapic depression, which separates it from the Salento peninsula, to the south. It is usually divided into Alta Murgia (High Murgia), the highest area, with poorer vegetation, and Bassa Murgia (Lower Murgia), with more fertile land, extensively planted with olive-tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
