|
IWW
The Industrial Workers of the World (IWW), members of which are commonly termed "Wobblies", is an international labor union that was founded in Chicago in 1905. The origin of the nickname "Wobblies" is uncertain. IWW ideology combines general unionism with industrial unionism, as it is a general union, subdivided between the various industries which employ its members. The philosophy and tactics of the IWW are described as "revolutionary industrial unionism", with ties to socialist, syndicalist, and anarchist labor movements. In the 1910s and early 1920s, the IWW achieved many of their short-term goals, particularly in the American West, and cut across traditional guild and union lines to organize workers in a variety of trades and industries. At their peak in August 1917, IWW membership was estimated at more than 150,000, with active wings in the United States, the UK, Canada, and Australia. The extremely high rate of IWW membership turnover during this era (estimated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Workers Of The World Philosophy And Tactics
The Industrial Workers of the World (IWW) is a union of wage workers which was formed in Chicago in 1905 by militant unionists and their supporters due to anger over the conservatism, philosophy, and craft-based structure of the American Federation of Labor (AFL). Throughout the early part of the 20th century, the philosophy and tactics of the IWW were frequently in direct conflict with those of the AFL (forerunner of the AFL–CIO) concerning the best ways to organize workers, and how to best improve the society in which they toiled. The AFL had one guiding principle—"pure and simple trade unionism", often summarized with the slogan " a fair day's pay for a fair day's work." The IWW embraced two guiding principles, fighting like the AFL for better wages, hours, and conditions, but also promoting an eventual, permanent solution to the problems of strikes, injunctions, bull pens, and union scabbing. The AFL and the IWW (whose members are referred to as Wobblies) had very diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Workers Of The World Organizational Evolution
The Industrial Workers of the World (IWW) is a union of wage workers which was formed in Chicago in 1905. The IWW experienced a number of divisions and splits during its early history. When the office of the IWW president was abolished at the convention in 1906, deposed President Sherman and his supporters, many from the Socialist Party and the Western Federation of Miners, formed a rump IWW, which ceased to exist after about a year.Paul Frederick Brissenden, ''The I.W.W. A Study of American Syndicalism'', Columbia University, 1919, pages 174-184 After the 1908 convention of the original IWW, at which Socialist Labor Party (SLP) head Daniel DeLeon was barred from voting via credentials challenges, DeLeon and the SLP bolted to form another rump IWW, which came to be called the Detroit IWW. In 1915, the Detroit IWW changed its name to the Workers' International Industrial Union (WIIU). The WIIU continued its close relationship with the SLP, but ceased to exist in 1924. There was ano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
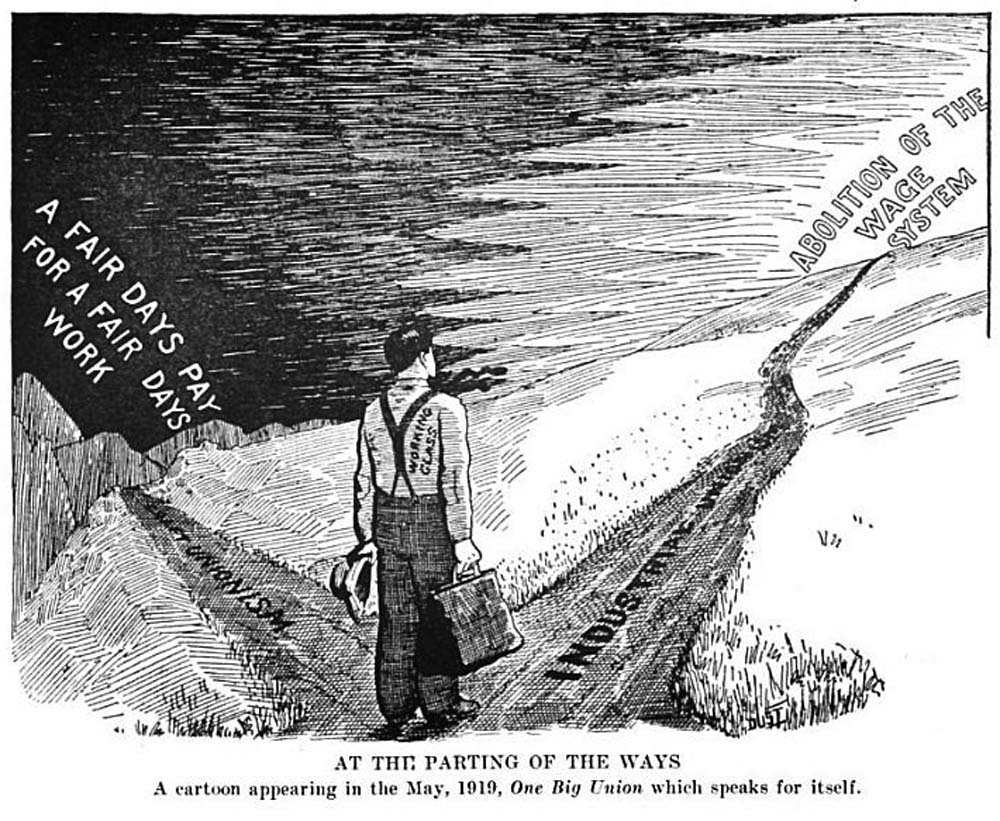
One Big Union (concept)
The One Big Union was an idea in the late 19th and early 20th centuries amongst trade unionists to unite the interests of workers and offer solutions to all labour problems. Unions initially organized as craft unions. Workers were organized by their skill: carpenters, plumbers, bricklayers, each into their respective unions. Capitalists could often divide craft unionists along these lines in demarcation disputes. As capitalist enterprises and state bureaucracies became more centralized and larger, some workers felt that their institutions needed to become similarly large. A simultaneous disenchantment with the perceived weakness of craft unions caused many unions to organize along industrial lines. The idea of the "one big union" is championed by anarchist syndicalists to organize effectively. As envisioned by the Industrial Workers of the World (IWW), which for many years prior to 1919 had been associated with the concept, One Big Union was not just the idea that all workers s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Unionism
Industrial unionism is a trade union organizing method through which all workers in the same industry are organized into the same union, regardless of skill or trade, thus giving workers in one industry, or in all industries, more leverage in bargaining and in strike situations. Industrial unionism contrasts with craft unionism, which organizes workers along lines of their specific trades. History Early history Eugene Debs formed the American Railway Union (ARU) as an industrial organization in response to limitations of craft unions. Railroad engineers and firemen had called a strike, but other employees, particularly conductors who were organized into a different craft, did not join that strike. The conductors piloted scab engineers on the train routes, helping their employers to break the strike. In June 1894, the newly formed, industrially organized ARU voted to join in solidarity with an ongoing strike against the Pullman company. The sympathy strike demonstrated the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anarcho-syndicalism
Anarcho-syndicalism is a political philosophy and anarchist school of thought that views revolutionary industrial unionism or syndicalism as a method for workers in capitalist society to gain control of an economy and thus control influence in broader society. The end goal of syndicalism is to abolish the wage system, regarding it as wage slavery. Anarcho-syndicalist theory generally focuses on the labour movement. Reflecting the anarchist philosophy from which it draws its primary inspiration, anarcho-syndicalism is centred on the idea that Power (philosophy), power corrupts and that any hierarchy that cannot be ethically justified must be dismantled. The basic principles of anarcho-syndicalism are solidarity, direct action (action undertaken without the intervention of third parties such as politicians, bureaucrats and arbitrators) and direct democracy, or workers' self-management. Anarcho-syndicalists believe their economic theories constitute a strategy for facilitating prole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The Socialist Movement In The United States
The history of the socialist movement in the United States spans a variety of tendencies, including Anarchism in the United States, anarchists, Communism in the United States, communists, democratic socialists, Marxists, Marxist–Leninists, Trotskyists and utopian socialists. It began with utopian communities in the early 19th century such as the Shakers, the activist visionary Josiah Warren and intentional communities inspired by Charles Fourier. Labor activists, usually British, German, or Jewish immigrants, founded the Socialist Labor Party of America in 1877. The Socialist Party of America was established in 1901. By that time, anarchism also rose to prominence around the country. Socialists of different tendencies were involved in early American labor organizations and struggles. These reached a high point in the Haymarket massacre in Chicago, which founded the International Workers' Day as the main labour holiday around the world, Labor Day and making the eight-hour day a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Worker
The ''Industrial Worker'', "the voice of revolutionary industrial unionism", is the magazine of the Industrial Workers of the World (IWW). It is currently released quarterly. The publication is printed and edited by union labor, and is frequently distributed at radical bookstores, demonstrations, strikes and labor rallies. It covers industrial conditions, strikes, workplace organizing experiences, and features on labor history. It used to be released as a newspaper. The newspaper was first printed in journal format in Joliet, Illinois, beginning in January 1906, incorporating ''The Voice of Labor'', the newspaper from the former American Labor Union which had joined the IWW, and ''International Metal Worker''. It was edited by A. S. Edwards, and early contributors include Eugene V. Debs, Jack London, Daniel DeLeon, Bill Haywood, and James H. Walsh, along with poetry by Covington Hall. When the group led by ousted President Charles O. Sherman retained physical control over the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anarchism In The United States
Anarchism in the United States began in the mid-19th century and started to grow in influence as it entered the American labor movements, growing an anarcho-communist current as well as gaining notoriety for violent propaganda of the deed and campaigning for diverse social reforms in the early 20th century. By around the start of the 20th century, the heyday of individualist anarchism had passed and anarcho-communism and other social anarchist currents emerged as the dominant anarchist tendency. Social anarchists, like Emma Goldman, can be credited with the introduction of LGBTQ social movements to the United States. In the post-World War II era, anarchism regained influence through new developments such as anarcho-pacifism, the American New Left and the counterculture of the 1960s. Contemporary anarchism in the United States influenced and became influenced and renewed by developments both inside and outside the worldwide anarchist movement such as platformism, insurrectiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Labor Union
The American Labor Union (ALU) was a radical labor organization launched as the Western Labor Union (WLU) in 1898. The organization was established by the Western Federation of Miners (WFM) in an effort to build a federation of trade unions in the aftermath of the failed Leadville Colorado, Miners' Strike, Leadville Miners' Strike of 1896. The group changed its name from WLU to the more familiar ALU moniker in 1902 at its fifth annual convention. The group had a peak membership of about 43,000 — of which 27,000 were members of the WFM. The ALU was a precursor to the Industrial Workers of the World (IWW), established in 1905, which effectively terminated it. Organizational history Forerunner The Western Labor Union (WLU) was a labor federation created by the Western Federation of Miners (WFM) after the disastrous Leadville Colorado, Miners' Strike, Leadville strike of 1896-97. The WLU was conceived in November, 1897 in a November 1897 proclamation, proclamation of the State Trad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
An Injury To One Is An Injury To All
An injury to one is an injury to all is a motto popularly used by the Industrial Workers of the World. In his autobiography, Bill Haywood credited David C. Coates with suggesting a labor slogan for the IWW: ''an injury to one is an injury to all''. The slogan has since been used by a number of labor organizations. The slogan reflects the fact that the IWW is " One Big Union" and organizes skilled and unskilled workers. Origin The expression is similar to, and may be derived from, a slogan popularized in the prior quarter century by the Knights of Labor, "that is the best government in which an injury to one is the concern of all". Gallery File:Anti Trump Protests in Baltimore (31167103245).jpg, Anti-Trump IWW anti-fascist protest with motto File:An injury to one is an injury to all (6356989695).jpg, Occupy Boston, November 2011 in Massachusetts File:Injury one Injury all.jpg, "An Injury to One is an Injury to All," a mural by Mike Alewitz in Los Angeles (now destroyed) 1993 See ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Federation Of Labor
The American Federation of Labor (A.F. of L.) was a national federation of labor unions in the United States that continues today as the AFL-CIO. It was founded in Columbus, Ohio, in 1886 by an alliance of craft unions eager to provide mutual support and disappointed in the Knights of Labor. Samuel Gompers was elected the full-time president at its founding convention and reelected every year, except one, until his death in 1924. He became the major spokesperson for the union movement. The A.F. of L. was the largest union grouping, even after the creation of the Congress of Industrial Organizations (CIO) by unions that were expelled by the A.F. of L. in 1935. The Federation was founded and dominated by craft unions. especially the building trades. In the late 1930s craft affiliates expanded by organizing on an industrial union basis to meet the challenge from the CIO. The A.F. of L. and CIO competed bitterly in the late 1930s, but then cooperated during World War II and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Red Scare
The First Red Scare was a period during History of the United States (1918–1945), the early 20th-century history of the United States marked by a widespread fear of Far-left politics, far-left movements, including Bolshevik, Bolshevism and anarchism, due to real and imagined events; real events included the Russian 1917 October Revolution and 1919 United States anarchist bombings, anarchist bombings. At its height in 1919–1920, concerns over the effects of radical political agitation in American society and the alleged spread of socialism, communism and Anarchism in the United States, anarchism in the American labor movement fueled a general sense of concern. The Scare had its origins in the hyper-nationalism of World War I as well as the Russian Revolution. At the war's end, following the October Revolution, American authorities saw the threat of communist revolution in the actions of Trade union, organized labor, including such disparate cases as the Seattle General Stri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |