 The
The Wobbly understanding of the world
 By 1912, after a number of defections and splits, the IWW numbered some twenty-five thousand, much smaller than many of its rival unions. But the IWW's influence was already outsized. The Congressional Commission on Industrial Relations noted in 1916 that "as a 'spirit and vocabulary' he IWWpermeates to a large extent enormous masses of workers..." Wobbly activists were those workers who not only reacted to economic forces, but who spent a considerable amount of time thinking, debating, and educating their co-workers about the impact of such forces upon society. John Reed observed, "Wherever, in the West, there is an IWW local, you will find an intellectual center ... a place where men read philosophy, economics, the latest plays, novels; where art and poetry are discussed, and international politics."
The IWW printed hundreds of thousands of leaflets, promoted Industrial Education Clubs, and organized Propaganda Leagues. Stickered slogans, referred to as " silent agitators", were printed by the million, and made available by the thousand. IWW libraries in union halls made available to any worker not only the organization's publications, but also practical topics about machinery and production, as well as classic works of scientists, theoreticians, and philosophers. Knowledge and experience were likewise shared—new members were sometimes invited to chair meetings, not just to share the experience, but to initiate them into the community. Indeed, a favorite Wobbly answer to the question, who are your leaders, was the united response, we are all leaders.
Wobblies believed not only that it took a working person to understand the needs of the workers, but in order to lead, that person must also be an educated worker. IWW publications seemed to enjoy reporting on "the amazement shown by college professors who heard Wobbly speakers deliver talks upon a wide variety of subjects and reveal a remarkable understanding of complex economic and social questions." By the time of the organization's founding in 1905, inquisitive workers already had a wide variety of union experiences and traditions to consider. In coming together as an organization, then, it is perhaps not surprising that the clash of ideas among IWW members resulted in passionate debate and an eventual winnowing of philosophies over several decades of evolution.
By 1912, after a number of defections and splits, the IWW numbered some twenty-five thousand, much smaller than many of its rival unions. But the IWW's influence was already outsized. The Congressional Commission on Industrial Relations noted in 1916 that "as a 'spirit and vocabulary' he IWWpermeates to a large extent enormous masses of workers..." Wobbly activists were those workers who not only reacted to economic forces, but who spent a considerable amount of time thinking, debating, and educating their co-workers about the impact of such forces upon society. John Reed observed, "Wherever, in the West, there is an IWW local, you will find an intellectual center ... a place where men read philosophy, economics, the latest plays, novels; where art and poetry are discussed, and international politics."
The IWW printed hundreds of thousands of leaflets, promoted Industrial Education Clubs, and organized Propaganda Leagues. Stickered slogans, referred to as " silent agitators", were printed by the million, and made available by the thousand. IWW libraries in union halls made available to any worker not only the organization's publications, but also practical topics about machinery and production, as well as classic works of scientists, theoreticians, and philosophers. Knowledge and experience were likewise shared—new members were sometimes invited to chair meetings, not just to share the experience, but to initiate them into the community. Indeed, a favorite Wobbly answer to the question, who are your leaders, was the united response, we are all leaders.
Wobblies believed not only that it took a working person to understand the needs of the workers, but in order to lead, that person must also be an educated worker. IWW publications seemed to enjoy reporting on "the amazement shown by college professors who heard Wobbly speakers deliver talks upon a wide variety of subjects and reveal a remarkable understanding of complex economic and social questions." By the time of the organization's founding in 1905, inquisitive workers already had a wide variety of union experiences and traditions to consider. In coming together as an organization, then, it is perhaps not surprising that the clash of ideas among IWW members resulted in passionate debate and an eventual winnowing of philosophies over several decades of evolution.
Inspiration
Where did initial inspirations for the Wobbly philosophy come from? Historian Melvyn Dubofsky is worth quoting at length:Wobblies ... took their basic concepts from others: fromMarx Karl Heinrich Marx (; 5 May 1818 – 14 March 1883) was a German philosopher, economist, historian, sociologist, political theorist, journalist, critic of political economy, and socialist revolutionary. His best-known titles are the 1848 ...the concepts of labor value, commodity value, surplus value, and class struggle; fromDarwin Darwin may refer to: Common meanings * Charles Darwin (1809–1882), English naturalist and writer, best known as the originator of the theory of biological evolution by natural selection * Darwin, Northern Territory, a territorial capital city i ...the idea of organic evolution and the struggle for survival as a paradigm for social evolution and the survival of the fittest class; fromBakunin Mikhail Alexandrovich Bakunin (; 1814–1876) was a Russian revolutionary anarchist, socialist and founder of collectivist anarchism. He is considered among the most influential figures of anarchism and a major founder of the revolutiona ...and the anarchists the "propaganda of the deed"* and the idea of direct action; and from Sorel the notion of the "militant minority." Hence, IWW beliefs became a peculiar amalgam of Marxism and Darwinism, anarchism and syndicalism—all overlaid with a singularly American patina.
 However, Dubofsky also identifies American traditions "dating back to the era of Jefferson and Jackson" from which the Wobblies derived inspiration, particularly the concepts of a society divided into " producers and nonproducers, productive classes and parasites." Paul Brissenden likewise stated that, " e main ideas of I.W.W.-ism—certainly of the I.W.W.-ism of the first few years after 1905—were of American origin, not French, as is commonly supposed.
Wobblies sought to familiarize theoretical terminology for a worker audience of varied educative experience. A
However, Dubofsky also identifies American traditions "dating back to the era of Jefferson and Jackson" from which the Wobblies derived inspiration, particularly the concepts of a society divided into " producers and nonproducers, productive classes and parasites." Paul Brissenden likewise stated that, " e main ideas of I.W.W.-ism—certainly of the I.W.W.-ism of the first few years after 1905—were of American origin, not French, as is commonly supposed.
Wobblies sought to familiarize theoretical terminology for a worker audience of varied educative experience. A Question of political action
By the time of the 1905 founding of the Industrial Workers of the World, the question of whether unionized workers could secure significant change by political actions of their unions had been in contention for some decades. The question had split the National Labor Union in 1872. It created divisions between the membership and the leadership of the Knights of Labor, with the leaders favoring various political agendas including Greenbackism, socialism, and land reform. Labor historian Joseph Rayback believed that significant losses for organized labor in the 1890s pointed the way toward either socialism, or industrial unionism in order to maintain organized labor's momentum. Yet Samuel Gompers, leader of theEarly philosophy a compromise
At its opening convention, the Industrial Workers of the World exhibited a "spirit of unity." Although nearly all of the delegates were committed to some form of Socialist politics, there were some significant philosophical differences just under the surface. Western Federation of Miners members and other union veterans wanted the participation of the two Socialist parties, theIWW vs. the AFL
In spite of the varied philosophies of the participants at the first IWW convention, there were a few compelling concerns which united all. Nearly all who attended acknowledged an "irrepressible conflict" between capital and labor. Nearly all could be described as adherents of industrial unionism, as opposed to the craft unionism of the American Federation of Labor. Acknowledging the common practice of AFL craft unions crossing each other's picket lines, the IWW adopted the WFM's description of the AFL as the "American Separation of Labor." In addition to the limitations of organizing by craft, the IWW criticized the AFL for emphasizing common interests between labor and capital, and for organizing only elite workers rather than acknowledging the needs of the entire working class. The AFL was bitterly attacked by speakers who organized the conference, such that many would have been pleased if the federation (although not necessarily its constituent unions) would simply cease to exist. Samuel Gompers responded by declaring that the IWW's organizers were "trying to divert, pervert, and disrupt the labor movement of the country," describing them as "pirates" and "kangaroos." Calling the AFL outdated was "inexcusably ignorant and maliciously false," said Gompers. Referring to the birth of the IWW, Gompers commented that " e mountain labored and brought forth a mouse, and a very silly little mouse at that... historians will record the Chicago ounding of the IWWas the most vapid and ridiculous in the annals of those who presume to speak in the name of labor..."
Gompers warned all AFL affiliates not to cooperate with IWW members, and told AFL members not to support IWW strikes. Permission was granted to cross IWW picket lines. Although the AFL had offered some support to the Western Federation of Miners in the aftermath of the Colorado Labor Wars, that assistance was discontinued because of WFM affiliation with the IWW. A number of AFL affiliates—machinists, carpenters, hat makers, leatherworkers, and others—decreed that any individual with an IWW card would not be allowed to work in their industries.
The IWW fought for workers' rights somewhat differently from the AFL.
The AFL was bitterly attacked by speakers who organized the conference, such that many would have been pleased if the federation (although not necessarily its constituent unions) would simply cease to exist. Samuel Gompers responded by declaring that the IWW's organizers were "trying to divert, pervert, and disrupt the labor movement of the country," describing them as "pirates" and "kangaroos." Calling the AFL outdated was "inexcusably ignorant and maliciously false," said Gompers. Referring to the birth of the IWW, Gompers commented that " e mountain labored and brought forth a mouse, and a very silly little mouse at that... historians will record the Chicago ounding of the IWWas the most vapid and ridiculous in the annals of those who presume to speak in the name of labor..."
Gompers warned all AFL affiliates not to cooperate with IWW members, and told AFL members not to support IWW strikes. Permission was granted to cross IWW picket lines. Although the AFL had offered some support to the Western Federation of Miners in the aftermath of the Colorado Labor Wars, that assistance was discontinued because of WFM affiliation with the IWW. A number of AFL affiliates—machinists, carpenters, hat makers, leatherworkers, and others—decreed that any individual with an IWW card would not be allowed to work in their industries.
The IWW fought for workers' rights somewhat differently from the AFL. IWW philosophy evolves
The IWW organized many who were "left out" of American society, including "timber beasts, hobo harvesters, itinerant construction workers, exploited eastern and southern European immigrants, racially excluded African Americans, Mexicans, and Asian Americans." Due to feelings of alienation and impotence, these workers embraced radical theories aimed at disrupting and replacing the established social order. The IWW maintained low initiation fees and dues, allowed universal transfer of union cards, and disdained apprenticeships in order to attract the lower strata of working society. As a result of the splits and de facto purges, the IWW distilled a core set of beliefs and practices. It eschewed political entanglements for revolutionary industrial unionism. the Wobblies of the IWW sought to "comprehend the nature and dynamics of capitalist society and through increased knowledge, as well as revolutionary activism, to develop a better system for the organization and functioning of the American economy."Two guiding principles
Labor Historian Melvyn Dubofsky has written that the IWW held "an instinctive distaste for the world as it was, as well as hope for the creation of a completely new world." Yet in addition to a belief in eventual revolution, the IWW "constantly sought opportunities to improve the immediate circumstances of its members." Marxist Labor Historian Philip S. Foner identifies the same points in the manifesto which called the labor activists to the founding conference in 1905. On the back of each manifesto was printed a declaration of the two requirements for any labor organization to properly represent the workers:First – It must combine the wage workers in such a way that it can most successfully fight the battles and protect the interests of the working people of to-day in their struggles for fewer hours, more wages and better conditions. Secondly – It must offer a final solution of the labor problem – an emancipation from strikes, injunctions and bull-pens.IWW co-founders Father Thomas J. Hagerty and William Trautmann continued promoting these two essential goals in their 1911 pamphlet, ''One Big Union''. The IWW needed to "combine the wage-workers in such a way that it can most successfully fight the battles and protect the interests of the workers of today in their struggles for fewer hours of toil, more wages and better conditions," and it also "must offer a final solution of the labor problem—an emancipation from strikes, injunctions, bull-pens, and scabbing of one against the other."
For and against the system
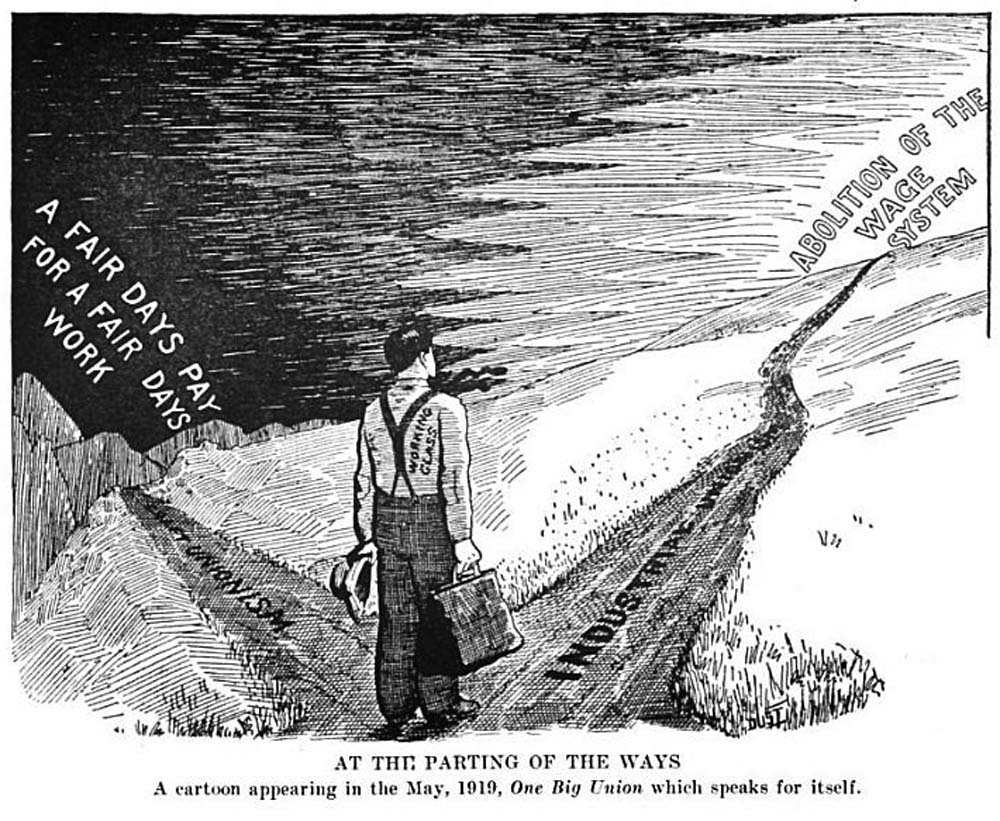
Historian Daniel R. Fusfeld referred to the conflicting labor philosophies held by the AFL and its rivals as job-consciousness (the AFL), and class-consciousness (organizations such as the Knights of Labor and the IWW). These philosophies resulted in oppositional alignment in regards to government. In ''Taking Care of Business'', Paul Buhle wrote that the AFL-affiliated United Mine Workers President John Mitchell declared in 1903, "The trade union movement in this country can make progress only by identifying itself with the state." ... eanwhile, thenew National Civic Federation (which was supported by the AFL) ... sought to promote labor peace (on the terms of the employers, critics claimed) and to make class consciousness and class struggle obsolete. While the AFL thus became more conservative, the IWW saw itself as a revolutionary organization dedicated to the "Abolition of the wage system."Preamble and Constitution of the Industrial Workers of the World
', Amended by Convention, 1908—Ratified by Referendum Vote, 1908, retrieved March 13, 2011
Political parties and union
While the AFL's Mitchell and Gompers nurtured their alliance with the Democrats, the IWW changed its Constitution in 1908 to prohibit just such alliances. The 1908 Constitution states, "to the end of promoting industrial unity and of securing necessary discipline within the organization, the I. W. W. refuses all alliances, direct or indirect, with existing political parties or anti-political sects..." This language is essentially unchanged in the 2011 IWW Constitution. The prohibition on alliances with "anti-political sects" is noteworthy. According to Verity Burgmann and others, the Chicago IWW was "non-political" rather than "anti-political." Joseph R. Conlin believes the deletion of a political clause from the Preamble in 1908 is only half the story; in 1911 the IWW rejected an amendment to the Preamble that referred to "the futility of political action." In other words, the ban on political involvement only went so far (presumably, banning any political or anti-political alliances ''in the name of the union''), and the balance of the IWW's membership saw nothing to be gained by outright hostility toward political action. Writing of the IWW's history through 1917, Foner (who, as a Marxist historian ''favored'' political action) noted that while most Wobblies disdained the ballot, several IWW leaders, individual members, and even entire locals did not necessarily reject politics, and some even participated in election campaigns. While offering skepticism about their accomplishing anything worthwhile, ''A working man may be an anarchist or a socialist, a Catholic or a Protestant, a republican or a democrat, but subscribing to the Preamble of the I.W.W. he is eligible for membership.
On war
 While the AFL identified with, and made accommodations for the benefit of government, the IWW was ardently opposed to what it viewed as capitalist wars.
While the AFL identified with, and made accommodations for the benefit of government, the IWW was ardently opposed to what it viewed as capitalist wars. Ideology and socialism
Melvyn Dubofsky notes that Wobbly ideology and Socialist party doctrine both opposed capitalism and advocated something better, but beyond that, they "conflicted more than they agreed." For nearly a decade, Bill Haywood tried to bridge the gap, acting as general secretary of the IWW, and as an officer of the Socialist Party. A fractious former hard rock miner, Haywood would tease audiences by telling them, "I'm a two gun man from the West, you know." After a moment to build the suspense, he would thrust hands into pockets, extracting a red IWW card with one hand, and a red Socialist card with the other. Haywood considered both ideologies vital to the cause of changing the economic system, frequently describing Wobblyism as "socialism with its working clothes on." Yet Haywood was embraced only by the left wing of the Socialist Party, and was eventually ejected from the Socialist Party's National Executive Committee by the conservative wing. Generally speaking, American Socialists were interested in acceptance and gradual reform. Wobblies were more cynical about capitalism, and wanted a real revolution. Dubofsky believes, however, that IWW ideology was compatible with Syndicalism.To be syndicalist, or not to be syndicalist?
The ''New International Year Book'' for 1912 observed that,"the Industrial Workers of the World would place an industry in the hands of its workers, as would socialism; it would organize society without any government, as would anarchism; and it would bring about a social revolution by direct action of the workers, as would syndicalism. Nevertheless, it claims to be distinct from all three."While noting general conformance in the language of IWW and Socialist doctrines, Helen Marot clarified in 1914,
"It is the interpretation of the WWpreamble by individual members of the organization which has attached the Industrial Workers of the World to the Syndicalist rather than to theMarot further notes that such classifications (Socialist or Syndicalist) are important to theorists, but not so important to organized labor itself. Labor historian Philip S. Foner observed in 1997 that "virtually every scholar" who has studied the IWW considers it to be a type of syndicalist organization. Yet he likewise notes key differences. For example, while European syndicalists operate within mainstream unions, the IWW has always displayed an antagonism toward, and disdain for existing craft based trade unions in the United States. This has led the IWW to embrace the concept of dual unionism. WhenSocialist Socialism is a left-wing economic philosophy and movement encompassing a range of economic systems characterized by the dominance of social ownership of the means of production as opposed to private ownership. As a term, it describes the ...movement. The declaration in the manifesto that the workers should own and operate their own tools, and that they alone should enjoy the fruits of their labor, would mean, according to American Socialists, that all workers, through a political state, or regulated by it, would operate, own, and enjoy collectively all tools and the product of industry. ..Buthe Preamble He or HE may refer to: Language * He (pronoun), an English pronoun * He (kana), the romanization of the Japanese kana へ * He (letter), the fifth letter of many Semitic alphabets * He (Cyrillic), a letter of the Cyrillic script called ''He'' ...interpreted by the leaders of the Industrial Workers, is directly opposed to the political Socialism of America. It is the declaration of the Syndicalists that the new social order will not be dependent on political action or a political state, but it will be an industrial commonwealth in which all governmental functions as we know them to-day will have ceased to exist, and in which each industry will be controlled by the workers in it without external interference."
In spite of certain misleading surface similarities, which are unduly stressed by shallow observers, the European anarcho-syndicalist movement and the I.W.W. differ considerably in more than one particular. This was made inevitable by reason of the fact that the I.W.W. was the result of a later and more mature period of industrial development. This accounts for the fact that European Syndicalism, unlike the I.W.W., is not organized into One Big Union on the basis of perfectly co-ordinated, centralized industrial departments. It also accounts for the fact that the form of the I.W.W. is designed to serve not only as a powerful combative force in the everyday class struggle, but also as the structure of the new society both as regards production and administration.In 1981 Conlin gave up the "non-syndicalist" cause as a semantic exercise, while simultaneously complimenting Dubofsky for his superior treatment of the IWW's American roots.
Anarchist swing?
Others note that the IWW draws upon socialist and anarchist traditions. In 1921, Robert Hoxie, author of ''Trade Unionism in the United States'', referred to the IWW as "quasi anarchistic." Just two years earlier, in 1919, Paul Frederick Brissenden described the revolutionary industrial unionism of the IWW as industrial unionism "animated and guided by the revolutionary (socialist or anarchist) spirit..." Brissenden wrote, "The anarchistic element was weak in 1905..."Anarcho-syndicalism
Wobblies have been called socialist, anarchist, and syndicalist. Some would argue that none of these fit well. Writing of French syndicalism in ''The revolutionary internationals, 1864-1943'',It did not occur to the syndicalists that the capitalist state, "eliminated" by the "expropriatoryThe IWW had explicitly rejected Leninism by 1921. (Of course—perhaps unlike the French Syndicalists—the Wobbly perception of any perceived "centralizing" tactics by IWW leaders split the organization on multiple occasions...) For those who feel compelled to "classify" the modern IWW's revolutionary industrial unionism in some broader category, the term used by Brissenden—anarcho-syndicalism—seems to be the current category of choice. However, even Brissenden's use of the term anarcho-syndicalism (in 1919) was met with dismay in some IWW circles, with a writer in ''One Big Union Monthly'' calling such terms "very misleading." A distinction should likewise be drawn between adopting tactics or principles from the anarchists, and ''actually being described as'' an anarchist organization. The IWW,general strike A general strike refers to a strike action in which participants cease all economic activity, such as working, to strengthen the bargaining position of a trade union or achieve a common social or political goal. They are organised by large coa ...", would be replaced by a new state with a new ruling class—the self-taught officials of the labor unions. It was only after theBolshevik Revolution The October Revolution,. officially known as the Great October Socialist Revolution. in the Soviet Union, also known as the Bolshevik Revolution, was a revolution in Russia led by the Bolshevik Party of Vladimir Lenin that was a key mome ...that most French syndicalists, dropping the last vestiges of anarchist anti-statism, adopted the slogan ''au syndicat le pouvoir'', i.e., all power to the labor union, which of course meant all power to the union leaders. Syndicalism, without the anarchist prefix, thus eventually became one of the heretical variants of Leninism.
... made a special effort to distinguish itself from the anarchists, emphasizing repeatedly that the two had "entirely different organizations and concepts of solving the social problem."
Contract question
In 1912, William E. Bohn could write in ''The Survey'' that "all those who properly call themselves industrial unionists ... refuse to bind themselves by means of contracts with their employers. Believing, as they do, that there is an inevitable and continuous struggle between employers and employed, it seems to them that a contract is a truce with their natural enemy, a truce, moreover, which gives him all the advantage." Within two decades, based upon experience with other unions whose philosophies did not preclude undercutting embattled groups of industrial workers for the sake of securing their own contract, this would no longer be the case. The... the IWW attracted a remarkable selection of young revolutionary militants to its banner. As a union, the organization led many strikes which swelled the membership momentarily. But after the strikes were over, whether won or lost, stable union organization was not maintained. After every strike, the membership settled down again to the die-hard cadre united on principle.This circumstance prompted a discussion in the IWW press of the question, "What's wrong with the IWW?" The job delegate system of the AWO proved successful and, for a time, allowed the IWW to ignore the problem of failing to retain members. Rather than soap boxing to sign up workers between jobs, carefully chosen union members with card kits were sent into the fields to sign up others on the job. The results were a considerable improvement. Between 1915 and 1917, the IWW's Agricultural Workers Organization (AWO) organized more than a hundred thousand migratory farm workers throughout the midwest and western United States. IWW members were routinely blacklisted from farm worker employment offices, prompting the IWW to advise job delegates to tear up their personal IWW cards in front of the boss to hold onto their own job. The AWO office would later provide a duplicate card. But signing up significant numbers of workers only eased, and did not in any way solve the problem of membership losses resulting from the no contract philosophy. The question of contract became an important factor that tended to divide members of the IWW from their leaders. The two principles of fighting for better wages, hours and conditions, and preparing for the ultimate triumph of labor often came into conflict. IWW members frequently chose the former, while their leadership often saw the latter principle as predominant. As Philip Foner put it, activities that were logical and necessary on the trade union front frequently had to be rejected because they conflicted with revolutionary aims. In ''Oil, Wheat & Wobblies'', a book about the Industrial Workers of the World in Oklahoma, Nigel Anthony Sellars wrote that although the CIO "inherited the egalitarian traditions and syndicalist ideals" of the IWW, the CIO succeeded where the IWW had failed (in mass organizing of industrial unions) "in part because the newer organization did not repeat the Wobblies' mistakes, such as refusing to sign time contracts and rejecting political action." The IWW view of political action has not been much affected by such analysis. However, in the period of the CIO's impressive ascent, the IWW philosophy about contracts was beginning to evolve. In military terms, the contract eventually came to be viewed somewhat as the role of the infantry, in that ground captured must in some fashion become ground held. There are two aspects of the contract question: official recognition of the union by the employer, and the labor contract itself. During its early years, the IWW rejected both. Foner observed that the larger, stronger IWW locals were able to live with this circumstance, for they achieved recognition by force of numbers. However, weak IWW unions lost job control because hostile employers were not bound by contractual recognition, and the companies therefore resorted to hiring workers who were not IWW members. Conlin observed, " e issues of time contracts and union recognition proved to be the Wobblies' Achilles' heel every time they organized a successful strike." Foner concludes that, "ironically, while the refusal to sign contracts was justified, in part, as a means of keeping the capitalists off balance, experience proved that it had the opposite effect of enabling the employers to use it to their own advantage." One example of membership loss and acquisition relating to the contract occurred in the Baltimore garment industry. By September 1913 the IWW had organized some of the largest garment shops in the city. During a fourteen-week strike, the IWW was undercut when the conservative AFL-affiliated United Garment Workers (UGW) brought in scab replacement workers. Shortly afterward, at their 1914 Nashville convention, a group of disenchanted UGW unionists split off to form the
e critical question is not whether or not to have a contract. The critical question is what is in the contract. Ninety-nine percent of AFL–CIO contracts contain a no-strike clause, whereby labor gives up its self-activity, and a management prerogative clause, whereby management retains its ability to act unilaterally, for instance in closing plants. No contract is better than such a contract.
No-strike clause
Contracts enforce "labor peace" through a clause that prohibits strikes for the duration of the contract. Some unions agree to a no-strike clause in exchange for a grievance arbitration provision, or some similar concession."No Strike Clause Law & Legal Definition"USLegal.com. retrieved March 28, 2011 Not all labor contracts have no-strike clauses. On some occasions, no-strike clauses have become a contract issue in dispute, with workers refusing to accept the no-strike clause, and employers refusing to agree to a contract without same. In 2005, Staughton Lynd discussed the historical and legal circumstances relating to the no-strike clause at the IWW's centenary in
When John L. Lewis, Philip Murray, and other men of power in the newWhile the NLRA protects the right to strike, some strikes do not have legal protection. For example, " a collective bargaining agreement contains a no-strike clause (the union agrees not to go on strike while the contract is in effect), a strike during the life of the contract would not be protected. The strikers could be fired." Some no-strike clauses, however, have qualifications which protect the workers, for example, if they refuse to perform assigned work that has been struck by other workers.CIO CIO may refer to: Organizations * Central Imagery Office, a predecessor of the American National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency * Central Intelligence Office, the national intelligence agency of the former Republic of Vietnam * Central Intellige ...negotiated the first contracts for auto workers and steelworkers, these contracts, even if only a few pages long, typically contained a no-strike clause. All workers in a given workplace were now prohibited from striking as particular crafts had been before. This remains the situation today. Nothing in labor law required a no-strike clause. Indeed, the drafters of the originalNational Labor Relations Act The National Labor Relations Act of 1935, also known as the Wagner Act, is a foundational statute of United States labor law that guarantees the right of private sector employees to organize into trade unions, engage in collective bargaining, and ...(or Wagner Act) went out of their way to ensure that the law would not be used to curtail the right to strike. Not only does federal labor law affirm the right "to engage in . . . concerted activities for the purpose of . . . mutual aid or protection"; even as amended by the Taft–Hartley Act of 1947, Section 502 of what is now called the Labor Management Relations Act declares: :Nothing in this Act shall be construed to require an individual employee to render labor or service without his consent, nor shall anything in this Act be construed to make the quitting of his labor by an individual employee an illegal act; nor shall any court issue any process to compel the performance by an individual employee of such labor or service, without his consent; nor shall the quitting of work by an employee or employees in good faith because of abnormally dangerous conditions for work at the place of employment of such employee or employees be deemed a strike under this chapter and for good measure, the drafters added in Section 13 of the NLRA, now section 163 of the LMRA: "Nothing in this Act, except as specifically provided for herein, shall be construed so as either to interfere with or impede or diminish in any way the right to strike."
Tactics and action
Direct action
The Industrial Workers of the World inherited the concept of economic action (as opposed to political action), in part, from the American Labor Union. Melvyn Dubofsky associates economic action with what the IWW would later call direct action. The IWW first mentioned the term "direct action" in a Wobbly publication in reference to a Chicago strike conducted in 1910. In this instance the specific methods of direct action are not recorded, but the account referred to a successful strike against Hansel & Elcock Construction which was followed by former strikers persuading former strike breakers to "dismiss themselves" from the job. Direct action in the labor movement initially referred to the actions taken by workers for themselves, as opposed to actions taken in their name by legislative or other representatives. For example, dual-card IWW members have been known to advocate direct action on the shop floor to force employers to provide safer working conditions, to be more responsive to workers' demands, and to avoid speedup situations. However, the expression has sometimes "been contorted to cover all the implications of mayhem and destruction..." Some of the confusion may result from varying definitions offered by different Wobbly publications. The '' Industrial Worker'' described direct action as "any effort made directly for the purpose of getting more of the goods from the boss." The eastern U.S. IWW publication ''Soapboxing and free speech fights
Although lauded by civil libertarians as an important part of the struggles for civil and constitutional rights, the IWW's free speech fights were carried out for more concrete goals. If they weren't allowed to talk to workers, they wouldn't be able to organize workers. Wobbly activists simultaneously demonstrated that direct action works, and that it was possible for members of the lower strata of society to challenge authority and, through determination and perseverance, to frequently win. The workers and the IWW had a common enemy in the communities that became free speech battlegrounds. These were the job sharks, agencies that controlled employment in agriculture and the timber industry. The combination of sharks, anti-union employers, and hostile or indifferent communities kept wages low, and employment uncertain for many workers. The attitude in some communities toward IWW members engaging in the fight for free speech is nicely characterized by an editorial in the ''San Diego Tribune'' on March 4, 1912:Hanging is none too good for them and they would be much better dead, for they are absolutely useless in the human economy. They are the waste material of creation and they should be drained off into the sewer of oblivion, there to rot in cold obstruction like any other excrement.The strategy of the IWW during free speech fights was to put out a call for "footloose" workers to come to the community, and to challenge a no speaking ordinance simply by violating it. Wobblies would talk about the job, the unfairness of the system, or would simply read the Declaration of Independence, or the Bill of Rights to the U.S. Constitution. In violation of the law, they would get arrested. By filling the jails with workers, the IWW was able to put pressure on the community's taxpayers, who ultimately had to pay the bill for feeding and housing the prisoners. The taxpayers presumably had the power to avoid such expenses by forcing the local administration to change its policies, or to overturn the ordinance itself.
Conventional strikes
A primary goal of unions is to improve the wages, hours, and working conditions of working people, and the strike, or threat of a strike is one mechanism by which that can be accomplished. However, the IWW also believe that the strike is a means by which working people can educate themselves to the issues of class struggle. Such education, according to the Wobblies, is necessary training in the effort to properly exercise the general strike, which (according to IWW theory) is the best means by which to establish an industrial democracy.Bill Haywood, ''The General Strike'' (Chicago, n.d.), pamphlet, published by Industrial Workers of the World, from a New York City speech delivered March 16, 1911. The IWW has engaged in a significant number of celebrated strikes throughout its colorful history. Each is rich in its own way. During the Colorado coal strike of 1927, IWW organizers had the opportunity to apply many of the strategies and tactics they'd adopted during the previous decades.=Colorado coal strike (a case study)
= Joseph Conlin has written that the 1927 coal strike was a "unique, indeed critical event in the social and economic history of the West." First, it was a coal strike run by Wobblies, rather than the United Mine Workers. Second, many of the miners had a company union, yet still elected to strike under the IWW. Third, it had the first positive result for Colorado coal miners in sixty years of struggle. The IWW had editorially criticized the leadership of the United Mine Workers (UMW) during the 1913-14 strike which had led to the Ludlow Massacre. Their view: the miners had been "sold out" by "politicians" who had timidly refused to employ the full power of an aroused working class. The United Mine Workers responded by banning IWW card holders from membership in the UMW. Because the United Mine Workers had essentially left Colorado in defeat a decade earlier, the IWW began organizing Colorado coal miners in 1925. Organizer Frank Jurich was joined by A.S. Embree, a popular and very capable IWW organizer. Embree had just come from prison, having been incarcerated on syndicalist charges. While in prison, Embree indicated his dedication to the cause. He had written, "The end in view he revolutionis well worth striving for, but in the struggle itself lies the happiness of the fighter." Embree initially began organizing outlying camps to avoid company opposition. In 1927 the IWW called for a three-day nationwide walkout to protest the execution of Sacco and Vanzetti. While the United Mine Workers predicted the IWW's walkout would fail in Colorado, Sheriff Harry Capps of Huerfano County commented that "fully two-thirds of the miners in the alsenburgdistrict remembers of the I.W.W." When the walkout occurred, out of a total 1,167 miners, 1,132 stayed off the job, and only 35 went to work. Under threat of injunction, the IWW leaders felt they'd demonstrated success, and they persuaded the miners to return to work one day early. Conlin wrote, "The tactical decision of the Wobblies was to give ground on this occasion to intensify organizing efforts for a statewide strike." Organizing proceeded apace. In one mine, the Supervisor went to work one morning and discovered "Wobbly stickers pasted on every timber and cross beam in the place:'' 'Join the Wobblies, Join the Wobblies.'"'' There were IWW posters "from the bottom of the shaft clear to the working face." IWW leader Kristin Svanum met in a mass meeting with 187 delegates from 43 of the state's 125 mines to work out the miners' demands. ''You'd think the coal miner was the dirtiest reptile that walked the earth. Everybody was down on the coal miner when he went on strike ... And the teachers were against us. And they had their favorites. The scabs' boys were in there too and, of course, we had gangs just like they do today. And the teachers would side with the scabs' side. Why hells bells man, we had to do something! So we organized (Junior Wobblies) at school just to protect ourselves.The State of Colorado and local law enforcement began to arrest every strike leader that they could identify, on vagrancy or other trumped up charges. Many were deported from the state. In Trinidad, in Walsenberg, and elsewhere, members of strikers' families stepped forward to take the place of arrested leaders, and lead the strike. Seventy-five IWW members in the Trinidad jail conducted protests that featured bonfires. Prisoners in the Lafayette jail carried on incessant singing. When they were offered their freedom, they refused to leave. A group of prisoners in Erie persuaded their jailers that deputies in Utah and Wyoming received higher pay, had better working conditions, and worked shorter hours. In Pueblo, the jail was secured by "200 deputies armed with tear bombs, machine guns, rifles, and fire engine pumpers." Newspapers began calling for the governor to no longer withhold the "mailed fist", to strike hard and strike swiftly, and for "Machine Guns Manned By Willing Shooters" at more of the state's coal mines. Within days, state police and mine guards fired machine guns, rifles, and pistols against 500 unarmed miners and their wives at the Columbine mine, killing six. Now faced with their own massacre, the IWW's leaders kept their focus on the immediate goal: winning the strike. After the memorial services, when some angry miners talked about getting their guns, organizers counseled them with the words of Joe Hill: "don't mourn, organize!" The miners won a dollar a day increase from the 1927 strike. The miners in the northern field won union recognition from the second largest coal operator in Colorado. It was not recognition of the IWW, as it turned out. The company picked a union for the miners, and it was the United Mine Workers. Nonetheless, these were the most substantial gains the miners had ever achieved from a strike in Colorado. It was the only increase obtained by coal miners in the country during the period from 1928 to 1930. Although the United Mine Workers in Colorado had vocally opposed the strike, they had established an official position of neutrality. However, United Mine Workers agents conducted overt actions against the strikers, including participation in vigilante raids against IWW property. Some UMW miners scabbed on the IWW strike, and others became informants for the state police. One popular United Mine Workers official, a union organizer from the Ludlow era by the name of Mike Livoda, hired himself out to the governor to spy on the Wobblies. The most pervasive spying during the 1927 strike was most probably conducted by Colorado Fuel and Iron, the coal and steel company owned by the Rockefeller dynasty. The company organized a network of spies to infiltrate, propagandize against, and disrupt the IWW. Archives currently held at the
Intermittent and short strikes
A long drawn out strike implies insufficient organization or that the strike has occurred at a time when the employer can best afford a shut down—or both. Under all ordinary circumstances a strike that is not won in four to six weeks cannot be won by remaining out longer. In trustified industry the employer can better afford to fight one strike that lasts six months than he can six strikes that take place in that period.Strikes are to be called "when the employers can least afford a cessation of work—during the busy season and when there are rush orders to be filled." If a strike does not succeed, St. John advises, then the employees go back to work and continue to conduct a job action while on the job. (See '' Strike on the job'', below.) St. John envisioned that strike breakers could be isolated by the union. "Interference by the government is resented by open violation of the government's orders, ndgoing to jail en masse..."
Sit-down strikes
When workers conduct a sit-down strike, they take possession of the workplace by "sitting down" at their work stations, preventing the employer from replacing them with strikebreakers, or moving production to other locations.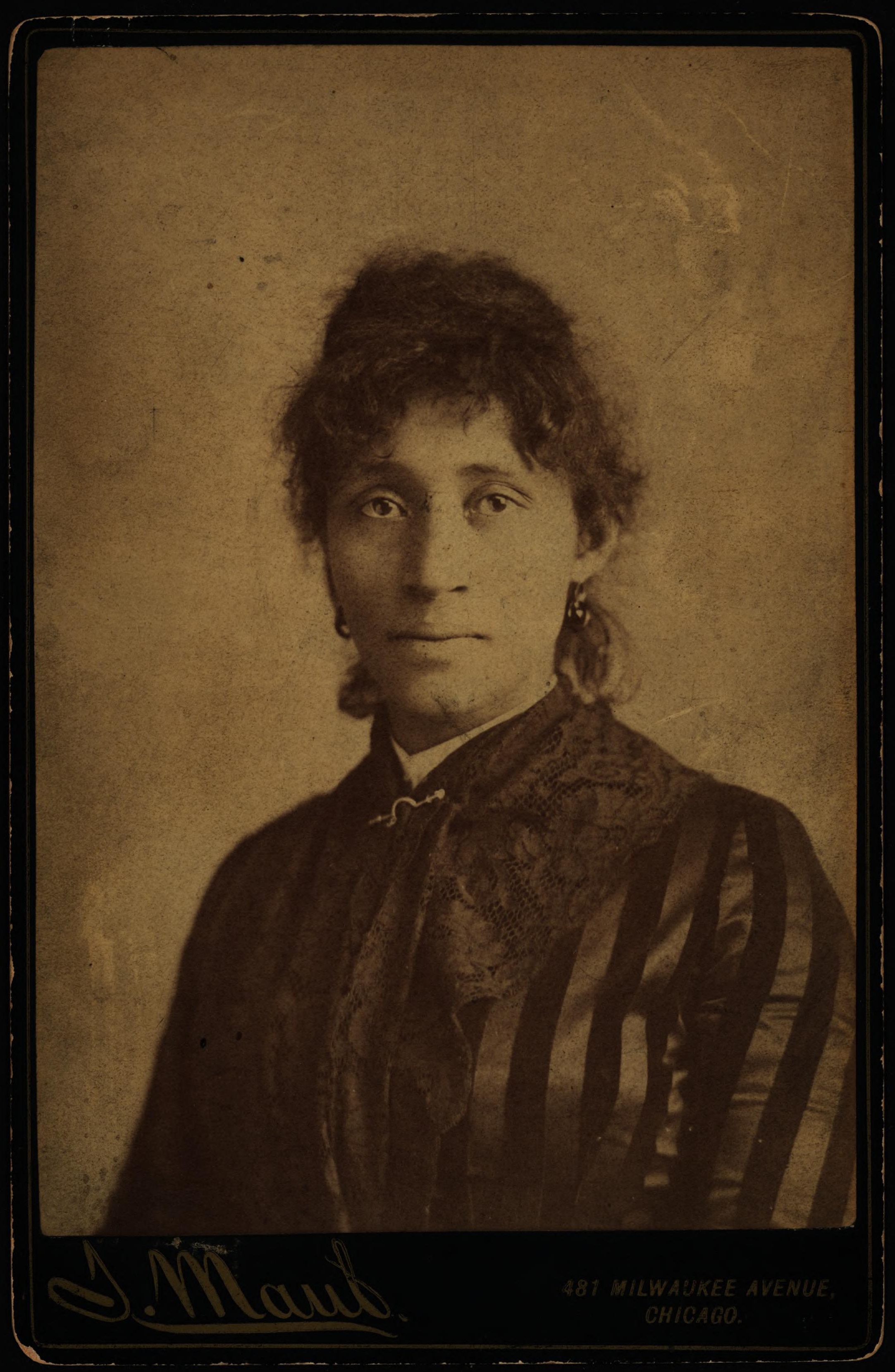 Lucy Parsons, whose husband was executed in the aftermath of the
Lucy Parsons, whose husband was executed in the aftermath of the Boycotts
Although the IWW pioneered the economic boycott, The New York ''Tribune'' suggested that the IWW was a German front, responsible for acts of sabotage throughout the nation. The IWW did not use the boycott frequently in its early days, primarily because IWW members were frequently not consumers of the products which might be boycotted. However, the organization did believe that the boycott could be an effective weapon in some situations. During the 1912 textile strike inGeneral strike
According to a pamphlet produced by the Industrial Workers of the World,A general strike is a strike involving workers across multiple trades or industries that involves enough workers to cause serious economic disruption. In essence, a general strike is the complete and total shutdown of the economy. A general strike can last for a day, a week, or longer depending on the severity of the crisis, the resolve of the strikers, and the extent of public solidarity. During the strike, large numbers of workers in many industries (excluding employees of crucial services, such as emergency/medical) will stop working and no money or labor is exchanged. All decisions regarding the length of the strike, the groups of workers who continue working, and demands of the strikers are decided by a strike committee.
The capitalists have wealth; they have money. They invest the money in machinery, in the resources of the earth. They operate a factory, a mine, a railroad, a mill. They will keep that factory running just as long as there are profits coming in. When anything happens to disturb the profits, what do the capitalists do? They go on strike, don't they? They withdraw their finances from that particular mill. They close it down because there are no profits to be made there. They don't care what becomes of the working class. But the working class, on the other hand, has always been taught to take care of the capitalist's interest in the property.Haywood acknowledged three different levels of general strike: * general strike in an industry; * general strike in a community; * general national strike. The ultimate goal of the general strike, according to the Industrial Workers of the World, is to displace capitalists and give control over the means of production to workers. Foner notes that the first person recorded mentioning the general strike as a weapon for the IWW was Lucy Parsons. The concept didn't receive much attention from the Wobbly press until 1910, and especially 1911.
=Industrial democracy
= According to Wobbly theory, the conventional strike is an important (but not the only) weapon for improving wages, hours, and working conditions for working people. These strikes are also good training to help workers educate themselves about the class struggle, and about what it will take to execute an eventual general strike for the purpose of achieving industrial democracy. During the final general strike, workers would not walk out of their shops, factories, mines, and mills, but would rather occupy their workplaces and take them over. Prior to taking action to initiate industrial democracy, workers would need to educate themselves with technical and managerial knowledge in order to operate industry. According to Foner, the Wobbly conception of industrial democracy is intentionally not presented in detail by IWW theorists; in that sense, the details are left to the "future development of society." However, certain concepts are implicit. Industrial democracy will be "a new society uiltwithin the shell of the old." Members of the industrial union educate themselves to operate industry according to democratic principles, and without the current hierarchical ownership/management structure. Issues such as production and distribution would be managed by the workers themselves.Strike on the job
A "strike on the job" was often called when a conventional strike seemed likely to lose. When some Wobblies were fired for exercising a strike on the job, they would move to a different job, unafraid to repeat the tactic as needed. (See '' Silent strike, slowdown, exceptional obedience (work to rule)'', below.)Silent strike, slowdown and exceptional obedience (work to rule)
Several labor historians have used the expression "silent strike" to identify one strike tactic among many ascribed to the IWW. However, it doesn't appear that the Industrial Workers of the World often used the expression "silent strike." One exception was a 1911 report from Frank Little to the ''Industrial Worker'' on his time working with California farmworkers. "We have the silent strike on. ... The slave drivers are wild—the slaves won't work as hard as they want them to." A definition of silent strike is offered in a book about the Filipino sugar strike of 1924–1925:Employees who do not receive the wages demanded will go on a silent strike, staying on the job, but doing only enough work to earn the wages they receive.According to the book, no IWW organizers were involved in a strike that erupted into a gunbattle, but the ''Honolulu Star-Bulletin'' blamed the IWW for the labor unrest anyway. ''
In case of failure to achieve any gains by a strike, the worker resorts to sabotage, the silent strike by which are gained all the advantages of the open strike without its dangers; i.e., the men keep their places at their machines, thus preventing and making unnecessary the employment of scabs, pretending to do the work for which they receive their pay, but actually doing only so much of it as is needed to deceive the overseers. At the same time the worker employs many methods of attacking the employer, such as breaking delicate parts of machinery, mixing wrong ingredients into compounds, telling truth or lies to customers, anything, in short, to force the employer to terms. It is useless to assert that these methods will not appeal to AngloSaxon workers, as does one writer on the subject. Certainly sabotage is not "fair-play," but neither is in the eyes of the laborer, the condition which forces him to it.The terms "exceptional obedience" and " work to rule" appear to be modern variations of a similar expression frequently used by the Wobblies—"striking on the job." This tactic went by other names (and descriptions) as well. In her introduction of the 1916 pamphlet "Sabotage", Elizabeth Gurley Flynn observed that "sabotage san instinctive defense hatexisted long before it was ever officially recognized by any labor organization. Sabotage means primarily: the withdrawal of efficiency." (See ''
Sometimes, it was claimed, the workers could even effect sabotage through exceptional obedience: Williams and Haywood were fond of noting that Italian and French workers had on occasion tied up the national railroads simply by observing every operating rule in their work regulations.The IWW withdrew the "official" status of Flynn's sabotage pamphlet, but it is still in circulation. In 1919 the IWW likewise advised its membership that the broad IWW definition of sabotage, essentially covering a range of activities from slacking on the job to disabling equipment, had become so distorted toward the latter (in the IWW's view) that the use of the word had become more trouble than it was worth (See ''
Workers have the power to inflict economic damage on a company without going on strike. They can use this power to extract concessions at the bargaining table by disrupting production, undermining management control on the shop floor, and hurting the company's profits—while still on the job. Such "inside strategies" are not easy, but they can be better than walking out, especially when the company is prepared for a strike.The ''Troublemaker's Handbook'' discusses some legal aspects of "inside strategies", including the fact that legality may depend, in part, upon the reasons offered for a work to rule campaign. The modern IWW likewise offers disclaimers on its website when introducing historical documents related to sabotage, for example,
xcerptThe IWW takes no official position on sabotage (i.e., the IWW neither condones nor condemns such actions). Workers who engage in some ... forms of sabotage risk legal sanctions.
Sabotage
When disgruntled workers damage or destroy equipment or interfere with the smooth running of a workplace, it is called workplace sabotage. WhileThe experience that had the most lasting impact on Haywood was witnessing a general strike on the French railroads. Tired of waiting for parliament to act on their demands, railroad workers walked off their jobs all across the country. The French government responded by drafting the strikers into the army and then ordering them back to work. Undaunted, the workers carried their strike to the job. Suddenly, they could not seem to do anything right. Perishables sat for weeks, sidetracked and forgotten. Freight bound for Paris was misdirected to Lyon or Marseille instead. This tactic—the French called it "sabotage"—won the strikers their demands and impressed Bill Haywood.For the IWW, sabotage came to mean any withdrawal of efficiency—including the slowdown, the strike, or creative bungling of job assignments.
Although there are contradictory opinions as to whether the IWW practices sabotage or not, it is interesting to note that no case of an IWW saboteur caught practicing sabotage or convicted of its practice is available.Melvyn Dubofsky has written, "...hard as they tried, state and federal authorities could never establish legal proof of IWW-instigated sabotage. Rudolph Katz ... was perhaps close to the truth when he informed federal investigators, 'The American Federation of Labor does not preach sabotage, but it practices sabotage; and the I.W.W. preaches sabotage, but does not practice it.'" Conlin seems not to accept the implied Wobbly innocence on the charge of sabotage. Rather, he puts any possible transgressions into a different perspective, writing (in 1969) that in the aftermath of the anti-war crackdown,
The I.W.W.'s actual culpability of wheatfield fires and sawmill wreckings had become unimportant because of the government's greater offenses.In 1918, sedition and anti-sabotage laws were passed in the United States. The General Executive Board of the IWW issued a statement referring to the anti-sabotage law,John Castell Hopkins, ''The Canadian Annual Review of Public Affairs'', 1919, pages 304–305. which concluded:
The membership will find it to their advantage to forget and drop the word. The word itself is not worth it. It may arise again in the future in its true light and in its true meaning. If so, the future will care for itself. We should be and are too busy building the One Big Union to argue with Congress or departments of justice as to the real meaning of a poor French word.Robert Hoxie, whose work was collected in the 1921 publication ''Trade Unionism in the United States'', was one of the foremost experts on the trade union movement in the early twentieth century. Hoxie considered the Industrial Workers of the World the "most clear representative" of revolutionary unionism in the United States. In his discussion of the IWW, he explained the nature of sabotage in detail that is worth quoting at length:
Sabotage is an elusive phenomena and is difficult of accurate definition. Briefly described it is called "striking on the job." J. A. Estey, in his "Revolutionary Unionism," does well when he says: "In Syndicalist practice it abotageis a comprehensive term, covering every process by which the laborer, while remaining at work, tries to damage the interests of his employer, whether by simple malingering, or by bad quality of work, or by doing actual damage to tools and machinery" (p. 96). This definition puts admirably the essential, underlying characteristics of sabotage, but in practice it ranges even beyond such limits. There are almost an indefinite number of ways of "putting the boots to the employer" which have come to properly be included under the general designation, and some of them have been employed by conservative unionists time out of mind. Ca' Canny or soldiering is one of them, which was a practice long before revolutionary unionism was known to the mass of workers. In essence it is practiced by every union that sets a limitation on output. Living strictly up to impossible safety rules enacted by the employers for their own protection is another method. Wasting materials, turning out goods of inferior quality or damaging them in the process, misdirecting shipments, telling the truth about the quality of products, changing price cards, sanding the bearings, salting the soup and the sheets, "throwing the monkey wrench into the machinery"—all are methods of practicing sabotage that have become familiar.
Violence
A study in 1969 concluded that "IWW activity was virtually free of violence." However, it was not uncommon for violence to be called for, and used against IWW organizers and members. In 1917, for example, popular organizer Frank Little, an officer of the IWW's General Executive Board, was hanged from a Butte, Montana railroad trestle, a victim of vigilante justice. And during the 1927 coal strike in Colorado, the ''Denver Morning Post'' editorialized that if the Wobblies picketed again, then it was time for the governor to stop withholding the "mailed fist", and to strike hard and strike swiftly against them. Two weeks later, the ''Boulder Daily Camera'' editorialized that "machine guns manned by willing shooters are wanted" at Colorado coal mines. The following week, striking miners were machine gunned by the state, and six died. Conlin has asserted that "few organizations in American history of any stripe have experienced repression so cynical as did the I.W.W." In a few cases, violence was met with violence. Who was at fault, and who initiated the attack, have been historical questions debated to the present day in both the Everett massacre and the Centralia massacre, although a study by Philip Taft and Philip Ross concludes that "the IWW in Everett and Centralia was the victim, and the violence was a response to attacks made upon its members for exercising their constitutional rights." Thus, it is no surprise that the question of violence was a perennial matter of discussion and debate within the IWW. Some, like Arturo Giovannitti, Elizabeth Gurley Flynn, andIt will be revolution, but it will be bloodless revolution. The world is turning against war. People are sickened at the thought. Even labor wars of the old type are passing. I should never think of conducting a strike in the old way. There will never be another Coeur d'Alene, another Cripple Creek. I, for one, have turned my back on violence. It wins nothing. When we strike now, we strike with our hands in our pockets. We have a new kind of violence—the havoc we raise with money by laying down our tools. Our strength lies in the overwhelming power of numbers.Conlin has also observed that "to dwell on the martyrs and the debacle that did in the I.W.W. (i.e., government repression after World War I) is to detract or at least to distract from the Wobblies' importance as a functioning and ... apparently successful union."
=Violence and sabotage as tactics
= In 1969 the ''History of Violence in America'' reported about the 1918 trial of IWW officers and members,Unlike the other national federations such as the Knights of Labor, the American Federation of Labor, and the Congress of Industrial Organizations, the IWW advocated direct action and sabotage. These doctrines were never clearly defined, but did not include violence against isolated individuals. Pamphlets on sabotage by Andre Tridon, Walker C. Smith, and Elizabeth Gurley Flynn were published, but Haywood and the lawyers for the defense at the Federal trial for espionage in Chicago in 1918 denied that sabotage meant destruction of property. Instead Haywood claimed it meant slowing down on the job when the employer refused to make concessions.Foner observes that the IWW's General Executive Board issued a statement opposing violence:
he IWWdoes not now and never has believed in or advocated either destruction or violence as a means of accomplishing industrial reform; first, because no principle was ever settled by such methods; second, because industrial history has taught us that when strikers resort to violence and unlawful methods, all the resources of Government are immediately arrayed against them and they lose their cause; third, because such methods destroy the constructive impulse which it is the purpose of this organization to foster and develop in order that the workers may fit themselves to assume their places in the new society.Robert Hoxie writes,
In the popular conception of things revolutionary unionism is generally distinguished by violence and sabotage. The tendency, however, to make violence the hall-mark of revolutionary unionists is a great mistake. The bulk of revolutionary unionists embraces the most peaceful citizens we have, and on principle. Most violence in labor troubles is committed by conservative unionists or by the unorganized.Hoxie continues,
In short, violence in labor troubles is a unique characteristic of no kind of unionism, but is a general and apparently inevitable incident of the rise of the working class to consciousness and power in capitalistic society. Secondly, revolutionary unionism is not to be marked off from other kinds of unionism by its employment of sabotage as an offensive and defensive weapon. It is true that sabotage is a weapon whose use is highly characteristic of revolutionary unionism, but the notion that its use is confined to revolutionary unionists fades out the moment its true character and varied forms are known. It is moreover distinctly repudiated by many revolutionary unionists, is not confined to revolutionary unions, and, it might be added, is not confined to workers alone.Hoxie explains,
As the unionists point out, essentially the same thing is practiced by employers and dealers who adulterate goods, make shoddy, conceal defects of products, and sell goods for what they are not.
Legislation, injunctions and law
In 1916, the Commission on Industrial Relations, created by the U.S. Congress, reported,The greatest uncertainty exists regarding the legal status of almost every act which may be done in connection with an industrial dispute. In fact, it may be said that it depends almost entirely upon the personal opinion and social ideas of the court in whose jurisdiction the acts may occur. The general effect of the decisions of American courts, however, has been to restrict the activities of labor organizations and deprive them of their most effective weapons, namely, the boycott and the power of picketing, while on the other hand the weapons of employers, namely, the power of arbitrary discharge, of blacklisting, and of bringing in strikebreakers, have been maintained and legislative attempts to restrict the employers' powers have generally been declared unconstitutional by the courts. Furthermore, an additional weapon has been placed in the hands of the employers by many courts in the form of sweeping injunctions, which render punishable acts which would otherwise be legal, and also result in effect in depriving the workers of the right to jury trial.The report includes the testimony of Judge Walter Clark, Chief Justice of the Supreme Court of North Carolina:
Chairman Walsh. Have you studied the effect of the use of injunctions in labor disputes generally in the United States, as a student of economics and the law? Judge Clark. I do not think they can be justified, sir, * * *The congressional report concludes from this exchange,heir effect Inheritance is the practice of receiving private property, titles, debts, entitlements, privileges, rights, and obligations upon the death of an individual. The rules of inheritance differ among societies and have changed over time. Officiall ...has been, of course, to irritate the men, because they feel that in an anglo-Saxon community every man has a right to a trial by jury and that to take him up and compel him to be tried by a judge, is not in accordance with the principles of equality, liberty, and justice. Chairman Walsh. Do you think that has been one of the causes of social unrest in the United States? Judge Clark. Yes, sir, and undoubtedly will be more so, unless it is remedied.
...opinions cited above are very impressive and are convincing that the workers have great reason for their attitude... such injunctions have in many cases inflicted grievous injury upon workmen engaged in disputes with their employers, and ... their interests have been seriously prejudiced by the denial of jury trial, which every criminal is afforded, and by trial before the judge against whom the contempt was alleged ... It is felt to be a duty, therefore, to register a solemn protest against this condition...By most accounts, in spite of its apparent candor, the U.S. Congress failed to act upon this investigation of the reasons for industrial unrest. One significant difference between the IWW and mainstream unions (specifically, the AFL) concerns their interpretation of, and reaction to the law. Laws are passed by the state. AFL unions concerned themselves with issues of law and order. In the eyes of the IWW, the state was variously considered irrelevant, illegitimate, or merely an extension of capitalist power. The IWW Preamble and Constitution, which encapsulate the organization's philosophy and to some extent, formulate policy, are silent on the specific question of government, yielding only a strong implication that government as constituted would cease to exist in a Wobbly world (a "new society within the shell of the old"). To Wobblies beaten by cops while picketing the job, the only law that mattered was the law of the jungle. In the words of historian Melvyn Dubofsky, the AFL sought industrial harmony, the IWW praised perpetual industrial war. Dubofsky concludes that while Wobbly speechmaking often created a wrong perception of IWW intentions and practices, the IWW actually practiced passive resistance and promoted non-violence. Yet passive resistance is distinct from pacifism. Dubofsky wrote,
Nonviolence was only a means to an end. If passive resistance resulted only in beatings and deaths, then the IWW threatened to respond in kind.Arturo Giovannitti summarized his perception of the Wobbly philosophy, "The generally accepted notion seems to be that to kill is a great crime, but to be killed is the greatest." Labor legislation can have a very significant impact upon union organizing, and efforts to organize the coal industry offer a good example. Coal miners had been struggling for sixty years to organize unions in the Western United States, with little success. All of that changed in the early 1930s when the companies began to perceive a difference between the business unionism of the United Mine Workers, and their more radical competitors. In 1933,
Minority unionism
In U.S. legal terminology, the concept of minority unionism refers to the situation in which workers who wish to engage in concerted activity, which means action taken by workers for mutual aid or protection. In the U.S., such activity is protected by federal labor law. Generally speaking, concerted activity takes place, and is therefore protected, whenever two or more employees act together to improve their terms and conditions of employment. (The protections are fairly broad, although corporations frequently benefit from employees not knowing their rights.) According to union activists, workers engaging in concerted activity may also be said to be engaging in minority unionism. While the status of concerted activity is well established, the precise legal status of bargaining rights for a minority union, or alternatively of bargaining rights for individual members of such a union, is not clear. In 2005, Charles Morris published a legal treatise called The Blue Eagle At Work: Reclaiming Democratic Rights in the American Workplace which offers an as yet untested legal theory about minority unionism. However, the Industrial Workers of the World have held from the organization's founding that workers, whether in a majority or not, nonetheless have the right and the ability to join together to act in their own best interest, whether through traditional bargaining, or by other means. This is quite different from more orthodox unions, which typically rely upon union recognition by a workplace majority and a collective bargaining agreement, accompanied by dues checkoff and other conventions, before they will represent a group of employees.Dues collection
The IWW relies upon members to submit dues voluntarily, instead of relying on the "dues check off" system, in which dues are automatically deducted from workers' paychecks by their employer. Throughout the organization's history, a constitutional provision has prohibited IWW organizations from allowing employers to handle union dues. IWW dues collection most typically operates according to the Job Delegate system, which was developed by the Agricultural Workers Organization (AWO) of the IWW.Boxcar Organizing
Beginning around 1915 with the rise of the Agricultural Workers Organization, the field delegates for the IWW used itinerant workers' means of transportation, illegally hopping freight trains, to grow to their ranks. Delegates rode trains and demanded to see a Red Card, proof of membership in the IWW, from each hobo bound for the harvests. If a rider could not produce a card, he or she either had to purchase one from the delegate or get off the train. IWW organizer Harry Howard describes an instance of this in a 1916 letter to ''Solidarity'', the union's national newspaper, writing, "We left on the night of August 10th with twenty-five or thirty other fellow workers. We took charge of the train and ditched all unorganized men at stops north of Fargo." In 1922, the U.S. Marshal to the Western District of Washington collected 19 affidavits from freight train riders in that state who admit seeing this practice. One reads, "The IWW tried to make me take out a card in North Dakota but I refused. When in the State of Washington… I was forced to take out a card or be thrown off in a desolate country." This tactic lost effectiveness as the automobile supplanted the freight train as the most popular form of transportation for itinerant laborers in the mid- to late-1920s.Arianne Hermida. "Wobbly Wheels: The IWW's Boxcar Strategy," ''IwW History Project,'' http://depts.washington.edu/iww/wobbly_trains.shtml#_edn33Publicity and the Wobbly image
The Industrial Workers of the World has enjoyed and occasionally suffered from a distinctive public image. The organization has been chronicled in fiction as varied as Zane Grey's anti-Wobbly book ''Desert of Wheat'', and James Jones' influential 1951 novel, ''From Here to Eternity''. Conlin attributes some of the chronicles to "fascination with the vitality of those on the bottom. He notes, however, that a romantic image of the Wobblies was not ever entirely inappropriate. For example, Haywood was frequently the recipient of invitations from Mabel Dodge Luhan and "other fashionable literati," and "a romanticized IWW" was the subject of books and poems throughout the 1910s. Conlin observes that "no later than 1908, the Wobblies were vividly conscious of their romantic aspect and took easily to self-dramatization." This was evident in their singing, in their song parodies, in their skits, in their poetry and in their cartoons. From soap boxing to the Paterson pageant, from their colorful lingo to "building the battleship" in the free speech fight jails, Wobblies seemed to instinctively comprehend the benefits of publicity for their cause. Conlin does note, however, that shortly after the 1913 Paterson Pageant at Madison Square Garden, the IWW officially disclaimed the utility of such productions, and "turned to more proper union activity" (in a period which coincided with the organization's dramatic growth) until the "apocalypse" of government intervention in 1917–1918.See also
* Anti-union violence * Labor federation competition in the United States * One Big Union (concept)Notes
External links
Wobbly Wheels: The IWW's Boxcar Strategy
An essay about the IWW using boxcars as organizing spaces, recruiting new members, and collecting dues.
The Industrial Workers of the World in the Seattle General Strike
The IWW, the Newspapers, and the 1913 Seattle Potlatch Riot
The Songbird and the Martyr: Katie Phar, Joe Hill, and the Songs of the IWW
Organizing.Work
A blog edited by long-time IWW organizer Marianne Garneau about contemporary solidarity union organizing with a special (although non-exclusive) emphasis on IWW tactics and strategy
References
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{IWW * Labor disputes Civil disobedience Labor relations Protest tactics Strikes (protest)