|
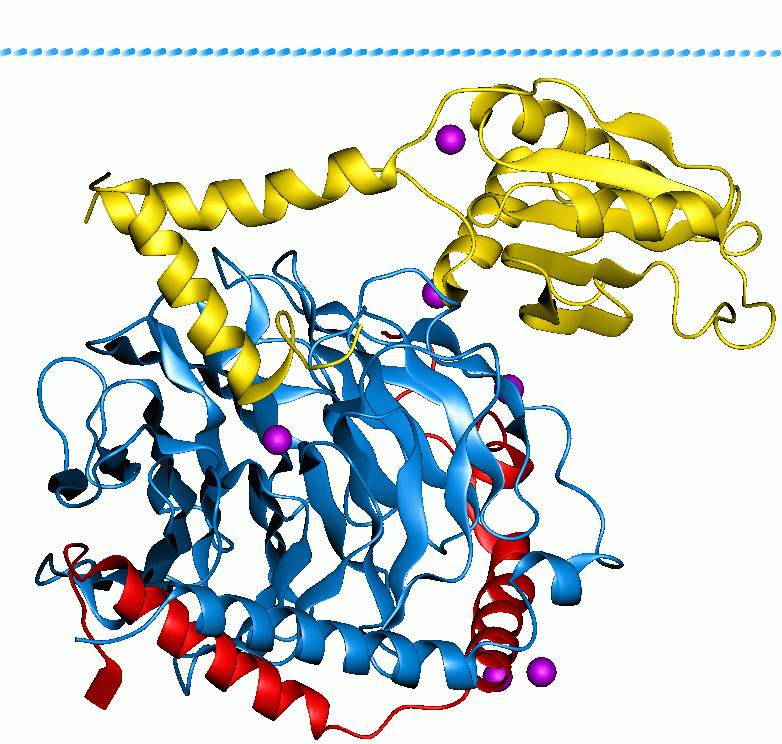
IQSEC2
IQ motif and Sec7 domain 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''IQSEC2'' gene. Function The IQSEC2 gene encodes a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for the ARF family of GTP-binding proteins (see for example ARF1). Clinical significance It is associated with X-Linked mental retardation X-linked intellectual disability refers to medical disorders associated with X-linked recessive inheritance that result in intellectual disability. As with most X-linked disorders, males are more heavily affected than females. Females with one aff ... 1. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * Human proteins {{gene-X-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-Linked Mental Retardation
X-linked intellectual disability refers to medical disorders associated with X-linked recessive inheritance that result in intellectual disability. As with most X-linked disorders, males are more heavily affected than females. Females with one affected X chromosome and one normal X chromosome tend to have milder symptoms. Unlike many other types of intellectual disability, the genetics of these conditions are relatively well understood. It has been estimated there are ~200 genes involved in this syndrome; of these ~100 have been identified. Many of these genes are found on the short 'p' arm of the chromosome, and duplications at Xp11.2 are associated with the syndromic form of the condition. X-linked intellectual disability accounts for ~16% of all cases of intellectual disability in males. Syndromes Several X-linked syndromes include intellectual disability as part of the presentation. These include: * Coffin–Lowry syndrome * DDX3X syndrome * MASA syndrome * MECP2 duplicati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor
Guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) are proteins or protein domains that activate monomeric GTPases by stimulating the release of guanosine diphosphate (GDP) to allow binding of guanosine triphosphate (GTP). A variety of unrelated structural domains have been shown to exhibit guanine nucleotide exchange activity. Some GEFs can activate multiple GTPases while others are specific to a single GTPase. Function Guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) are proteins or protein domains involved in the activation of small GTPases. Small GTPases act as molecular switches in intracellular signaling pathways and have many downstream targets. The most well-known GTPases comprise the Ras superfamily and are involved in essential cell processes such as cell differentiation and proliferation, cytoskeletal organization, vesicle trafficking, and nuclear transport. GTPases are active when bound to GTP and inactive when bound to GDP, allowing their activity to be regulated by GEFs and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G Protein
G proteins, also known as guanine nucleotide-binding proteins, are a family of proteins that act as molecular switches inside cells, and are involved in transmitting signals from a variety of stimuli outside a cell to its interior. Their activity is regulated by factors that control their ability to bind to and hydrolyze guanosine triphosphate (GTP) to guanosine diphosphate (GDP). When they are bound to GTP, they are 'on', and, when they are bound to GDP, they are 'off'. G proteins belong to the larger group of enzymes called GTPases. There are two classes of G proteins. The first function as monomeric small GTPases (small G-proteins), while the second function as heterotrimeric G protein complexes. The latter class of complexes is made up of '' alpha'' (α), ''beta'' (β) and ''gamma'' (γ) subunits. In addition, the beta and gamma subunits can form a stable dimeric complex referred to as the beta-gamma complex . Heterotrimeric G proteins located within the cell are activ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARF1
ADP-ribosylation factor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ARF1'' gene. Function ADP-ribosylation factor 1 (ARF1) is a member of the human ARF gene family. The family members encode small guanine nucleotide-binding proteins that stimulate the ADP-ribosyltransferase activity of cholera toxin and play a role in vesicular trafficking as activators of phospholipase D. The gene products, including 6 ARF proteins and 11 ARF-like proteins, constitute a family of the RAS superfamily. The ARF proteins are categorized as class I (ARF1, ARF2 and ARF3), class II (ARF4 and ARF5) and class III (ARF6), and members of each class share a common gene organization. The ARF1 protein is localized to the Golgi apparatus and has a central role in intra-Golgi transport. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene. The major mechanism of action of Brefeldin A is through inhibition of ARF1. Interactions ARF1 has been shown ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |