|
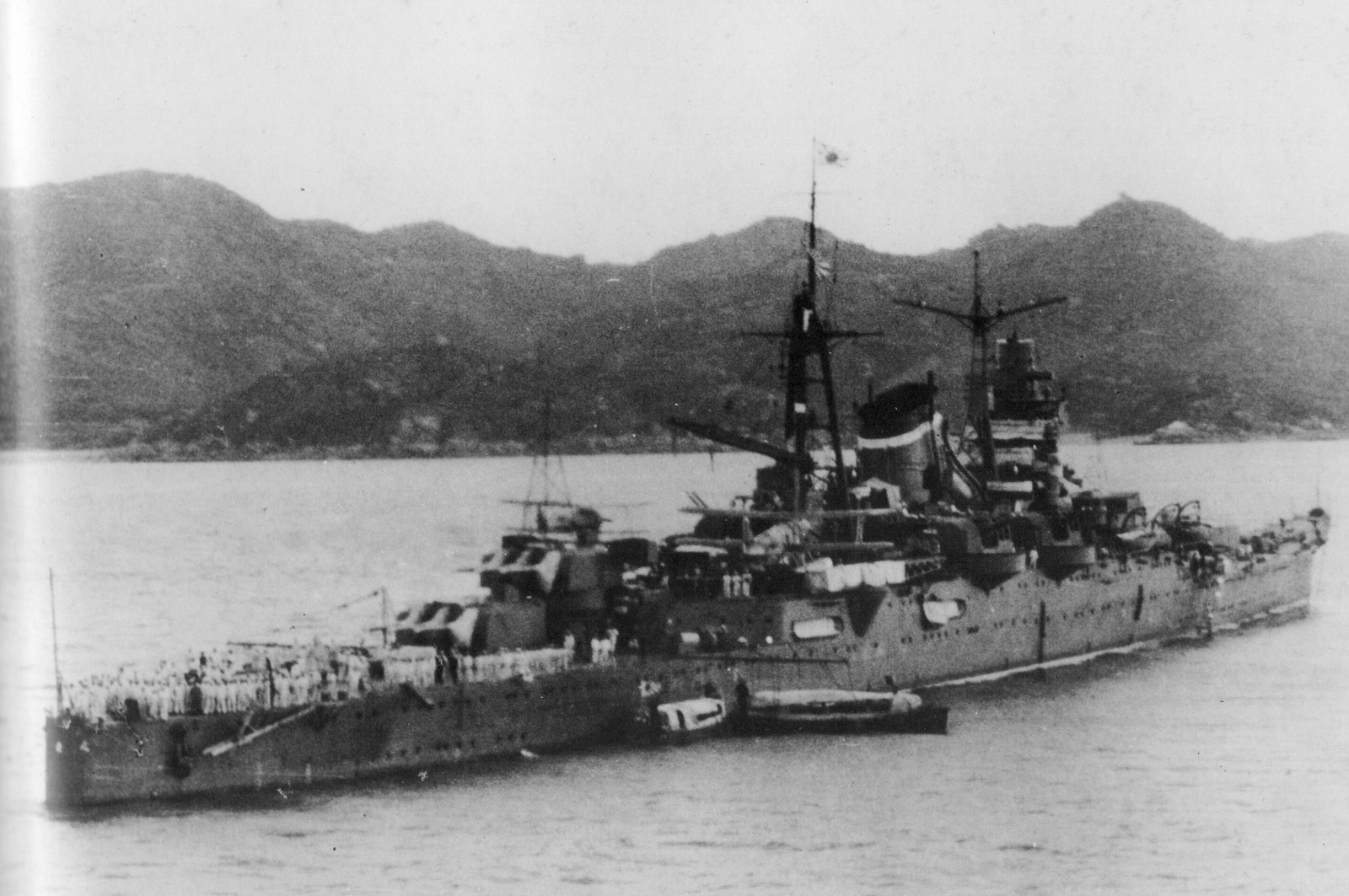
IJN 2nd Fleet
The was a fleet of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) created as a mobile strike force in response to hostilities with Russia, and saw action in every IJN military operation until the end of World War II. History Established on 27 October 1903, the 2nd Fleet was created by the Imperial General Headquarters as a mobile strike force of cruisers and destroyers to pursue the Imperial Russian Navy's Vladivostok-based cruiser squadron while the remaining bulk of the Japanese fleet (the IJN 1st Fleet) continued to blockade Port Arthur in hopes of luring the battleships of the Russian Pacific Fleet into an open sea classic line of battle confrontation. As the main mobile force in the IJN, the 2nd Fleet saw the bulk of all future IJN combat operations from the time of its inception until IJN dissolution at the end of World War II. Order of Battle at time of Pearl Harbor Based at Samah, Hainan Island 4th Division : CA '' Takao'' (fleet flagship) :CA '' Atago'' :CA '' Chōkai'' :CA ''Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific War
The Pacific War, sometimes called the Asia–Pacific War, was the theater of World War II that was fought in Asia, the Pacific Ocean, the Indian Ocean, and Oceania. It was geographically the largest theater of the war, including the vast Pacific Ocean theater, the South West Pacific theater, the Second Sino-Japanese War, and the Soviet–Japanese War. The Second Sino-Japanese War between the Empire of Japan and the Republic of China had been in progress since 7 July 1937, with hostilities dating back as far as 19 September 1931 with the Japanese invasion of Manchuria. However, it is more widely accepted that the Pacific War itself began on 7 December (8 December Japanese time) 1941, when the Japanese simultaneously invaded Thailand, attacked the British colonies of Malaya, Singapore, and Hong Kong as well as the United States military and naval bases in Hawaii, Wake Island, Guam, and the Philippines. The Pacific War saw the Allies pitted against Japan, the latter ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanya
Sanya (; also spelled Samah) is the southernmost city on Hainan Island, and one of the four prefecture-level cities of Hainan Province in South China. According to the 2020 census, the total population of Sanya was 1,031,396 inhabitants, living in an area of . Nevertheless, its built-up (or metro) area encompassing Haitang and Jiyang Districts was home to 801,020 inhabitants as of 2020. The city is renowned for its tropical climate and has emerged as a popular tourist destination, also serving as the training site of the Chinese national beach volleyball team. Sanya is home to small concentrations of Utsul people. Sanya is also the location of Yulin Naval Base, a major military facility on the South China Sea which is home to the People's Liberation Army Navy ballistic nuclear missile fleet. History Known in ancient times as Yazhou, postal romanization: Aichow (), literally "cliff state or prefecture", Sanya's history dates to the Qin Dynasty (221–206 BCE). Due to its r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
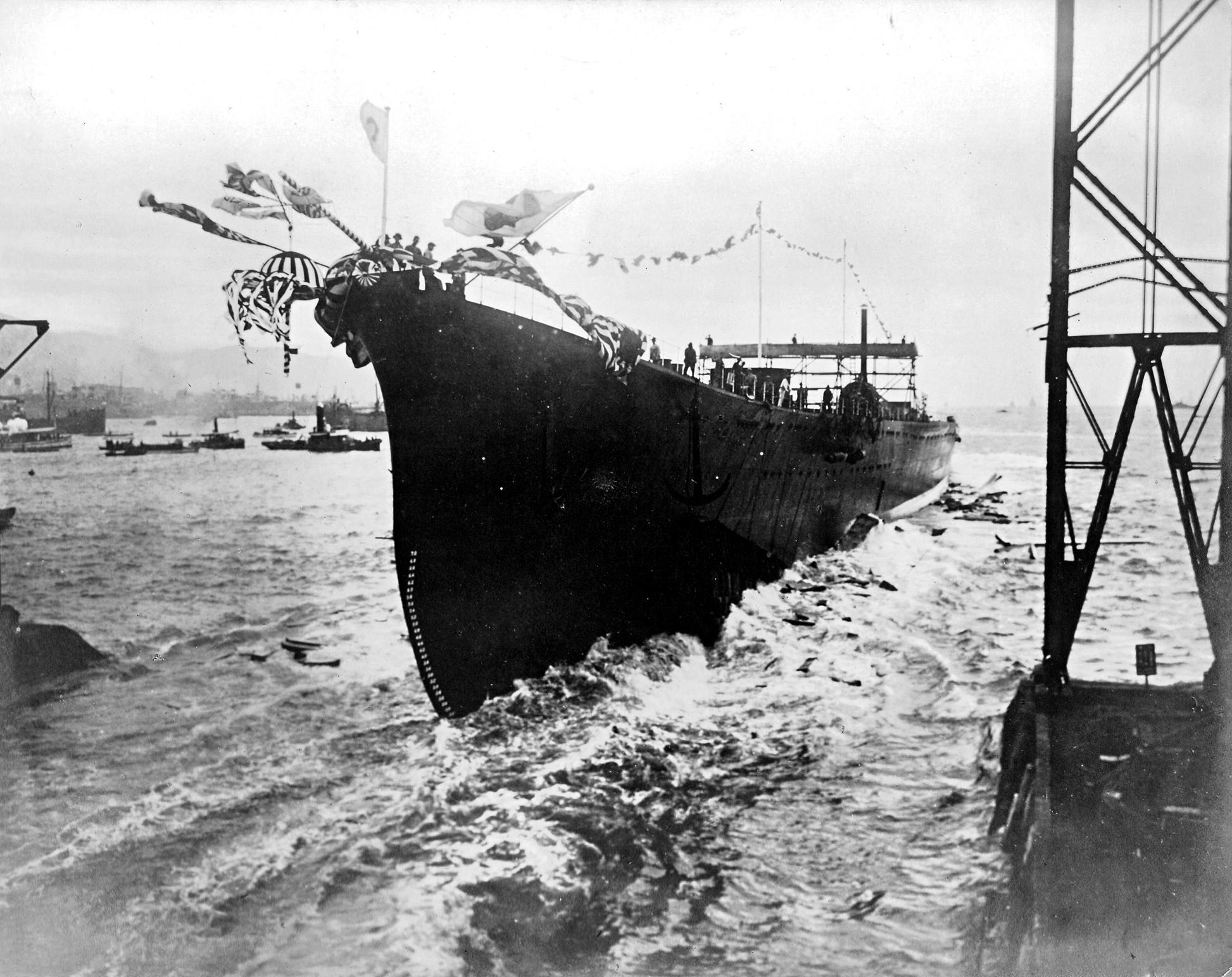
Japanese Cruiser Suzuya (1934)
was the third of four vessels in the of heavy cruisers in the Imperial Japanese Navy.Whitley, ''Cruisers of World War Two'', pp. 181–184 She was named after the Suzuya River on Karafuto, (Sakhalin). Background and design Built under the Maru-1 Naval Armaments Supplement Programme, the ''Mogami''-class cruisers were designed to the maximum limits allowed by the Washington Naval Treaty, using the latest technology. This resulted in the choice of the dual purpose (DP) 15.5 cm/60 3rd Year Type naval guns as the main battery in five triple turrets capable of 55° elevation. These were the first Japanese cruisers with triple turrets.Patton, ''Japanese Heavy Cruisers of World War Two'', pp. 47-52 Secondary armament included eight 12.7 cm/40 Type 89 naval guns in four twin turrets, and 24 Type 93 Long Lance torpedoes in four rotating triple mounts. To save weight, electric welding was used, as was aluminum in the superstructure, and a single funnel stack. New impulse geare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
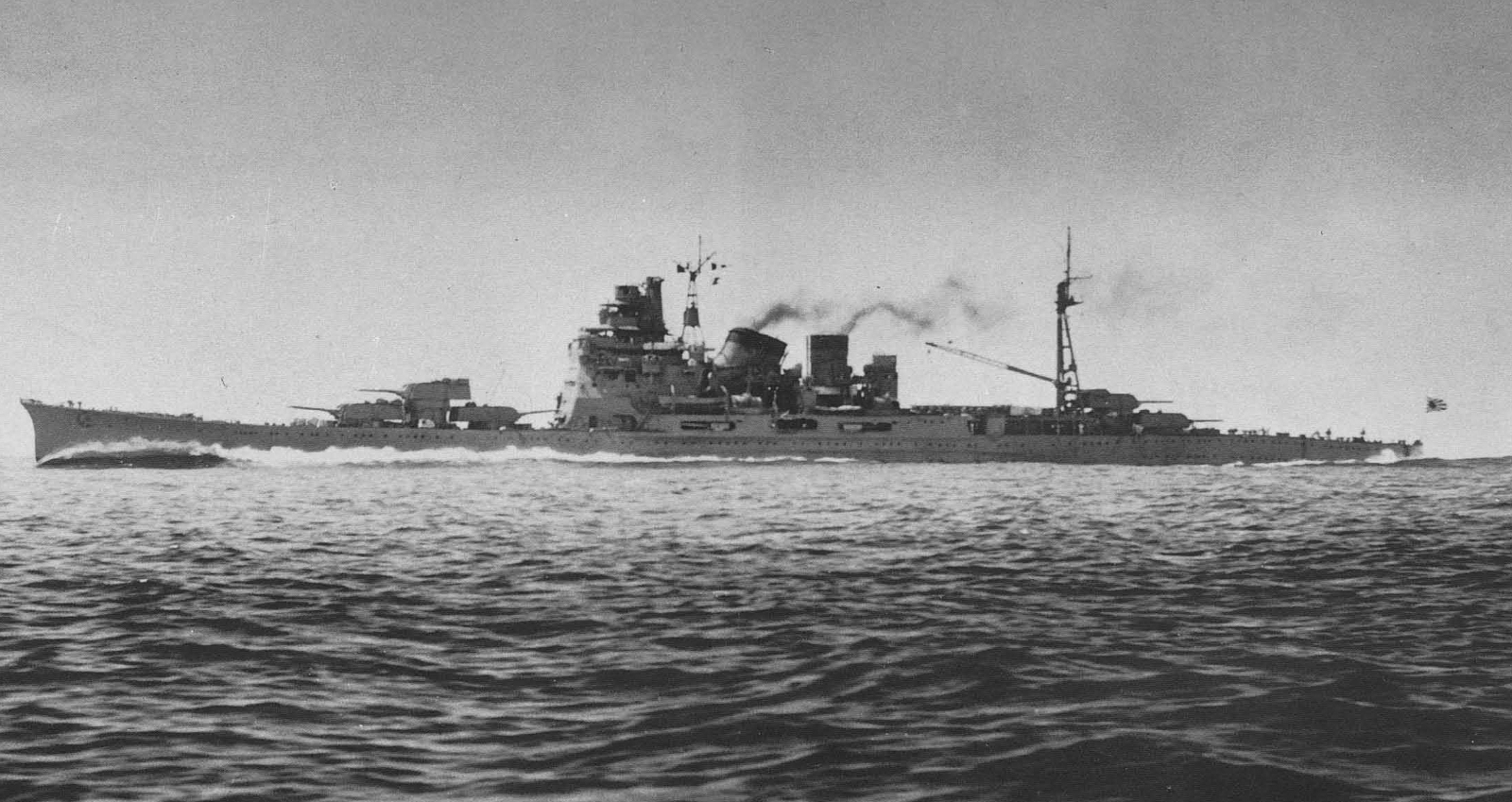
Japanese Cruiser Mogami (1934)
was the lead ship in the four-vessel of heavy cruisers in the Imperial Japanese Navy. She was named after the Mogami River in Tōhoku region of Japan. The ''Mogami''-class ships were constructed as "light cruisers" (per the London Naval Treaty) with five triple 155 mm dual purpose guns. They were exceptionally large for light cruisers, and the barbettes for the main battery were designed for quick refitting with twin 8-inch guns. In 1937 all four ships were "converted" to heavy cruisers in this fashion.Whitley, ''Cruisers of World War Two'', pp. 181-184 ''Mogami'' served in numerous combat engagements in World War II, until she was sunk at the Battle of Leyte Gulf in October 1944. Background and design Built under the Maru-1 Naval Armaments Supplement Programme, the ''Mogami''-class cruisers were designed to the maximum limits allowed by the Washington Naval Treaty, using the latest technology. This resulted in the choice of the dual purpose (DP) 15.5 cm/60 3rd Year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Cruiser Mikuma
was a heavy cruiser of the Imperial Japanese Navy. The second vessel in the four-ship ,Whitley, ''Cruisers of World War Two'', pp. 181-184 she was laid down in 1931 and commissioned in 1935. During World War II she participated in the Battle of Sunda Strait in February 1942 and the Battle of Midway in June 1942, being sunk the last day of the latter engagement, on 6 June. The ship was named after the Mikuma river in Oita prefecture, Japan. Background Built under the 1931 Fleet Replenishment Program, the ''Mogami''-class cruisers were designed to the maximum limits allowed by the Washington Naval Treaty, using the latest technology. This resulted in the choice of a 155 mm dual purpose (DP) main battery in five triple turrets capable of 55° elevation. To save weight, electric welding was used, as was aluminum in the superstructure, and the use of a single funnel stack. New impulse geared turbine engines, coupled with very heavy anti-aircraft protection, gave the cla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Cruiser Kumano
was one of four of heavy cruisers in the Imperial Japanese Navy, serving in World War II. She was named after the Kumano River Kii Peninsula on the island of Honshu in central Japan. The ''Mogami''-class ships were constructed as "light cruisers" (per the Washington Naval Treaty) with five triple 6.1-inch dual purpose guns. They were exceptionally large for light cruisers, and the barbettes for the main battery were designed for quick refitting with twin 8-inch guns. In 1937 all four ships were "converted" to heavy cruisers in this fashion. ''Kumano'' served in numerous combat engagements in the Pacific War, until she was eventually sunk by carrier aircraft from Task Force 38 while she was undergoing repairs at Santa Cruz, Zambales, Philippines, in November 1944. Background and design Built under the 1st Naval Armaments Supplement Programme, Maru-1 Naval Armaments Supplement Programme, the ''Mogami''-class cruisers were designed to the maximum limits allowed by the Washingto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Cruiser Nachi
was the second vessel completed of the four-member of heavy cruisers of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN), which were active in World War II. page 81 The other ships of the class were , , and . She was named after a mountain in Wakayama Prefecture. Background The ''Myōkō'' class was approved under the 1922–1929 Fleet Modernization Program as the first heavy cruisers to be built by Japan within the design constraints imposed by the Washington Naval Treaty, and was the first of the "10,000-ton" cruisers built by any nation.Chesneau, '' All the World’s Fighting Ships'', p. 118. Naval architect Vice admiral Yuzuru Hiraga was able to keep the design from becoming dangerously top-heavy in its early years by continually rejecting demands from the Imperial Japanese Navy General Staff for additional equipment to the upper decks. However, during modifications and rebuildings in the 1930s, the final displacement rose to 15,933 tons, well over the treaty limits.Patton, ''Japanese Heav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Cruiser Myōkō
was the lead ship of the four-member of heavy cruisers of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN), which were active in World War II. page 81 She was named after Mount Myōkō in Niigata Prefecture. The other ships of the class were , , and . Background ''Myōkō'' was approved under the 1922–1929 Fleet Modernization Program, as the first heavy cruiser to be built by Japan within the design constraints imposed by the Washington Naval Treaty, and was the first of the "10,000 ton" cruisers built by any nation.Chesneau, '' All the World’s Fighting Ships'', p. 118. Naval architect Vice-admiral Yuzuru Hiraga was able to keep the design from becoming dangerously top-heavy in its early years by continually rejecting demands from the Imperial Japanese Navy General Staff for additional equipment to the upper decks. However, during modifications and rebuildings in the 1930s, the final displacement rose to 15,933 tons, well over the treaty limits.Patton, ''Japanese Heavy Cruisers of World W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Cruiser Haguro
''Haguro'' (羽黒) was a heavy cruiser of the Imperial Japanese Navy, named after Mount Haguro in Yamagata Prefecture. Commissioned in 1929, ''Haguro'' saw significant service during World War II, participating in nine naval engagements. She was sunk in 1945 during a fight with Royal Navy destroyers, one of the last major Japanese warships to be sunk in open waters during World War II. Design ''Haguro'' was the third of the four-member of heavy cruiser; the other ships were (妙高), (那智), and (足柄). The ships of this class displaced 13,300 tons, were long, and were capable of . They carried two aircraft and their main armament was ten guns in five twin turrets. At the time they were built, this was the heaviest armament of any cruiser class in the world. Construction and career ''Haguro'' was laid down at the Mitsubishi shipyard in Nagasaki on 16 March 1925, launched and named on 24 March 1928, and was commissioned into the Imperial Navy on 25 April 1929. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Cruiser Maya
was one of four heavy cruisers, active in World War II with the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN). These were the largest and most modern cruisers in the Japanese fleet, and were intended to form the backbone of a multipurpose long-range strike force. These ships were fast, powerful and heavily armed, with enough firepower to hold their own against any cruiser in any other navy in the world. Her sister ships were , and . page 84 Background The ''Takao''-class ships were approved under the 1927 to 1931 supplementary fiscal year budget, and were each named after a mountain. Mount Maya is located outside Kobe. Design The ''Takao''-class cruisers were an improved version of the previous design, incorporating technical elements learned with the development of the experimental light cruiser . They had a distinctive profile with a large, raked main smokestack, and a smaller, straight, second smokestack. Intended to address issues with the '' Myōkō '' class, the ''Takao'' class had th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Cruiser Chōkai
was a heavy cruiser, armed with ten guns, four guns, eight tubes for the Type 93 torpedo, and assorted anti-aircraft guns. ''Chōkai'' was designed with the Imperial Japanese Navy strategy of the great "Decisive Battle" in mind, and built in 1932 by Mitsubishi's shipyard in Nagasaki. She was sunk in the Battle off Samar in October 1944. ''Chōkai'' was named for Mount Chōkai. Operational history At the start of the Pacific War, ''Chōkai'' supported the invasion of Malaya and participated in the pursuit of the Royal Navy's battleship Force Z. During January and February 1942, ''Chōkai'' was involved in operations to seize the oil-rich Dutch East Indies and the island of Borneo. Steaming near Cape St. Jacques, ''Chōkai'' struck a reef, sustaining hull damage on 22 February 1942. On 27 February, she reached Singapore for repairs. After repairs, ''Chōkai'' was once again assigned to a support role in an invasion, this time the landings at Iri, Sumatra, and the inv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Cruiser Atago
was the second vessel in the heavy cruisers, active in World War II with the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN). These were among the largest and most modern cruisers in the Japanese fleet, designed with the intention to form the backbone of a multipurpose long-range strike force. Her sister ships were , and . Background The ''Takao''-class ships were approved under the 1927 to 1931 supplementary fiscal year budget, and ''Atago'', like her sister ships, was named after a mountain. In this case, she was named after Mount Atago, located outside Kyoto. Even though Takao was the name ship of the class, Atago was actually finished before Takao. Design The ''Takao''-class cruisers were an improved version of the previous design, incorporating technical elements learned with the development of the experimental light cruiser . They had a distinctive profile with a large, raked main smokestack, and a smaller, straight, second smokestack. Intended to address issues with the ''Myōkō'' c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |