|
IGFBP7
Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''IGFBP7'' gene. The major function of the protein is the regulation of availability of insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) in tissue as well as in modulating IGF binding to its receptors. IGFBP7 binds to IGF with low affinity compared to IGFBPs 1-6. It also stimulates cell adhesion. The protein is implicated in some cancers. Interactions IGFBP7 has been shown to interact with Insulin-like growth factor 1, VPS24, and the IGF-1 receptor (IGF1R). RNA Editing The pre-mRNA of this protein is subject to RNA editing. The two editing sites were previously recorded as single nucleotide polymorphisms in dbSNP. Editing type A to I RNA editing is catalyzed by a family of adenosine deaminases acting on RNA (ADARs) that specifically recognize adenosines within double-stranded regions of pre-mRNAs and deaminate them to inosine. Inosines are recognised as guanosine by the cell's translational machi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insulin-like Growth Factor
The insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) are proteins with high sequence similarity to insulin. IGFs are part of a complex system that cells use to communicate with their physiologic environment. This complex system (often referred to as the IGF "axis") consists of two cell-surface receptors (IGF1R and IGF2R), two ligands (IGF-1 and IGF-2), a family of seven high-affinity IGF-binding proteins (IGFBP1 to IGFBP7), as well as associated IGFBP degrading enzymes, referred to collectively as proteases. IGF1/GH axis The IGF "axis" is also commonly referred to as the Growth Hormone/IGF-1 Axis. Insulin-like growth factor 1 (commonly referred to as IGF-1 or at times using Roman numerals as IGF-I) is mainly secreted by the liver as a result of stimulation by growth hormone (GH). IGF-1 is important for both the regulation of normal physiology, as well as a number of pathological states, including cancer. The IGF axis has been shown to play roles in the promotion of cell proliferation and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insulin-like Growth Factor-binding Protein
The insulin-like growth factor-binding protein (IGFBP) serves as a transport protein for insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1). Function Approximately 98% of IGF-1 is always bound to one of six binding proteins (IGF-BP). IGFBP-3, the most abundant protein, accounts for 80% of all IGF binding. IGF-1 binds to IGFBP-3 in a 1:1 molar ratio. IGF-BP also binds to IGF-1 inside the liver, allowing growth hormone to continuously act upon the liver to produce more IGF-1. IGF binding proteins (IGFBPs) are proteins of 24 to 45 kDa. All six IGFBPs share 50% homology with each other and have binding affinities for IGF-I and IGF-II at the same order of magnitude as the ligands have for the IGF-IR. The IGFBPs help to lengthen the half-life of circulating IGFs in all tissues, including the prostate. Individual IGFBPs may act to enhance or attenuate IGF signaling depending on their physiological context (i.e. cell type). Even with these similarities, some characteristics are different: chromoso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insulin-like Growth Factor 1
Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), also called somatomedin C, is a hormone similar in molecular structure to insulin which plays an important role in childhood growth, and has anabolic effects in adults. IGF-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''IGF1'' gene. IGF-1 consists of 70 amino acids in a single chain with three intramolecular disulfide bridges. IGF-1 has a molecular weight of 7,649 Daltons. In dogs, an ancient mutation in IGF1 is the primary cause of the toy phenotype. IGF-1 is produced primarily by the liver. Production is stimulated by growth hormone (GH). Most of IGF-1 is bound to one of 6 binding proteins (IGF-BP). IGFBP-1 is regulated by insulin. IGF-1 is produced throughout life; the highest rates of IGF-1 production occur during the pubertal growth spurt. The lowest levels occur in infancy and old age. A synthetic analog of IGF-1, mecasermin, is used in children for the treatment of growth failure. Cyclic glycine-proline (cGP) is metabolite o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VPS24
Charged multivesicular body protein 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''VPS24'' gene. Function This gene encodes a protein that acts in the sorting of transmembrane proteins into lysosomes/vacuoles via the multivesicular body (MVB) pathway. This protein, along with other soluble coiled-coil containing proteins, forms part of the ESCRT-III protein complex that binds to the endosomal membrane and recruits additional cofactors for protein sorting into the MVB. This protein may also co-immunoprecipitate with a member of the IFG-binding protein superfamily. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. Interactions VPS24 has been shown to interact with IGFBP7 Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''IGFBP7'' gene. The major function of the protein is the regulation of availability of insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) in tissue as well as in modulati .... References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IGF2
Insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF-2) is one of three protein hormones that share structural similarity to insulin. The MeSH definition reads: "A well-characterized neutral peptide believed to be secreted by the liver and to circulate in the blood. It has growth-regulating, insulin-like and mitogenic activities. The growth factor has a major, but not absolute, dependence on somatotropin. It is believed to be a major fetal growth factor in contrast to insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), which is a major growth factor in adults." Gene structure In humans, the gene is located on chromosome 11p15.5, a region which contains numerous imprinted genes. In mice this homologous region is found at distal chromosome 7. In both organisms, ''IGF2'' is imprinted, with expression resulting favourably from the paternally inherited allele. However, in some human brain regions a loss of imprinting occurs resulting in both ''IGF2'' and being transcribed from both parental alleles. The prote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
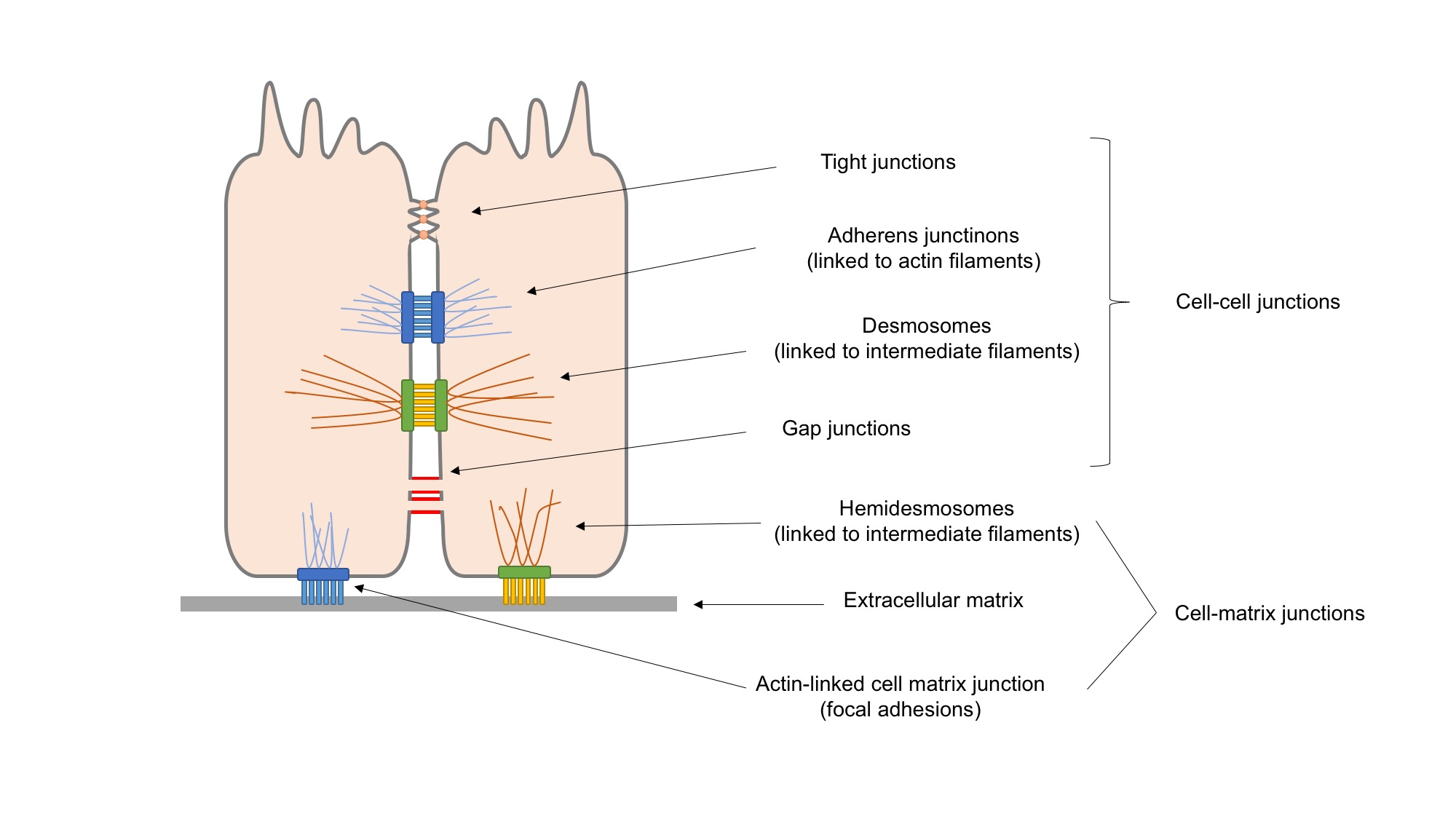
Cell Adhesion
Cell adhesion is the process by which cells interact and attach to neighbouring cells through specialised molecules of the cell surface. This process can occur either through direct contact between cell surfaces such as cell junctions or indirect interaction, where cells attach to surrounding extracellular matrix, a gel-like structure containing molecules released by cells into spaces between them. Cells adhesion occurs from the interactions between cell-adhesion molecules (CAMs), transmembrane proteins located on the cell surface. Cell adhesion links cells in different ways and can be involved in signal transduction for cells to detect and respond to changes in the surroundings. Other cellular processes regulated by cell adhesion include cell migration and tissue development in multicellular organisms. Alterations in cell adhesion can disrupt important cellular processes and lead to a variety of diseases, including cancer and arthritis. Cell adhesion is also essential for in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 Receptor
The insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) receptor is a protein found on the surface of human cells. It is a transmembrane receptor that is activated by a hormone called insulin-like growth factor 1 ( IGF-1) and by a related hormone called IGF-2. It belongs to the large class of tyrosine kinase receptors. This receptor mediates the effects of IGF-1, which is a polypeptide protein hormone similar in molecular structure to insulin. IGF-1 plays an important role in growth and continues to have anabolic effects in adults – meaning that it can induce hypertrophy of skeletal muscle and other target tissues. Mice lacking the IGF-1 receptor die late in development, and show a dramatic reduction in body mass. This testifies to the strong growth-promoting effect of this receptor. Structure Two alpha subunits and two beta subunits make up the IGF-1 receptor. Both the α and β subunits are synthesized from a single mRNA precursor. The precursor is then glycosylated, proteolytically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heparin
Heparin, also known as unfractionated heparin (UFH), is a medication and naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan. Since heparins depend on the activity of antithrombin, they are considered anticoagulants. Specifically it is also used in the treatment of heart attacks and unstable angina. It is given intravenously or by injection under the skin. Other uses for its anticoagulant properties include inside blood specimen test tubes and kidney dialysis machines. Common side effects include bleeding, pain at the injection site, and low blood platelets. Serious side effects include heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Greater care is needed in those with poor kidney function. Heparin is contraindicated for suspected cases of vaccine-induced pro-thrombotic immune thrombocytopenia (VIPIT) secondary to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination, as heparin may further increase the risk of bleeding in an anti-PF4/heparin complex autoimmune manner, in favor of alternative anticoagulant medications (such as arg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurogenesis
Neurogenesis is the process by which nervous system cells, the neurons, are produced by neural stem cells (NSCs). It occurs in all species of animals except the porifera (sponges) and placozoans. Types of NSCs include neuroepithelial cells (NECs), radial glial cells (RGCs), basal progenitors (BPs), intermediate neuronal precursors (INPs), subventricular zone astrocytes, and subgranular zone radial astrocytes, among others. Neurogenesis is most active during embryonic development and is responsible for producing all the various types of neurons of the organism, but it continues throughout adult life in a variety of organisms. Once born, neurons do not divide (see mitosis), and many will live the lifespan of the animal. Neurogenesis in mammals Developmental neurogenesis During embryonic development, the mammalian central nervous system (CNS; brain and spinal cord) is derived from the neural tube, which contains NSCs that will later generate neurons. However, neurogenesis does ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |