|
IDistance
In pattern recognition, the iDistance is an indexing and query processing technique for k-nearest neighbor queries on point data in multi-dimensional metric spaces. The kNN query is one of the hardest problems on multi-dimensional data, especially when the dimensionality of the data is high. The iDistance is designed to process kNN queries in high-dimensional spaces efficiently and it is especially good for skewed data distributions, which usually occur in real-life data sets. The iDistance can be augmented with machine learning models to learn the data distributions for searching and storing the multi-dimensional data. Indexing Building the iDistance index has two steps: #A number of reference points in the data space are chosen. There are various ways of choosing reference points. Using cluster centers as reference points is the most efficient way. Succinctly, the data points are partitioned into Voronoi cells based on well-chosen reference points. #The distance between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pattern Recognition
Pattern recognition is the automated recognition of patterns and regularities in data. It has applications in statistical data analysis, signal processing, image analysis, information retrieval, bioinformatics, data compression, computer graphics and machine learning. Pattern recognition has its origins in statistics and engineering; some modern approaches to pattern recognition include the use of machine learning, due to the increased availability of big data and a new abundance of processing power. These activities can be viewed as two facets of the same field of application, and they have undergone substantial development over the past few decades. Pattern recognition systems are commonly trained from labeled "training" data. When no labeled data are available, other algorithms can be used to discover previously unknown patterns. KDD and data mining have a larger focus on unsupervised methods and stronger connection to business use. Pattern recognition focuses more on the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
K-nearest Neighbor Algorithm
In statistics, the ''k''-nearest neighbors algorithm (''k''-NN) is a non-parametric supervised learning method first developed by Evelyn Fix and Joseph Hodges in 1951, and later expanded by Thomas Cover. It is used for classification and regression. In both cases, the input consists of the ''k'' closest training examples in a data set. The output depends on whether ''k''-NN is used for classification or regression: :* In ''k-NN classification'', the output is a class membership. An object is classified by a plurality vote of its neighbors, with the object being assigned to the class most common among its ''k'' nearest neighbors (''k'' is a positive integer, typically small). If ''k'' = 1, then the object is simply assigned to the class of that single nearest neighbor. :* In ''k-NN regression'', the output is the property value for the object. This value is the average of the values of ''k'' nearest neighbors. If ''k'' = 1, then the output is simply assigned to the v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimension
In physics and mathematics, the dimension of a Space (mathematics), mathematical space (or object) is informally defined as the minimum number of coordinates needed to specify any Point (geometry), point within it. Thus, a Line (geometry), line has a dimension of one (1D) because only one coordinate is needed to specify a point on itfor example, the point at 5 on a number line. A Surface (mathematics), surface, such as the Boundary (mathematics), boundary of a Cylinder (geometry), cylinder or sphere, has a dimension of two (2D) because two coordinates are needed to specify a point on itfor example, both a latitude and longitude are required to locate a point on the surface of a sphere. A two-dimensional Euclidean space is a two-dimensional space on the Euclidean plane, plane. The inside of a cube, a cylinder or a sphere is three-dimensional (3D) because three coordinates are needed to locate a point within these spaces. In classical mechanics, space and time are different categ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metric Space
In mathematics, a metric space is a set together with a notion of ''distance'' between its elements, usually called points. The distance is measured by a function called a metric or distance function. Metric spaces are the most general setting for studying many of the concepts of mathematical analysis and geometry. The most familiar example of a metric space is 3-dimensional Euclidean space with its usual notion of distance. Other well-known examples are a sphere equipped with the angular distance and the hyperbolic plane. A metric may correspond to a metaphorical, rather than physical, notion of distance: for example, the set of 100-character Unicode strings can be equipped with the Hamming distance, which measures the number of characters that need to be changed to get from one string to another. Since they are very general, metric spaces are a tool used in many different branches of mathematics. Many types of mathematical objects have a natural notion of distance and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curse Of Dimensionality
The curse of dimensionality refers to various phenomena that arise when analyzing and organizing data in high-dimensional spaces that do not occur in low-dimensional settings such as the three-dimensional physical space of everyday experience. The expression was coined by Richard E. Bellman when considering problems in dynamic programming. Dimensionally cursed phenomena occur in domains such as numerical analysis, sampling, combinatorics, machine learning, data mining and databases. The common theme of these problems is that when the dimensionality increases, the volume of the space increases so fast that the available data become sparse. In order to obtain a reliable result, the amount of data needed often grows exponentially with the dimensionality. Also, organizing and searching data often relies on detecting areas where objects form groups with similar properties; in high dimensional data, however, all objects appear to be sparse and dissimilar in many ways, which prevents co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skewed Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, skewness is a measure of the asymmetry of the probability distribution of a real-valued random variable about its mean. The skewness value can be positive, zero, negative, or undefined. For a unimodal distribution, negative skew commonly indicates that the ''tail'' is on the left side of the distribution, and positive skew indicates that the tail is on the right. In cases where one tail is long but the other tail is fat, skewness does not obey a simple rule. For example, a zero value means that the tails on both sides of the mean balance out overall; this is the case for a symmetric distribution, but can also be true for an asymmetric distribution where one tail is long and thin, and the other is short but fat. Introduction Consider the two distributions in the figure just below. Within each graph, the values on the right side of the distribution taper differently from the values on the left side. These tapering sides are called ''tail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idistance
In pattern recognition, the iDistance is an indexing and query processing technique for k-nearest neighbor queries on point data in multi-dimensional metric spaces. The kNN query is one of the hardest problems on multi-dimensional data, especially when the dimensionality of the data is high. The iDistance is designed to process kNN queries in high-dimensional spaces efficiently and it is especially good for skewed data distributions, which usually occur in real-life data sets. The iDistance can be augmented with machine learning models to learn the data distributions for searching and storing the multi-dimensional data. Indexing Building the iDistance index has two steps: #A number of reference points in the data space are chosen. There are various ways of choosing reference points. Using cluster centers as reference points is the most efficient way. Succinctly, the data points are partitioned into Voronoi cells based on well-chosen reference points. #The distance between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cluster Analysis
Cluster analysis or clustering is the task of grouping a set of objects in such a way that objects in the same group (called a cluster) are more similar (in some sense) to each other than to those in other groups (clusters). It is a main task of exploratory data analysis, and a common technique for statistics, statistical data analysis, used in many fields, including pattern recognition, image analysis, information retrieval, bioinformatics, data compression, computer graphics and machine learning. Cluster analysis itself is not one specific algorithm, but the general task to be solved. It can be achieved by various algorithms that differ significantly in their understanding of what constitutes a cluster and how to efficiently find them. Popular notions of clusters include groups with small Distance function, distances between cluster members, dense areas of the data space, intervals or particular statistical distributions. Clustering can therefore be formulated as a multi-object ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voronoi Diagram
In mathematics, a Voronoi diagram is a partition of a plane into regions close to each of a given set of objects. In the simplest case, these objects are just finitely many points in the plane (called seeds, sites, or generators). For each seed there is a corresponding region, called a Voronoi cell, consisting of all points of the plane closer to that seed than to any other. The Voronoi diagram of a set of points is dual to that set's Delaunay triangulation. The Voronoi diagram is named after mathematician Georgy Voronoy, and is also called a Voronoi tessellation, a Voronoi decomposition, a Voronoi partition, or a Dirichlet tessellation (after Peter Gustav Lejeune Dirichlet). Voronoi cells are also known as Thiessen polygons. Voronoi diagrams have practical and theoretical applications in many fields, mainly in science and technology, but also in visual art. The simplest case In the simplest case, shown in the first picture, we are given a finite set of points in the Euclidean p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
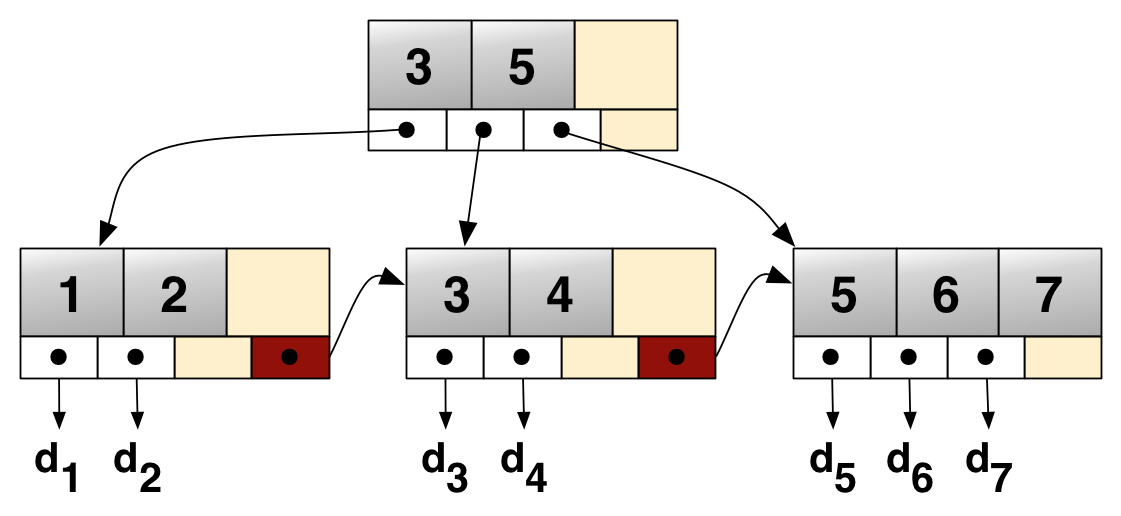
B+ Tree
A B+ tree is an m-ary tree with a variable but often large number of children per node. A B+ tree consists of a root, internal nodes and leaves. The root may be either a leaf or a node with two or more children. A B+ tree can be viewed as a B-tree in which each node contains only keys (not key–value pairs), and to which an additional level is added at the bottom with linked leaves. The primary value of a B+ tree is in storing data for efficient retrieval in a block-oriented storage context — in particular, filesystems. This is primarily because unlike binary search trees, B+ trees have very high fanout (number of pointers to child nodes in a node, typically on the order of 100 or more), which reduces the number of I/O operations required to find an element in the tree. History There is no single paper introducing the B+ tree concept. Instead, the notion of maintaining all data in leaf nodes is repeatedly brought up as an interesting variant. Douglas Comer notes in an ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sort Key
Collation is the assembly of written information into a standard order. Many systems of collation are based on numerical order or alphabetical order, or extensions and combinations thereof. Collation is a fundamental element of most office filing systems, library catalogs, and reference books. Collation differs from ''classification'' in that the classes themselves are not necessarily ordered. However, even if the order of the classes is irrelevant, the identifiers of the classes may be members of an ordered set, allowing a sorting algorithm to arrange the items by class. Formally speaking, a collation method typically defines a total order on a set of possible identifiers, called sort keys, which consequently produces a total preorder on the set of items of information (items with the same identifier are not placed in any defined order). A collation algorithm such as the Unicode collation algorithm defines an order through the process of comparing two given character strings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Retrieval
An image retrieval system is a computer system used for browsing, searching and retrieving images from a large database of digital images. Most traditional and common methods of image retrieval utilize some method of adding metadata such as captioning, keywords, title or descriptions to the images so that retrieval can be performed over the annotation words. Manual image annotation is time-consuming, laborious and expensive; to address this, there has been a large amount of research done on automatic image annotation. Additionally, the increase in social web applications and the semantic web have inspired the development of several web-based image annotation tools. The first microcomputer-based image database retrieval system was developed at MIT, in the 1990s, by Banireddy Prasaad, Amar Gupta, Hoo-min Toong, and Stuart Madnick. A 2008 survey article documented progresses after 2007. All image retrieval systems as of 2021 were designed for 2D images, not 3D ones. Search method ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |