|
Pattern Recognition
Pattern recognition is the task of assigning a class to an observation based on patterns extracted from data. While similar, pattern recognition (PR) is not to be confused with pattern machines (PM) which may possess PR capabilities but their primary function is to distinguish and create emergent patterns. PR has applications in statistical data analysis, signal processing, image analysis, information retrieval, bioinformatics, data compression, computer graphics and machine learning. Pattern recognition has its origins in statistics and engineering; some modern approaches to pattern recognition include the use of machine learning, due to the increased availability of big data and a new abundance of processing power. Pattern recognition systems are commonly trained from labeled "training" data. When no labeled data are available, other algorithms can be used to discover previously unknown patterns. KDD and data mining have a larger focus on unsupervised methods and str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Categorical Variable
In statistics, a categorical variable (also called qualitative variable) is a variable that can take on one of a limited, and usually fixed, number of possible values, assigning each individual or other unit of observation to a particular group or nominal category on the basis of some qualitative property. In computer science and some branches of mathematics, categorical variables are referred to as enumerations or enumerated types. Commonly (though not in this article), each of the possible values of a categorical variable is referred to as a level. The probability distribution associated with a random categorical variable is called a categorical distribution. Categorical data is the statistical data type consisting of categorical variables or of data that has been converted into that form, for example as grouped data. More specifically, categorical data may derive from observations made of qualitative data that are summarised as counts or cross tabulations, or from observat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classification (machine Learning)
When classification is performed by a computer, statistical methods are normally used to develop the algorithm. Often, the individual observations are analyzed into a set of quantifiable properties, known variously as explanatory variables or ''features''. These properties may variously be categorical data, categorical (e.g. "A", "B", "AB" or "O", for blood type), ordinal data, ordinal (e.g. "large", "medium" or "small"), integer, integer-valued (e.g. the number of occurrences of a particular word in an email) or real number, real-valued (e.g. a measurement of blood pressure). Other classifiers work by comparing observations to previous observations by means of a similarity function, similarity or metric (mathematics), distance function. An algorithm that implements classification, especially in a concrete implementation, is known as a classifier. The term "classifier" sometimes also refers to the mathematical function (mathematics), function, implemented by a classification algo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supervised Learning
In machine learning, supervised learning (SL) is a paradigm where a Statistical model, model is trained using input objects (e.g. a vector of predictor variables) and desired output values (also known as a ''supervisory signal''), which are often human-made labels. The training process builds a function that maps new data to expected output values. An optimal scenario will allow for the algorithm to accurately determine output values for unseen instances. This requires the learning algorithm to Generalization (learning), generalize from the training data to unseen situations in a reasonable way (see inductive bias). This statistical quality of an algorithm is measured via a ''generalization error''. Steps to follow To solve a given problem of supervised learning, the following steps must be performed: # Determine the type of training samples. Before doing anything else, the user should decide what kind of data is to be used as a Training, validation, and test data sets, trainin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Word Processor
A word processor (WP) is a device or computer program that provides for input, editing, formatting, and output of text, often with some additional features. Early word processors were stand-alone devices dedicated to the function, but current word processors are word processor programs running on general purpose computers, including smartphones, tablets, laptops and desktop computers. The functions of a word processor program are typically between those of a simple text editor and a desktop publishing program; Many word processing programs have gained advanced features over time providing similar functionality to desktop publishing programs. Common word processor programs include LibreOffice Writer, Google Docs and Microsoft Word. Background Word processors developed from mechanical machines, later merging with computer technology. The history of word processing is the story of the gradual automation of the physical aspects of writing and editing, and then to the refinement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Text Editor
A text editor is a type of computer program that edits plain text. An example of such program is "notepad" software (e.g. Windows Notepad). Text editors are provided with operating systems and software development packages, and can be used to change files such as configuration files, documentation files and programming language source code. Plain text and rich text There are important differences between plain text (created and edited by text editors) and rich text (such as that created by word processors or desktop publishing software). Plain text exclusively consists of character representation. Each character is represented by a fixed-length sequence of one, two, or four bytes, or as a variable-length sequence of one to four bytes, in accordance to specific character encoding conventions, such as ASCII, ISO/IEC 2022, ISO/IEC 2022, Shift JIS, UTF-8, or UTF-16. These conventions define many printable characters, but also whitespace character, non-printing characters th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regular Expression
A regular expression (shortened as regex or regexp), sometimes referred to as rational expression, is a sequence of characters that specifies a match pattern in text. Usually such patterns are used by string-searching algorithms for "find" or "find and replace" operations on strings, or for input validation. Regular expression techniques are developed in theoretical computer science and formal language theory. The concept of regular expressions began in the 1950s, when the American mathematician Stephen Cole Kleene formalized the concept of a regular language. They came into common use with Unix text-processing utilities. Different syntaxes for writing regular expressions have existed since the 1980s, one being the POSIX standard and another, widely used, being the Perl syntax. Regular expressions are used in search engines, in search and replace dialogs of word processors and text editors, in text processing utilities such as sed and AWK, and in lexical analysis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pattern Matching
In computer science, pattern matching is the act of checking a given sequence of tokens for the presence of the constituents of some pattern. In contrast to pattern recognition, the match usually must be exact: "either it will or will not be a match." The patterns generally have the form of either sequences or tree structures. Uses of pattern matching include outputting the locations (if any) of a pattern within a token sequence, to output some component of the matched pattern, and to substitute the matching pattern with some other token sequence (i.e., search and replace). Sequence patterns (e.g., a text string) are often described using regular expressions and matched using techniques such as backtracking. Tree patterns are used in some programming languages as a general tool to process data based on its structure, e.g. C#, F#, Haskell, Java, ML, Python, Ruby, Rust, Scala, Swift and the symbolic mathematics language Mathematica have special syntax for expressing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
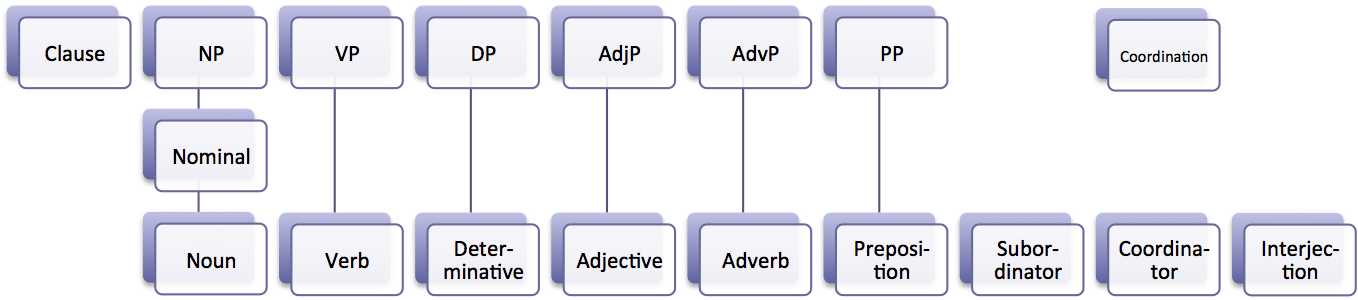
Syntactic Structure
In linguistics, syntax ( ) is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure (constituency), agreement, the nature of crosslinguistic variation, and the relationship between form and meaning (semantics). Diverse approaches, such as generative grammar and functional grammar, offer unique perspectives on syntax, reflecting its complexity and centrality to understanding human language. Etymology The word ''syntax'' comes from the ancient Greek word , meaning an orderly or systematic arrangement, which consists of (''syn-'', "together" or "alike"), and (''táxis'', "arrangement"). In Hellenistic Greek, this also specifically developed a use referring to the grammatical order of words, with a slightly altered spelling: . The English term, which first appeared in 1548, is partly borrowed from Latin () and Greek, though the Lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parse Tree
A parse tree or parsing tree (also known as a derivation tree or concrete syntax tree) is an ordered, rooted tree that represents the syntactic structure of a string according to some context-free grammar. The term ''parse tree'' itself is used primarily in computational linguistics; in theoretical syntax, the term ''syntax tree'' is more common. Concrete syntax trees reflect the syntax of the input language, making them distinct from the abstract syntax trees used in computer programming. Unlike Reed-Kellogg sentence diagrams used for teaching grammar, parse trees do not use distinct symbol shapes for different types of constituents. Parse trees are usually constructed based on either the constituency relation of constituency grammars ( phrase structure grammars) or the dependency relation of dependency grammars. Parse trees may be generated for sentences in natural languages (see natural language processing), as well as during processing of computer languages, such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parsing
Parsing, syntax analysis, or syntactic analysis is a process of analyzing a String (computer science), string of Symbol (formal), symbols, either in natural language, computer languages or data structures, conforming to the rules of a formal grammar by breaking it into parts. The term ''parsing'' comes from Latin ''pars'' (''orationis''), meaning Part of speech, part (of speech). The term has slightly different meanings in different branches of linguistics and computer science. Traditional Sentence (linguistics), sentence parsing is often performed as a method of understanding the exact meaning of a sentence or word, sometimes with the aid of devices such as sentence diagrams. It usually emphasizes the importance of grammatical divisions such as subject (grammar), subject and predicate (grammar), predicate. Within computational linguistics the term is used to refer to the formal analysis by a computer of a sentence or other string of words into its constituents, resulting in a par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Part Of Speech
In grammar, a part of speech or part-of-speech ( abbreviated as POS or PoS, also known as word class or grammatical category) is a category of words (or, more generally, of lexical items) that have similar grammatical properties. Words that are assigned to the same part of speech generally display similar syntactic behavior (they play similar roles within the grammatical structure of sentences), sometimes similar morphological behavior in that they undergo inflection for similar properties and even similar semantic behavior. Commonly listed English parts of speech are noun, verb, adjective, adverb, pronoun, preposition, conjunction, interjection, numeral, article, and determiner. Other terms than ''part of speech''—particularly in modern linguistic classifications, which often make more precise distinctions than the traditional scheme does—include word class, lexical class, and lexical category. Some authors restrict the term ''lexical category'' to refer only to a par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Part Of Speech Tagging
In corpus linguistics, part-of-speech tagging (POS tagging, PoS tagging, or POST), also called grammatical tagging, is the process of marking up a word in a text ( corpus) as corresponding to a particular part of speech, based on both its definition and its context. A simplified form of this is commonly taught to school-age children, in the identification of words as nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, etc. Once performed by hand, POS tagging is now done in the context of computational linguistics, using algorithms which associate discrete terms, as well as hidden parts of speech, by a set of descriptive tags. POS-tagging algorithms fall into two distinctive groups: rule-based and stochastic. E. Brill's tagger, one of the first and most widely used English POS taggers, employs rule-based algorithms. Principle Part-of-speech tagging is harder than just having a list of words and their parts of speech, because some words can represent more than one part of speech at different time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |