|
IDCSP
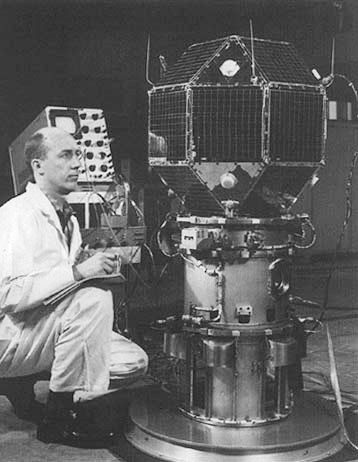
The Initial Defense Communications Satellite Program or IDCSP was the first United States Department of Defense communications satellite constellation and the first stage of the Defense Communications Satellite Program (DCSP). Launched in five groups by Titan IIIC launch vehicles to near equatorial, subsynchronous orbits between 1966 and 1968, they were intended to be experimental testbeds. They were so successful that, by the time of the launch of the last set of eight satellites, the IDCSP was deemed operational and renamed Initial Defense Satellite Communications System or IDSCS. This system allowed real-time collection of battlefield intelligence during the Vietnam War. A total of 35 IDCSP satellites were launched, 27 successfully. Background The Initial Defense Communications Satellite Program or IDCSP was the first stage in the Defense Communications Satellite Program (DCSP) commissioned by United States Secretary of Defense Robert McNamara in 1962. Under the DCSP, se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IDCSP 001
The Initial Defense Communications Satellite Program or IDCSP was the first United States Department of Defense communications satellite constellation and the first stage of the Defense Communications Satellite Program (DCSP). Launched in five groups by Titan IIIC launch vehicles to near equatorial, subsynchronous orbits between 1966 and 1968, they were intended to be experimental testbeds. They were so successful that, by the time of the launch of the last set of eight satellites, the IDCSP was deemed operational and renamed Initial Defense Satellite Communications System or IDSCS. This system allowed real-time collection of battlefield intelligence during the Vietnam War. A total of 35 IDCSP satellites were launched, 27 successfully. Background The Initial Defense Communications Satellite Program or IDCSP was the first stage in the Defense Communications Satellite Program (DCSP) commissioned by United States Secretary of Defense Robert McNamara in 1962. Under the DCSP, se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titan IIIC
The Titan IIIC was an expendable launch system used by the United States Air Force from 1965 until 1982. It was the first Titan booster to feature large solid rocket motors and was planned to be used as a launcher for the Dyna-Soar, though the spaceplane was cancelled before it could fly. The majority of the launcher's payloads were DoD satellites, for military communications and early warning, though one flight (ATS-6) was performed by NASA. The Titan IIIC was launched exclusively from Cape Canaveral while its sibling, the Titan IIID, was launched only from Vandenberg AFB. History The Titan rocket family was established in October 1955 when the Air Force awarded the Glenn L. Martin Company (later Martin Marietta and now Lockheed Martin) a contract to build an intercontinental ballistic missile (SM-68). It became known as the Titan I, the nation's first two-stage ICBM, and replaced the Atlas ICBM as the second underground, vertically stored, silo-based ICBM. Both stages of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
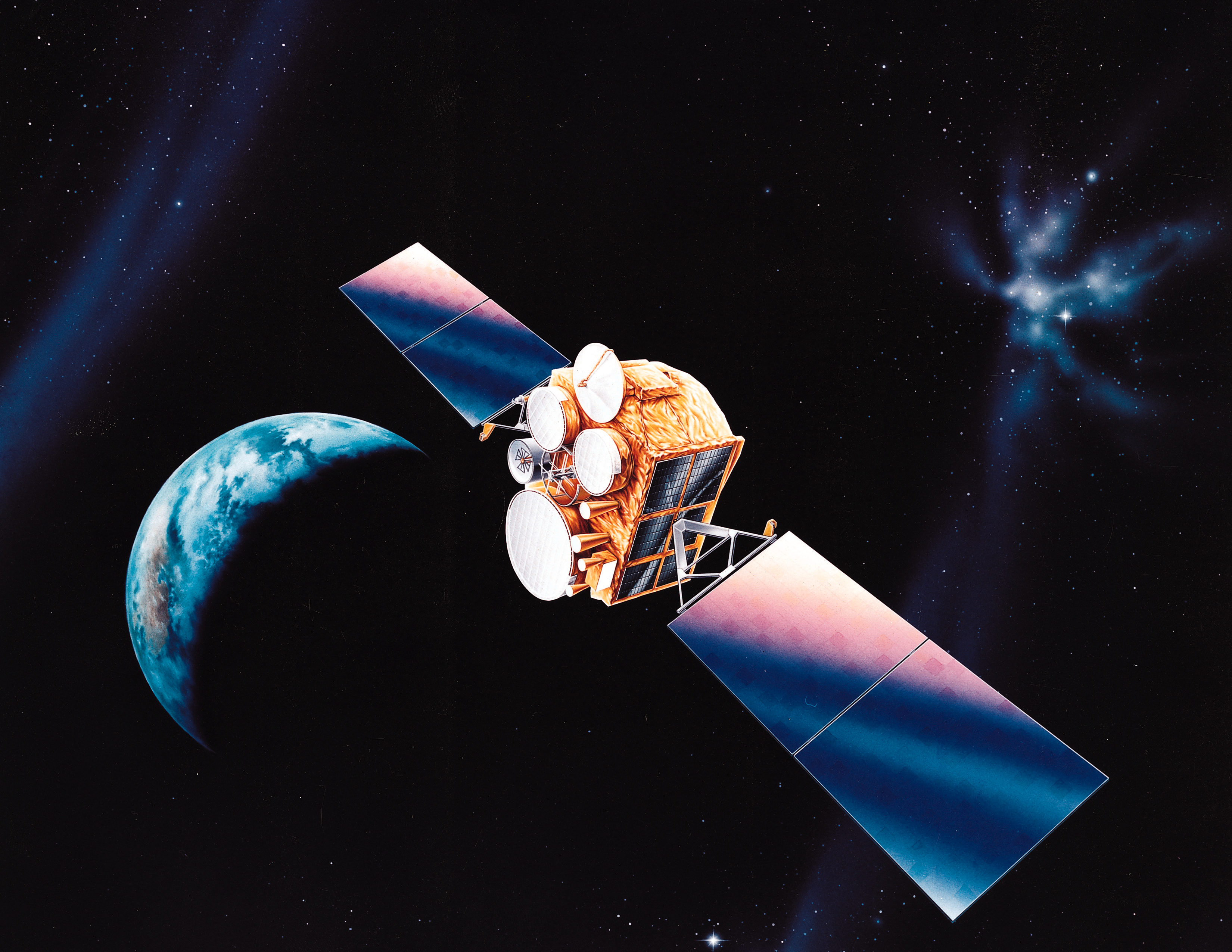
Defense Satellite Communications System
The Defense Satellite Communications System (DSCS) is a United States Space Force satellite constellation that provides the United States with military communications to support globally distributed military users. Beginning in 2007, DSCS is being replaced by the Wideband Global SATCOM system. A total of 14 DSCS-III satellites were launched between the early 1980s and 2003. Two satellites were launched aboard the Space Shuttle ''Atlantis'' in 1985 during the STS-51-J flight. As of 14 September 2021, six DSCS-III satellites were still operational. DSCS operations are currently run by the 4th Space Operations Squadron out of Schriever Space Force Base. Background DSCS went through three major phases — IDCSP (Interim Defense Communication Satellite Program), DSCS-II, and DSCS-III. Since the first launch, DSCS has been the "workhorse" of military satellite communications. All DSCS III satellites have exceeded their 10-year design life. The National Science Foundation use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TRW Inc
TRW Inc., was an American corporation involved in a variety of businesses, mainly aerospace, electronics, automotive, and credit reporting.http://www.fundinguniverse.com/company-histories/TRW-Inc-Company-History.html TRW Inc. It was a pioneer in multiple fields including electronic components, integrated circuits, computers, software and systems engineering. TRW built many spacecraft, including Pioneer 1, Pioneer 10, and several space-based observatories. It was #57 on the 1986 Fortune 500 list, and had 122,258 employees. The company was called Thompson Ramo Wooldridge Inc., after the 1958 merger of the Ramo-Wooldridge Corporation and Thompson Products. This was later shortened to TRW. The company was founded in 1901 and lasted for just over a century until being acquired by Northrop Grumman in 2002. It spawned a variety of corporations, including Pacific Semiconductors, The Aerospace Corporation, Bunker-Ramo and Experian. Its automotive businesses were sold off by Northrop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the air service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part of the United States Army Signal Corps, the USAF was established as a separate branch of the United States Armed Forces in 1947 with the enactment of the National Security Act of 1947. It is the second youngest branch of the United States Armed Forces and the fourth in order of precedence. The United States Air Force articulates its core missions as air supremacy, global integrated intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance, rapid global mobility, global strike, and command and control. The United States Air Force is a military service branch organized within the Department of the Air Force, one of the three military departments of the Department of Defense. The Air Force through the Department of the Air Force is headed by the civilian Secretary of the Air Force ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Frequency-shift Keying
Multiple frequency-shift keying (MFSK) is a variation of frequency-shift keying (FSK) that uses more than two frequencies. MFSK is a form of M-ary orthogonal modulation, where each symbol consists of one element from an alphabet of orthogonal waveforms. M, the size of the alphabet, is usually a power of two so that each symbol represents log2M bits. * M is usually between 4 and 64 * Error correction is generally also used Fundamentals In a M-ary signaling system like MFSK, an "alphabet" of M tones is established and the transmitter selects one tone at a time from the alphabet for transmission. M is usually a power of 2, so each tone transmission from the alphabet represents log2 M data bits. MFSK is classed as an M-ary orthogonal signaling scheme because each of the M tone detection filters at the receiver responds only to its tone and not at all to the others; this independence provides the orthogonality. Like other M-ary orthogonal schemes, the required Eb/N0 ratio for a given ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase Shift Keying
Phase-shift keying (PSK) is a digital modulation process which conveys data by changing (modulating) the phase of a constant frequency reference signal (the carrier wave). The modulation is accomplished by varying the sine and cosine inputs at a precise time. It is widely used for wireless LANs, RFID and Bluetooth communication. Any digital modulation scheme uses a finite number of distinct signals to represent digital data. PSK uses a finite number of phases, each assigned a unique pattern of binary digits. Usually, each phase encodes an equal number of bits. Each pattern of bits forms the symbol that is represented by the particular phase. The demodulator, which is designed specifically for the symbol-set used by the modulator, determines the phase of the received signal and maps it back to the symbol it represents, thus recovering the original data. This requires the receiver to be able to compare the phase of the received signal to a reference signal such a system is term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency Modulation
Frequency modulation (FM) is the encoding of information in a carrier wave by varying the instantaneous frequency of the wave. The technology is used in telecommunications, radio broadcasting, signal processing, and Run-length limited#FM: .280.2C1.29 RLL, computing. In Analog signal, analog frequency modulation, such as radio broadcasting, of an audio signal representing voice or music, the instantaneous frequency deviation, i.e. the difference between the frequency of the carrier and its center frequency, has a functional relation to the modulating signal amplitude. Digital data can be encoded and transmitted with a type of frequency modulation known as frequency-shift keying (FSK), in which the instantaneous frequency of the carrier is shifted among a set of frequencies. The frequencies may represent digits, such as '0' and '1'. FSK is widely used in computer modems, such as fax modems, telephone caller ID systems, garage door openers, and other low-frequency transmissions. R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
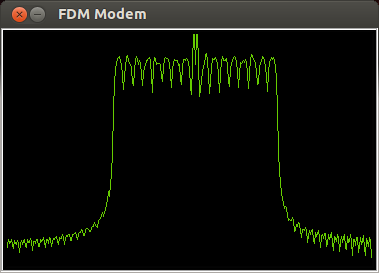
Frequency-division Multiplexing
In telecommunications, frequency-division multiplexing (FDM) is a technique by which the total bandwidth available in a communication medium is divided into a series of non-overlapping frequency bands, each of which is used to carry a separate signal. This allows a single transmission medium such as a microwave radio link, cable or optical fiber to be shared by multiple independent signals. Another use is to carry separate serial bits or segments of a higher rate signal in parallel. The most common example of frequency-division multiplexing is radio and television broadcasting, in which multiple radio signals at different frequencies pass through the air at the same time. Another example is cable television, in which many television channels are carried simultaneously on a single cable. FDM is also used by telephone systems to transmit multiple telephone calls through high capacity trunklines, communications satellites to transmit multiple channels of data on uplink and downl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teletype
A teleprinter (teletypewriter, teletype or TTY) is an electromechanical device that can be used to send and receive typed messages through various communications channels, in both point-to-point and point-to-multipoint configurations. Initially they were used in telegraphy, which developed in the late 1830s and 1840s as the first use of electrical engineering, though teleprinters were not used for telegraphy until 1887 at the earliest. The machines were adapted to provide a user interface to early mainframe computers and minicomputers, sending typed data to the computer and printing the response. Some models could also be used to create punched tape for data storage (either from typed input or from data received from a remote source) and to read back such tape for local printing or transmission. Teleprinters could use a variety of different communication media. These included a simple pair of wires; dedicated non-switched telephone circuits (leased lines); switched network ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lincoln Experimental Satellite
The Lincoln Experimental Satellite series was designed and built by Lincoln Laboratory at Massachusetts Institute of Technology between 1965 and 1976, under USAF sponsorship, for testing devices and techniques for satellite communication. Development After the successful development and deployment of Project West Ford, a passive communications system consisting of orbiting copper needles, MIT's Lincoln Laboratory turned to improving active-satellite space communications. In particular, Lincoln aimed to increase the transmission capability of communications satellites ("downlink"), which was necessarily constrained by their limited size. After receiving a charter in 1963 to build and demonstrate military space communications, Lincoln focused on a number of engineering solutions to the downlink problem including improved antennas, better stabilization of satellites in orbit (which would benefit both downlink and "uplink"—communications from the ground), high-efficiency systems of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantify the rate of energy transfer. The watt is named after James Watt (1736–1819), an 18th-century Scottish inventor, mechanical engineer, and chemist who improved the Newcomen engine with his own steam engine in 1776. Watt's invention was fundamental for the Industrial Revolution. Overview When an object's velocity is held constant at one metre per second against a constant opposing force of one newton, the rate at which work is done is one watt. : \mathrm In terms of electromagnetism, one watt is the rate at which electrical work is performed when a current of one ampere (A) flows across an electrical potential difference of one volt (V), meaning the watt is equivalent to the volt-ampere (the latter unit, however, is used for a different quantity from the real power of an electrical circuit). : ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |