|
Lincoln Experimental Satellite
The Lincoln Experimental Satellite series was designed and built by Lincoln Laboratory at Massachusetts Institute of Technology between 1965 and 1976, under USAF sponsorship, for testing devices and techniques for satellite communication. Development After the successful development and deployment of Project West Ford, a passive communications system consisting of orbiting copper needles, MIT's Lincoln Laboratory turned to improving active-satellite space communications. In particular, Lincoln aimed to increase the transmission capability of communications satellites ("downlink"), which was necessarily constrained by their limited size. After receiving a charter in 1963 to build and demonstrate military space communications, Lincoln focused on a number of engineering solutions to the downlink problem including improved antennas, better stabilization of satellites in orbit (which would benefit both downlink and "uplink"—communications from the ground), high-efficiency systems of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
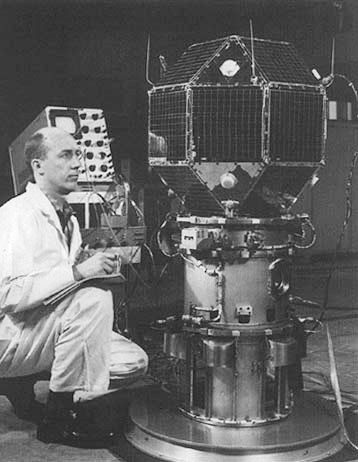
Lincoln Laboratory LES-1 1965
Lincoln most commonly refers to: * Lincoln (president), Abraham Lincoln (1809–1865), the sixteenth president of the United States * Lincoln, England, cathedral city and county town of Lincolnshire, England * Lincoln, Nebraska, the capital of Nebraska, U.S. * Lincoln (name), a surname and given name * Lincoln Motor Company, a Ford brand Lincoln may also refer to: Places Canada * Lincoln, Alberta * Lincoln, New Brunswick * Lincoln Parish, New Brunswick * Lincoln, Ontario ** Lincoln (electoral district) (former), Ontario ** Lincoln (provincial electoral district) (former), Ontario United Kingdom * Lincoln, England ** Lincoln (UK Parliament constituency) * Lincoln Green, Leeds United States * Lincoln, Alabama * Lincoln, Arkansas * Lincoln, California, in Placer County * Lincoln, former name of Clinton, California, in Amador County * Lincoln, Delaware * Lincoln, Idaho * Lincoln, Illinois * Lincoln, Indiana * Lincoln, Iowa * Lincoln Center, Kansas * Lincoln Parish, Louisi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MHW-RTG
The Multihundred-Watt radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MHW RTG) is a type of US radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG) developed for the Voyager spacecraft, ''Voyager 1'' and ''Voyager 2''. Each RTG has a total weight of 37.7 kg including about 4.5 kg of Pu-238"Space Nuclear Power" G.L.Bennett 2006 and uses 24 pressed plutonium-238 oxide spheres to provide enough heat to generate approximately 157 s of electrical power initially – halving every 87.7 years. Each RTG initially generated about 2400 Watts of thermal power. Conversion of the decay heat of the plutonium to electrical power uses 312 [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communications Satellites
A communications satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunication signals via a Transponder (satellite communications), transponder; it creates a communication channel between a source transmitter and a Radio receiver, receiver at different locations on Earth. Communications satellites are used for television, telephone, radio, internet, and military applications. Many communications satellites are in geostationary orbit above the equator, so that the satellite appears stationary at the same point in the sky; therefore the satellite dish antennas of ground stations can be aimed permanently at that spot and do not have to move to track the satellite. Others form satellite constellations in low Earth orbit, where antennas on the ground have to follow the position of the satellites and switch between satellites frequently. The high frequency radio waves used for telecommunications links travel by Line-of-sight propagation, line of sight and so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voyager Program
The Voyager program is an American scientific program that employs two robotic interstellar probes, ''Voyager 1'' and ''Voyager 2''. They were launched in 1977 to take advantage of a favorable alignment of Jupiter and Saturn, to Flyby (spaceflight), fly near them while collecting data for transmission back to Earth. After launch the decision was taken to send ''Voyager 2'' near Uranus and Neptune to collect data for transmission back to Earth. As of 2022, the Voyagers are still in operation past the outer boundary of the heliosphere in interstellar space. They collect and transmit useful data to Earth. , ''Voyager 1'' was moving with a velocity of , or 17 km/s, relative to the Sun, and was from the Sun reaching a distance of from Earth as of February 10, 2022. On 25 August 2012, data from ''Voyager 1'' indicated that it had entered interstellar space. , ''Voyager 2'' was moving with a velocity of , or 15 km/s, relative to the Sun, and was from the Sun reaching a distan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amateur Radio
Amateur radio, also known as ham radio, is the use of the radio frequency spectrum for purposes of non-commercial exchange of messages, wireless experimentation, self-training, private recreation, radiosport, contesting, and emergency communications. The term "amateur" is used to specify "a duly authorised person interested in radioelectric practice with a purely personal aim and without pecuniary interest;" (either direct monetary or other similar reward) and to differentiate it from commercial broadcasting, public safety (such as police and fire), or professional two-way radio services (such as maritime, aviation, taxis, etc.). The amateur radio service (''amateur service'' and '' amateur-satellite service'') is established by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) through the Radio Regulations. National governments regulate technical and operational characteristics of transmissions and issue individual station licenses with a unique identifying call sign, which mus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LES-4
Lincoln Experimental Satellite 4, also known as LES-4, was a communications satellite, the fourth of nine in the Lincoln Experimental Satellite, and the first of the series designed for operations at geosynchronous altitudes. Launched by the United States Air Force (USAF) on 21 December 1965, it demonstrated many then-advanced technologies including active use of the military's SHF (super high frequency) band (7 to 8 GHz) to service hundreds of users. Background After the successful development and deployment of Project West Ford, a passive communications system consisting of orbiting copper needles, MIT's Lincoln Laboratory turned to improving active-satellite space communications. In particular, Lincoln aimed to increase the transmission capability of communications satellites ("downlink"), which was necessarily constrained by their limited size. After receiving a charter in 1963 to build and demonstrate military space communications, Lincoln focused on a number of engineeri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LES-3
Lincoln Experimental Satellite 3, also known as LES-3, was a communications satellite, the third of nine in the Lincoln Experimental Satellite. Launched by the United States Air Force (USAF) on 21 Dec 1965, it was stranded in a Geostationary Transfer Orbit rather than its planned circular high orbit. Despite this, LES-3 returned good data on communications propagation in the UHF band. Background After the successful development and deployment of Project West Ford, a passive communications system consisting of orbiting copper needles, MIT's Lincoln Laboratory turned to improving active-satellite space communications. In particular, Lincoln aimed to increase the transmission capability of communications satellites ("downlink"), which was necessarily constrained by their limited size. After receiving a charter in 1963 to build and demonstrate military space communications, Lincoln focused on a number of engineering solutions to the downlink problem including improved antennas, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LES-2
Lincoln Experimental Satellite 2, also known as LES-2, was a communications satellite, the second of nine in the Lincoln Experimental Satellite. Launched by the United States Air Force (USAF) on 6 May 1965, it demonstrated many then-advanced technologies including active use of the military's Super high frequency, SHF (super high frequency) band (7 to 8 Hertz, GHz) to service hundreds of users. Background After the successful development and deployment of Project West Ford, a passive communications system consisting of orbiting copper needles, MIT Lincoln Laboratory, MIT's Lincoln Laboratory turned to improving active-satellite space communications. In particular, Lincoln aimed to increase the transmission capability of communications satellites ("downlink"), which was necessarily constrained by their limited size. After receiving a charter in 1963 to build and demonstrate military space communications, Lincoln focused on a number of engineering solutions to the downlink proble ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LES-1
Lincoln Experimental Satellite 1, also known as LES-1, was a communications satellite, the first of nine in the Lincoln Experimental Satellite program. Launched by the United States Air Force (USAF) on February 11, 1965, it pioneered many then-advanced technologies including active use of the military's SHF (super high frequency) band (7 to 8 GHz) to service hundreds of users. LES-1 did not have a successful operational life due to being placed in a suboptimal orbit, and it ceased transmissions in 1967. After 45 years of inactivity, LES-1 spontaneously resumed transmissions in 2012 making it one of the oldest zombie satellites. Background The Lincoln Experimental Satellite (LES) series was MIT's Lincoln Laboratory's first active communications satellite project. Lincoln had previously successfully developed and deployed Project West Ford, a passive communications system consisting of orbiting copper needles. The goal of LES was to increase the transmission capability of commu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FLTSATCOM
FLTSATCOM (also FLTSAT) is a satellite communication system of the U.S. Space Force which was used for UHF radio communications between ships, submarines, airplanes and ground stations of the Navy. Most of the transponders on these satellites were simple repeaters with no authentication or control over what they retransmitted. FLTSATCOM Altogether eight satellites were launched from 1978 to 1989 by Atlas-Centaur rockets into geostationary orbit. The system became operational in 1981. The satellites were manufactured by TRW. The solar array of each satellite had a span of over 13.2 m. A special characteristic was a UHF transmit antenna reflector 4.9 m in diameter. Each satellite had 12 transponders, which worked in the UHF range from 240 - 400 megahertz. Additionally FLTSATCOM 7 and 8 included an experimental EHF transponder built by Lincoln Laboratory intended to test the MILSTAR ground terminals. The first seven satellites each had a launch mass of 1884 kg and the rema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lincoln Laboratory
The MIT Lincoln Laboratory, located in Lexington, Massachusetts, is a United States Department of Defense federally funded research and development center chartered to apply advanced technology to problems of national security. Research and development activities focus on long-term technology development as well as rapid system prototyping and demonstration. Its core competencies are in sensors, integrated sensing, signal processing for information extraction, decision-making support, and communications. These efforts are aligned within ten mission areas. The laboratory also maintains several field sites around the world. The laboratory transfers much of its advanced technology to government agencies, industry, and academia, and has launched more than 100 start-ups. History Origins At the urging of the United States Air Force, the Lincoln Laboratory was created in 1951 at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) as part of an effort to improve the U.S. air defense syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TDRSS
The U.S. Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System (TDRSS) is a network of American communications satellites (each called a tracking and data relay satellite, TDRS) and ground stations used by NASA for space communications. The system was designed to replace an existing network of ground stations that had supported all of NASA's crewed flight missions. The prime design goal was to increase the time spacecraft were in communication with the ground and improve the amount of data that could be transferred. Many Tracking and Data Relay Satellites were launched in the 1980s and 1990s with the Space Shuttle and made use of the Inertial Upper Stage, a two-stage solid rocket booster developed for the shuttle. Other TDRS were launched by Atlas IIa and Atlas V rockets. The most recent generation of satellites provides ground reception rates of 6 Mbit/s in the S-band and 800 Mbit/s in the Ku- and Ka-bands. This is mainly used by the United States military. Origins To satisfy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |