|
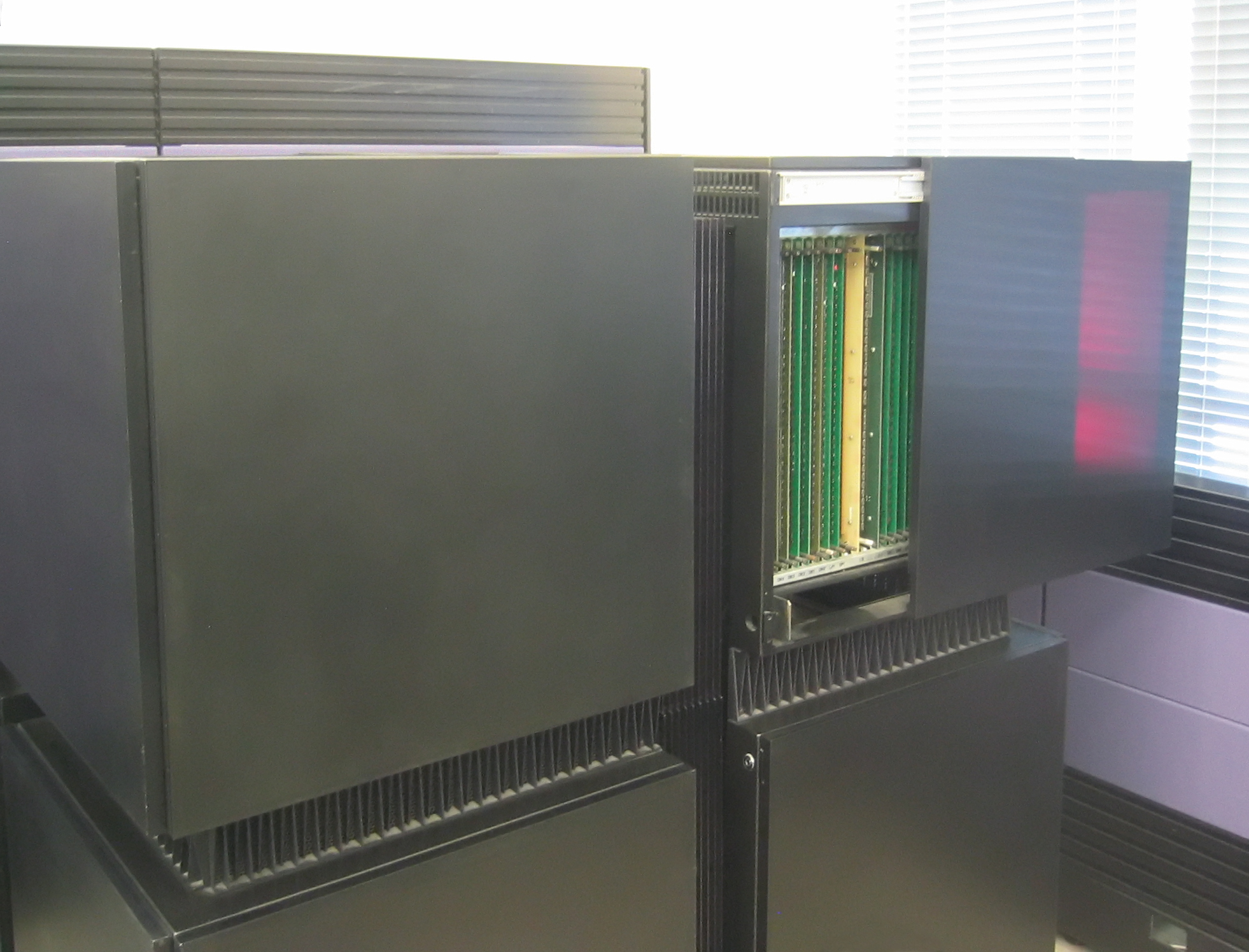
ICL Distributed Array Processor
The Distributed Array Processor (DAP) produced by International Computers Limited (ICL) was the world's first commercial massively parallel computer. The original paper study was complete in 1972 and building of the prototype began in 1974. The first machine was delivered to Queen Mary College in 1979. Development The initial 'Pilot DAP' was designed and implemented by Dr Stewart F Reddaway with the aid of David J Hunt and Peter M Flanders at the ICL Stevenage Labs. Their manager and a major contributor was John K Iliffe who had designed the Basic Language Machine—he is well known nowadays for Iliffe vectors. The ICL DAP had 64×64 single bit processing elements (PEs) with 4096 bits of storage per PE. It was attached to an ICL mainframe and its memory was mapped into the mainframe's memory. Programs for the DAP were written in DAP FORTRAN which was FORTRAN extended with 64×64 matrix and 64 element vector primitives. DAP Fortran compiled to an assembly language called APAL (A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Computers Limited
International Computers Limited (ICL) was a British computer hardware, computer software and computer services company that operated from 1968 until 2002. It was formed through a merger of International Computers and Tabulators (ICT), English Electric Computers (EEC) and Elliott Automation in 1968. The company's most successful product line was the ICL 2900 Series range of mainframe computers. In later years, ICL diversified its product line but the bulk of its profits always came from its mainframe customers. New ventures included marketing a range of powerful IBM clones made by Fujitsu, various minicomputer and personal computer ranges and (more successfully) a range of retail point-of-sale equipment and back-office software. Although it had significant sales overseas, ICL's mainframe business was dominated by large contracts from the UK public sector, including Post Office Ltd, the Inland Revenue, the Department for Work and Pensions and the Ministry of Defence. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge Parallel Processors
Cambridge ( ) is a university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cambridge became an important trading centre during the Roman and Viking ages, and there is archaeological evidence of settlement in the area as early as the Bronze Age. The first town charters were granted in the 12th century, although modern city status was not officially conferred until 1951. The city is most famous as the home of the University of Cambridge, which was founded in 1209 and consistently ranks among the best universities in the world. The buildings of the university include King's College Chapel, Cavendish Laboratory, and the Cambridge University Library, one of the largest legal deposit libraries in the world. The city's skyline is dominated by several college buildings, along with the spire of the Our Lady and the English Martyrs Chu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massively Parallel Computers
Massively may refer to: *Mass Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different element ... * Massively (blog), a blog about MMOs {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ICL Mainframe Computers
ICL may refer to: Companies and organizations * Idaho Conservation League * Imperial College London, a UK university * Indian Confederation of Labour * Indian Cricket League * Inorganic Chemistry Laboratory of the University of Oxford * Israel Chemicals, an Israeli multi-national chemical company that produces and markets fertilizers, metals and other special-purpose chemical products * International Computers Limited, a UK company acquired by Fujitsu * International Confederation of Labor, a global anarcho-syndicalist union federation * International Consortium on Landslides, Kyoto, Japan Computing * Ice Lake series Intel CPUs * Icon library filename extension * Clean (programming language) source filename extension * Inter-Chassis Link, Brocade's name for an InterSwitch Trunk link Chemistry and biology * Idiopathic CD4+ lymphocytopenia, a medical condition * Implantable collamer lens * Isocitrate lyase, an enzyme * ICl, chemical symbol for iodine monochloride * Intracaval leio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SUPRENUM
SUPRENUM (german: SUPerREchner für NUMerische Anwendungen, en, super-computer for numerical applications) was a German research project to develop a parallel computer from 1985 through 1990. It was a major effort which was aimed at developing a national expertise in massively parallel processing both at hardware and at software level. Although the Suprenum-1 computer was the fastest massively parallel MIMD computer in the world during a period in 1992,SUPRENUM: Perspectives and Performance Oliver A. McBryan, 1994 the project was set and is considered a commercial failure. History Funded by the[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parsytec
ISRA VISION PARSYTEC AG is a company of ISRA VISION AG and was founded in 1985 as Parsytec (PARallel SYstem TEChnology) in Aachen, Germany. Parsytec has become known in the late 1980s and early 1990s as a manufacturer of transputer-based parallel systems. Products ranged from a single transputer plug-in board for the IBM PC up to large massively-parallel systems with thousands of transputers (or processors, respectively) such as the Parsytec GC. Some sources call the latter ''ultracomputer sized, scalable multicomputers (smC)''. As part of the ISRA VISION AG, today the company focusses on solutions in the machine vision and industrial image procession sector. The ISRA Parsytec products are used for quality and surface inspection especially in the metal and paper industries. History In 1985, Parsytec was founded by Falk-Dietrich Kübler, Gerhard H. Peise, and Bernd Wolff in Aachen, Germany, with an 800000 DM grant from Federal Ministry for Research and Technology (BMFT). [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
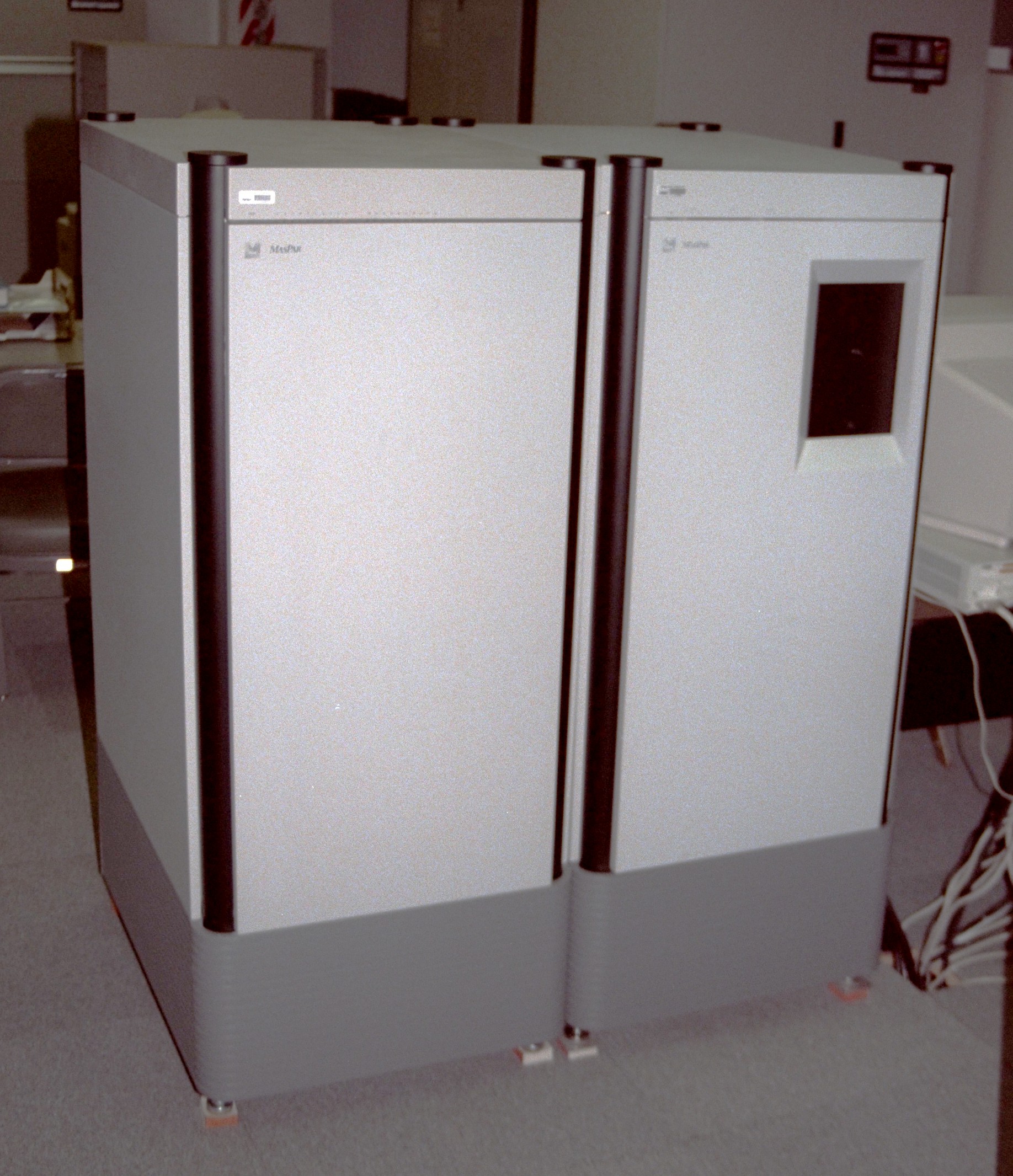
MasPar
MasPar Computer Corporation was a minisupercomputer vendor that was founded in 1987 by Jeff Kalb. The company was based in Sunnyvale, California. History While Kalb was the vice-president of the division of Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) that built integrated circuits, some researchers in that division were building a supercomputer based on the Goodyear MPP (massively parallel processor) supercomputer. The DEC researchers enhanced the architecture by: * making the processor elements to be 4-bit instead of 1-bit John Culver"MasPar: Massively Parallel Computers – 32 cores on a chip" * increasing the connectivity of each processor element to 8 neighbors from 4. * adding a global interconnect for all of the processing elements, which was a triple-redundant switch which was easier to implement than a full crossbar switch. After Digital decided not to commercialize the research project, Kalb decided to start a company to sell this minisupercomputer. In 1990, the first generat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connection Machine
A Connection Machine (CM) is a member of a series of massively parallel supercomputers that grew out of doctoral research on alternatives to the traditional von Neumann architecture of computers by Danny Hillis at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in the early 1980s. Starting with CM-1, the machines were intended originally for applications in artificial intelligence (AI) and symbolic processing, but later versions found greater success in the field of computational science. Origin of idea Danny Hillis and Sheryl Handler founded Thinking Machines Corporation (TMC) in Waltham, Massachusetts, in 1983, moving in 1984 to Cambridge, MA. At TMC, Hillis assembled a team to develop what would become the CM-1 Connection Machine, a design for a massively parallel hypercube-based arrangement of thousands of microprocessors, springing from his PhD thesis work at MIT in Electrical Engineering and Computer Science (1985). The dissertation won the ACM Distinguished Dissertation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thinking Machines Corporation
Thinking Machines Corporation was a supercomputer manufacturer and artificial intelligence (AI) company, founded in Waltham, Massachusetts, in 1983 by Sheryl Handler and W. Daniel "Danny" Hillis to turn Hillis's doctoral work at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) on massively parallel computing architectures into a commercial product named the Connection Machine. The company moved in 1984 from Waltham to Kendall Square in Cambridge, Massachusetts, close to the MIT AI Lab. Thinking Machines made some of the most powerful supercomputers of the time, and by 1993 the four fastest computers in the world were Connection Machines. The firm filed for bankruptcy in 1994; its hardware and parallel computing software divisions were acquired in time by Sun Microsystems. Supercomputer products On the hardware side, Thinking Machines produced several Connection Machine models (in chronological order): the CM-1, CM-2, CM-200, CM-5, and CM-5E. The CM-1 and 2 came first in models wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goodyear MPP
The Goodyear Massively Parallel Processor (MPP) was a massively parallel processing supercomputer built by Goodyear Aerospace for the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. It was designed to deliver enormous computational power at lower cost than other existing supercomputer architectures, by using thousands of simple processing elements, rather than one or a few highly complex CPUs. Development of the MPP began circa 1979; it was delivered in May 1983, and was in general use from 1985 until 1991. It was based on Goodyear's earlier STARAN array processor, a 4x256 1-bit processing element (PE) computer. The MPP was a 128x128 2-dimensional array of 1-bit wide PEs. In actuality 132x128 PEs were configured with a 4x128 configuration added for fault tolerance to substitute for up to 4 rows (or columns) of processors in the presence of problems. The PEs operated in a single instruction, multiple data (SIMD) fashioneach PE performed the same operation simultaneously, on different data elem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PERQ
The PERQ, also referred to as the Three Rivers PERQ or ICL PERQ, was a pioneering workstation computer produced in the late 1970s through the early 1980s. In June 1979, the company took its very first order from the UK's Rutherford Appleton Laboratory and the computer was officially launched in August 1979 at SIGGRAPH in Chicago. It was the first commercially produced personal workstation with a Graphical User Interface. The design was heavily influenced by the original workstation computer, the Xerox Alto, which was never commercially produced. The origin of the name "PERQ" was chosen both as an acronym of "Pascal Engine that Runs Quicker," and to evoke the word '' perquisite'' commonly called ''perks'', that is employee additional benefits. The workstation was conceived by six former Carnegie Mellon University alumni and employees, Brian S. Rosen, James R. Teter, William H. Broadley, J. Stanley Kriz, Raj Reddy and Paul G. Newbury, who formed the startup Three Rivers Compute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer History Museum
The Computer History Museum (CHM) is a museum of computer history, located in Mountain View, California. The museum presents stories and artifacts of Silicon Valley and the information age, and explores the computing revolution and its impact on society. History The museum's origins date to 1968 when Gordon Bell began a quest for a historical collection and, at that same time, others were looking to preserve the Whirlwind computer. The resulting ''Museum Project'' had its first exhibit in 1975, located in a converted coat closet in a DEC lobby. In 1978, the museum, now ''The Digital Computer Museum'' (TDCM), moved to a larger DEC lobby in Marlborough, Massachusetts. Maurice Wilkes presented the first lecture at TDCM in 1979 – the presentation of such lectures has continued to the present time. TDCM incorporated as '' The Computer Museum'' (TCM) in 1982. In 1984, TCM moved to Boston, locating on Museum Wharf. In 1996/1997, the TCM History Center (TCMHC) was established; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |