|
IBM Quantum Experience
IBM Quantum Platform (previously known as IBM Quantum Experience) is an online platform allowing public and premium access to cloud-based quantum computing services provided by IBM. This includes access to a set of IBM's quantum processors, a set of tutorials on quantum computation, and access to interactive courses. As of June 2025, there are 12 devices on the service, all of which are freely accessible by the public. This service can be used to run quantum algorithm, algorithms and experiments, and explore tutorials and simulations around what might be possible with quantum computing. IBM's quantum processors are made up of Superconducting quantum computing, superconducting transmon qubits, located in dilution refrigerators at the IBM Research headquarters at the Thomas J. Watson Research Center. Users interact with a quantum processor through the quantum circuit model of computation, typically through code written in Qiskit. This code can be compiled down to OpenQASM for exec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cloud-based Quantum Computing
Cloud computing, Cloud-based quantum computing refers to the remote access of quantum computing resources—such as quantum emulators, simulators, or processor (computing), processors—via the internet. Cloud access enables users to develop, test, and execute quantum algorithms without the need for direct interaction with specialized hardware, facilitating broader participation in quantum software development and experimentation. In 2016, IBM launched the IBM Quantum Experience, one of the first publicly accessible quantum processors connected to the cloud. In early 2017, researchers at Rigetti Computing demonstrated programmable quantum cloud access through their software platform Forest, which included the Python library. Since the early-2020s, cloud-based quantum computing has grown significantly, with multiple providers offering access to a variety of quantum hardware modalities, including superconducting qubits, trapped ions, neutral atoms, and photonic systems. Major platfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphical User Interface
A graphical user interface, or GUI, is a form of user interface that allows user (computing), users to human–computer interaction, interact with electronic devices through Graphics, graphical icon (computing), icons and visual indicators such as secondary notation. In many applications, GUIs are used instead of text-based user interface, text-based UIs, which are based on typed command labels or text navigation. GUIs were introduced in reaction to the perceived steep learning curve of command-line interfaces (CLIs), which require commands to be typed on a computer keyboard. The actions in a GUI are usually performed through direct manipulation interface, direct manipulation of the graphical elements. Beyond computers, GUIs are used in many handheld mobile devices such as MP3 players, portable media players, gaming devices, smartphones and smaller household, office and Distributed control system, industrial controls. The term ''GUI'' tends not to be applied to other lower-displa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM Cloud Services
International Business Machines Corporation (using the trademark IBM), nicknamed Big Blue, is an American multinational technology company headquartered in Armonk, New York, and present in over 175 countries. It is a publicly traded company and one of the 30 companies in the Dow Jones Industrial Average. IBM is the largest industrial research organization in the world, with 19 research facilities across a dozen countries; for 29 consecutive years, from 1993 to 2021, it held the record for most annual U.S. patents generated by a business. IBM was founded in 1911 as the Computing-Tabulating-Recording Company (CTR), a holding company of manufacturers of record-keeping and measuring systems. It was renamed "International Business Machines" in 1924 and soon became the leading manufacturer of punch-card tabulating systems. During the 1960s and 1970s, the IBM mainframe, exemplified by the System/360 and its successors, was the world's dominant computing platform, with the company p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Measurement In Quantum Mechanics
In quantum physics, a measurement is the testing or manipulation of a physical system to yield a numerical result. A fundamental feature of quantum theory is that the predictions it makes are probabilistic. The procedure for finding a probability involves combining a quantum state, which mathematically describes a quantum system, with a mathematical representation of the measurement to be performed on that system. The formula for this calculation is known as the Born rule. For example, a quantum particle like an electron can be described by a quantum state that associates to each point in space a complex number called a probability amplitude. Applying the Born rule to these amplitudes gives the probabilities that the electron will be found in one region or another when an experiment is performed to locate it. This is the best the theory can do; it cannot say for certain where the electron will be found. The same quantum state can also be used to make a prediction of how the electro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Register
In quantum computing, a quantum register is a system comprising multiple qubits. It is the quantum analogue of the classical processor register. Quantum computers perform calculations by manipulating qubits within a quantum register. Definition It is usually assumed that the register consists of qubits. It is also generally assumed that registers are not density matrices, but that they are pure, although the definition of "register" can be extended to density matrices. An n size quantum register is a quantum system comprising n pure qubits. The Hilbert space, \mathcal, in which the data is stored in a quantum register is given by \mathcal = \mathcal\otimes\mathcal\otimes\ldots\otimes\mathcal where \otimes is the tensor product. The number of dimensions of the Hilbert spaces depends on what kind of quantum systems the register is composed of. Qubits are 2-dimensional complex spaces (\mathbb^2), while qutrits are 3-dimensional complex spaces (\mathbb^3), etc. For a regist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Gate
In quantum computing and specifically the quantum circuit model of computation, a quantum logic gate (or simply quantum gate) is a basic quantum circuit operating on a small number of qubits. Quantum logic gates are the building blocks of quantum circuits, like classical logic gates are for conventional digital circuits. Unlike many classical logic gates, quantum logic gates are reversible computing, reversible. It is possible to perform classical computing using only reversible gates. For example, the reversible Toffoli gate can implement all Boolean functions, often at the cost of having to use ancilla bits. The Toffoli gate has a direct quantum equivalent, showing that quantum circuits can perform all operations performed by classical circuits. Quantum gates are unitary operators, and are described as unitary matrix, unitary matrices relative to some orthonormal Basis (linear algebra), basis. Usually the ''computational basis'' is used, which unless comparing it with somethin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wave-function Collapse
In various interpretations of quantum mechanics, wave function collapse, also called reduction of the state vector, occurs when a wave function—initially in a superposition of several eigenstates—reduces to a single eigenstate due to interaction with the external world. This interaction is called an ''observation'' and is the essence of a measurement in quantum mechanics, which connects the wave function with classical observables such as position and momentum. Collapse is one of the two processes by which quantum systems evolve in time; the other is the continuous evolution governed by the Schrödinger equation. : In the Copenhagen interpretation, wave function collapse connects quantum to classical models, with a special role for the observer. By contrast, objective-collapse proposes an origin in physical processes. In the many-worlds interpretation, collapse does not exist; all wave function outcomes occur while quantum decoherence accounts for the appearance of co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
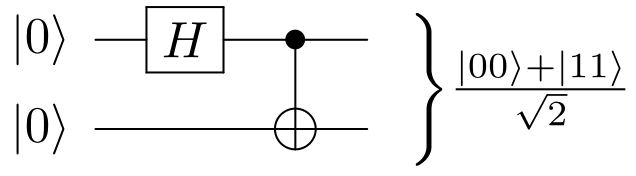
Bell State
In quantum information science, the Bell's states or EPR pairs are specific quantum states of two qubits that represent the simplest examples of quantum entanglement. The Bell's states are a form of entangled and normalized basis vectors. This normalization implies that the overall probability of the particles being in one of the mentioned states is 1: \langle \Phi, \Phi \rangle = 1. Entanglement is a basis-independent result of superposition. Due to this superposition, measurement of the qubit will " collapse" it into one of its basis states with a given probability. Because of the entanglement, measurement of one qubit will "collapse" the other qubit to a state whose measurement will yield one of two possible values, where the value depends on which Bell's state the two qubits are in initially. Bell's states can be generalized to certain quantum states of multi-qubit systems, such as the GHZ state for three or more subsystems. Understanding of Bell's states is useful in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenberger–Horne–Zeilinger State
In physics, in the area of quantum information theory, a Greenberger–Horne–Zeilinger (GHZ) state is an entangled quantum state that involves at least three subsystems (particle states, qubits, or qudits). Named for the three authors that first described this state, the GHZ state predicts outcomes from experiments that directly contradict predictions by every classical local hidden-variable theory. The state has applications in quantum computing. History The four-particle version was first studied by Daniel Greenberger, Michael Horne and Anton Zeilinger in 1989. The following year Abner Shimony joined in and they published a three-particle version based on suggestions by N. David Mermin. Experimental measurements on such states contradict intuitive notions of locality and causality. GHZ states for large numbers of qubits are theorized to give enhanced performance for metrology compared to other qubit superposition states. Definition The GHZ state is an entangled q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum State
In quantum physics, a quantum state is a mathematical entity that embodies the knowledge of a quantum system. Quantum mechanics specifies the construction, evolution, and measurement of a quantum state. The result is a prediction for the system represented by the state. Knowledge of the quantum state, and the rules for the system's evolution in time, exhausts all that can be known about a quantum system. Quantum states may be defined differently for different kinds of systems or problems. Two broad categories are * wave functions describing quantum systems using position or momentum variables and * the more abstract vector quantum states. Historical, educational, and application-focused problems typically feature wave functions; modern professional physics uses the abstract vector states. In both categories, quantum states divide into pure versus mixed states, or into coherent states and incoherent states. Categories with special properties include stationary states for tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qubit
In quantum computing, a qubit () or quantum bit is a basic unit of quantum information—the quantum version of the classic binary bit physically realized with a two-state device. A qubit is a two-state (or two-level) quantum-mechanical system, one of the simplest quantum systems displaying the peculiarity of quantum mechanics. Examples include the spin of the electron in which the two levels can be taken as spin up and spin down; or the polarization of a single photon in which the two spin states (left-handed and the right-handed circular polarization) can also be measured as horizontal and vertical linear polarization. In a classical system, a bit would have to be in one state or the other. However, quantum mechanics allows the qubit to be in a coherent superposition of multiple states simultaneously, a property that is fundamental to quantum mechanics and quantum computing. Etymology The coining of the term ''qubit'' is attributed to Benjamin Schumacher. In the acknow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphic User Interface
A graphical user interface, or GUI, is a form of user interface that allows users to interact with electronic devices through graphical icons and visual indicators such as secondary notation. In many applications, GUIs are used instead of text-based UIs, which are based on typed command labels or text navigation. GUIs were introduced in reaction to the perceived steep learning curve of command-line interfaces (CLIs), which require commands to be typed on a computer keyboard. The actions in a GUI are usually performed through direct manipulation of the graphical elements. Beyond computers, GUIs are used in many handheld mobile devices such as MP3 players, portable media players, gaming devices, smartphones and smaller household, office and industrial controls. The term ''GUI'' tends not to be applied to other lower-display resolution types of interfaces, such as video games (where head-up displays (''HUDs'') are preferred), or not including flat screens like volumetric disp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |