|
IBM 602
The IBM 602 Calculating Punch, introduced in 1946, was an electromechanical calculator capable of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. The 602 was IBM's first machine that did division. (The IBM 601, introduced in 1931, only multiplied.) Like other IBM calculators, it was programmed using a control panel. Input data was read from a punched card, the results could be punched in the same card or a trailing card. The 602 was available in four models: Model 1, Model 2, Model 50, and Model 51. The "Series 50" models were low-cost versions that ran at a slower speed, with half as many program steps, and fewer storage registers and counters. Two additional counters were available as an optional feature. Program steps execute in one machine cycle, except for steps performing multiplication or division which take as many machine cycles as needed for the operation. Punching rate is roughly four columns per machine cycle. The total number of machine cycles required per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM CPC
The IBM Card-Programmed Electronic Calculator or ''CPC'' was announced by IBM in May 1949. Later that year an improved machine, the CPC-II, was also announced. The original CPC Calculator has the following units interconnected by cables: *Electronic Calculating Punch ** IBM 604 with reader/punch unit IBM 521 *Accounting Machine ** IBM 402 or ** IBM 417 The CPC-II Calculator has the following units interconnected by cables: *Electronic Calculating Punch ** IBM 605 with punch unit IBM 527 *Accounting Machine **IBM 407 or ** IBM 412 or ** IBM 418 *''Optional'' Auxiliary Storage Units (up to 3) ** IBM 941, each could store 16 decimal numbers with ten digits plus sign. From the IBM Archives: The IBM Card-Programmed Electronic Calculator was announced in May 1949 as a versatile general purpose computer designed to perform any predetermined sequence of arithmetical operations coded on standard 80-column punched cards. It was also capable of selecting and following one of several sequ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM 604
The IBM 604 Electronic Calculating Punch was the world's first mass-produced electronic calculator along with its predecessor the IBM 603.IBM 603 The First Commercial Electronic Calculator IBM History, accessed September 21, 2020] It was an electronic unit record equipment, unit record machine that could perform multiple calculations, including division. It was invented and developed by Ralph Palmer, Jerrier A. Haddad, Jerrier Haddad and Byron Phelps. It was introduced by IBM in 1948. It could read a punched card from a deck, do some calculations based on the wiring of its plugboard, and punch results onto the same card. A separate IBM 521 Card Read/Punch processed the cards and had its own plugboard which selected the columns to be read and those to be punched. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calculator
An electronic calculator is typically a portable electronic device used to perform calculations, ranging from basic arithmetic to complex mathematics. The first solid-state electronic calculator was created in the early 1960s. Pocket-sized devices became available in the 1970s, especially after the Intel 4004, the first microprocessor, was developed by Intel for the Japanese calculator company Busicom. Modern electronic calculators vary from cheap, give-away, credit-card-sized models to sturdy desktop models with built-in printers. They became popular in the mid-1970s as the incorporation of integrated circuits reduced their size and cost. By the end of that decade, prices had dropped to the point where a basic calculator was affordable to most and they became common in schools. Computer operating systems as far back as early Unix have included interactive calculator programs such as dc and hoc, and interactive BASIC could be used to do calculations on most 1970s a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM 601
The IBM 601 Multiplying Punch was a unit record machine that could read two numbers from a punched card and punch their product in a blank field on the same card. The factors could be up to eight decimal digits long. The 601 was introduced in 1931 and was the first IBM machine that could do multiplication. In 1936 W. J. Eckert connected a modified 601 to a 285 tabulator and an 016 duplicating punch through a custom switch he designed and used the combined setup to perform scientific calculations. Eckert, W.J.Punched Card Methods in Scientific Computation The Thomas J. Watson Astronomical Computing Bureau, Columbia University (1940) See also * IBM 602 * IBM 603 *IBM 604 The IBM 604 Electronic Calculating Punch was the world's first mass-produced electronic calculator along with its predecessor the IBM 603. References [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM 603
The IBM 603 Electronic Multiplier was the first mass-produced commercial electronic calculating device; it used full-size vacuum tubes to perform multiplication and addition.IBM 603 The First Commercial Electronic Calculator IBM History, accessed September 21, 2020] (The earlier IBM 600 and released in the same year used .) The IBM 603 was adapted as the arithmetic unit in the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unit Record Equipment
Starting at the end of the nineteenth century, well before the advent of electronic computers, data processing was performed using electromechanical machines collectively referred to as unit record equipment, electric accounting machines (EAM) or tabulating machines. Unit record machines came to be as ubiquitous in industry and government in the first two-thirds of the twentieth century as computers became in the last third. They allowed large volume, sophisticated data-processing tasks to be accomplished before electronic computers were invented and while they were still in their infancy. This data processing was accomplished by processing punched cards through various unit record machines in a carefully choreographed progression. This progression, or flow, from machine to machine was often planned and documented with detailed flowcharts that used standardized symbols for documents and the various machine functions. All but the earliest machines had high-speed mechanical feeders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plugboard
A plugboard or control panel (the term used depends on the application area) is an array of jacks or sockets (often called hubs) into which patch cords can be inserted to complete an electrical circuit. Control panels are sometimes used to direct the operation of unit record equipment, cipher machines, and early computers. Unit record equipment Main article: Unit record equipment The earliest machines were hardwired for specific applications. Control panels were introduced in 1906 for the Hollerith Type 1 Tabulatorphoto of Type 3 with built-in control panel here. Removable control panels were introduced with the Hollerith ( IBM) type 3-S tabulator in the 1920s. Applications then could be wired on separate control panels, and inserted into tabulators as needed. Removable control panels came to be used in all unit record machines where the machines use for different applications required rewiring. IBM removable control panels ranged in size from 6 1/4" by 10 3/4" (for ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punched Card
A punched card (also punch card or punched-card) is a piece of stiff paper that holds digital data represented by the presence or absence of holes in predefined positions. Punched cards were once common in data processing applications or to directly control automated machinery. Punched cards were widely used through much of the 20th century in the data processing industry, where specialized and increasingly complex unit record equipment, unit record machines, organized into semiautomatic data processing systems, used punched cards for data input, output, and storage. The IBM 12-row/80-column punched card format came to dominate the industry. Many early digital computers used punched cards as the primary medium for input of both computer programs and Data (computing), data. While punched cards are now obsolete as a storage medium, as of 2012, some voting machines still used punched cards to record votes. They also had a significant cultural impact. History The idea of contr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memoria Elettromeccanica Per Il Calcolatore IBM 602A - Museo Scienza Tecnologia Milano D1191
Memoria was the term for aspects involving memory in Western classical rhetoric. The word is Latin, and can be translated as "memory". It was one of five canons in classical rhetoric (the others being inventio, dispositio, elocutio, and pronuntiatio) concerned with the crafting and delivery of speeches and prose. The art of rhetoric grew out of oratory, which was the central medium for intellectual and political life in ancient Greece. Legal proceedings, political debates, philosophical inquiry were all conducted through spoken discourse. Many of the great texts from that age were not written texts penned by the authors we associate them with, but were instead orations written down by followers and students. In Roman times, while there was a much greater body of written work, oration was still the medium for critical debate. Unlike public speakers of today, who use notes or who read their speeches, good orators were expected to deliver their speeches without such aids. ''Memori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
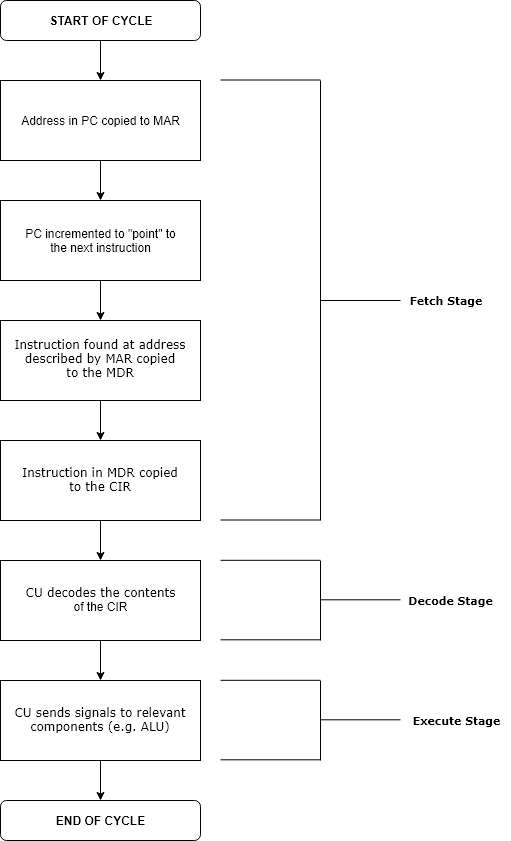
Machine Cycle
The instruction cycle (also known as the fetch–decode–execute cycle, or simply the fetch-execute cycle) is the cycle that the central processing unit (CPU) follows from boot-up until the computer has shut down in order to process instructions. It is composed of three main stages: the fetch stage, the decode stage, and the execute stage. In simpler CPUs, the instruction cycle is executed sequentially, each instruction being processed before the next one is started. In most modern CPUs, the instruction cycles are instead executed concurrently, and often in parallel, through an instruction pipeline: the next instruction starts being processed before the previous instruction has finished, which is possible because the cycle is broken up into separate steps. Role of components The program counter (PC) is a special register that holds the memory address of the next instruction to be executed. During the fetch stage, the address stored in the PC is copied into the memory addres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM 608
The IBM 608 Transistor Calculator, a plugboard-programmable unit, was the first IBM product to use transistor circuits without any vacuum tubes and is believed to be the world's first all-transistorized calculator to be manufactured for the commercial market. Announced in April 1955, it was released in December 1957. The 608 was withdrawn from marketing in April 1959. History The chief designer of the circuits used in the IBM 608 was Robert A. Henle, who later oversaw the development of emitter-coupled logic (ECL) class of circuits. The development of the 608 was preceded by the prototyping of an experimental all-transistor version of the 604. Although this was built and demonstrated in October 1954, it was not commercialized. To spur the adoption of transistor technology, shortly before the first IBM 608 shipped, Tom Watson directed that a date be set after which no new vacuum-tube-based products would be released. This decision constrained IBM product managers, who otherwise h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)




.jpg)