|
Plugboard
A plugboard or control panel (the term used depends on the application area) is an array of jacks or sockets (often called hubs) into which patch cords can be inserted to complete an electrical circuit. Control panels are sometimes used to direct the operation of unit record equipment, cipher machines, and early computers. Unit record equipment Main article: Unit record equipment The earliest machines were hardwired for specific applications. Control panels were introduced in 1906 for the Hollerith Type 1 Tabulatorphoto of Type 3 with built-in control panel here. Removable control panels were introduced with the Hollerith ( IBM) type 3-S tabulator in the 1920s. Applications then could be wired on separate control panels, and inserted into tabulators as needed. Removable control panels came to be used in all unit record machines where the machines use for different applications required rewiring. IBM removable control panels ranged in size from 6 1/4" by 10 3/4" (for ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unit Record Equipment
Starting at the end of the nineteenth century, well before the advent of electronic computers, data processing was performed using electromechanical machines collectively referred to as unit record equipment, electric accounting machines (EAM) or tabulating machines. Unit record machines came to be as ubiquitous in industry and government in the first two-thirds of the twentieth century as computers became in the last third. They allowed large volume, sophisticated data-processing tasks to be accomplished before electronic computers were invented and while they were still in their infancy. This data processing was accomplished by processing punched cards through various unit record machines in a carefully choreographed progression. This progression, or flow, from machine to machine was often planned and documented with detailed flowcharts that used standardized symbols for documents and the various machine functions. All but the earliest machines had high-speed mechanical feeders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unit Record Equipment
Starting at the end of the nineteenth century, well before the advent of electronic computers, data processing was performed using electromechanical machines collectively referred to as unit record equipment, electric accounting machines (EAM) or tabulating machines. Unit record machines came to be as ubiquitous in industry and government in the first two-thirds of the twentieth century as computers became in the last third. They allowed large volume, sophisticated data-processing tasks to be accomplished before electronic computers were invented and while they were still in their infancy. This data processing was accomplished by processing punched cards through various unit record machines in a carefully choreographed progression. This progression, or flow, from machine to machine was often planned and documented with detailed flowcharts that used standardized symbols for documents and the various machine functions. All but the earliest machines had high-speed mechanical feeders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herman Hollerith
Herman Hollerith (February 29, 1860 – November 17, 1929) was a German-American statistician, inventor, and businessman who developed an electromechanical tabulating machine The tabulating machine was an electromechanical machine designed to assist in summarizing information stored on punched cards. Invented by Herman Hollerith, the machine was developed to help process data for the 1890 U.S. Census. Later models w ... for punched cards to assist in summarizing information and, later, in accounting. His invention of the punched card tabulating machine, patented in 1884, marks the beginning of the era of mechanized binary code and semiautomatic data processing systems, and his concept dominated that landscape for nearly a century. Hollerith founded a company that was amalgamated in 1911 with several other companies to form the Computing-Tabulating-Recording Company. In 1924, the company was renamed "International Business Machines" (IBM) and became one of the largest and mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tabulating Machine
The tabulating machine was an electromechanical machine designed to assist in summarizing information stored on punched cards. Invented by Herman Hollerith, the machine was developed to help process data for the 1890 U.S. Census. Later models were widely used for business applications such as accounting and inventory control. It spawned a class of machines, known as unit record equipment, and the data processing industry. The term "Super Computing" was used by the ''New York World'' newspaper in 1931 to refer to a large custom-built tabulator that IBM made for Columbia University. 1890 census The 1880 census had taken eight years to process. Since the U.S. Constitution mandates a census every ten years to apportion both congressional representatives and direct taxes among the states, a combination of larger staff and faster-recording systems was required. In the late 1880s Herman Hollerith, inspired by conductors using holes punched in different positions on a railway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptanalysis Of The Enigma
Cryptanalysis of the Enigma ciphering system enabled the western Allies in World War II to read substantial amounts of Morse-coded radio communications of the Axis powers that had been enciphered using Enigma machines. This yielded military intelligence which, along with that from other decrypted Axis radio and teleprinter transmissions, was given the codename '' Ultra''. The Enigma machines were a family of portable cipher machines with rotor scramblers. Good operating procedures, properly enforced, would have made the plugboard Enigma machine unbreakable. However, most of the German military forces, secret services, and civilian agencies that used Enigma employed poor operating procedures, and it was these poor procedures that allowed the Enigma machines to be reverse-engineered and the ciphers to be read. The German plugboard-equipped Enigma became Nazi Germany's principal crypto-system. In December 1932 it was "broken" by mathematician Marian Rejewski at the Polish G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM 407
The IBM 407 Accounting Machine, introduced in 1949, was one of a long line of IBM tabulating machines dating back to the days of Herman Hollerith. It had a card reader and printer; a summary punch could be attached. Processing was directed by a control panel. The 407 was the central component of many unit record equipment shops which were the mainstay of IBM's business at the time. It could print digits, letters and several special characters in any of 120 print positions, spaced . In 1976 the IBM 407 Accounting Machine was withdrawn from marketing. Description The 407 read punched cards, totaled fields on the cards, made simple decisions, printed results, and, with the aid of a summary punch, output results on punched cards that could be input to other processing steps. The operation of the 407 was directed by the use of a removable control panel and a carriage tape. Exit hubs (impulse emitting) on the control panel are wired to entry hubs (impulse accepting) for the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punched Card
A punched card (also punch card or punched-card) is a piece of stiff paper that holds digital data represented by the presence or absence of holes in predefined positions. Punched cards were once common in data processing applications or to directly control automated machinery. Punched cards were widely used through much of the 20th century in the data processing industry, where specialized and increasingly complex unit record equipment, unit record machines, organized into semiautomatic data processing systems, used punched cards for data input, output, and storage. The IBM 12-row/80-column punched card format came to dominate the industry. Many early digital computers used punched cards as the primary medium for input of both computer programs and Data (computing), data. While punched cards are now obsolete as a storage medium, as of 2012, some voting machines still used punched cards to record votes. They also had a significant cultural impact. History The idea of contr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time-division Multiplexing
Time-division multiplexing (TDM) is a method of transmitting and receiving independent signals over a common signal path by means of synchronized switches at each end of the transmission line so that each signal appears on the line only a fraction of time in an alternating pattern. This method transmits two or more digital signals or analog signals over a common channel. It can be used when the bit rate of the transmission medium exceeds that of the signal to be transmitted. This form of signal multiplexing was developed in telecommunications for telegraphy systems in the late 19th century, but found its most common application in digital telephony in the second half of the 20th century. History Time-division multiplexing was first developed for applications in telegraphy to route multiple transmissions simultaneously over a single transmission line. In the 1870s, Émile Baudot developed a time-multiplexing system of multiple Hughes telegraph machines. In 1944, the Britis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
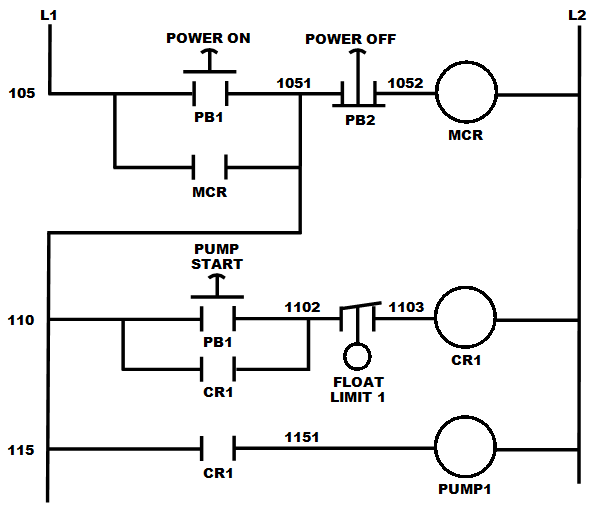
Relay Logic
Relay logic is a method of implementing combinational logic in electrical control circuits by using several electrical relays wired in a particular configuration. Ladder logic The schematic diagrams for relay logic circuits are often called line diagrams, because the inputs and outputs are essentially drawn in a series of lines. A relay logic circuit is an electrical network consisting of lines, or rungs, in which each line or rung must have continuity to enable the output device. A typical circuit consists of a number of rungs, with each rung controlling an output. This output is controlled by a combination of input or output conditions, such as input switches and control relays. The conditions that represent the inputs are connected in series, parallel, or series-parallel to obtain the logic required to drive the output. The relay logic circuit forms an electrical schematic diagram for the control of input and output devices. Relay logic diagrams represent the physical inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nines Complement
In mathematics and computing, the method of complements is a technique to encode a symmetric range of positive and negative integers in a way that they can use the same algorithm (hardware) for addition throughout the whole range. For a given number of places half of the possible representations of numbers encode the positive numbers, the other half represents their respective additive inverses. The pairs of mutually additive inverse numbers are called ''complements''. Thus subtraction of any number is implemented by adding its complement. Changing the sign of any number is encoded by generating its complement, which can be done by a very simple and efficient algorithm. This method was commonly used in mechanical calculators and is still used in modern computers. The generalized concept of the ''radix complement'' (as described below) is also valuable in number theory, such as in Midy's theorem. The ''nines' complement'' of a number given in decimal representation is fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XOR Gate
XOR gate (sometimes EOR, or EXOR and pronounced as Exclusive OR) is a digital logic gate that gives a true (1 or HIGH) output when the number of true inputs is odd. An XOR gate implements an exclusive or (\nleftrightarrow) from mathematical logic; that is, a true output results if one, and only one, of the inputs to the gate is true. If both inputs are false (0/LOW) or both are true, a false output results. XOR represents the inequality function, i.e., the output is true if the inputs are not alike otherwise the output is false. A way to remember XOR is "must have one or the other but not both". An XOR gate may serve as a "programmable inverter" in which one input determines whether to invert the other input, or to simply pass it along with no change. Hence it functions as a inverter A power inverter, inverter or invertor is a power electronic device or circuitry that changes direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). The resulting AC frequency obtained depends on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)