|
I. Armeekorps (Wehrmacht)
I Army Corps (I. Armeekorps) was a corps in the German Army during World War II. It was established by upgrading the former staff of the 1st Division of the Reichsheer at Konigsberg on 1 October 1934.Axis History Factbook Commanders Area of operations * Poland - September 1939 to May 1940 * France - May 1940 to June 1941 * Eastern Front, Northern Sector - June 1941 to October 1944 * Courland Pocket - October 1944 to May 1945 See also * List of German corps in World War II List of German corps in World War II This is a list of German Army corps that existed during World War II. Army (Heer) Infantry corps I–IX * I Army Corps * II Army Corps * III Army Corps * IV Army Corps * V Army Corps * VI Army Corps * ... References External links Army,01 Military units and formations established in 1934 Military units and formations disestablished in 1945 {{Germany-mil-unit-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Army (Wehrmacht)
The German Army (, "army") is the land component of the armed forces of Federal Republic of Germany, Germany. The present-day German Army was founded in 1955 as part of the newly formed West German ''Bundeswehr'' together with the German Navy, ''Marine'' (German Navy) and the German Air Force, ''Luftwaffe'' (German Air Force). , the German Army had a strength of 62,766 soldiers. History Overview A German army equipped, organized, and trained following a single doctrine and permanently unified under one command in 1871 during the unification of Germany under the leadership of Prussia. From 1871 to 1919, the title ''German Army (German Empire), Deutsches Heer'' (German Army) was the official name of the German land forces. Following the German defeat in World War I and the end of the German Empire, the main army was dissolved. From 1921 to 1935 the name of the German land forces was the ''Reichswehr, Reichsheer'' (Army of the Empire) and from 1935 to 1945 the name ''German Army (We ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodor Busse
Ernst Hermann August Theodor Busse (15 December 1897 – 21 October 1986) was a German officer during World War I and World War II. Early life and career Busse, a native of Frankfurt (Oder), joined the Imperial German Army as an officer cadet in 1915 and was commissioned in February 1917. He also won the Knight's Cross with Swords of the Hohenzollern Order. After the armistice, he was accepted as one of 2,000 officers into the new Reichswehr in which he steadily rose in rank. World War II Busse was a General Staff officer in April 1939 and prepared a training program that was approved by the Chief of the General Staff in August and covered a period from 1 October 1939 to 30 September 1940. Between 1940 and 1942, he served as the Chief of Operations to General (later Field Marshal) Erich von Manstein in the 11th Army on the Eastern Front. He remained serving on von Manstein's staff from 1942 to 1943 as Chief of Operations of Army Group Don and then from 1943 to 1944 he was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corps Of Germany In World War II
Corps (; plural ''corps'' ; from French , from the Latin "body") is a term used for several different kinds of organization. A military innovation by Napoleon I, the formation was first named as such in 1805. The size of a corps varies greatly, but from two to five divisions and anywhere from 40,000 to 80,000 are the numbers stated by the US Department of Defense. Within military terminology a corps may be: *an operational formation, sometimes known as a field corps, which consists of two or more divisions, such as the , later known as ("First Corps") of Napoleon I's ); *an administrative corps (or mustering) – that is a specialized branch of a military service (such as an artillery corps, a medical corps, or a force of military police) or; *in some cases, a distinct service within a national military (such as the United States Marine Corps). These usages often overlap. Corps may also be a generic term for a non-military organization, such as the US Peace Corps and E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of German Corps In World War II
List of German corps in World War II This is a list of German Army corps that existed during World War II. Army (Heer) Infantry corps I–IX * I Army Corps * II Army Corps * III Army Corps * IV Army Corps * V Army Corps * VI Army Corps * VII Army Corps * VIII Army Corps * IX Army Corps X–XIX * X Army Corps * XI Army Corps * XII Army Corps * XIII Army Corps * XIV Army Corps * XV Army Corps * XVI Army Corps * XVII Army Corps * XVIII Army Corps * XIX Army Corps XX–XXIX * XX Army Corps * XXI Army Corps * XXII Army Corps * XXIII Army Corps * XXIV Army Corps * XXV Army Corps * XXVI Army Corps * XXVII Army Corps * XXVIII Army Corps * XXIX Army Corps XXX–XXXIX * XXX Army Corps * XXXI Army Corps * XXXII Army Corps * XXXIII Army Corps * XXXIV Army Corps * XXXV Army Corps * XXXVI Army Corps * XXXVIII Army Corps * XXXIX Army Corps XXXX–XXXXIX * XXXX Army Corps * XXXXI Army Corps * XXXXII Army Corps * XXXXIII Army Corps * XXXXIV Army Corps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
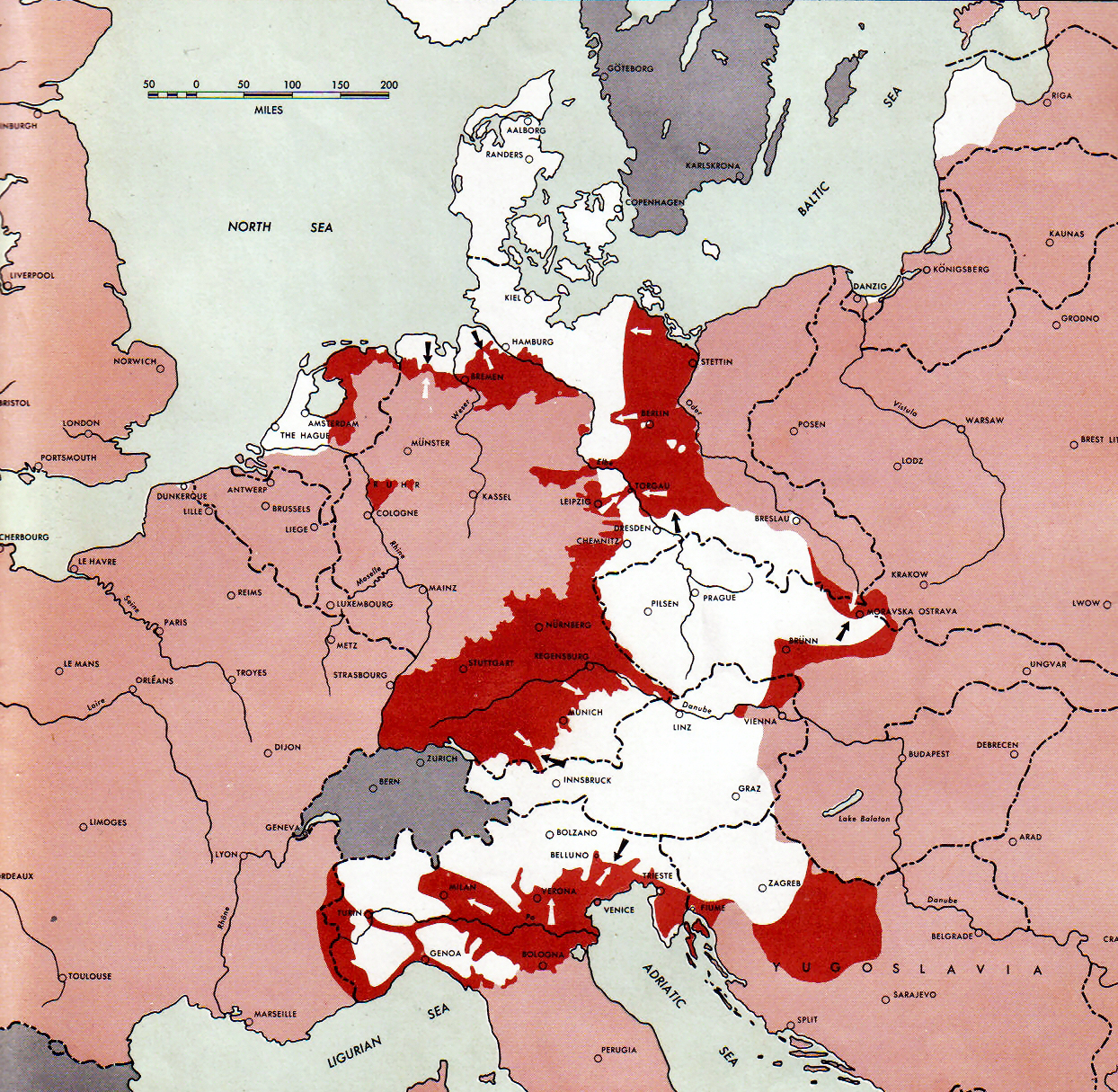
Courland Pocket
The Courland Pocket (Blockade of the Courland army group), (german: Kurland-Kessel)/german: Kurland-Brückenkopf (Courland Bridgehead), lv, Kurzemes katls (Courland Cauldron) or ''Kurzemes cietoksnis'' (Courland Fortress)., group=lower-alpha was an area of the Courland Peninsula where Army Group North of Nazi Germany and the Reichskommissariat Ostland were cut off and surrounded by the Red Army for almost a year, lasting from July 1944 until 10 May 1945. The pocket was created during the Red Army's Baltic Offensive, when forces of the 1st Baltic Front reached the Baltic Sea near Memel (Klaipėda) during its lesser Memel Offensive Operation phases. This action isolated the German Army Group North from the rest of the German forces, having been pushed from the south by the Red Army, standing in a front between Tukums and Libau in Latvia, with the Baltic Sea in the West, the Irbe Strait in the North and the Gulf of Riga in the East behind the Germans. Renamed Army Group Courl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Front (World War II)
The Eastern Front of World War II was a Theater (warfare), theatre of conflict between the European Axis powers against the Soviet Union (USSR), Polish Armed Forces in the East, Poland and other Allies of World War II, Allies, which encompassed Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Northern Europe, Northeast Europe (Baltic states, Baltics), and Southeast Europe (Balkans) from 22 June 1941 to 9 May 1945. It was known as the Great Patriotic War (term), Great Patriotic War in the Soviet Union – and still is in some of its successor states, while almost everywhere else it has been called the ''Eastern Front''. In present-day German and Ukrainian historiography the name German-Soviet War is typically used. The battles on the Eastern Front of the Second World War constituted the largest military confrontation in history. They were characterised by unprecedented ferocity and brutality, wholesale destruction, mass deportations, and immense loss of life due to combat, starvation, expos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of France
The Battle of France (french: bataille de France) (10 May – 25 June 1940), also known as the Western Campaign ('), the French Campaign (german: Frankreichfeldzug, ) and the Fall of France, was the Nazi Germany, German invasion of French Third Republic, France during the Second World War. On 3 September 1939, France French declaration of war on Germany (1939), declared war on Germany following the German invasion of Poland. In early September 1939, France began the limited Saar Offensive and by mid-October had withdrawn to their start lines. German armies German invasion of Belgium (1940), invaded Belgium, German invasion of Luxembourg, Luxembourg and German invasion of the Netherlands, the Netherlands on 10 May 1940. Fascist Italy (1922-1943), Italy entered the war on 10 June 1940 and attempted an Italian invasion of France, invasion of France. France and the Low Countries were conquered, ending land operations on the Western Front (World War II), Western Front until the Normandy l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Campaign
The invasion of Poland (1 September – 6 October 1939) was a joint attack on the Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union which marked the beginning of World War II. The German invasion began on 1 September 1939, one week after the signing of the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact between Germany and the Soviet Union, and one day after the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union had approved the pact. The Soviets invaded Poland on 17 September. The campaign ended on 6 October with Germany and the Soviet Union dividing and annexing the whole of Poland under the terms of the German–Soviet Frontier Treaty. The invasion is also known in Poland as the September campaign ( pl, kampania wrześniowa) or 1939 defensive war ( pl, wojna obronna 1939 roku, links=no) and known in Germany as the Poland campaign (german: Überfall auf Polen, Polenfeldzug). German forces invaded Poland from the north, south, and west the morning after the Gleiwitz incident. Slovak military forces adva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Usinger
__NOTOC__ Christian Usinger (21 August 1894 – 2 April 1949) was a German general during World War II who commanded the I Army Corps. He was a recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross of Nazi Germany. Usinger surrendered to the Soviet Forces in 1945 in the Courland Pocket. He died in a POW camp in the Soviet Union in early 1949. Awards and decorations * German Cross in Gold on 19 September 1942 as ''Oberst'' in Arko 110 * Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross on 9 June 1944 as ''Generalmajor is the Germanic variant of major general, used in a number of Central and Northern European countries. Austria Belgium Denmark is the second lowest general officer rank in the Royal Danish Army and Royal Danish Air Force. As a two-star ...'' and leader of the 81. Infanterie-DivisionFellgiebel 2000, p. 428. References Citations Bibliography * * Patzwall, Klaus D. and Scherzer, Veit (2001). ''Das Deutsche Kreuz 1941–1945 Geschichte und Inhaber Band II''. Norderstedt, G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Fangohr
__NOTOC__ Friedrich Fangohr (12 August 1899 – 17 April 1956) was a general in the Wehrmacht of Nazi Germany during World War II who commanded the I Army Corps. He was also a recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross. Awards and decorations * Iron Cross (1914) 2nd Class (24 December 1917) & 1st Class (25 October 1918) * Silesian Eagle 2nd Class (2 July 1919) & 1st Class (23 July 1919) * Clasp to the Iron Cross (1939) 2nd Class (25 September 1939) & 1st Class (12 October 1939) * Eastern Front Medal (22 August 1942) * Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross The Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross (german: Ritterkreuz des Eisernen Kreuzes), or simply the Knight's Cross (), and its variants, were the highest awards in the military and paramilitary forces of Nazi Germany during World War II. The Knight' ... on 9 June 1944 as '' Generalleutnant'' and Chief of Generalstab of Panzer-A.O.K. 4 References Citations Bibliography * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Fangohr, Fried ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter Hartmann
__NOTOC__ Walter Hartmann (23 July 1891 – 11 March 1977) was a German general in the Wehrmacht during World War II. He was a recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross with Oak Leaves and Swords of Nazi Germany. During the evacuation of Crimea in 1944, he escaped on the Romanian minelayer ''Amiral Murgescu'' and reached the Romanian port of Constanța. Life Hartmann joined the 1st Field Artillery Regiment No. 12 of the Saxon Army on 1 October 1910 as an officer candidate. On May 4, 1912, he was promoted to lieutenant by patent of May 24, 1910. During the First World War, Hartmann fought with his regiment on the Eastern Front and was awarded the Knight's Cross of the Military St. Order of Henry. In the course of the war, he became a lieutenant colonel on 13 March 1916 and came a month later as an observer to the Flieger-Ersatzabteilung 7. From January 1917 he served as First Adjutant of the Artillery Air School East and on 1 June 1918 he was transferred to Fliegergruppen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corps
Corps (; plural ''corps'' ; from French , from the Latin "body") is a term used for several different kinds of organization. A military innovation by Napoleon I, the formation was first named as such in 1805. The size of a corps varies greatly, but from two to five divisions and anywhere from 40,000 to 80,000 are the numbers stated by the US Department of Defense. Within military terminology a corps may be: *an military organization, operational formation, sometimes known as a field corps, which consists of two or more division (military), divisions, such as the I Corps (Grande Armée), , later known as ("First Corps") of Napoleon I's ); *an administrative corps (or Muster (military), mustering) – that is a #Administrative corps, specialized branch of a military service (such as an artillery corps, a medical corps, or a force of military police) or; *in some cases, a distinct service within a national military (such as the United States Marine Corps). These usages often ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |