|
Hydrostannylation
In chemistry, hydrostannylation is the insertion of unsaturated substrates into an Sn-H bond. The reaction occurs under free-radical conditions, but the stereochemistry and regiochemistry are often complex. The reaction gained synthetic importance with the discovery that palladium complexes catalyze the reaction. The reaction is analogous to hydrosilylation and is a subset of hydroelementation. Hydrostannylation is a versatile route to organotin compounds, many of which are versatile synthetic intermediates, e.g. in Stille coupling. Substrates and scope The typical Pd-based catalyst is tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(0). The typical unsaturated substrates are alkynes. The typical stannane is tributyltin hydride. The reaction mechanism is assumed to operate via oxidative addition Oxidative addition and reductive elimination are two important and related classes of reactions in organometallic chemistry. Oxidative addition is a process that increases both the oxidatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tributyltin Hydride
Tributyltin hydride is an organotin compound with the formula (C4H9)3SnH. It is a colorless liquid that is soluble in organic solvents. The compound is used as a source of hydrogen atoms in organic synthesis. Synthesis and characterization The compound is produced by reduction of tributyltin oxide with polymethylhydrosiloxane: : 2 " eSi(H)Osub>n" + (Bu3Sn)2O → " eSi(OH)Osub>n" + 2 Bu3SnH The hydride is a distillable liquid that is mildly sensitive to air, decomposing to (Bu3Sn)2O. Its IR spectrum exhibits a strong band at 1814 cm−1 for ''ν''Sn−H. Applications It is a specialized reagent in organic synthesis. Combined with azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN) or by irradiation with light, tributyltin hydride converts organic halides (and related groups) to the corresponding hydrocarbon. This process occurs via a radical chain mechanism involving the radical Bu3Sn•. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science, scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a natural science that covers the Chemical element, elements that make up matter to the chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions: their composition, structure, properties, behavior and the changes they undergo during a Chemical reaction, reaction with other Chemical substance, substances. Chemistry also addresses the nature of chemical bonds in chemical compounds. In the scope of its subject, chemistry occupies an intermediate position between physics and biology. It is sometimes called the central science because it provides a foundation for understanding both Basic research, basic and Applied science, applied scientific disciplines at a fundamental level. For example, chemistry explains aspects of plant growth (botany), the formation of igneous rocks (geology), how atmospheric ozone is formed and how environmental pollutants are degraded (ecology), the properties ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrosilylation
Hydrosilylation, also called catalytic hydrosilation, describes the addition of Si-H bonds across unsaturated bonds."Hydrosilylation A Comprehensive Review on Recent Advances" B. Marciniec (ed.), Advances in Silicon Science, Springer Science, 2009. Ordinarily the reaction is conducted catalytically and usually the substrates are unsaturated organic compounds. Alkenes and alkynes give alkyl and vinyl silanes; aldehydes and ketones give silyl ethers. Hydrosilylation has been called the "most important application of platinum in homogeneous catalysis." Scope and mechanism Hydrosilylation of alkenes represents a commercially important method for preparing organosilicon compounds. The process is mechanistically similar to the hydrogenation of alkenes. In fact, similar catalysts are sometimes employed for the two catalytic processes. The prevalent mechanism, called the Chalk-Harrod mechanism, assumes an intermediate metal complex that contains a hydride, a silyl ligand (R3Si), and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organotin Compound
Organotin compounds or stannanes are chemical compounds based on tin with hydrocarbon substituents. Organotin chemistry is part of the wider field of organometallic chemistry. The first organotin compound was diethyltin diiodide (), discovered by Edward Frankland in 1849. The area grew rapidly in the 1900s, especially after the discovery of the Grignard reagents, which are useful for producing Sn–C bonds. The area remains rich with many applications in industry and continuing activity in the research laboratory. Structure Organotin compounds are generally classified according to their oxidation states. Tin(IV) compounds are much more common and more useful. Organic derivatives of tin(IV) The tetraorgano derivatives are invariably tetrahedral. Compounds of the type SnRR'R''R have been resolved into individual enantiomers. Organotin halides Organotin chlorides have the formula for values of ''n'' up to 3. Bromides, iodides, and fluorides are also known but less important. These ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
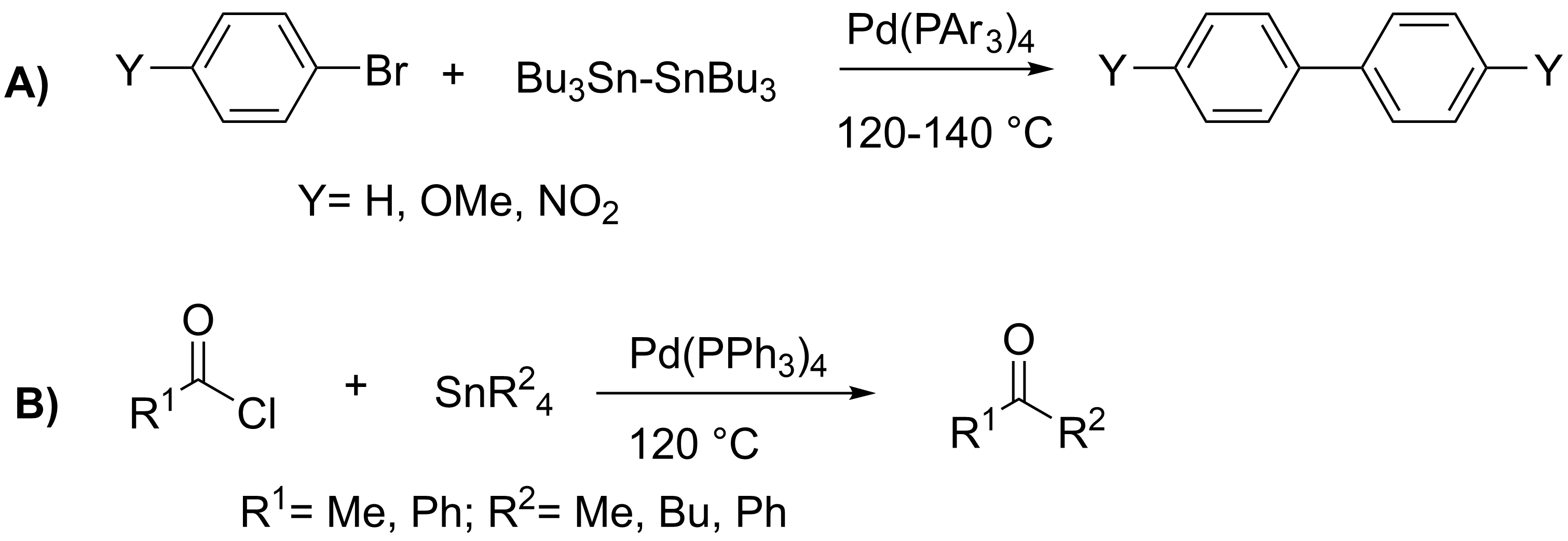
Stille Coupling
The Stille reaction is a chemical reaction widely used in organic synthesis. The reaction involves the coupling of two organic groups, one of which is carried as an organotin compound (also known as organostannanes). A variety of organic electrophiles provide the other coupling partner. The Stille reaction is one of many palladium-catalyzed coupling reactions.Hartwig, J. F. ''Organotransition Metal Chemistry, from Bonding to Catalysis''; University Science Books: New York, 2010. Stille, J. K. '' Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl.'' 1986, ''25'', 508–524.ReviewFarina, V.; Krishnamurthy, V.; Scott, W. J. ''Org. React.'' 1998, ''50'', 1–652.Review : + \ \ce \ \overbrace^ + \!-\! :*\!,\ : Allyl, alkenyl, aryl, benzyl,acyl :*: halides (Cl, Br, I), pseudohalides (, OPO(OR)2), OAc The R1 group attached to the trialkyltin is normally sp2-hybridized, including vinyl, and aryl groups. These organostannanes are also stable to both air and moisture, and many of these reagents either are com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(0)
Tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(0) (sometimes called quatrotriphenylphosphine palladium) is the chemical compound d(P(C6H5)3)4 often abbreviated Pd( PPh3)4, or rarely PdP4. It is a bright yellow crystalline solid that becomes brown upon decomposition in air. Structure and properties The four phosphorus atoms are at the corners of a tetrahedron surrounding the palladium(0) center. This structure is typical for four-coordinate 18 e− complexes. The corresponding complexes Ni(PPh3)4 and Pt(PPh3)4 are also well known. Such complexes reversibly dissociate PPh3 ligands in solution, so reactions attributed to Pd(PPh3)4 often in fact arise from Pd(PPh3)3 or even Pd(PPh3)2. Preparation Tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(0) was first prepared by Lamberto Malatesta et al. in the 1950s by reduction of sodium chloropalladate with hydrazine in the presence of the phosphine. It is commercially available, but can be prepared in two steps from Pd(II) precursors: :PdCl2 + 2 PPh3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkyne
\ce \ce Acetylene \ce \ce \ce Propyne \ce \ce \ce \ce 1-Butyne In organic chemistry, an alkyne is an unsaturated hydrocarbon containing at least one carbon—carbon triple bond. The simplest acyclic alkynes with only one triple bond and no other functional groups form a homologous series with the general chemical formula . Alkynes are traditionally known as acetylenes, although the name ''acetylene'' also refers specifically to , known formally as ethyne using IUPAC nomenclature. Like other hydrocarbons, alkynes are generally hydrophobic. Structure and bonding In acetylene, the H–C≡C bond angles are 180°. By virtue of this bond angle, alkynes are rod-like. Correspondingly, cyclic alkynes are rare. Benzyne cannot be isolated. The C≡C bond distance of 121 picometers is much shorter than the C=C distance in alkenes (134 pm) or the C–C bond in alkanes (153 pm). : The triple bond is very strong with a bond strength of 839 kJ/mol. The sigma bond contribute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidative Addition
Oxidative addition and reductive elimination are two important and related classes of reactions in organometallic chemistry. Oxidative addition is a process that increases both the oxidation state and coordination number of a metal centre. Oxidative addition is often a step in catalytic cycles, in conjunction with its reverse reaction, reductive elimination. Role in transition metal chemistry For transition metals, oxidative reaction results in the decrease in the d''n'' to a configuration with fewer electrons, often 2e fewer. Oxidative addition is favored for metals that are (i) basic and/or (ii) easily oxidized. Metals with a relatively low oxidation state often satisfy one of these requirements, but even high oxidation state metals undergo oxidative addition, as illustrated by the oxidation of Pt(II) with chlorine: : tCl4sup>2− + Cl2 → tCl6sup>2− In classical organometallic chemistry, the formal oxidation state of the metal and the electron count of the complex both in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organotin Compounds
Organotin compounds or stannanes are chemical compounds based on tin with hydrocarbon substituents. Organotin chemistry is part of the wider field of organometallic chemistry. The first organotin compound was diethyltin diiodide (), discovered by Edward Frankland in 1849. The area grew rapidly in the 1900s, especially after the discovery of the Grignard reagents, which are useful for producing Sn–C bonds. The area remains rich with many applications in industry and continuing activity in the research laboratory. Structure Organotin compounds are generally classified according to their oxidation states. Tin(IV) compounds are much more common and more useful. Organic derivatives of tin(IV) The tetraorgano derivatives are invariably tetrahedral. Compounds of the type SnRR'R''R have been resolved into individual enantiomers. Organotin halides Organotin chlorides have the formula for values of ''n'' up to 3. Bromides, iodides, and fluorides are also known but less important. These ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |