|
Hurwitz Polynomial
In mathematics, a Hurwitz polynomial, named after Adolf Hurwitz, is a polynomial whose root of a function, roots (zeros) are located in the left half-plane of the complex plane or on the imaginary axis, that is, the complex number, real part of every root is zero or negative. Such a polynomial must have coefficients that are positive real numbers. The term is sometimes restricted to polynomials whose roots have real parts that are strictly negative, excluding the imaginary axis (i.e., a Hurwitz stable polynomial). A polynomial function ''P''(''s'') of a complex variable ''s'' is said to be Hurwitz if the following conditions are satisfied: :1. ''P''(''s'') is real when ''s'' is real. :2. The roots of ''P''(''s'') have real parts which are zero or negative. Hurwitz polynomials are important in control system, control systems theory, because they represent the Characteristic polynomial#Characteristic equation, characteristic equations of Stability theory, stable linear systems. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting points of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Control System
A control system manages, commands, directs, or regulates the behavior of other devices or systems using control loops. It can range from a single home heating controller using a thermostat controlling a domestic boiler to large industrial control systems which are used for controlling processes or machines. The control systems are designed via control engineering process. For continuously modulated control, a feedback controller is used to automatically control a process or operation. The control system compares the value or status of the process variable (PV) being controlled with the desired value or setpoint (SP), and applies the difference as a control signal to bring the process variable output of the plant to the same value as the setpoint. For sequential and combinational logic, software logic, such as in a programmable logic controller, is used. Open-loop and closed-loop control There are two common classes of control action: open loop and closed loop. In an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complex Conjugate
In mathematics, the complex conjugate of a complex number is the number with an equal real part and an imaginary part equal in magnitude but opposite in sign. That is, (if a and b are real, then) the complex conjugate of a + bi is equal to a - bi. The complex conjugate of z is often denoted as \overline or z^*. In polar form, the conjugate of r e^ is r e^. This can be shown using Euler's formula. The product of a complex number and its conjugate is a real number: a^2 + b^2 (or r^2 in polar coordinates). If a root of a univariate polynomial with real coefficients is complex, then its complex conjugate is also a root. Notation The complex conjugate of a complex number z is written as \overline z or z^*. The first notation, a vinculum, avoids confusion with the notation for the conjugate transpose of a matrix, which can be thought of as a generalization of the complex conjugate. The second is preferred in physics, where dagger (†) is used for the conjugate tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadratic Formula
In elementary algebra, the quadratic formula is a formula that provides the solution(s) to a quadratic equation. There are other ways of solving a quadratic equation instead of using the quadratic formula, such as factoring (direct factoring, grouping, AC method), completing the square, graphing and others. Given a general quadratic equation of the form :ax^2+bx+c=0 with representing an unknown, with , and representing constants, and with , the quadratic formula is: :x = \frac where the plus–minus symbol "±" indicates that the quadratic equation has two solutions. Written separately, they become: : x_1=\frac\quad\text\quad x_2=\frac Each of these two solutions is also called a root (or zero) of the quadratic equation. Geometrically, these roots represent the -values at which ''any'' parabola, explicitly given as , crosses the -axis. As well as being a formula that yields the zeros of any parabola, the quadratic formula can also be used to identify the axis of s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadratic Polynomial
In mathematics, a quadratic polynomial is a polynomial of degree two in one or more variables. A quadratic function is the polynomial function defined by a quadratic polynomial. Before 20th century, the distinction was unclear between a polynomial and its associated polynomial function; so "quadratic polynomial" and "quadratic function" were almost synonymous. This is still the case in many elementary courses, where both terms are often abbreviated as "quadratic". For example, a univariate (single-variable) quadratic function has the form :f(x)=ax^2+bx+c,\quad a \ne 0, where is its variable. The graph of a univariate quadratic function is a parabola, a curve that has an axis of symmetry parallel to the -axis. If a quadratic function is equated with zero, then the result is a quadratic equation. The solutions of a quadratic equation are the zeros of the corresponding quadratic function. The bivariate case in terms of variables and has the form : f(x,y) = a x^2 + bx y+ c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Routh–Hurwitz Stability Criterion
In control system theory, the Routh–Hurwitz stability criterion is a mathematical test that is a necessary and sufficient condition for the stability of a linear time-invariant (LTI) dynamical system or control system. A stable system is one whose output signal is bounded; the position, velocity or energy do not increase to infinity as time goes on. The Routh test is an efficient recursive algorithm that English mathematician Edward John Routh proposed in 1876 to determine whether all the roots of the characteristic polynomial of a linear system have negative real parts. German mathematician Adolf Hurwitz independently proposed in 1895 to arrange the coefficients of the polynomial into a square matrix, called the Hurwitz matrix, and showed that the polynomial is stable if and only if the sequence of determinants of its principal submatrices are all positive. The two procedures are equivalent, with the Routh test providing a more efficient way to compute the Hurwitz determinants ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
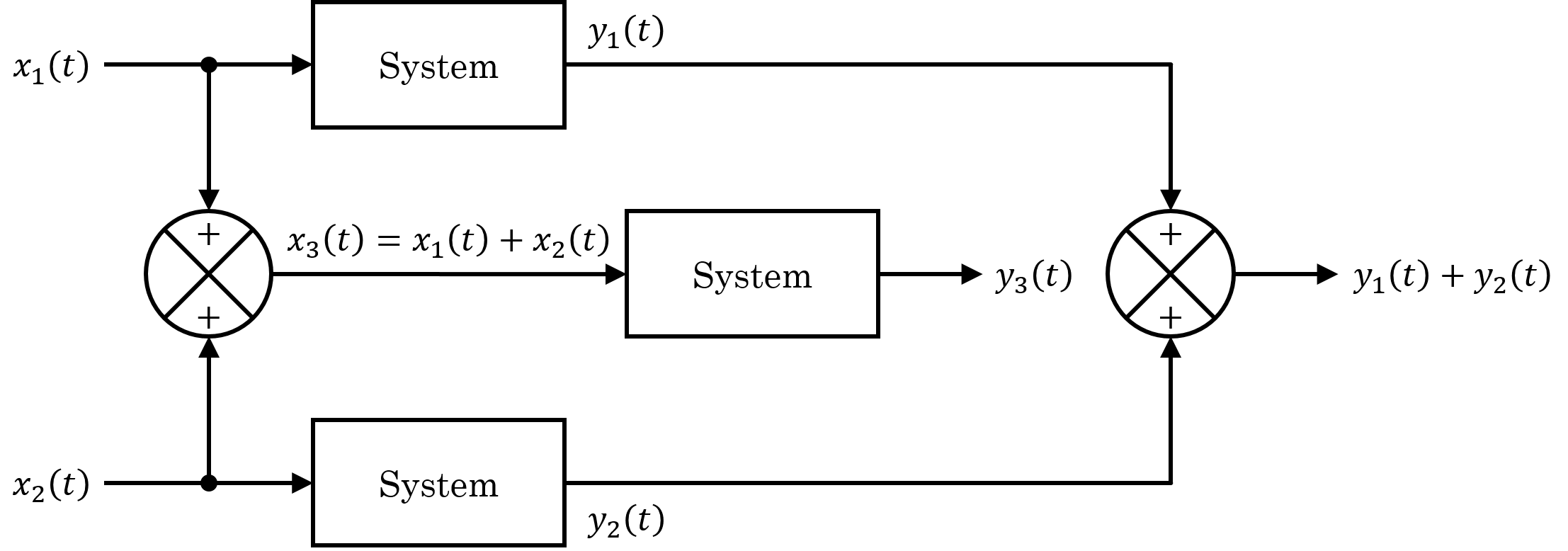
Linear System
In systems theory, a linear system is a mathematical model of a system based on the use of a linear operator. Linear systems typically exhibit features and properties that are much simpler than the nonlinear case. As a mathematical abstraction or idealization, linear systems find important applications in automatic control theory, signal processing, and telecommunications. For example, the propagation medium for wireless communication systems can often be modeled by linear systems. Definition A general deterministic system can be described by an operator, that maps an input, as a function of to an output, a type of black box description. A system is linear if and only if it satisfies the superposition principle, or equivalently both the additivity and homogeneity properties, without restrictions (that is, for all inputs, all scaling constants and all time.) The superposition principle means that a linear combination of inputs to the system produces a linear combination ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
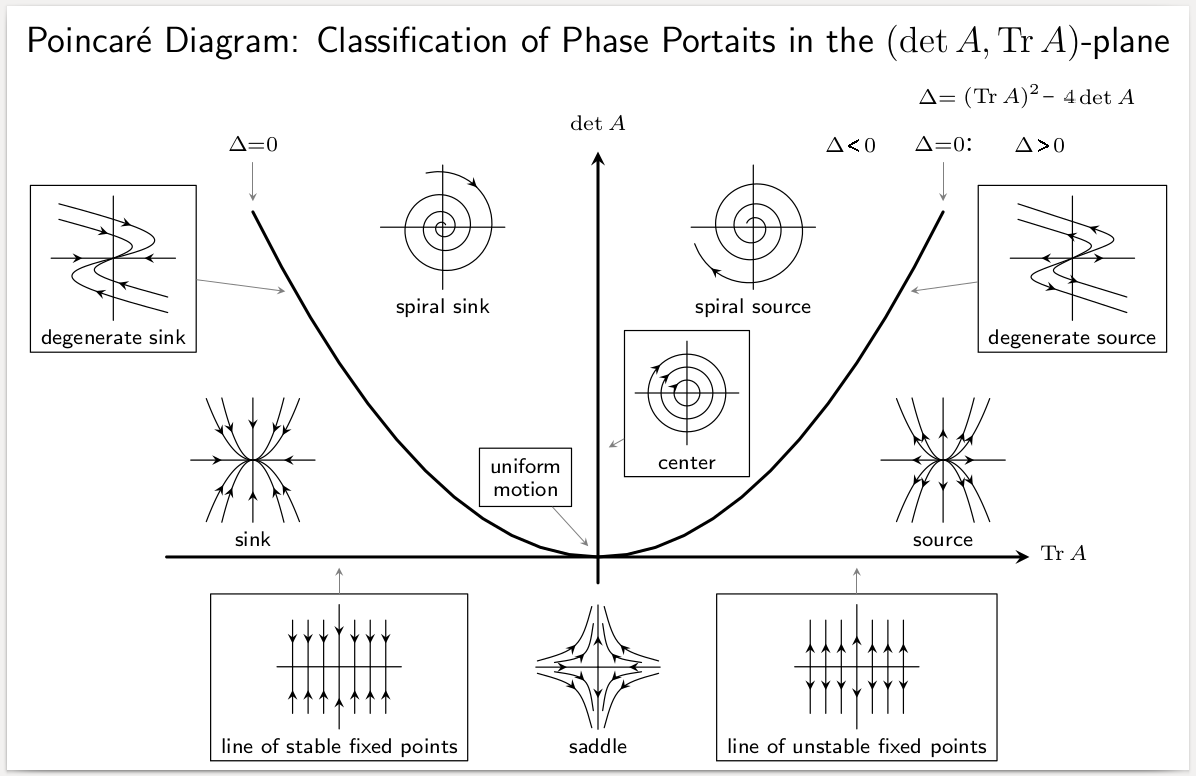
Stability Theory
In mathematics, stability theory addresses the stability of solutions of differential equations and of trajectories of dynamical systems under small perturbations of initial conditions. The heat equation, for example, is a stable partial differential equation because small perturbations of initial data lead to small variations in temperature at a later time as a result of the maximum principle. In partial differential equations one may measure the distances between functions using Lp norms or the sup norm, while in differential geometry one may measure the distance between spaces using the Gromov–Hausdorff distance. In dynamical systems, an orbit is called ''Lyapunov stable'' if the forward orbit of any point is in a small enough neighborhood or it stays in a small (but perhaps, larger) neighborhood. Various criteria have been developed to prove stability or instability of an orbit. Under favorable circumstances, the question may be reduced to a well-studied problem involvi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Characteristic Polynomial
In linear algebra, the characteristic polynomial of a square matrix is a polynomial which is invariant under matrix similarity and has the eigenvalues as roots. It has the determinant and the trace of the matrix among its coefficients. The characteristic polynomial of an endomorphism of a finite-dimensional vector space is the characteristic polynomial of the matrix of that endomorphism over any base (that is, the characteristic polynomial does not depend on the choice of a basis). The characteristic equation, also known as the determinantal equation, is the equation obtained by equating the characteristic polynomial to zero. In spectral graph theory, the characteristic polynomial of a graph is the characteristic polynomial of its adjacency matrix. Motivation In linear algebra, eigenvalues and eigenvectors play a fundamental role, since, given a linear transformation, an eigenvector is a vector whose direction is not changed by the transformation, and the corresponding eigenva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complex Variable
Complex analysis, traditionally known as the theory of functions of a complex variable, is the branch of mathematical analysis that investigates functions of complex numbers. It is helpful in many branches of mathematics, including algebraic geometry, number theory, analytic combinatorics, applied mathematics; as well as in physics, including the branches of hydrodynamics, thermodynamics, and particularly quantum mechanics. By extension, use of complex analysis also has applications in engineering fields such as nuclear, aerospace, mechanical and electrical engineering. As a differentiable function of a complex variable is equal to its Taylor series (that is, it is analytic), complex analysis is particularly concerned with analytic functions of a complex variable (that is, holomorphic functions). History Complex analysis is one of the classical branches in mathematics, with roots in the 18th century and just prior. Important mathematicians associated with complex numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adolf Hurwitz
Adolf Hurwitz (; 26 March 1859 – 18 November 1919) was a German mathematician who worked on algebra, analysis, geometry and number theory. Early life He was born in Hildesheim, then part of the Kingdom of Hanover, to a Jewish family and died in Zürich, in Switzerland. His father Salomon Hurwitz, a merchant, was not wealthy. Hurwitz's mother, Elise Wertheimer, died when he was three years old. Family records indicate that he had siblings and cousins, but their names have yet to be confirmed except for an older brother, Julius, with whom he developed an arithmetical theory for complex continued fractions circa 1890. Hurwitz entered the in Hildesheim in 1868. He was taught mathematics there by Hermann Schubert. Schubert persuaded Hurwitz's father to allow him to attend university, and arranged for Hurwitz to study with Felix Klein at Munich. Salomon Hurwitz could not afford to send his son to university, but his friend, Mr. Edwards, assisted financially. Educational career Hur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stable Polynomial
In the context of the characteristic polynomial of a differential equation or difference equation, a polynomial is said to be stable if either: * all its roots lie in the open left half-plane, or * all its roots lie in the open unit disk. The first condition provides stability for continuous-time linear systems, and the second case relates to stability of discrete-time linear systems. A polynomial with the first property is called at times a Hurwitz polynomial and with the second property a Schur polynomial. Stable polynomials arise in control theory and in mathematical theory of differential and difference equations. A linear, time-invariant system (see LTI system theory) is said to be BIBO stable if every bounded input produces bounded output. A linear system is BIBO stable if its characteristic polynomial is stable. The denominator is required to be Hurwitz stable if the system is in continuous-time and Schur stable if it is in discrete-time. In practice, stability is det ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)