|
Huahine - Fare Airport
Huahine is an island located among the Society Islands, in French Polynesia, an overseas territory of France in the Pacific Ocean. It is part of the Leeward Islands group ''(Îles sous le Vent).'' At the 2017 census it had a population of 6,075.Répartition de la population en Polynésie française en 2017 Institut de la statistique de la Polynésie française History Human presence on Huahine dates back to ancient times, as evidenced by the numerous Marae on the island. Archaeologists estimate that the ancient Tahitian Ma'ohi people colonized Huahine from at least the 9th century AD. Huahine is home to one of the largest concentrations of Polynesian archaeo ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communes Of France
The () is a level of administrative division in the French Republic. French are analogous to civil townships and incorporated municipalities in the United States and Canada, ' in Germany, ' in Italy, or ' in Spain. The United Kingdom's equivalent are civil parishes, although some areas, particularly urban areas, are unparished. are based on historical geographic communities or villages and are vested with significant powers to manage the populations and land of the geographic area covered. The are the fourth-level administrative divisions of France. vary widely in size and area, from large sprawling cities with millions of inhabitants like Paris, to small hamlets with only a handful of inhabitants. typically are based on pre-existing villages and facilitate local governance. All have names, but not all named geographic areas or groups of people residing together are ( or ), the difference residing in the lack of administrative powers. Except for the municipal arrondi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tupaia (navigator)
Tupaia (also spelled Tupaea or Tupia; 1725 – December 20, 1770) was a Tahitian Polynesian navigator and ''arioi'' (a kind of priest), originally from the island of Ra'iatea in the Pacific Islands group known to Europeans as the Society Islands. His remarkable navigational skills and Pacific geographical knowledge were to be utilised by Lt. James Cook, R.N. when he took him aboard HMS ''Endeavour'' as guide on its voyage of exploration to ''Terra Australis Incognita''. Tupaia travelled with Cook to New Zealand, acting as the expedition's interpreter to the Polynesian Māori, and Australia. He died in December 1770 from a shipborne illness contracted when ''Endeavour'' was docked in Batavia for repairs ahead of its return journey to England. Early life Tupaia was born at Ha'amanino Harbour on Ra'iatea around 1725 and became a leading ''ariori'' priest for the Taputapuatea marae. Tupaia was trained in the ''fare-'ai-ra'a-'upu'', or schools of learning, about the origin of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brackish Water
Brackish water, sometimes termed brack water, is water occurring in a natural environment that has more salinity than freshwater, but not as much as seawater. It may result from mixing seawater (salt water) and fresh water together, as in estuaries, or it may occur in brackish fossil aquifers. The word comes from the Middle Dutch root '' brak''. Certain human activities can produce brackish water, in particular civil engineering projects such as dikes and the flooding of coastal marshland to produce brackish water pools for freshwater prawn farming. Brackish water is also the primary waste product of the salinity gradient power process. Because brackish water is hostile to the growth of most terrestrial plant species, without appropriate management it is damaging to the environment (see article on shrimp farms). Technically, brackish water contains between 0.5 and 30 grams of salt per litre—more often expressed as 0.5 to 30 parts per thousand (‰), which is a specific gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low Tide
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another. Tide tables can be used for any given locale to find the predicted times and amplitude (or "tidal range"). The predictions are influenced by many factors including the alignment of the Sun and Moon, the phase and amplitude of the tide (pattern of tides in the deep ocean), the amphidromic systems of the oceans, and the shape of the coastline and near-shore bathymetry (see '' Timing''). They are however only predictions, the actual time and height of the tide is affected by wind and atmospheric pressure. Many shorelines experience semi-diurnal tides—two nearly equal high and low tides each day. Other locations have a diurnal tide—one high and low tide each day. A "mixed tide"—two uneven magnitude tides a day—is a third regular category. Tides va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spit (landform)
A spit or sandspit is a deposition bar or beach landform off coasts or lake shores. It develops in places where re-entrance occurs, such as at a cove's headlands, by the process of longshore drift by longshore currents. The drift occurs due to waves meeting the beach at an oblique angle, moving sediment down the beach in a zigzag pattern. This is complemented by longshore currents, which further transport sediment through the water alongside the beach. These currents are caused by the same waves that cause the drift. Hydrology and geology Where the direction of the shore inland ''re-enters'', or changes direction, for example at a headland, the longshore current spreads out or dissipates. No longer able to carry the full load, much of the sediment is dropped. This is called deposition. This submerged bar of sediment allows longshore drift or littoral drift to continue to transport sediment in the direction the waves are breaking, forming an above-water spit. Without the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islets
An islet is a very small, often unnamed island. Most definitions are not precise, but some suggest that an islet has little or no vegetation and cannot support human habitation. It may be made of rock, sand and/or hard coral; may be permanent or tidal (i.e. surfaced reef or seamount); and may exist in the sea, lakes, rivers or any other sizeable bodies of water. Definition As suggested by its origin ''islette'', an Old French diminutive of "isle", use of the term implies small size, but little attention is given to drawing an upper limit on its applicability. The World Landforms website says, "An islet landform is generally considered to be a rock or small island that has little vegetation and cannot sustain human habitation", and further that size may vary from a few square feet to several square miles, with no specific rule pertaining to size. Other terms * Ait (/eɪt/, like eight) or eyot (/aɪ(ə)t, eɪt/), a small island. It is especially used to refer to river ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tehaapapa III
Princess Teri'i-na-vaha-roa (8 August 1879 – 27 April 1917) was the last sovereign monarch of the Kingdom of Huahine and Mai'ao from 1893 to 1895. Comteporary sources seems to call her Tehaapapa II instead, disregarding the ruling Tehaapapa I, queen by the same name at the time James Cook visited the island. Biography Te-ha'apapa III was a member of a royal Tahitians, Tahitian dynasty, the deposed royal family Teururai of Huahine. As a Tahitian Princess, she became Queen regnant, Queen of Huahine. She was the last Queen of Huahine from 1893 to 1895. She was the eldest daughter of Marama Teururai, prince regent of Huahine by his wife Tetuanuimarama a Te-u-ru-ari'i, Princess of Rurutu. She was crowned with the regnal name Te-ha'apapa III in 1893, and was deposed when Huahine was annexed by the France, French in September 1895. Marriage She married first at Fare on 15 May 1895 (divorced 6 August 1897) to Highness, His Highness Teri'i-te-vae-a-ra'i-a-Mai, a descendant of Ma' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protectorate
A protectorate, in the context of international relations, is a State (polity), state that is under protection by another state for defence against aggression and other violations of law. It is a dependent territory that enjoys autonomy over most of its internal affairs, while still recognizing the suzerainty of a more powerful sovereign state without being a possession. In exchange, the protectorate usually accepts specified obligations depending on the terms of their arrangement. Usually protectorates are established de jure by a treaty. Under certain conditions—as with History of Egypt under the British#Veiled Protectorate (1882–1913), Egypt under British rule (1882–1914)—a state can also be labelled as a de facto protectorate or a veiled protectorate. A protectorate is different from a colony as it has local rulers, is not directly possessed, and rarely experiences colonization by the suzerain state. A state that is under the protection of another state while retain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Empire
The German Empire (),Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary empire led by an emperor, although has been used in German to denote the Roman Empire because it had a weak hereditary tradition. In the case of the German Empire, the official name was , which is properly translated as "German Empire" because the official position of head of state in the constitution of the German Empire was officially a "presidency" of a confederation of German states led by the King of Prussia who would assume "the title of German Emperor" as referring to the German people, but was not emperor of Germany as in an emperor of a state. –The German Empire" ''Harper's New Monthly Magazine''. vol. 63, issue 376, pp. 591–603; here p. 593. also referred to as Imperial Germany, the Second Reich, as well as simply Germany, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SMS Bismarck
SMS ''Bismarck'' was a built for the German Imperial Navy (''Kaiserliche Marine'') in the late 1870s. She was the lead ship of her class, which included five other vessels. The ''Bismarck''-class corvettes were ordered as part of a major naval construction program in the early 1870s, and she was designed to serve as a fleet scout and on extended tours in Germany's colonial empire. ''Bismarck'' was laid down in November 1875, launched in July 1877, and was commissioned into the fleet in August 1878. She was armed with a battery of sixteen guns and had a full ship rig to supplement her steam engine on long cruises abroad. ''Bismarck'' went on two major overseas cruises, the first in late 1878 to late 1880, which saw the ship visit South American ports and patrol the Central Pacific, where Germany had economic interests but no formal colonies at that time. During this cruise, she interfered with Samoan internal affairs and protected German interests in South America during the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Independence
Independence is a condition of a person, nation, country, or state in which residents and population, or some portion thereof, exercise self-government, and usually sovereignty, over its territory. The opposite of independence is the status of a dependent territory. The commemoration of the independence day of a country or nation celebrates when a country is free from all forms of foreign colonialism; free to build a country or nation without any interference from other nations. Definition of independence Whether the attainment of independence is different from revolution has long been contested, and has often been debated over the question of violence as legitimate means to achieving sovereignty. In general, revolutions aim only to redistribute power with or without an element of emancipation,such as in democratization ''within'' a state, which as such may remain unaltered. For example, the Mexican Revolution (1910) chiefly refers to a multi-factional conflict that e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
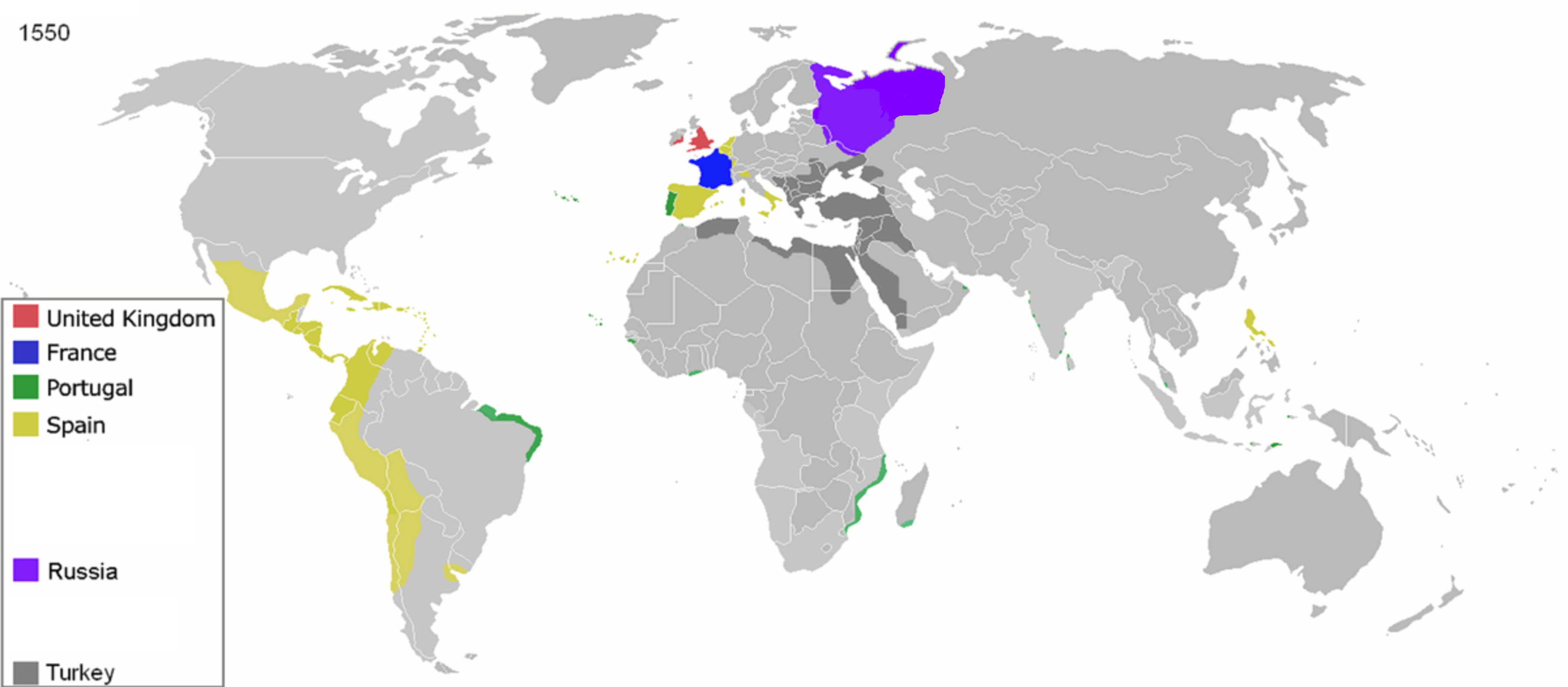
Colonization
Colonization, or colonisation, constitutes large-scale population movements wherein migrants maintain strong links with their, or their ancestors', former country – by such links, gain advantage over other inhabitants of the territory. When colonization takes place under the protection of Colonialism, colonial structures, it may be termed settler colonialism. This often involves the settlers dispossessing Indigenous peoples, indigenous inhabitants, or instituting legal and other structures which disadvantage them. Colonization can be defined as a process of establishing foreign control over target territory, territories or people, peoples for the purpose of colonialism, cultivation, often by establishing Colony, colonies and possibly by settling them. In colonies established by Western European countries in the Americas, Australia, and New Zealand, settlers (supplemented by Central European, Eastern European, Asian, and African people) eventually formed a large majority of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



%2C_by_John_Trumbull.jpg)