|
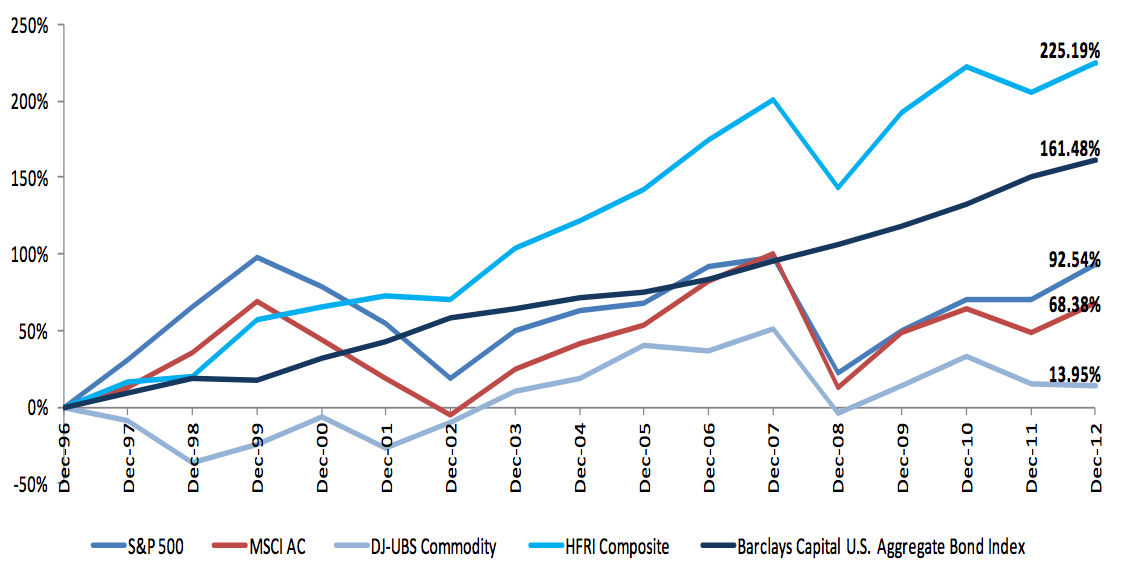
Holy Grail Distribution
In economics and finance, a holy grail distribution is a probability distribution with positive mean and right fat tail — a returns profile of a hypothetical investment vehicle that produces small returns centered on zero and occasionally exhibits outsized positive returns. The distribution of historical returns of most asset classes and investment managers is negatively skewed and exhibits fat left tail (abnormal negative returns). Asset classes tend to have strong negative returns when stock market crises take place. For example, in October 2008 stocks, most hedge funds, real estate and corporate bonds suffered strong downward price corrections. At the same time vehicles following the Holy Grail distribution such as US dollar (as a DXY index), treasury bonds and certain hedge fund strategies that bought credit default swaps (CDS) and other derivative instruments had strong positive returns. Market forces that pushed the first category of assets down pulled the latter category ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taleb And Holy Grail Distributions
Taleb may refer to: People Surname * Loay Taleb (born 1975), Syrian footballer * Nassim Nicholas Taleb (born 1960), Lebanese-American writer and statistician * Nordine Taleb (born 1981), French mixed martial artist * Oday Taleb (born 1977), Iraqi football goalkeeper Given name * Taleb Alrefai (born 1958), Kuwaiti journalist and writer * Taleb Nematpour (born 1984), Iranian wrestler * Taleb Tawatha (born 1992), Israeli-Bedouin footballer Places * Taleb, Iran, a village in East Azerbaijan Province, Iran * Taleb, Khuzestan Sheykh Taleb ( fa, شيخ طالب, also Romanized as Sheykh Ţāleb; also known as Ţāleb) is a village in Seyyed Abbas Rural District, Shavur District, Shush County, Khuzestan Province, Iran Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of ..., a village in Khuzestan Province, Iran See also * Taleb distribution, a type of returns profile * Talib (other) {{disambig, surname, given name, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Credit Default Swap
A credit default swap (CDS) is a financial swap agreement that the seller of the CDS will compensate the buyer in the event of a debt default (by the debtor) or other credit event. That is, the seller of the CDS insures the buyer against some reference asset defaulting. The buyer of the CDS makes a series of payments (the CDS "fee" or "spread") to the seller and, in exchange, may expect to receive a payoff if the asset defaults. In the event of default, the buyer of the credit default swap receives compensation (usually the face value of the loan), and the seller of the CDS takes possession of the defaulted loan or its market value in cash. However, anyone can purchase a CDS, even buyers who do not hold the loan instrument and who have no direct insurable interest in the loan (these are called "naked" CDSs). If there are more CDS contracts outstanding than bonds in existence, a protocol exists to hold a credit event auction. The payment received is often substantially less ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurtosis Risk
In statistics and decision theory, kurtosis risk is the risk that results when a statistical model assumes the normal distribution, but is applied to observations that have a tendency to occasionally be much farther (in terms of number of standard deviations) from the average than is expected for a normal distribution. Overview Kurtosis risk applies to any kurtosis-related quantitative model that assumes the normal distribution for certain of its independent variables when the latter may in fact have kurtosis much greater than does the normal distribution. Kurtosis risk is commonly referred to as "fat tail" risk. The "fat tail" metaphor explicitly describes the situation of having more observations at either extreme than the tails of the normal distribution would suggest; therefore, the tails are "fatter". Ignoring kurtosis risk will cause any model to understate the risk of variables with high kurtosis. For instance, Long-Term Capital Management, a hedge fund cofounded by Myron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Risk
Financial risk is any of various types of risk associated with financing, including financial transactions that include company loans in risk of default. Often it is understood to include only downside risk, meaning the potential for financial loss and uncertainty about its extent. A science has evolved around managing market and financial risk under the general title of modern portfolio theory initiated by Dr. Harry Markowitz in 1952 with his article, "Portfolio Selection". In modern portfolio theory, the variance (or standard deviation) of a portfolio is used as the definition of risk. Types According to Bender and Panz (2021), financial risks can be sorted into five different categories. In their study, they apply an algorithm-based framework and identify 193 single financial risk types, which are sorted into the five categories market risk, liquidity risk, credit risk, business risk and investment risk. Market risk The four standard market risk factors are equity ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Put Option
In finance, a put or put option is a derivative instrument in financial markets that gives the holder (i.e. the purchaser of the put option) the right to sell an asset (the ''underlying''), at a specified price (the ''strike''), by (or at) a specified date (the ''expiry'' or ''maturity'') to the ''writer'' (i.e. seller) of the put. The purchase of a put option is interpreted as a negative sentiment about the future value of the underlying stock. page 15 , 4.2.3 Positive and negative sentiment The term "put" comes from the fact that the owner has the right to "put up for sale" the stock or index. Puts may also be combined with other derivatives as part of more complex investment strategies, and in particular, may be useful for hedging. Holding a European put option is equivalent to holding the corresponding call option and selling an appropriate forward contract. This equivalence is called " put-call parity". Put options are most commonly used in the stock market to protect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taleb Distribution
In economics and finance, a Taleb distribution is the statistical profile of an investment which normally provides a payoff of small positive returns, while carrying a small but significant risk of catastrophic losses. The term was coined by journalist Martin Wolf and economist John Kay to describe investments with a "high probability of a modest gain and a low probability of huge losses in any period." The concept is named after Nassim Nicholas Taleb, based on ideas outlined in his book ''Fooled by Randomness''. According to Taleb in ''Silent Risk'', the term should be called "payoff" to reflect the importance of the payoff function of the underlying probability distribution, rather than the distribution itself. The term is meant to refer to an investment returns profile in which there is a high probability of a small gain, and a small probability of a very large loss, which more than outweighs the gains. In these situations the expected value is very much less than zero, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tail Risk Parity
Tail risk parity is an extension of the risk parity concept that takes into account the behavior of the portfolio components during tail risk events. The goal of the tail risk parity approach is to protect investment portfolios at the times of economic crises and reduce the cost of such protection during normal market conditions. In the tail risk parity framework risk is defined as expected tail loss. The tail risk parity concept is similar to drawdown parity Traditional portfolio diversification relies on the correlations among assets and among asset classes, but these correlations are not constant. Because correlations among assets and asset classes increase during tail risk events and can go to 100%, TRP divides asset classes into buckets that behave differently under market stress conditions, while assets in each bucket behave similarly. During tail risk events asset prices can fall significantly creating deep portfolio drawdowns. Asset classes in each tail risk bucket fall s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Market Crash
A stock market crash is a sudden dramatic decline of stock prices across a major cross-section of a stock market, resulting in a significant loss of paper wealth. Crashes are driven by panic selling and underlying economic factors. They often follow speculation and economic bubbles. A stock market crash is a social phenomenon where external economic events combine with crowd psychology in a positive feedback loop where selling by some market participants drives more market participants to sell. Generally speaking, crashes usually occur under the following conditions: a prolonged period of rising stock prices (a bull market) and excessive economic optimism, a market where price–earnings ratios exceed long-term averages, and extensive use of margin debt and leverage by market participants. Other aspects such as wars, large corporate hacks, changes in federal laws and regulations, and natural disasters within economically productive areas may also influence a significant dec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treasury Bonds
United States Treasury securities, also called Treasuries or Treasurys, are government debt instruments issued by the United States Department of the Treasury to finance government spending as an alternative to taxation. Since 2012, U.S. government debt has been managed by the Bureau of the Fiscal Service, succeeding the Bureau of the Public Debt. There are four types of marketable Treasury securities: Treasury bills, Treasury notes, Treasury bonds, and Treasury Inflation Protected Securities (TIPS). The government sells these securities in auctions conducted by the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, after which they can be traded in secondary markets. Non-marketable securities include savings bonds, issued to the public and transferable only as gifts; the State and Local Government Series (SLGS), purchaseable only with the proceeds of state and municipal bond sales; and the Government Account Series, purchased by units of the federal government. Treasury securities are back ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probability Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, a probability distribution is the mathematical function that gives the probabilities of occurrence of different possible outcomes for an experiment. It is a mathematical description of a random phenomenon in terms of its sample space and the probabilities of events (subsets of the sample space). For instance, if is used to denote the outcome of a coin toss ("the experiment"), then the probability distribution of would take the value 0.5 (1 in 2 or 1/2) for , and 0.5 for (assuming that the coin is fair). Examples of random phenomena include the weather conditions at some future date, the height of a randomly selected person, the fraction of male students in a school, the results of a survey to be conducted, etc. Introduction A probability distribution is a mathematical description of the probabilities of events, subsets of the sample space. The sample space, often denoted by \Omega, is the set of all possible outcomes of a random phe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hedge Fund
A hedge fund is a pooled investment fund that trades in relatively liquid assets and is able to make extensive use of more complex trading, portfolio-construction, and risk management techniques in an attempt to improve performance, such as short selling, leverage, and derivatives. Financial regulators generally restrict hedge fund marketing to institutional investors, high net worth individuals, and accredited investors. Hedge funds are considered alternative investments. Their ability to use leverage and more complex investment techniques distinguishes them from regulated investment funds available to the retail market, commonly known as mutual funds and ETFs. They are also considered distinct from private equity funds and other similar closed-end funds as hedge funds generally invest in relatively liquid assets and are usually open-ended. This means they typically allow investors to invest and withdraw capital periodically based on the fund's net asset value, whereas pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skewness
In probability theory and statistics, skewness is a measure of the asymmetry of the probability distribution of a real-valued random variable about its mean. The skewness value can be positive, zero, negative, or undefined. For a unimodal distribution, negative skew commonly indicates that the ''tail'' is on the left side of the distribution, and positive skew indicates that the tail is on the right. In cases where one tail is long but the other tail is fat, skewness does not obey a simple rule. For example, a zero value means that the tails on both sides of the mean balance out overall; this is the case for a symmetric distribution, but can also be true for an asymmetric distribution where one tail is long and thin, and the other is short but fat. Introduction Consider the two distributions in the figure just below. Within each graph, the values on the right side of the distribution taper differently from the values on the left side. These tapering sides are called ''tail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |