|
Hoche
Louis Lazare Hoche (; 24 June 1768 – 19 September 1797) was a French military leader of the French Revolutionary Wars. He won a victory over Royalist forces in Brittany. His surname is one of the names inscribed under the Arc de Triomphe, on Column 3. Richard Holmes (military historian), Richard Holmes describes him as "quick-thinking, stern, and ruthless... a general of real talent whose early death was a loss to France." Early life Hoche was born on 24 June 1768 in the village of Montreuil, today part of Versailles, to Anne Merlière and Louis Hoche, a Groom (profession), stable servant of the king. His mother died when he was two years old, and Hoche was mostly raised by an aunt, who was a fruit-seller in Montreuil, and was educated by the Abbé Merlière, his maternal uncle, parish priest of Saint-Germain-en-Laye, who arranged for Hoche to become a choirboy at his church. Early career In 1782, Hoche began working as an aide at the royal stables, but soon left in order to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Of The Coasts Of The Ocean (1796)
The Army of the Coasts of the Ocean (''Armée des côtes de l'Océan'') was a French Revolutionary Army that was only in existence during 1796. The army was formed by combining the three armies that were engaged in the War in the Vendée and appointing Lazare Hoche to command. While the army's nominal strength was 182,956 men at the time of its formation, this declined to 117,746 during the year. Because its operations were successful, the army was disbanded in September 1796 and approximately half its personnel sent to other armies. History The ''Army of the Coasts of the Ocean'' was created by an order of 26 December 1795 which was executed on 5–8 January 1796. The army was formed by combining the '' Army of the West'', the ''Army of the Coasts of Brest'' and the '' Army of the Coasts of Cherbourg''. Its first and only commander-in-chief was Lazare Hoche, although from 10 July until mid-August the chief of staff Gabriel Marie Joseph, comte d'Hédouville carried out the orders o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Expedition To Ireland (1796)
The French expedition to Ireland, known in French as the ''Expédition d'Irlande'' ("Expedition to Ireland"), was an unsuccessful attempt by the French Republic to assist the outlawed Society of United Irishmen, a popular rebel Irish republican group, in their planned rebellion against British rule during the French Revolutionary Wars. The French intended to land a large expeditionary force in Ireland during the winter of 1796–1797 which would join with the United Irishmen and drive the British out of Ireland. The French anticipated that this would be a major blow to British morale, prestige and military effectiveness, and was also intended to possibly be the first stage of an eventual invasion of Britain itself. To this end, the Directory gathered a force of approximately 15,000 soldiers at Brest under General Lazare Hoche during late 1796, in readiness for a major landing at Bantry Bay in December. The operation was launched during one of the stormiest winters of the 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chouannerie
The Chouannerie (from the Chouan brothers, two of its leaders) was a royalist uprising or counter-revolution in twelve of the western ''départements'' of France, particularly in the provinces of Brittany and Maine, against the First Republic during the French Revolution. It played out in three phases and lasted from spring 1794 to 1800. Albert Soboul (dir.), ''Dictionnaire historique de la Révolution française'', Quadrige/PUF, 1989, p. 217, "Chouans/Chouannerie" entry by Roger Dupu.] The uprising was provoked principally by the Civil Constitution of the Clergy (1790) and the mass conscription, or ''levée en masse'' (1793), which was decided by the National Convention. A first attempt at staging an uprising was carried out by the ''Association bretonne'' to defend the French monarchy and reinstate the specific laws and customs of Brittany, which had been repealed in 1789. The first confrontations broke out in 1792 and developed in stages into a peasant revolt, guerrill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invasion Of France (1795)
The invasion of France in 1795 or the Battle of Quiberon was a major landing on the Quiberon peninsula by émigré, counter-revolutionary troops in support of the Chouannerie and Vendée Revolt, beginning on 23 June and finally definitively repulsed on 21 July. It aimed to raise the whole of western France in revolt, bring an end to the French Revolution and restore the French monarchy. The invasion failed; it had a major negative impact, dealing a disastrous blow to the royalist cause. Preparations Louis XVIII and the comte d’Artois (the future Charles X of France) divided the counter-revolutionary activities and theatres between them - to Louis went political generalities and the region from the Alps to the Pyrénées (including Lyon), and to the comte the western provinces (Vendée, Brittany, Normandy). The comte named Joseph de Puisaye général en chef of Brittany, a good choice since de Puisaye had military talent and political and diplomatic experience. Playing t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Of The West (France)
The Army of the West (''armée de l'Ouest'') was one of the French Revolutionary Armies that was sent to fight in the War in the Vendée in western France. The army was created on 2 October 1793 by merging the Army of the Coasts of La Rochelle, the so-called Army of Mayence and part of the Army of the Coasts of Brest. In 1793 the army or its component forces fought at Second Châtillon, First Noirmoutier, La Tremblaye, Cholet, Laval, Entrames, Fougères, Granville, Dol, Angers, Le Mans and Savenay. After the main Vendean army was crushed, the revolt evolved into guerilla warfare and there were few pitched battles. In 1794 Louis Marie Turreau tried to suppress the rebellion with extremely brutal methods using the infamous infernal columns. Calmer heads finally prevailed and Turreau was recalled. On 6 January 1796, the army was absorbed into the newly formed Army of the Coasts of the Ocean. The Army of the West came into existence a second time on 17 January 1800 and was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Revolutionary Wars
The French Revolutionary Wars (french: Guerres de la Révolution française) were a series of sweeping military conflicts lasting from 1792 until 1802 and resulting from the French Revolution. They pitted France against Britain, Austria, Prussia, Russia, and several other monarchies. They are divided in two periods: the War of the First Coalition (1792–97) and the War of the Second Coalition (1798–1802). Initially confined to Europe, the fighting gradually assumed a global dimension. After a decade of constant warfare and aggressive diplomacy, France had conquered territories in the Italian Peninsula, the Low Countries and the Rhineland in Europe and abandoned Louisiana in North America. French success in these conflicts ensured the spread of revolutionary principles over much of Europe. As early as 1791, the other monarchies of Europe looked with outrage at the revolution and its upheavals; and they considered whether they should intervene, either in support of King Louis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War In The Vendée
The war in the Vendée (french: link=no, Guerre de Vendée) was a counter-revolution from 1793 to 1796 in the Vendée region of France during the French Revolution. The Vendée is a coastal region, located immediately south of the river Loire in Western France. Initially, the revolt was similar to the 14th-century Jacquerie peasant uprising, but the Vendée quickly became counter-revolutionary and Royalist. The revolt headed by the newly-formed Catholic and Royal Army was comparable to the Chouannerie, which took place in the area north of the Loire. While elsewhere in France the revolts against the were repressed, an insurgent territory, called the by historians, formed south of the Loire-Inférieure (Brittany), south-west of Maine-et-Loire (Anjou), north of Vendée and north-west of Deux-Sèvres ( Poitou). Gradually referred to as the "Vendeans", the insurgents established in April a " Catholic and Royal Army" which won a succession of victories in the spring and summ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Of The Coasts Of Brest
The Army of the Coasts of Brest (french: Armée des côtes de Brest) was a French Revolutionary Army formed on 30 April 1793 by splitting the '' Army of the Coasts'' into this army and the '' Army of the Coasts of Cherbourg''. The formation was first put under the command of Jean Baptiste Camille Canclaux and charged with fighting the War in the Vendée, combatting the Chouannerie and protecting the coasts of Brittany against a British invasion. After successfully defending Nantes and suffering setbacks at Tiffauges and Montaigu, Canclaux was recalled on 5 October 1793 and many of the army's soldiers were absorbed into the Army of the West. Over the next few years, Jean Antoine Rossignol, Jean-François-Auguste Moulin, Thomas-Alexandre Dumas, Lazare Hoche and Gabriel Venance Rey led the army in turn. In June–July 1795 the army crushed a Royalist invasion at Quiberon. On 5 January 1796 the formation and two other armies were merged into the '' Army of the Coasts of the Ocea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
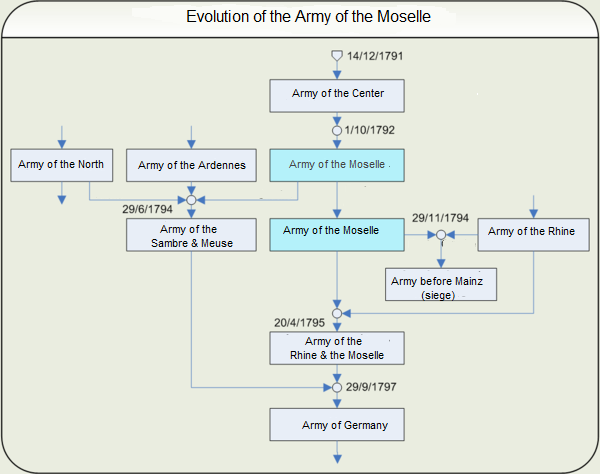
Army Of Moselle
The Army of the Moselle (''Armée de la Moselle'') was a French Revolutionary Army from 1791 through 1795. It was first known as the ''Army of the Centre'' and it fought at Valmy. In October 1792 it was renamed and subsequently fought at Trier, First Arlon, Biesingen, Kaiserslautern, Froeschwiller and Second Wissembourg. In the spring of 1794 the left wing was detached and fought at Second Arlon, Lambusart and Fleurus before being absorbed by the ''Army of Sambre-et-Meuse''. In late 1794, the army captured Trier and initiated the Siege of Luxembourg. During the siege, the army was discontinued and its divisions were assigned to other armies. History Originally known as the ''Army of the Centre'', it was renamed by decree of the National Convention on 1 October 1792 and kept under that name in the decrees of 1 March and 30 April 1793. By the decree of 29 June 1794 its left wing joined with the ''Army of the Ardennes'' and the right wing of the ''Army of the North'' to form th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Of Sambre And Meuse
The Army of Sambre and Meuse (french: Armée de Sambre-et-Meuse) was one of the armies of the French Revolution. It was formed on 29 June 1794 by combining the Army of the Ardennes, the left wing of the Army of the Moselle and the right wing of the Army of the North. Its maximum paper strength (in 1794) was approximately 120,000. After an inconclusive campaign in 1795, the French planned a co-ordinated offensive in 1796 using Jean-Baptiste Jourdan's Army of the Sambre et Meuse and the Army of the Rhine and Moselle commanded by his superior, Jean Victor Moreau. The first part of the operation called for Jourdan to cross the Rhine north of Mannheim and divert the Austrians while the Army of the Moselle crossed the southern Rhine at Kehl and Huningen. This was successful and, by July 1796, a series of victories forced the Austrians, commanded by Archduke Charles to retreat into the German states. By late July, most of the southern German states had been coerced into an armi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars. From the accession of Otto I in 962 until the twelfth century, the Empire was the most powerful monarchy in Europe. Andrew Holt characterizes it as "perhaps the most powerful European state of the Middle Ages". The functioning of government depended on the harmonic cooperation (dubbed ''consensual rulership'' by Bernd Schneidmüller) between monarch and vassals but this harmony was disturbed during the Salian period. The empire reached the apex of territorial expansion and power under the House of Hohenstaufen in the mid-thirteenth century, but overextending led to partial collapse. On 25 December 800, Pope Leo III crowned the Frankish king Charlemagne as emperor, reviving the title in Western Europe, more than three centuries after the fall of the earlier ancient Weste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Names Inscribed Under The Arc De Triomphe
The following is a list of the 660 names inscribed under the Arc de Triomphe, in Paris. Most of them represent generals who served during the French First Republic (1792–1804) and the First French Empire (1804–1815). Underlined names signify those killed in action. Additionally, the names of specific armies are listed, grouped together by the four compass facades of the arch: North (northern France, lower Rhine, Netherlands), East (Central Europe, Switzerland, Italy), South (Mediterranean Europe, Egypt, southern France) and West (Pyrenees, western France, notable units). Related list: Battles inscribed on the Arc de Triomphe. File:Paris Arc de Triomphe inscriptions 2.jpg, Northern pillar Armies of northern France, the lower Rhine and the Netherlands. File:Paris Arc de Triomphe inscriptions 3.jpg, Eastern pillar Armies of Central Europe, Switzerland and Italy. File:Paris Arc de Triomphe inscriptions 7.jpg, Southern pillar Armies of Mediterranean Europe, Egypt and south ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |